几个经典基础算法题目
2016-09-18 08:48
260 查看
练习1,判断是否为素数:
// ConsoleAppIsPrime1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。//
/*
*函数功能:判断一个输入的数是否为素数
*函数原形:bool Prime( int x )
*参数:int x:将要判断的数
*返回值:bool型变量,判断是否是素数
*备注:需要包含头文件<math.h>
*日期:2014/11/25
*原创:否
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:tangyibiao520@163.com
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
bool Prime( int x );
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
bool flag;
int a;
while (true)
{
cout<<"Please enter a number:";
cin>>a;
flag=Prime(a);
if (flag==true)
cout<<"Prime!!!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Not Prime!";
}
system("pasue");
return 0;
}
/*原理:将输入的x与2到sqrt(x)整除一遍,若其中任意一个能整除则x不是素数*/
bool Prime( int x )
{
x=abs( x );
if ( x < 1 )
return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= int( sqrt( float( x ))) ; i++ )
{
if ( x % i==0 )//一旦可以整除立马返回他不是素数
return false;
}
return true;
}
练习2,指定范围内的素数:
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppIsPrime.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*函数功能:判断指定范围内素数个数
*函数原形:int Primes( int n ,int m )
*参数:
int n:请输入想要确认的素数范围下限
int m:请输入想要确认的素数范围上限
*返回值:n到m范围内素数的个数
*备注:
*日期:2014/11/25
*原创:是
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:tangyibiao520@163.com
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "math.h"
using namespace std;
int Primes( int n ,int m );
bool Prime( int x );
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int countprimes=0;
int a=0;
int b=0;
while (true)
{
cout<<"请输入想要确认的素数范围上限:";
cin>> a ;
cout<<"请输入想要确认的素数范围下限:";
cin>> b;
countprimes=Primes(a,b);
cout<<"在 "<< a <<"到 "<< b <<"之间的素数个数为: "<< countprimes<<endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
bool Prime( int x )//判断素数
{
x=abs( x );
if ( x < 1 )
return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= int( sqrt( float( x ))) ; i++ )
if ( x % i==0 )
return false;
return true;
}
int Primes( int n ,int m )//统计素数
{
int count=0;
bool flag=false;
for (; n <= m ; n++)
{
flag=Prime( n );
if (flag==true)
count++;
}
return count;
}
练习3,某整数是否为2的次幂:
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
/*
*函数功能:判断一个整数是否为2的次幂
*函数原形:bool IsTwoN(int n);
*参数:int n,要判断的整数
*返回值:bool型变量,表征是与否
*时间复杂度:O(1)
*备注:无
*日期:2014/11/23
*原创:否
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:tangyibiao520@163.com
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "math.h"
using namespace std;
bool IsTwoN(int n);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
while(1)
{
bool flag;
int m;
cout<<"请输入一个整数:"<<endl;
cin>>m;
flag=IsTwoN(m);
if (flag==true)
cout<<m<<"是2的次幂,恭喜你!"<<endl<<endl;
else
cout<<m<<"不是2的次幂"<<endl<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
bool IsTwoN(int n)
{
//若是,必定与其自身减1后的数相“与”为假,比如8,1000&0111=0000,
//if(n>0&&((n&(n-1))==0))/*第一种方法*/
//如果n==2的log以2为底数的n对数的pow函数后,则是
if (n==pow(2,(int)(log10(n)/log10(2.))))/*第二种方法*/
return true;
else
return false;
}
练习4,整数的二进制数中1的个数:
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
/*
*函数功能:求取整数对应二进制数中1的个数
*函数原形:int Count(int z);
*参数:int z,要计算的整数
*返回值:返回整数对应二进制数中1的个数
*时间复杂度:O(1)
*备注:无
*日期:2014/11/23
*原创:否
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:tangyibiao520@163.com
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int Count(int z);
int main()
{
int number;
int z;
char asn='n';
do
{
cout<<"请输入一个整数:"<<endl;
cin>>z;
number=Count(z);
cout<<"该整数对应二进制数1的个数为:"<<endl;
cout<<number<<endl;
cout<<"是否继续?(y/n)";
cin>>asn;
} while (asn=='y');
return 0;
}
int Count(int v)
{
int num=0;
while (v)
{
//第一种算法:复杂度较低
// num+=v & 0x01;
// v >>=1;
//第二种算法:
// v&=(v-1);
// num++;
/*第三种算法:算法复杂度较高*/
if(v%2==1)
num++;
v=v/2;
}
return num;
}
练习5,统计指定数据出现次数:
[html]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppDigitCount.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描述:用随机函数生成100个在100到999之间的整数,设计程序统计这些三位数中十位是分别是0-9出现次数
*问题示例:无
*函数功能:统计三位数中十位数0-9出现的次数
*函数原形:void DigitCount(int num[], int count[])
