tensorflow 双LSTM实现地址相似性判断
2017-04-05 00:00
411 查看
摘要: 地址相似性判断应用较广,基于双向LSTM可以较为有效的实现。
基本思路如下
1.输入由两个地址组成
2.每个地址进入经过双向LSTM之后,经过全连接层输出后,再计算余弦距离,距离越大,说明地址的相似性越高。
main函数对应的代码main.py
Training Metrics, Batch 10: Loss=0.104, Accuracy=0.690.
Training Metrics, Batch 20: Loss=0.117, Accuracy=0.755.
Training Metrics, Batch 30: Loss=0.089, Accuracy=0.705.
Training Metrics, Batch 40: Loss=0.032, Accuracy=0.715.
Training Metrics, Batch 50: Loss=0.033, Accuracy=0.690.
Training Metrics, Batch 60: Loss=0.026, Accuracy=0.730.
Training Metrics, Batch 70: Loss=-0.035, Accuracy=0.795.
Training Metrics, Batch 80: Loss=0.013, Accuracy=0.735.
Training Metrics, Batch 90: Loss=0.034, Accuracy=0.745.
Training Metrics, Batch 100: Loss=0.038, Accuracy=0.690.
Training Metrics, Batch 110: Loss=-0.002, Accuracy=0.790.
Training Metrics, Batch 120: Loss=-0.003, Accuracy=0.765.
Training Metrics, Batch 130: Loss=-0.001, Accuracy=0.780.
Training Metrics, Batch 140: Loss=0.013, Accuracy=0.785.
Training Metrics, Batch 150: Loss=0.002, Accuracy=0.735.
Training Metrics, Batch 160: Loss=-0.002, Accuracy=0.805.
Training Metrics, Batch 170: Loss=-0.002, Accuracy=0.740.
Training Metrics, Batch 180: Loss=0.004, Accuracy=0.765.
Training Metrics, Batch 190: Loss=-0.004, Accuracy=0.725.
Training Metrics, Batch 200: Loss=-0.001, Accuracy=0.765.
Training Metrics, Batch 210: Loss=0.012, Accuracy=0.745.
Training Metrics, Batch 220: Loss=-0.015, Accuracy=0.800.
Training Metrics, Batch 230: Loss=0.006, Accuracy=0.740.
Training Metrics, Batch 240: Loss=-0.021, Accuracy=0.745.
Training Metrics, Batch 250: Loss=-0.018, Accuracy=0.745.
Training Metrics, Batch 260: Loss=0.007, Accuracy=0.800.
Training Metrics, Batch 270: Loss=-0.012, Accuracy=0.765.
Training Metrics, Batch 280: Loss=-0.020, Accuracy=0.790.
Training Metrics, Batch 290: Loss=0.009, Accuracy=0.750.
