Codeforces 767C 树形dp
2017-02-20 14:36
381 查看
Garland
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Once at New Year Dima had a dream in which he was presented a fairy garland. A garland is a set of lamps, some pairs of which are connected by wires. Dima remembered that each two lamps in the garland were connected directly or indirectly via some wires. Furthermore,
the number of wires was exactly one less than the number of lamps.
There was something unusual about the garland. Each lamp had its own brightness which depended on the temperature of the lamp. Temperatures could be positive, negative or zero. Dima has two friends, so he decided to share the garland with them. He wants to
cut two different wires so that the garland breaks up into three parts. Each part of the garland should shine equally, i. e. the sums of lamps' temperatures should be equal in each of the parts. Of course, each of the parts should be non-empty, i. e. each
part should contain at least one lamp.

Help Dima to find a suitable way to cut the garland, or determine that this is impossible.
While examining the garland, Dima lifted it up holding by one of the lamps. Thus, each of the lamps, except the one he is holding by, is now hanging on some wire. So, you should print two lamp ids as the answer which denote that Dima should cut the wires these
lamps are hanging on. Of course, the lamp Dima is holding the garland by can't be included in the answer.
Input
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 106) —
the number of lamps in the garland.
Then n lines follow. The i-th
of them contain the information about the i-th lamp: the number lamp ai,
it is hanging on (and 0, if is there is no such lamp), and its temperature ti ( - 100 ≤ ti ≤ 100).
The lamps are numbered from 1 to n.
Output
If there is no solution, print -1.
Otherwise print two integers — the indexes of the lamps which mean Dima should cut the wires they are hanging on. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
The garland and cuts scheme for the first example:
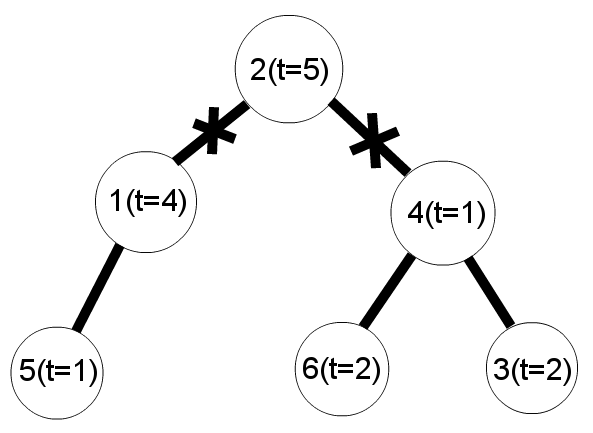
题意:给出一棵树,问能不能切去两条边,分成的三颗子树的点权和相同。
题解:首先算出sum,如果sum不能被3整除,肯定不行。
然后sum/3
dp[i]代表i点和i点的子树的权值和,所以从1结点开始dfs,dp记录,如果当前点的子树和自身的和为sum/3就删掉这颗子树。
如果在下的代码细节看不明白可以留言
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int head[3000005],cnt=0,n,num[3000005],dp[3000005],vis[3000005],ans[3],d,sum;
struct node{
int to,nex;
}edge[6000005];
void add(int u,int v){
edge[cnt].to=v;
edge[cnt].nex=head[u];
head[u]=cnt++;
}
int flag;
void travel(int s,int e,int fa){
for(int i=head[s];~i;i=edge[i].nex){
int v=edge[i].to;
if(v==fa)continue;
if(v==e){
ans[++d]=i/2+1;
flag=1;
return ;
}
else{
travel(v,e,s);
if(flag)return ;
}
}
}
void dfs(int t){
int i;
for(i=head[t];~i;i=edge[i].nex){
int v=edge[i].to;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v]=1;
dfs(v);
dp[t]+=dp[v];
if(d==2)return ;
}
}
if(dp[t]==sum){
flag=0;
travel(1,t,1);
dp[t]=0;
}
}
int main(){
int i,j,x,y;
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(x!=0){
add(i,x);
add(x,i);
}
else cnt+=2;
num[i]=dp[i]=y;
sum+=y;
}
if(sum%3){
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
sum/=3;
vis[1]=1;
dfs(1);
if(d>=2)printf("%d %d\n",ans[1],ans[2]);
else printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Once at New Year Dima had a dream in which he was presented a fairy garland. A garland is a set of lamps, some pairs of which are connected by wires. Dima remembered that each two lamps in the garland were connected directly or indirectly via some wires. Furthermore,
the number of wires was exactly one less than the number of lamps.
There was something unusual about the garland. Each lamp had its own brightness which depended on the temperature of the lamp. Temperatures could be positive, negative or zero. Dima has two friends, so he decided to share the garland with them. He wants to
cut two different wires so that the garland breaks up into three parts. Each part of the garland should shine equally, i. e. the sums of lamps' temperatures should be equal in each of the parts. Of course, each of the parts should be non-empty, i. e. each
part should contain at least one lamp.