*参数:int num[], 欲统计的数组,int count[]存储统计结果
*返回值: 无
*时间复杂度:O(n)
*备注:无
*日期:2014/12/31
*算法描述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100
using namespace std;
/*
*函数功能:生成100到999的随机整数数
*函数原形:void RandNumIn(int num[])
*参数:int num[],用于存储随机整数
*返回值:无
*/
void RandNumIn(int num[])
{
srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //设置随机种子
for( int i=0; i<MAX; i++)
num[i]=100+rand()%900; //生成100到999的随机整数数
}
/*
*函数功能:输出生成的100个随机整数
*函数原形:void output(int num[])
*参数:int num[],即将输出的整数
*返回值:无
*/
void RandNumOut(int num[])
{
int count=0;
for( int i=0; i<MAX; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
count++;
if(0==count%10)//每个10个数字就换行
cout<<endl;
}
cout<<endl;
}
/*
*函数功能:统计三位数中十位数0-9出现的次数
*函数原形:void DigitCount(int num[], int count[])
*参数:int num[], 欲统计的数组,int count[]存储统计结果
*返回值: 无
*/
void DigitCount(int num[], int count[])
{
int mod;
for(int i=0; i<MAX; i++)
{
mod=num[i]/10%10; //得到十位数字
count[mod]++;
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int num[MAX], count[10];
memset(count, 0, 10*sizeof(int)); /* 初始化统计数组 */
memset(num, 0, 100*sizeof(int)); /* 初始化随机数组 */
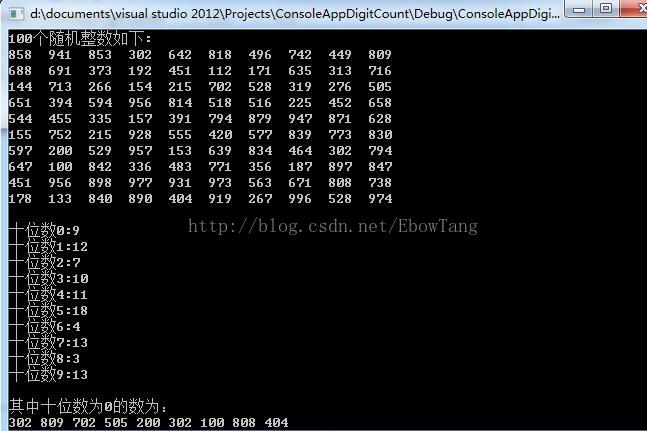
cout<<"100个随机整数如下:"<<endl;
RandNumIn(num);//生成100个随机数
RandNumOut(num);//输出100个随机数
DigitCount(num, count);//统计十位数的出现个数
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
cout<<"十位数"<<i<<":"<<count[i]<<endl;
cout<<endl;
cout<<"其中十位数为0的数为:"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<MAX;i++)
{
if (num[i]/10%10==0)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
}
}
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习6,进制的转换:
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppHexadecimalTrans.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描述:将十进制转换成二进制或者八进制,16进制
*问题示例:输入50 2,输出110010
*函数功能:
*函数原形:void HexadecimalTrans(int n, int d)
*参数:int n,十进制整数 int d,进制数
*返回值:无
*时间复杂度:
*备注:无
*日期:2014/11/30
*算法描述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int flag=1;
void HexadecimalTrans(int n, int d)
{
int mod;
mod=n%d; //n表示数字,d表示进制
n=n/d;
while(flag && n) //辗转相除
HexadecimalTrans(n,d);
switch(mod)
{
case 10:
cout<<"A";
break;
case 11:
cout<<"B";
break;
case 12:
cout<<"C";
break;
case 13:
cout<<"D";
break;
case 14:
cout<<"E";
break;
case 15:
cout<<"F";
break;
default:
cout<<mod; //二进制和八进制均在这里输出,mod保存了辗转相除的每次结果
}
flag=0;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int n, d;
cout<<"输入十进制数字:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
cout<<"请输入将要进行的进制转换(2,8,16):"<<endl;
cin>>d;
HexadecimalTrans(n,d); //调用转换函数
cout<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习7,查找指定数据的位置(暴力搜索):
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppSpecifiedSearch.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描述:暴力搜索遍历查找,从100个随机函数中(100-999)查找指定数字的位置
*问题示例:
*函数功能:查找指定的数
*函数原形:int FindNum(int num[], int x)
*参数:int num[],要查找的数组, int x,要查找的数
*返回值:数字的位置
*时间复杂度:O()
*备注:无
*日期:2014/7/30
*算法描述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 100
/*
*函数功能:产生指定的随机数
*函数原形:void RandNumIn(int num[])
*参数:int num[],产生的随机数保存到数组num中
*返回值:无
*/
void RandNumIn(int num[])
{
int i;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //得到随机种子
for(i=0; i<MAX; i++)
num[i]=100+rand()%900; //生成100--999以内的随机三位整数
}
/*
*函数功能:输出产生的随机数
*函数原形:void RandNumOut(int num[])
*参数:int num[],将要输出的数组
*返回值:无
*/
void RandNumOut(int num[])
{
int count=0;
for(int i=0; i<MAX; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
count++;
if(0==count%10)
cout<<endl;
}
}
/*
*函数功能:查找指定的数
*函数原形:int FindNum(int num[], int x)
*参数:int num[],要查找的数组, int x,要查找的数
*返回值:数字的位置
*/
int FindNum(int num[], int x)
{
for(int i=0; i<MAX; i++)
if(x == num[i]) //遍历查找指定数字的位置
return i;
return 0;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int x, pos, num[MAX]; //设置存储数组
RandNumIn(num);
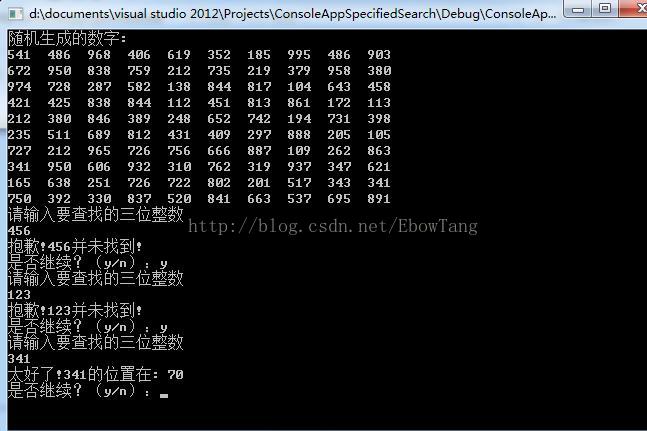
cout<<"随机生成的数字: "<<endl;
RandNumOut(num);
cout<<"请输入要查找的三位整数"<<endl;
cin>>x;
pos=FindNum(num, x); //调用查找函数
if(pos)
cout<<"太好了!"<<x<< "的位置在: "<< pos<<endl;