Query Addresses: ['111 abbey ln', '271 doner cicle', '314 king avenue', 'tensorflow is fun']
Model Found Matches: ['123 abbey ln', '217 donner cir', '314 kings ave', 'tensorflow is so fun']
基本思路如下
1.输入由两个地址组成
2.每个地址进入经过双向LSTM之后,经过全连接层输出后,再计算余弦距离,距离越大,说明地址的相似性越高。
基本环境
tensorflow 1.0代码结构
双向LSTM模型对应的代码文件siamese_similarity_model.pymain函数对应的代码main.py
代码siamese_similarity_model.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- # Siamese Address Similarity with TensorFlow (Model File) #------------------------------------------ # # Here, we show how to perform address matching # with a Siamese RNN model import tensorflow as tf def snn(address1, address2, dropout_keep_prob, vocab_size, num_features, input_length): # Define the siamese double RNN with a fully connected layer at the end def siamese_nn(input_vector, num_hidden): cell_unit = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell#tf.nn.rnn_cell.BasicLSTMCell # Forward direction cell lstm_forward_cell = cell_unit(num_hidden, forget_bias=1.0) lstm_forward_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_forward_cell, output_keep_prob=dropout_keep_prob) # Backward direction cell lstm_backward_cell = cell_unit(num_hidden, forget_bias=1.0) lstm_backward_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.DropoutWrapper(lstm_backward_cell, output_keep_prob=dropout_keep_prob) # Split title into a character sequence input_embed_split = tf.split(axis=1, num_or_size_splits=input_length, value=input_vector) input_embed_split = [tf.squeeze(x, axis=[1]) for x in input_embed_split] # Create bidirectional layer try: outputs, _, _ = tf.contrib.rnn.static_bidirectional_rnn(lstm_forward_cell, lstm_backward_cell, input_embed_split, dtype=tf.float32) except Exception: outputs = tf.contrib.rnn.static_bidirectional_rnn(lstm_forward_cell, lstm_backward_cell, input_embed_split, dtype=tf.float32) # Average The output over the sequence temporal_mean = tf.add_n(outputs) / input_length # Fully connected layer output_size = 10 A = tf.get_variable(name="A", shape=[2*num_hidden, output_size], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1)) b = tf.get_variable(name="b", shape=[output_size], dtype=tf.float32, initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(stddev=0.1)) final_output = tf.matmul(temporal_mean, A) + b final_output = tf.nn.dropout(final_output, dropout_keep_prob) return(final_output) output1 = siamese_nn(address1, num_features) # Declare that we will use the same variables on the second string with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope(), reuse=True): output2 = siamese_nn(address2, num_features) # Unit normalize the outputs output1 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(output1, 1) output2 = tf.nn.l2_normalize(output2, 1) # Return cosine distance # in this case, the dot product of the norms is the same. dot_prod = tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(output1, output2), 1) return(dot_prod) def get_predictions(scores): predictions = tf.sign(scores, name="predictions") return(predictions) def loss(scores, y_target, margin): # Calculate the positive losses pos_loss_term = 0.25 * tf.square(tf.subtract(1., scores)) # If y-target is -1 to 1, then do the following #pos_mult = tf.add(tf.multiply(0.5, y_target), 0.5) # Else if y-target is 0 to 1, then do the following pos_mult = tf.cast(y_target, tf.float32) # Make sure positive losses are on similar strings positive_loss = tf.multiply(pos_mult, pos_loss_term) # Calculate negative losses, then make sure on dissimilar strings # If y-target is -1 to 1, then do the following: #neg_mult = tf.add(tf.mul(-0.5, y_target), 0.5) # Else if y-target is 0 to 1, then do the following neg_mult = tf.subtract(1., tf.cast(y_target, tf.float32)) negative_loss = neg_mult*tf.square(scores) # Combine similar and dissimilar losses loss = tf.add(positive_loss, negative_loss) # Create the margin term. This is when the targets are 0., # and the scores are less than m, return 0. # Check if target is zero (dissimilar strings) target_zero = tf.equal(tf.cast(y_target, tf.float32), 0.) # Check if cosine outputs is smaller than margin less_than_margin = tf.less(scores, margin) # Check if both are true both_logical = tf.logical_and(target_zero, less_than_margin) both_logical = tf.cast(both_logical, tf.float32) # If both are true, then multiply by (1-1)=0. multiplicative_factor = tf.cast(1. - both_logical, tf.float32) total_loss = tf.multiply(loss, multiplicative_factor) # Average loss over batch avg_loss = tf.reduce_mean(total_loss) return(avg_loss) def accuracy(scores, y_target): predictions = get_predictions(scores) # Cast into integers (outputs can only be -1 or +1) y_target_int = tf.cast(y_target, tf.int32) # Change targets from (0,1) --> (-1, 1) # via (2 * x - 1) #y_target_int = tf.sub(tf.mul(y_target_int, 2), 1) predictions_int = tf.cast(tf.sign(predictions), tf.int32) correct_predictions = tf.equal(predictions_int, y_target_int) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_predictions, tf.float32)) return(accuracy)
代码main.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Siamese Address Similarity with TensorFlow (Driver File)
#------------------------------------------
#
# Here, we show how to perform address matching
# with a Siamese RNN model
import random
import string
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
ops.reset_default_graph()
import siamese_similarity_model as model
# Start a graph session
sess = tf.Session()
# Model parameters
batch_size = 200
n_batches = 300
max_address_len = 20
margin = 0.25
num_features = 50
dropout_keep_prob = 0.8
# Function to randomly create one typo in a string w/ a probability
def create_typo(s):
rand_ind = random.choice(range(len(s)))
s_list = list(s)
s_list[rand_ind]=random.choice(string.ascii_lowercase + '0123456789')
s = ''.join(s_list)
return(s)
# Generate data
street_names = ['abbey', 'baker', 'canal', 'donner', 'elm', 'fifth',
'grandvia', 'hollywood', 'interstate', 'jay', 'kings']
street_types = ['rd', 'st', 'ln', 'pass', 'ave', 'hwy', 'cir', 'dr', 'jct']
# Define test addresses
test_queries = ['111 abbey ln', '271 doner cicle',
'314 king avenue', 'tensorflow is fun']
test_references = ['123 abbey ln', '217 donner cir', '314 kings ave',
'404 hollywood st', 'tensorflow is so fun']
# Get a batch of size n, half of which is similar addresses, half are not
def get_batch(n):
# Generate a list of reference addresses with similar addresses that have
# a typo.
numbers = [random.randint(1, 9999) for i in range(n)]
streets = [random.choice(street_names) for i in range(n)]
street_suffs = [random.choice(street_types) for i in range(n)]
full_streets = [str(w) + ' ' + x + ' ' + y for w,x,y in zip(numbers, streets, street_suffs)]
typo_streets = [create_typo(x) for x in full_streets]
reference = [list(x) for x in zip(full_streets, typo_streets)]
# Shuffle last half of them for training on dissimilar addresses
half_ix = int(n/2)
bottom_half = reference[half_ix:]
true_address = [x[0] for x in bottom_half]
typo_address = [x[1] for x in bottom_half]
typo_address = list(np.roll(typo_address, 1))
bottom_half = [[x,y] for x,y in zip(true_address, typo_address)]
reference[half_ix:] = bottom_half
# Get target similarities (1's for similar, -1's for non-similar)
target = [1]*(n-half_ix) + [-1]*half_ix
reference = [[x,y] for x,y in zip(reference, target)]
return(reference)
# Define vocabulary dictionary (remember to save '0' for padding)
vocab_chars = string.ascii_lowercase + '0123456789 '
vocab2ix_dict = {char:(ix+1) for ix, char in enumerate(vocab_chars)}
vocab_length = len(vocab_chars) + 1
# Define vocab one-hot encoding
def address2onehot(address,
vocab2ix_dict = vocab2ix_dict,
max_address_len = max_address_len):
