Codeforce 438D-The Child and Sequence
2014-10-06 20:20
495 查看
D. The Child and Sequence
time limit per test
4 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then
he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
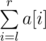
.
Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for
each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in
other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
Input
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers, separated by space:a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) —
initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type
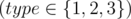
.
If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n),
which correspond the operation 1.
If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 2.
If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 3.
Output
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
Sample test(s)
input
output
input
output
Note
Consider the first testcase:
At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
另一种的线段树写法:
time limit per test
4 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then
he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
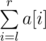
.
Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for
each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in
other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
Input
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers, separated by space:a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) —
initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type
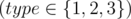
.
If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n),
which correspond the operation 1.
If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 2.
If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109),
which correspond the operation 3.
Output
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
Sample test(s)
input
5 5 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 5 4 3 3 5 1 2 5 2 1 3 3 1 1 3
output
8 5
input
10 10 6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5 1 3 9 2 7 10 9 2 5 10 8 1 4 7 3 3 7 2 7 9 9 1 2 4 1 6 6 1 5 9 3 1 10
output
49 15 23 1 9
Note
Consider the first testcase:
At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct node{
long long l, r, s, maxx;
}num[800005];
long long n, m, key;
template <class T>
inline bool scan_d(T &ret) {
char c; int sgn;
if(c=getchar(),c==EOF) return 0; //EOF
while(c!='-'&&(c<'0'||c>'9')) c=getchar();
sgn=(c=='-')?-1:1;
ret=(c=='-')?0:(c-'0');
while(c=getchar(),c>='0'&&c<='9') ret=ret*10+(c-'0');
ret*=sgn;
return 1;
}
inline void out(long long x) {
if(x>9) out(x/10);
putchar(x%10+'0');
}
void build(int l,int r,int k)
{
num[k].l = l;
num[k].r = r;
num[k].s = 0;
num[k].maxx = 0;
if(l == r) return;
int mi = (l+r)>>1;
build(l,mi,k+k);
build(mi+1,r,k+k+1);
return;
}
void update(int l, int r, int k)
{
if(num[k].l==num[k].r)
{
num[k].s = key;
num[k].maxx = key;
return;
}
int mi = (num[k].l+num[k].r)>>1;
if(l > mi) update(l,r,k+k+1);
else if(r <= mi) update(l,r,k+k);
else
{
update(l,mi,k+k);
update(mi+1,r,k+k+1);
}
num[k].s = num[k+k].s + num[k+k+1].s;
num[k].maxx = max(num[k+k].maxx,num[k+k+1].maxx);
return;
}
void upmod(int l, int r, int k)
{
if(num[k].maxx<key) return;
if(num[k].l==num[k].r)
{
num[k].s%=key;
num[k].maxx = num[k].s;
return;
}
int mi = (num[k].l+num[k].r)>>1;
if(l > mi) upmod(l,r,k+k+1);
else if(r <= mi) upmod(l,r,k+k);
else
{
upmod(l,mi,k+k);
upmod(mi+1,r,k+k+1);
}
num[k].s = num[k+k].s + num[k+k+1].s;
num[k].maxx = max(num[k+k].maxx,num[k+k+1].maxx);
return;
}
long long query(int k,int l,int r)
{
if(num[k].l==l && num[k].r==r)
{
return num[k].s;
}
else
{
int mi = (num[k].l+num[k].r)>>1;
if(r<=mi) return query(k+k,l,r);
else if(l>mi) return query(k+k+1,l,r);
else return query(k+k,l,mi)+query(k+k+1,mi+1,r);
}
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);
int Case;
int a, b, c;
memset(num,0,sizeof(num));
scan_d(n);
scan_d(m);
build(1,n,1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scan_d(key);
update(i,i,1);
}
while(m--)
{
scan_d(c);
switch(c)
{
case 1:
scan_d(a);
scan_d(b);
out(query(1,a,b));
putchar('\n');
break;
case 2:
scan_d(a);
scan_d(b);
scan_d(key);
upmod(a,b,1);
break;
case 3:
scan_d(a);
scan_d(key);
update(a,a,1);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}另一种的线段树写法:
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <deque>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define lson l , m , rt << 1
#define rson m + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
const int maxn = 100010;
LL sum[maxn<<2], ma[maxn<<2];
void PushUP(int rt) {
sum[rt] = sum[rt<<1] + sum[rt<<1|1];
}
void PushUP2(int rt) {
ma[rt] = max(ma[rt<<1], ma[rt<<1|1]);
}
void build(int l,int r,int rt) {
if (l == r) {
//scanf("%I64d",&sum[rt]);
cin >> sum[rt];
ma[rt] = sum[rt];
return ;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
build(lson);
build(rson);
PushUP(rt);
PushUP2(rt);
}
//#define lson l , m , rt << 1
//#define rson m + 1 , r , rt << 1 | 1
void MOD(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt, LL mod)
{
// if(R < l || L > r) return ;
// if(L <= l && r <= R && ma[rt] < mod) return ;
if(ma[rt] < mod) return ;
if(l == r) {sum[rt] %= mod; ma[rt] = sum[rt];return ;}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (L <= m) MOD(L, R , lson, mod);
if (R > m) MOD(L, R , rson, mod);
PushUP(rt);
PushUP2(rt);
}
void update(int p,LL add,int l,int r,int rt) {
if (l == r) {
//sum[rt] += add;
sum[rt] = add;
ma[rt] = sum[rt];
return ;
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (p <= m) update(p , add , lson);
else update(p , add , rson);
PushUP(rt);
PushUP2(rt);
}
LL query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) {
if (L <= l && r <= R) {
return sum[rt];
}
int m = (l + r) >> 1;
LL ret = 0;
if (L <= m) ret += query(L , R , lson);
if (R > m) ret += query(L , R , rson);
return ret;
}
int main() {
int n, m, op, l, r, k;
LL x, mod;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
build(1, n, 1);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d",&op);
if(op == 1)
{
//scanf("%d%d",&l, &r);
cin >> l >> r;
cout << query(l, r, 1, n, 1) << endl;
//printf("%I64d\n",query(l, r, 1, n, 1));
}
else if(op == 2)
{
cin >> l >> r >> mod;
//scanf("%d%d%I64d",&l, &r, &mod);
MOD(l, r, 1, n, 1, mod);
}
else
{
cin >> k >> x;
//scanf("%d%d",&k,&x);
update(k, x, 1, n, 1);
}
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- CF(438D) The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- [均摊复杂度线段树]Codeforces 438D. The Child and Sequence
- 【Codeforces 438 D】The Child and Sequence
- Codefroces 438D. The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- 438D - The Child and Sequence
- codeforces 438D. The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- codeforces438 D The Child and Sequence
- CF(438D) The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence(线段树暴力)
- CodeForces 438 E.The Child and Binary Tree(生成函数+FFT)
- The Child and Sequence(线段树)
- CodeForces 438 C.The Child and Polygon(dp+计算几何)
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence (线段树)
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence 线段树 区间求和+点修改+区间取模
- codeforce 437 D The Child and Zoo
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence
- The Child and Sequence
- 有趣的线段树小集合 Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) D. The Child and Sequence
- AC日记——The Child and Sequence codeforces 250D