else
cout<<"抱歉!"<<x<< "并未找到! "<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习8,二分法查找指定数据位置:
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppSpecifiedSearch.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描述:二分法遍历查找,从100个随机函数中(100-999)查找指定数字的位置
*问题示例:
*函数功能:二分查找法查找指定的数
*函数原形:int SpecialFindNum(int num[], int x, int low, int high)
*参数:
int num[],要查找的数组,
int x,要查找的数
int low, 查找的起始位置
int high,查找的末端位置
*返回值:数字的位置
*时间复杂度:O()
*备注:无
*日期:2014/7/30
*算法描述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 101
/*
*函数功能:产生指定的随机数
*函数原形:void RandNumIn(int num[])
*参数:int num[],产生的随机数保存到数组num中
*返回值:无
*/
void RandNumIn(int num[])
{
int i;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL)); //得到随机种子
for(i=1; i<MAX; i++)
num[i]=100+rand()%900; //生成100--999以内的随机三位整数
}
/*
*函数功能:输出产生的随机数
*函数原形:void RandNumOut(int num[])
*参数:int num[],将要输出的数组
*返回值:无
*/
void RandNumOut(int num[])
{
int count=0;
for(int i=1; i<MAX; i++)
{
cout<<num[i]<<" ";
count++;
if(0==count%10)
cout<<endl;
}
}
/*
*函数功能:快速排序法
*函数原形:void QuickSort(int num[], int low, int high)
*参数:
int num[],要排序的数组,
int low, 查找的起始位置
int high,查找的末端位置
*返回值:无
*/
void QuickSort(int num[], int low, int high)
{
int l, h;
if(low<high)
{
l=low;
h=high;
num[0]=num[l];
while(l<h)
{
while(l<h && num[h]>=num[0])
h--; //利用快速排序是数据有序
num[l]=num[h];
while(l<h && num[l]<=num[0])
l++;
num[h]=num[l];
}
num[l]=num[0];
QuickSort(num, low, l-1);
QuickSort(num, l+1, high);
}
}
/*
*函数功能:二分查找法查找指定的数
*函数原形:int SpecialFindNum(int num[], int x, int low, int high)
*参数:
int num[],要查找的数组,
int x,要查找的数
int low, 查找的起始位置
int high,查找的末端位置
*返回值:数字的位置
*/
int SpecialFindNum(int num[], int x, int low, int high)
{
int mid; //中间位置
while(low<=high)
{
mid=(low+high)/2; /* 找到 */
if(x==num[mid])
return mid;
else if(x<num[mid]) //两边的游标不停往中间移动比较
high=mid-1;
else
low=mid+1;
}
return 0;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int x, pos, num[MAX];
RandNumIn(num);
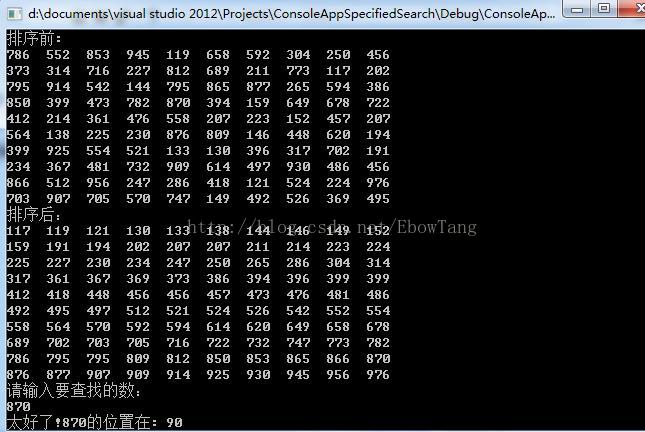
cout<<"排序前:"<<endl;
RandNumOut(num);
QuickSort(num, 1, MAX-1);
cout<<"排序后:"<<endl;
RandNumOut(num);
cout<<"请输入要查找的数:"<<endl;
cin>>x;
pos=SpecialFindNum(num, x, 1, MAX-1); //调用查找函数
if(pos)
cout<<"太好了!"<<x<< "的位置在: "<< pos<<endl;
else
cout<<"抱歉"<<x<< "没有找到 "<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习9,字符串中指定数据出现次数
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppCharCount.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描述:设计一个程序,统计随机给出的字符串的数字的个数,字母的个数,特殊字符的个数
*问题示例:123asd,数字3,字母3,特殊字符0
*函数功能:统计字符串中的数据
*函数原形:void CharCal(char *str, int count[])
*参数:char *str,欲统计的字符串, int count[],用于存储统计结果
*返回值:无
*时间复杂度:O()
*备注:无
*日期:2014/7/30
*算法描述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX 1024
using namespace std;
/*
*函数功能:统计字符串中的数据
*函数原形:void CharCal(char *str, int count[])
*参数:char *str,欲统计的字符串, int count[],用于存储统计结果
*返回值:无
*/
void CharCal(char *str, int count[])
{
while(*str)
{
if((*str>='0')&&(*str<='9')) //统计数字型字符
count[0]++;
else if(((*str>='a')&&(*str<='z')) || ((*str>='A')&&(*str<='Z'))) //统计字符型字符
count[1]++;
else //其他特殊字符
count[2]++;
str++;//指针移动
}
}
/*
*函数功能:输出统计结果
*函数原形:void CharCount( int count[])
*参数: int count[],存储统计结果的数组
*返回值:无
*/
void CharCount( int count[])
{
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
{
switch(i)
{
case 0:
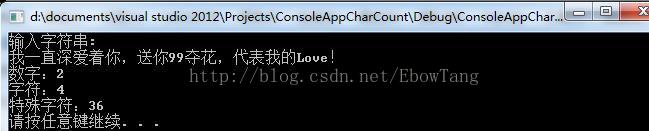
cout<<"数字:"<<count[i]<<endl;
break;
case 1:
cout<<"字符:"<< count[i]<<endl;
break;
case 2:
cout<<"特殊字符:"<<count[i]<<endl;
break;
}
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
char str[MAX]; //定义存储输入字符串的数组
int count[3]; //用于存储统计结果0->数字; 1->字符; 2->其他
memset(count, 0, 3*sizeof(int)); //初始化统计数组
cout<<"输入字符串: "<<endl;
cin>>str;
CharCal(str, count);//统计
CharCount(count);//输出显示
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习10,逆序输出字符串
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppCharTest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描述:输入字符串,将其逆序输出
*问题示例:输入,asdfgh,输出hgfdsa
*函数功能:逆序输出字符串的内容