# translate address string into indices
address_ix = [vocab2ix_dict[x] for x in list(address)]
# Pad or crop to max_address_len
address_ix = (address_ix + [0]*max_address_len)[0:max_address_len]
return(address_ix)
# Define placeholders
address1_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, max_address_len], name="address1_ph")
address2_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None, max_address_len], name="address2_ph")
y_target_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [None], name="y_target_ph")
dropout_keep_prob_ph = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="dropout_keep_prob")
# Create embedding lookup
identity_mat = tf.diag(tf.ones(shape=[vocab_length]))
address1_embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(identity_mat, address1_ph)
address2_embed = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(identity_mat, address2_ph)
# Define Model
text_snn = model.snn(address1_embed, address2_embed, dropout_keep_prob_ph,
vocab_length, num_features, max_address_len)
# Define Accuracy
batch_accuracy = model.accuracy(text_snn, y_target_ph)
# Define Loss
batch_loss = model.loss(text_snn, y_target_ph, margin)
# Define Predictions
predictions = model.get_predictions(text_snn)
# Declare optimizer
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.01)
# Apply gradients
train_op = optimizer.minimize(batch_loss)
# Initialize Variables
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# Train loop
train_loss_vec = []
train_acc_vec = []
for b in range(n_batches):
# Get a batch of data
batch_data = get_batch(batch_size)
# Shuffle data
np.random.shuffle(batch_data)
# Parse addresses and targets
input_addresses = [x[0] for x in batch_data]
target_similarity = np.array([x[1] for x in batch_data])
address1 = np.array([address2onehot(x[0]) for x in input_addresses])
address2 = np.array([address2onehot(x[1]) for x in input_addresses])
train_feed_dict = {address1_ph: address1,
address2_ph: address2,
y_target_ph: target_similarity,
dropout_keep_prob_ph: dropout_keep_prob}
_, train_loss, train_acc = sess.run([train_op, batch_loss, batch_accuracy],
feed_dict=train_feed_dict)
# Save train loss and accuracy
train_loss_vec.append(train_loss)
train_acc_vec.append(train_acc)
# Print out statistics
if b%10==0:
print('Training Metrics, Batch {0}: Loss={1:.3f}, Accuracy={2:.3f}.'.format(b, train_loss, train_acc))
# Calculate the nearest addresses for test inputs
# First process the test_queries and test_references
test_queries_ix = np.array([address2onehot(x) for x in test_queries])
test_references_ix = np.array([address2onehot(x) for x in test_references])
num_refs = test_references_ix.shape[0]
best_fit_refs = []
for query in test_queries_ix:
test_query = np.repeat(np.array([query]), num_refs, axis=0)
test_feed_dict = {address1_ph: test_query,
address2_ph: test_references_ix,
y_target_ph: target_similarity,
dropout_keep_prob_ph: 1.0}
test_out = sess.run(text_snn, feed_dict=test_feed_dict)
best_fit = test_references[np.argmax(test_out)]
best_fit_refs.append(best_fit)
print('Query Addresses: {}'.format(test_queries))
print('Model Found Matches: {}'.format(best_fit_refs))
# Plot the loss and accuracy
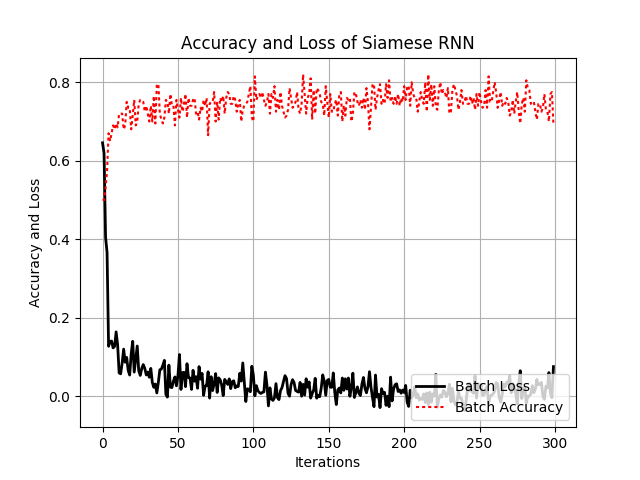
plt.plot(train_loss_vec, 'k-', lw=2, label='Batch Loss')
plt.plot(train_acc_vec, 'r:', label='Batch Accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy and Loss')
plt.title('Accuracy and Loss of Siamese RNN')
plt.grid()
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()输出结果
Training Metrics, Batch 0: Loss=0.671, Accuracy=0.500.Training Metrics, Batch 10: Loss=0.104, Accuracy=0.690.
Training Metrics, Batch 20: Loss=0.117, Accuracy=0.755.
Training Metrics, Batch 30: Loss=0.089, Accuracy=0.705.
Training Metrics, Batch 40: Loss=0.032, Accuracy=0.715.
Training Metrics, Batch 50: Loss=0.033, Accuracy=0.690.