Help Dima to find a suitable way to cut the garland, or determine that this is impossible.
While examining the garland, Dima lifted it up holding by one of the lamps. Thus, each of the lamps, except the one he is holding by, is now hanging on some wire. So, you should print two lamp ids as the answer which denote that Dima should cut the wires these
lamps are hanging on. Of course, the lamp Dima is holding the garland by can't be included in the answer.
Input
The first line contains single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 106) —
the number of lamps in the garland.
Then n lines follow. The i-th
of them contain the information about the i-th lamp: the number lamp ai,
it is hanging on (and 0, if is there is no such lamp), and its temperature ti ( - 100 ≤ ti ≤ 100).
The lamps are numbered from 1 to n.
Output
If there is no solution, print -1.
Otherwise print two integers — the indexes of the lamps which mean Dima should cut the wires they are hanging on. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
Examples
input
6 2 4 0 5 4 2 2 1 1 1 4 2
output
1 4
input
6 2 4 0 6 4 2 2 1 1 1 4 2
output
-1
Note
The garland and cuts scheme for the first example:

题意:给出一棵树,问能不能切去两条边,分成的三颗子树的点权和相同。
题解:首先算出sum,如果sum不能被3整除,肯定不行。
然后sum/3
dp[i]代表i点和i点的子树的权值和,所以从1结点开始dfs,dp记录,如果当前点的子树和自身的和为sum/3就删掉这颗子树。
如果在下的代码细节看不明白可以留言
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int head[3000005],cnt=0,n,num[3000005],dp[3000005],vis[3000005],ans[3],d,sum;
struct node{
int to,nex;
}edge[6000005];
void add(int u,int v){
edge[cnt].to=v;
edge[cnt].nex=head[u];
head[u]=cnt++;
}
int flag;
void travel(int s,int e,int fa){
for(int i=head[s];~i;i=edge[i].nex){
int v=edge[i].to;
if(v==fa)continue;
if(v==e){
ans[++d]=i/2+1;
flag=1;
return ;
}
else{
travel(v,e,s);
if(flag)return ;
}
}
}
void dfs(int t){
int i;
for(i=head[t];~i;i=edge[i].nex){
int v=edge[i].to;
if(!vis[v]){
vis[v]=1;
dfs(v);
dp[t]+=dp[v];
if(d==2)return ;
}
}
if(dp[t]==sum){
flag=0;
travel(1,t,1);
dp[t]=0;
}
}
int main(){
int i,j,x,y;
scanf("%d",&n);
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(x!=0){
add(i,x);
add(x,i);
}
else cnt+=2;
num[i]=dp[i]=y;
sum+=y;
}
if(sum%3){
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
sum/=3;
vis[1]=1;
dfs(1);
if(d>=2)printf("%d %d\n",ans[1],ans[2]);
else printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- 【CodeForces 767C】Garland (树形DP)
- CodeForces 543d Road Improvement(巧妙地树形dp)
- Codeforces 935E.Fafa and Ancient Mathematics-树形dp
- codeforces 23E 树形DP
- CodeForces 500 D. New Year Santa Network(树形DP)
- Codeforces 711C. Bear and Tree Jumps【树形dp好题】
- Road Improvement - CodeForces 543 D 树形dp
- Codeforces 462D Appleman and Tree 树形dp
- codeforces 337D D. Book of Evil(树形dp)
- Codeforces 461B. Appleman and Tree[树形DP 方案数]
- CodeForces - 219D Choosing Capital for Treeland【树形dp*好题】
- codeforces 161D Distance in Tree(树形dp)
- [树形DP] Codeforces 856D. Masha and Cactus
- codeforces 533B B. Work Group(树形dp)
- Codeforces 280C Game on Tree 树形期望dp
- codeforces contest 855 problem C(树形DP)
- Codeforces 219D - Choosing Capital for Treeland(树形dp)
- bzoj 4424: Cf19E Fairy && codeforces 19E. Fairy【树形dp】
- codeforces 61D Eternal Victory 树形DP
- Codeforces 61D--树形dp