*函数原形:void Reverse( char* s, int left, int right );
*参数:
char *,欲逆序的字符串,
int left, 逆序的左起点
int right,逆序的右尾点
*返回值:无
*时间复杂度:O(n)
*备注:无
*日期:2014/7/30
*算法描述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void Reverse( char* s, int left, int right );
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int len;
char a[100];
while(1)
{
cout<<"请输入字符串a:"<<endl;
cin>>a;
len=strlen(a);
Reverse(a,0,len-1);
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
cout<<a[i];
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
//算法一: 对字符串s在指定区间left和right之间进行逆序,递归法
void Reverse( char* s, int left, int right )
{
if(left >= right)
return;
char t = s[left] ;
s[left] = s[right] ;
s[right] = t ;
Reverse(s, left + 1, right - 1) ;
}
/*
//算法二:与上面的方法没有太大区别
void Reverse( char* s, int left, int right )
{
while( left < right )
{
char t = s[left] ;
s[left++] = s[right] ;
s[right--] = t ;
}
}*/
练习11,字符串包含判断
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppCharTest.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*问题描述:输入两个字符串,判断相互之间字符串是否包含
*问题示例:输入,asdfgh,输出asd,结果,包含!
*函数功能:判断两个字符串是否包含
*函数原形:bool IsContain(char *pStrA, char *pStrB);
*参数:
char *pStrA, 第一个字符串
char *pStrB,第二个字符串
*返回值:布尔变量
*时间复杂度:O(n)
*备注:无
*日期:2014/7/30
*算法描述:
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
bool IsContain(char *pStrA, char *pStrB);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
char a[10],b[10];
bool flag;
while(true)
{
cout<<"Please Enter characters A:"<<endl;
cin>>a;
cout<<"Please Enter characters B:"<<endl;
cin>>b;
flag=IsContain(a, b);
if (flag==false)
cout<<"Not Contain!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Contain!"<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
//算法1
bool IsContain(char *pStrA, char *pStrB)
{
int lenA = strlen(pStrA);
int lenB = strlen(pStrB);
int i,j;
char temp;
for( i = 0; i < lenA; i++)
{//直接对字符数组A进行循环移位再立马进行字符包含判断
temp = pStrA[0];
for( j = 0; j < lenA - 1; j++)
pStrA[ lenA - 1] = pStrA[j + 1];
pStrA[j] = temp;
if(strncmp(pStrA, pStrB, lenB) == 0)
return true;
}
//若果执行到最后都还没有匹配成功,则返回false
if(i == lenA)
return false;
}/*
//算法2
bool IsContain(char *pStrA, char *pStrB)
{
int lenp = strlen(pStrA);
char *temp = (char*)malloc(2 * lenp + 1);//动态分配内存
strcpy_s(temp,2 * lenp + 1,pStrA);
strcpy_s(temp + lenp, 2 * lenp + 1,pStrA);
if(strstr(temp, pStrB))
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}*/
练习12,打印任意位元的格雷码序列:
比如3位的所有格雷码:000
001
011
010
110
111
101
100
代码如下:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?

// ConsoleAppGrayCode.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
bool GrayCode(int nBits);
int changeBit(int a);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int nBits=0;
cout<<"请输入位元长度:"<<endl;
cin>>nBits;
GrayCode(nBits);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
bool GrayCode(int nBits)
{
bool flag=true;
do
{
if (nBits<0)
{
cout<<"你的输入有误,请重新输入:"<<endl;
cin>>nBits;
}else
{
flag=false;
}
} while (flag);
int *pGray=new int[nBits];
for (int i=0;i<nBits;i++)
{
pGray[i]=0;
cout<<0;
}
cout<<endl;
for (int j=1;j<pow(2,nBits);j++)
{
if (j%2==1)
{
pGray[nBits-1]=changeBit(pGray[nBits-1]);
for (int i=0;i<nBits;i++)
{
cout<<pGray[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}else
{
int j=0;
for ( j=nBits-1;j>=0;j--)
{
if (pGray[j]==1)
{
pGray[j-1]=changeBit(pGray[j-1]);
break;
}
}
for (int i=0;i<nBits;i++)
{
cout<<pGray[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
return true;
}
int changeBit(int a)
{
if (a==0)
{
return 1;
}else
{
return 0;
}
}
另一份可参考代码:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define CHANGE_BIT(a) a=((a=='0')? '1':'0') //定义宏实现改变位元值
#define NEXT_BIT(x) x=(1-(x)) //设定奇数项或偶数项
/***************构建n位元的格雷码***************/
void findGrayCode(int n){
if (n <=0)
{
cout<<"输入超出有效范围"<<endl; //验证输入值是否合法
return;
}
char* gray=new char
; //声明存储每个格雷码的数组
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) //初始化数组为0
{
gray[i] = '0';
cout<<'0'; //打印其实格雷码0000...
