C语言-数据结构-骑士周游-马踏棋盘问题-源代码
2016-12-04 10:43
260 查看
1. 目标
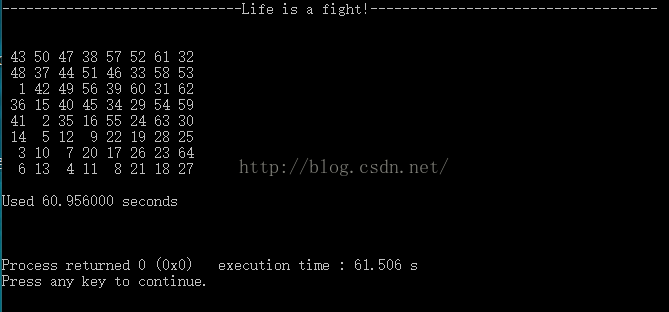
对于一个指定的起始坐标,按照‘马’的走棋规则,从该坐标开始搜索一条可以覆盖棋盘每个位置的走棋路径。例如下面是从(2,0)坐标开始搜索得到的一个解。
2. 代码结构
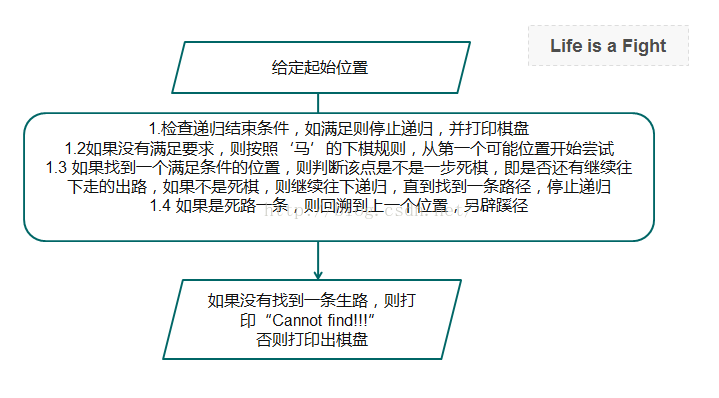
3. 源代码
该代码仅仅是寻找到一条生路,即停止。另外对选择的起始点,和寻找下一点的顺序不同(即sposition()中case的顺序不同,对于程序执行的时间影响会很大)。
另外程序中调用了time.h头文件中的clock相关函数,对代码的执行时间进行了统计,具体见代码。
对于一个指定的起始坐标,按照‘马’的走棋规则,从该坐标开始搜索一条可以覆盖棋盘每个位置的走棋路径。例如下面是从(2,0)坐标开始搜索得到的一个解。

2. 代码结构

3. 源代码
该代码仅仅是寻找到一条生路,即停止。另外对选择的起始点,和寻找下一点的顺序不同(即sposition()中case的顺序不同,对于程序执行的时间影响会很大)。
另外程序中调用了time.h头文件中的clock相关函数,对代码的执行时间进行了统计,具体见代码。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<time.h>
#define title "------------------------------Life is a fight!------------------------------------"
#define X 8 //定义棋盘大小
#define Y 8
int chess[X][Y]= {
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0},
{0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0}
};
int sposition(int *x, int *y, int p)
{
switch(p)//特别需要注意每个case 中的顺序,对程序执行的时间有很大影响
{
case 0:
if( *x+2<=X-1 && *y-1>=0 && chess[*x+2][*y-1]==0 )
{
*x = *x + 2;
*y = *y - 1;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
case 1:
if( *x+2<=X-1 && *y+1<=Y-1 && chess[*x+2][*y+1]==0 )
{
*x = *x + 2;
*y = *y + 1;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
case 2:
if( *x+1<=X-1 && *y-2>=0 && chess[*x+1][*y-2]==0 )
{
*x = *x + 1;
*y = *y - 2;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
case 3:
if( *x+1<=X-1 && *y+2<=Y-1 && chess[*x+1][*y+2]==0 )
{
*x = *x + 1;
*y = *y + 2;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
case 4:
if( *x-2>=0 && *y-1>=0 && chess[*x-2][*y-1]==0 )
{
*x = *x - 2;
*y = *y - 1;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
case 5:
if( *x-2>=0 && *y+1<=Y-1 && chess[*x-2][*y+1]==0 )
{
*x = *x - 2;
*y = *y + 1;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
case 6:
if( *x-1>=0 && *y-2>=0 && chess[*x-1][*y-2]==0 )
{
*x = *x - 1;
*y = *y - 2;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
case 7:
if( *x-1>=0 && *y+2<=Y-1 && chess[*x-1][*y+2]==0 )
{
*x = *x - 1;
*y = *y + 2;
return 1;
}
else
return 0;
default:
return 0;
}
}
void prfChess(int t_chess[][Y])
{
int i, j;
for(i=0;i<X;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<Y;j++)
{
printf("%3d", t_chess[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int searchp(int x, int y, int c)
{
int x1, y1, p=0;
int i, j, flag=0;
x1=x; y1=y;
chess[x1][y1]=c;
//printf("%d\n",c);
if(X*Y==c) //递归结束条件
{
prfChess(chess);
return 1;
}
flag=sposition(&x1, &y1, p);//找到第一个符合条件的位置
while(0==flag && p<X-1)
{
p++;
flag=sposition(&x1,&y1,p);
}
while(flag) //如果不是死路,即存在往下走的位置
{
if(searchp(x1,y1,c+1)) //继续往下搜索,直到满足c==X*Y,返回1,结束递归
return 1;
x1=x; //如果是死路一条,则要向后退,回溯到上一个位置
y1=y;
p++; //将P向后移一个位置,继续搜索其他的可能位置
flag=sposition(&x1,&y1,p);
while(0==flag && p<X-1)
{
flag=sposition(&x1,&y1,++p);
}
}
if(0==flag) //如果经过搜索,没有满足条件的位置,则将该位置的值改回去,变为零
{
chess [x][y]=0;
}
return 0;
}
int main(void)
{
clock_t start, end;
double t;
printf("%s\n\n\n",title);
start=clock();
if(!searchp(2,0,1))
printf("Cannot find!!!\n\n\n");
end=clock();
t=(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf("\nUsed %f seconds\n\n\n", t);
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 马踏棋盘算法(骑士周游问题)- 数据结构和算法60
- 小甲鱼数据结构和算法--马踏棋盘(骑士周游问题)
- 马踏棋盘算法(骑士周游问题)- 数据结构和算法60
- 数据结构学习之启发式搜索求解骑士周游问题
- 转:数据结构与算法1:马踏棋盘问题(骑士周游问题)
- 数据结构与算法10:马踏棋盘问题(骑士周游问题)
- 骑士周游问题(马踏棋盘问题)DFS
- 15骑士周游问题(马踏棋盘问题)
- 马踏棋盘算法(骑士周游问题)
- 马踏棋盘算法 [骑士周游问题] --->图
- 马踏棋盘问题(骑士周游问题)及其优化算法java实现
- 棋盘覆盖问题(分治)(C语言)
- C语言数据结构之单向链表(已经调试可以实现相应的功能了,可是还是有几个问题现在还是不大理解,希望大家能够一起探讨)
- 关于c语言写数据结构时类型替换的问题
- 【DS】骑士周游问题
- HDU 1372(骑士周游问题)
- 马踏棋盘算法(骑士周游问题)
- 跳马问题(骑士周游问题)初探
- 再探跳马问题(骑士周游问题)
- scau实验题 8600 骑士周游问题(有障碍物)
