The Child and Sequence(线段树)
2014-08-26 20:41
453 查看
The Child and Sequence
| Time Limit: 4000MS | Memory Limit: 262144KB | 64bit IO Format: %I64d & %I64u |
[Go Back] [Status]
Description
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations.
An operation can be one of the following:
Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
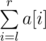
.
Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for
each i(l ≤ i ≤ r).
Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in
other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
Input
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m(1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line
contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) —
initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type
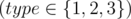
.
If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond
the operation 1.
If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 2.
If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 3.
Output
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
Sample Input
Input
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
Output
8 5
Input
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
Output
49 15 23 1 9
Hint
Consider the first testcase:
At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 100000
long long tree[MAXN*4+9];
int mv[MAXN*4+9];
void build(int s,int t,int start)
{
if(s==t)
{
cin>>tree[start];
mv[start]=tree[start];
return ;
}
int mid=(s+t)/2;
build(s,mid,start*2);
build(mid+1,t,start*2+1);
tree[start]=tree[start*2]+tree[start*2+1];
mv[start]=max(mv[start*2],mv[start*2+1]);
}
void sets(int k,int x,int s,int t,int start)
{
if(s==t)
{
tree[start]=x;
mv[start]=x;
return ;
}
int mid=(s+t)/2;
if(k<=mid) sets(k,x,s,mid,start*2);
else sets(k,x,mid+1,t,start*2+1);
tree[start]=tree[start*2]+tree[start*2+1];
mv[start]=max(mv[start*2],mv[start*2+1]);
}
void update(int ll,int rr,int x,int s,int t,int start)
{
if(s==t)
{
tree[start]=tree[start]%x;
mv[start]=tree[start];
return ;
}
if(mv[start]<x) return ;
int mid=(s+t)/2;
if(ll<=mid) update(ll,rr,x,s,mid,start*2);
if(rr>mid) update(ll,rr,x,mid+1,t,start*2+1);
tree[start]=tree[start*2]+tree[start*2+1];
mv[start]=max(mv[start*2],mv[start*2+1]);
}
long long query(int ll,int rr,int s,int t,int start)
{
if(ll<=s&&rr>=t)
return tree[start];
long long sum=0;
int mid=(s+t)/2;
if(ll<=mid) sum+=query(ll,rr,s,mid,start*2);
if(rr>mid) sum+=query(ll,rr,mid+1,t,start*2+1);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int n,m,type,ll,rr,k,x;
while(cin>>n>>m)
{
build(1,n,1);
for(int i=1; i<=m; i++)
{
cin>>type;
if(type==1)
{
cin>>ll>>rr;
cout<<query(ll,rr,1,n,1)<<endl;
}
if(type==2)
{
cin>>ll>>rr>>x;
update(ll,rr,x,1,n,1);
}
if(type==3)
{
cin>>k>>x;
sets(k,x,1,n,1);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- CF(438D) The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- CF(438D) The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence(线段树暴力)
- [均摊 平衡树 || 线段树] Codeforces 438D #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence (线段树)
- 线段树【CF620E】The Child and Sequence
- [均摊复杂度线段树]Codeforces 438D. The Child and Sequence
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树
- 有趣的线段树小集合 Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树 区间求和+点修改+区间取模
- codeforces 438D. The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树 区间取摸
- Codefroces 438D. The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- Codeforces Round #250 D - The Child and Sequence/[TYVJ3838] DQS和序列(by 帝江&Darkfalmes)
- 【Codeforces 438 D】The Child and Sequence
- Codeforce 438D-The Child and Sequence
- 438D - The Child and Sequence
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence
- codeforces438 D The Child and Sequence
- The Child and Sequence