}
cout<<endl;
int odd = 1; &
4d35e
nbsp; //定义奇数标志,1为奇数项,0为偶数项
int i=0;
/**********************循环构造并输出格雷码*************************/
while(1){
if (odd) //如果为奇数项,更改最右边位元值为相反值
{
CHANGE_BIT(gray[0]); //本题为反向存储
}else{
/***********************如果为偶数项则查找从数的右边起第一个1的位置*************/
for (i=0;i<n && gray[i]=='0';i++);
if (i==n-1) //如果i为数的最左边位,则退出循环,所有格雷码查找完成
break;
CHANGE_BIT(gray[i+1]); //更改第一个1左边的以为的值
}
for (i=n-1;i>=0;i--) //输出改格雷码
{
cout<<gray[i];
}
cout<<endl;
NEXT_BIT(odd); //更改奇偶属性
}
}
/**************************测试主函数*************************/
int main(){
int n;
cout<<"输入位元数:"<<endl;
cin>>n;
cout<<n<<"位元的格雷码为:"<<endl;
findGrayCode(n);
return 0;
}
练习14,约舍夫出局
N个人围成一圈,从第一个开始报数,第M个将出局,最后剩下一个,其余人都将出局。例如N=6,M=5,被出局的顺序是:5,4,6,2,3,1。
(1)CircleList.h的代码如下:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
template<class DataType>class LinkList;
template<class DataType>
class LinkNode
{
public:
LinkNode()
{
next = NULL;
data = 0;
}
//函数参数表中的形参允许有默认值,但是带默认值的参数需要放后面
LinkNode(DataType item)
{
next = NULL;
data = item;
}
friend class LinkList<DataType>;
private:
DataType data;
LinkNode<DataType> *next;
};
/* 带头结点的单链表定义 */
template<class DataType>
class LinkList
{
public:
//无参数的构造函数
LinkList(int size)
{
head = new LinkNode<DataType>;//头结点
maxSize=size;
nLength=0;
}
//析构函数
~LinkList()
{
}
//获取链表长度
int Length() const
{
return nLength;
}
//定位指定的位置,返回该位置上的结点指针
LinkNode<DataType>* Locate(int pos);
//在指定位置pos插入值为item的结点,失败返回false
bool Insert(DataType item, int pos);
//打印链表
void Print() const;
//创建一个链表环
void CreatCircle();
//判断是否纯在单链表环
bool IsCircle();
//数数移动
bool CountMove( int nStep=0 ,int i=0 );
private:
LinkNode<DataType> *head;
int maxSize;
int nLength;
};
/* 返回链表中第pos个元素的地址,如果pos<0或pos超出链表最大个数返回NULL */
template<class DataType>
LinkNode<DataType>* LinkList<DataType>::Locate(int pos)
{
LinkNode<DataType> *p = head;//head和p指向共同的内容,头结点无数据,只是个指针
if (pos < 0)
{
cerr<<"位置参数有错误"<<endl;
return NULL;
}
int i = 0;
while (p != NULL && i < pos)
{
p = p->next;
i++;
}
return p;
}
template<class DataType>
bool LinkList<DataType>::Insert(DataType item, int pos)
{
if (Length() >= maxSize)
{
cout<<"错误:链表已满"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
LinkNode<DataType> *p = Locate(pos);
LinkNode<DataType> *newNode = new LinkNode<DataType>(item);//创建新节点
if (NULL == newNode)
{
cerr << "分配内存失败!" << endl;
exit(1);
}
newNode->next = p->next;
p->next = newNode;
nLength++;
return true;
}
template<class DataType>
void LinkList<DataType>::Print() const
{
int count = 0;
LinkNode<DataType> *p = head;
while (NULL != p->next)
{
p = p->next;
std::cout << p->data << " ";
if (++count % 15 == 0) //每隔十个元素,换行打印
cout << std::endl;
}
}
//创建一个链表环
template<class DataType>
void LinkList<DataType>:: CreatCircle()
{
int nLen=Length();
int nLen1=1;
LinkNode<DataType> *ptail=Locate(nLen);
LinkNode<DataType> *pcirStart=Locate(nLen1);
ptail->next=pcirStart;
}
//是否纯在链表环?
template<class DataType>
bool LinkList<DataType>::IsCircle()
{
if ( head ==NULL)
{
cerr<<"空链表"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
LinkNode<DataType> *pFast,*pSlow;
pSlow=head;
pFast=head;
while(pFast!=NULL&&pFast->next!=NULL)
{
pFast=pFast->next->next;
pSlow=pSlow->next;
if (pSlow==pFast)
{
return true;
break;
}
}
return false;
}
<pre name="code" class="html">template<class DataType>
bool LinkList<DataType>::CountMove( int nStep,int k)//指定出局人数
{
if ( k > Length() )
{
cerr<<"写你麻痹,滚回去检查!"<<endl;
return false;
}
LinkNode<DataType> *pCurr=NULL,*pPrev=NULL;
int i = 0; // 计数
int n=0;
pCurr = pPrev = head;
while( n < k )
{
if (i == nStep)
{
// 踢出环
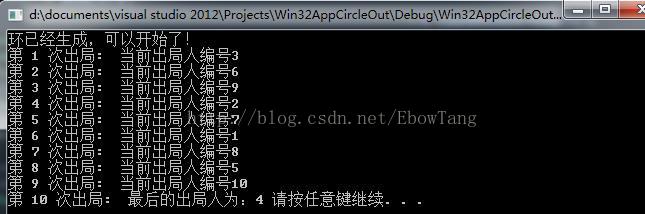
cout<<"第 "<<n+1<<" 次出局"<<": ";
cout<<"当前出局人编号"<<pCurr->data<<endl; // 显示出圈循序
pPrev->next = pCurr->next;
delete pCurr;
pCurr = pPrev->next;
i = 1;
n++;
}
pPrev = pCurr;
pCurr = pCurr->next;
if (pPrev == pCurr)
{
// 最后一个
cout<<"第 "<<n+1<<" 次出局"<<": ";