Training Metrics, Batch 60: Loss=0.026, Accuracy=0.730.
Training Metrics, Batch 70: Loss=-0.035, Accuracy=0.795.
Training Metrics, Batch 80: Loss=0.013, Accuracy=0.735.
Training Metrics, Batch 90: Loss=0.034, Accuracy=0.745.
Training Metrics, Batch 100: Loss=0.038, Accuracy=0.690.
Training Metrics, Batch 110: Loss=-0.002, Accuracy=0.790.
Training Metrics, Batch 120: Loss=-0.003, Accuracy=0.765.
Training Metrics, Batch 130: Loss=-0.001, Accuracy=0.780.
Training Metrics, Batch 140: Loss=0.013, Accuracy=0.785.
Training Metrics, Batch 150: Loss=0.002, Accuracy=0.735.
Training Metrics, Batch 160: Loss=-0.002, Accuracy=0.805.
Training Metrics, Batch 170: Loss=-0.002, Accuracy=0.740.
Training Metrics, Batch 180: Loss=0.004, Accuracy=0.765.
Training Metrics, Batch 190: Loss=-0.004, Accuracy=0.725.
Training Metrics, Batch 200: Loss=-0.001, Accuracy=0.765.
Training Metrics, Batch 210: Loss=0.012, Accuracy=0.745.
Training Metrics, Batch 220: Loss=-0.015, Accuracy=0.800.
Training Metrics, Batch 230: Loss=0.006, Accuracy=0.740.
Training Metrics, Batch 240: Loss=-0.021, Accuracy=0.745.
Training Metrics, Batch 250: Loss=-0.018, Accuracy=0.745.
Training Metrics, Batch 260: Loss=0.007, Accuracy=0.800.
Training Metrics, Batch 270: Loss=-0.012, Accuracy=0.765.
Training Metrics, Batch 280: Loss=-0.020, Accuracy=0.790.
Training Metrics, Batch 290: Loss=0.009, Accuracy=0.750.
Query Addresses: ['111 abbey ln', '271 doner cicle', '314 king avenue', 'tensorflow is fun']
Model Found Matches: ['123 abbey ln', '217 donner cir', '314 kings ave', 'tensorflow is so fun']

参考书籍
TensorFlow Machine Learning Cookbook,Author: Nick McClurePub 书籍链接相关文章推荐
- 判断单链表中是否有环,计算出环的首地址 C语言实现
- 利用 TensorFlow 高级 API Keras 实现 MLP,CNN,LSTM
- 如何用 TensorFlow 实现基于 LSTM 的文本分类
- RNN-LSTM循环神经网络-03Tensorflow进阶实现
- 基于tensorflow的RNN-LSTM(一)实现RNN
- javascript实现判断图片地址是否失效
- Tensorflow实现LSTM
- 深度学习(08)_RNN-LSTM循环神经网络-03-Tensorflow进阶实现
- 深度学习(08)_RNN-LSTM循环神经网络-03-Tensorflow进阶实现
- 使用MNIST数据集,在TensorFlow上实现基础LSTM网络
- CNN在句子相似性建模的应用--tensorflow实现篇1
- TensorFlow入门(六) 双端 LSTM 实现序列标注(分词)
- TensorFlow实战12:实现基于LSTM的语言模型
- tensorflow实现基于LSTM的文本分类方法
- TensorFlow (RNN)深度学习下 双向LSTM(BiLSTM)+CRF 实现 sequence labeling 双向LSTM+CRF跑序列标注问题
- tensorflow实现基于LSTM的文本分类方法
- tensorflow39《TensorFlow实战》笔记-07-03 TensorFlow实现Bidirectional LSTM Classifier code
- TensorFlow (RNN)深度学习 双向LSTM(BiLSTM)+CRF 实现 sequence labeling 序列标注问题 源码下载
- 如何基于TensorFlow使用LSTM和CNN实现时序分类任务
- 86、使用Tensorflow实现,LSTM的时间序列预测,预测正弦函数