cout<<"最后的出局人为:"<<pCurr->data<<" "; // 显示出圈循序
delete pCurr;
//最后一个节点删除后的“擦屁股”处理
pCurr=NULL;
head->next=head;
n++;
break;
}
i++;
}
return true;
}
(2)主测试代码:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
// Win32AppCircleOut.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "CircleList.h"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int nlen=10;
LinkList<int> s(nlen);
for (int i=0;i<nlen;i++)
{
s.Insert(i+1,i);
}
s.CreatCircle();
if (s.IsCircle())
{
cout<<"环已经生成,可以开始了!"<<endl;
}
s.CountMove(3,10);//数到3出局,记录前30个人的出局情况
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习15,汉诺塔递归
汉诺塔递归问题:[html]
view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppHanoi.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int Hanoicount=0;
bool HanoiMove(int n,char a,char b,char c);//将n个盘从a借助b移动到c
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
HanoiMove(5,'A','B','C');
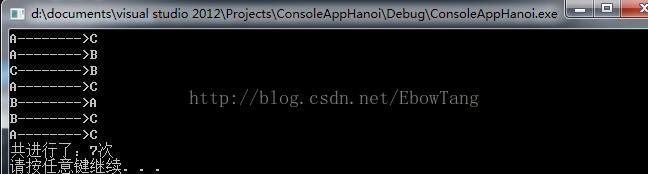
cout<<"共进行了:"<<Hanoicount<<"次"<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
bool HanoiMove(int n,char a,char b,char c)
{
if ( n == 1 )
{
cout<<a<<"-------->"<<c<<endl;
Hanoicount++;
}else
{
HanoiMove(n-1,a,c,b);
cout<<a<<"-------->"<<c<<endl;
HanoiMove(n-1,b,a,c);
Hanoicount++;
}
return true;
}
练习,16求某年某月某日是当年的第几天
[html]view plain
copy
print?
/ ConsoleAppRunNian.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "windows.h"
using namespace std;
int leap(int a) /*自定义函数leap用来指定年份是否为闰年*/
{
if (a % 4 == 0 && a % 100 != 0 || a % 400 == 0) /*闰年判定条件*/
return 1; /*是闰年返回1*/
else
return 0; /*不是闰年返回0*/
}
int number(int year, int m, int d) /*自定义函数number计算输入日期为该年第几天*/
{
if ( m>12 || d > 31 || d < 0 || m<0)
{
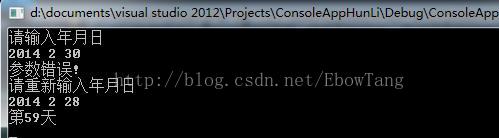
cerr<<"参数错误!"<<endl;
return -1;
}
if (m ==2)
{
if (d > 29)
{
cerr<<"参数错误!"<<endl;
return -1;
}
}
int sum = 0, i;
/*数组a存放平年每月的天数*/
int a[12] ={31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
int b[12] ={31, 29, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31}; /*数组b存放闰年每月的天数*/
if (leap(year) == 1) /*判断是否为闰年*/
for (i = 0; i < m - 1; i++)
sum += b[i]; /*是闰年,累加数组b前m-1个月份天数*/
else
for (i = 0; i < m - 1; i++)
sum += a[i]; /*不是闰年,累加数组a钱m-1个月份天数*/
sum += d; /*将前面累加的结果加上日期,求出总天数*/
return sum; /*将计算的天数返回*/
}
void main()
{
int year, month, day, n; /*定义变量为基本整型*/
cout<<"请输入年月日"<<endl;
cin>>year>>month>>day; /*输入年月日*/
n = number(year, month, day); /*调用函数number*/
while (n == -1)
{
cout<<"请重新输入年月日"<<endl;
cin>>year>>month>>day; /*输入年月日*/
n = number(year, month, day); /*调用函数number*/
}
cout<<"第"<<n<<"天"<<endl;
Sleep(5000);
}
练习17,逻辑推理题
婚礼上的谎言
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppHunLi.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "windows.h"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int a, b, c;
for (a = 1; a <= 3; a++) /*穷举a的所有可能*/
for (b = 1; b <= 3; b++) /*穷举b的所有可能*/
for (c = 1; c <= 3; c++) /*穷举c的所有可能*/
if (a != 1 && c != 1 && c != 3 && a != b && a != c && b != c)
/*如果表达式为真,则输出结果,否则继续下次循环*/
{
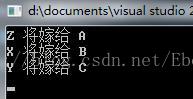
cout<<char('X' + a - 1)/*转换数据类型*/<<" 将嫁给 A"<<endl;
cout<<char('X' + b - 1)<<" 将嫁给 B"<<endl;
cout<<char('X' + c - 1)<<" 将嫁给 C"<<endl;
}
Sleep(5000);
return 0;
}
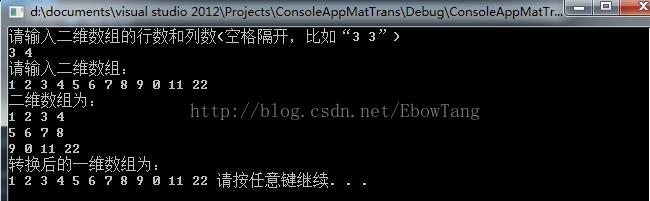
练习18,二维数组转换为一维数组:
[html]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppMatTrans.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
/******************
定义二维数组char array[x][y];
1.只定义个一维的就可以了
char *array;
array = new char[x*y]; 这种方式等价于char *array = new char[x*y];
访问的时候*(array+i*y+j)表示array[i][j]
2.定义一个二维数组
char **array1
array1 = new char *[x];
for(i=0;i<x;++i)
array1[i] = new char[y];
...用的时候可以直接array1[i][j]
注意delete
*************/
int Trans2DArray(int **src2dArr,int nrow,int ncol,int *dst1dArr);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int** mat;
int row=3,col=3;//row为行数
cout<<"请输入二维数组的行数和列数(空格隔开,比如“3 3”)"<<endl;
cin>>row>>col;
mat =new int*[row];//二维数组的每行的指针
cout<<"请输入二维数组:"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
mat[i] = new int[col];
for (int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
cin>>mat[i][j];
}
}
cout<<"二维数组为:"<<endl;
int count=0;
for (int i=0;i<row;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<col;j++)
{
cout<<mat[i][j]<<" ";
count++;
}
if ( count%col == 0 )
{
cout<<endl;
}
}
int *arr =new int[row*col];
for (int n=0;n<row*col;n++)
{
arr
=0;
}
Trans2DArray(mat,row,col,arr);
cout<<"转换后的一维数组为:"<<endl;
for (int k=0;k < row*col;k++)
{
cout<<arr[k]<<" ";
}
delete[] arr;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int Trans2DArray(int **src2dArr,int nRow,int nCol,int *dst1dArr)
{
if (src2dArr == NULL || nRow < 0 || nCol <0)
{
cerr<<"参数错误"<<endl;
return 0;
}
for (int i=0;i<nRow;i++)
{
for (int j=0;j<nCol;j++)
{
dst1dArr[j+i*nCol]=src2dArr[i][j];//j+i*nCol表示第i行j列的数据
}
}
return 1;
}
练习19,求取一个二进制数的长度
定义:二进制长度就是最高位1的下标值+1(下标从0开始),比如16 = 10000,则长度是5, 2= 0010,长度为2[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int BitLength(unsigned int n);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int count=0,a;
do
{
cout<<"请输入一个整数"<<endl;
cin>>a;
count=BitLength(a);
cout<<"该整数对应二进制数的长度为:"<<count<<endl;
} while (a>0);
return 0;
}
//算法一:易阅读
int BitLength(unsigned int n)
{
int c = 0 ; //计数
while (n)
{
++c ;
n >>= 1 ;
}
return c ;
}
//算法二:与上面的解法本质一样
int BitLength(unsigned int n)
{
return n ? BitLength1(n >>=1) + 1 : 0 ;
}
//算法三:以空间换时间(参考网络)
int BitLength(unsigned int n)
{
// pow of 2, 2^0 - 2 ^31
int powof2[32] =
{
1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32,
64, 128, 256, 512, 1024, 2048,
4096, 8192, 16384, 32768, 65536, 131072,
262144, 524288, 1048576, 2097152, 4194304, 8388608,
16777216, 33554432, 67108864, 134217728, 268435456, 536870912,
1073741824, 2147483648
} ;
int left = 0 ;
int right = 31 ;
while (left <= right)
{
int mid = (left + right) / 2 ;
if (powof2[mid] <= n)
{
if (powof2[mid + 1] > n)
return mid + 1; // got it!
else // powof2[mid] < n, search right part
left = mid + 1 ;
}
else // powof2[mid] > n, search left part
right = mid - 1 ;
}
return -1 ;
}
练习20,求两个正整数的最大公约数
碾转相除法:假设f(a,b)是a,b的最大公约数,则f(b,a%b)=f(a,b),即f(b,a%b)同样也是其最大公约数[cpp]
view plain
copy
print?
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int GyueNum(int x,int y);
int main()
{
int a,b,result;
cout<<"请输入两个任意的整数"<<endl;
cin>>a>>b;
result=GyueNum(a,b);
cout<<result<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//算法实现1:
int GyueNum(int x,int y)
{
return (!y)?x:GyueNum(y,x%y);//碾转相除法
}
练习21,栈的顺序输出(STL库实现)
[cpp]view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppStackTest1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
/*
*函数功能:以 23 56 11 4 87 98入栈,以11 4 56 98 87 23出栈
*函数原形:无
*参数:无
*返回值:无
*时间复杂度:无
*备注:无
*日期:2014/12/13
*原创:是
*作者:EbowTang
*Email:tangyibiao520@163.com
*/
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
//顺序入栈,三个参数
stack<int> sta;
sta.push( 23 );
sta.push( 56 );
sta.push( 11 );
cout << sta.top( )<< " ";//输出顶值11
sta.pop( );//删除元素11
sta.push( 4 );
cout << sta.top( )<< " ";//输出顶值4
sta.pop( );//删除元素4
cout << sta.top( ) << " ";//输出顶值56
sta.pop( );//删除元素56
sta.push( 87 );
sta.push( 98 );
cout << sta.top( ) << " ";//输出顶值98
sta.pop( );//删除元素98
cout << sta.top( ) << " ";//输出顶值87
sta.pop( );//删除元素87
cout << sta.top( ) << " ";//输出顶值23
system( "PAUSE" );
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
练习22,括号配对问题
描述现在,有一行括号序列,请你检查这行括号是否配对。
输入第一行输入一个数N(0<N<=100),表示有N组测试数据。后面的N行输入多组输入数据,每组输入数据都是一个字符串S(S的长度小于10000,且S不是空串),测试数据组数少于5组。数据保证S中只含有"[","]","(",")"四种字符
输出每组输入数据的输出占一行,如果该字符串中所含的括号是配对的,则输出Yes,如果不配对则输出No
样例输入
3 [(]) (]) ([[]()])
样例输出
No No Yes
难度3,第2题
方法:(栈的基本运用)
解题思路依次扫描整个字符串,并使用栈进行模拟。对于输入括号(如果不特殊指出,这里的
括号均指的是含圆括号和中括号)
1,如果为左型的括号(比如 “[” “(”)则入栈
2,如果为右型括号且栈为空或栈顶元素与之不配对则输出No,反之弹出栈顶元素
3,重复1和2步骤直到扫描结束,最后检查栈是否为空,若为空输出Yes反之输出No。
“括号配对”代码实现如下:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
<span style="font-size:12px;">#include "iostream"
#include "string"
#include "stack"
using namespace std;
bool BracketMatch(const string srcStr);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
system("color 0A");
int N = 0;
//申请内存
string src;
while (cin>>N)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cin >> src;
if (BracketMatch(src))
cout << "YES" << endl;
else
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
bool BracketMatch(const string srcStr)
{
stack<char> s;
//例子[]()[];
if (srcStr[0] == ')' || srcStr[0] == ']')//如果第一个字符就是右括号,则直接pass掉
return false;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < srcStr.length(); i++)//从左往右开始遍历
{
switch (srcStr[i])
{
//对左括号仅作压栈处理,同时值得注意的是栈中只有左括号
case '[':
s.push(srcStr[i]);
break;
case '(':
s.push(srcStr[i]);
break;
//对于右括号总是判断他是否与栈顶元素配对,否则即可判断不配对
case ']':
if (s.top() == '[')
s.pop();
break;
case ')':
if (s.top() == '(')
s.pop();
break;
default:
cerr << "错误的括号" << endl;
exit(1);
}
}
//判断栈中的情况
if (s.empty())
return true;
else//如果栈中有数据则说明存在不匹配
return false;
}</span>
练习23,奇偶数分离
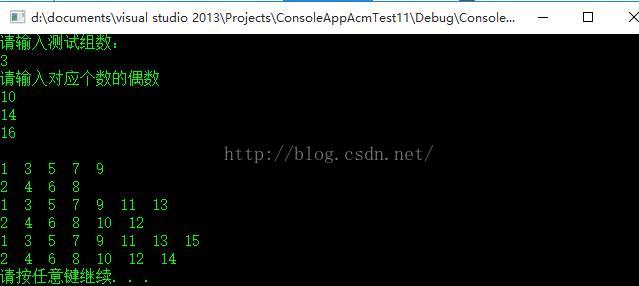
描述有一个整型偶数n(2<= n <=10000),你要做的是:先把1到n中的所有奇数从小到大输出,再把所有的偶数从小到大输出。
输入第一行有一个整数i(2<=i<30)表示有 i 组测试数据;
每组有一个整型偶数n。
输出第一行输出所有的奇数
第二行输出所有的偶数
样例输入
2 10 14
样例输出
1 3 5 7 9 2 4 6 8 10 1 3 5 7 9 11 13 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
难度1,第11题
方法:直接破题,即直接根据题意输出指定内容“奇偶数分离”代码实现如下:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppAcmTest11.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
void OddEvenSepar(int *num, int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
int k = 1;
while (k < num[i])
{
if (k % 2 == 1)
{
cout << k << " ";
}
k++;
}
cout << endl;
int kk = 1;
while (kk < num[i])
{
if (kk % 2 == 0)
{
cout << kk << " ";
}
kk++;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
system("color 0A");
int N = 0;
cout << "请输入测试组数:" << endl;
cin >> N;
int *num = new int
;
cout << "请输入对应个数的偶数" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < N;i++)
{
cin>>num[i];
}
cout << endl;
OddEvenSepar(num, N);
delete[] num;
num = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习24,五个数求最值
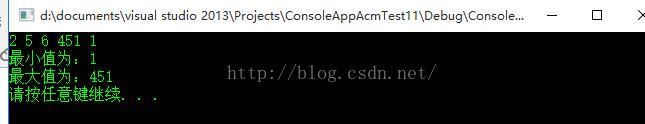
描述设计一个从5个整数中取最小数和最大数的程序
输入输入只有一组测试数据,为五个不大于1万的正整数
输出输出两个数,第一个为这五个数中的最小值,第二个为这五个数中的最大值,两个数字以空格格开。
样例输入
1 2 3 4 5
样例输出
1 5
难度:1,第31题
方法:
排序法,或者直接求取
“五个数求最值”代码实现如下:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppAcmTest31.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
void getMinMax(int *num,int n)
{
int min = num[0], max = num[0];
for (int j = 0; j < n;j++)
{
if (min>num[j])
{
min = num[j];
}
if (max < num[j])
{
max = num[j];
}
}
cout << "最小值为:" << min << endl;
cout << "最大值为:" << max << endl;
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
system("color 0A");
int num[5] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < 5;i++)
{
cin >> num[i];
}
getMinMax(num,5);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习25,韩信点兵
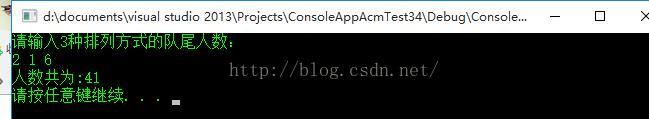
描述相传韩信才智过人,从不直接清点自己军队的人数,只要让士兵先后以三人一排、五人一排、七人一排地变换队形,而他每次只掠一眼队伍的排尾就知道总人数了。输入3个非负整数a,b,c ,表示每种队形排尾的人数(a<3,b<5,c<7),输出总人数的最小值(或报告无解)。已知总人数不小于10,不超过100 。
输入输入3个非负整数a,b,c ,表示每种队形排尾的人数(a<3,b<5,c<7)。例如,输入:2 4 5
输出输出总人数的最小值(或报告无解,即输出No answer)。实例,输出:89
样例输入
2 1 6
样例输出
41
难度1,第34题
方法:
暴力破解,遍历出答案
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppAcmTest34.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int HanXinCount(int *num);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
system("color 0A");
int *num = new int[3];
cout << "请输入3种排列方式的队尾人数:"<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3;i++)
{
cin >> num[i];
}
int persons = HanXinCount(num);
if (persons==-1)
{
cout << "No Answer" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "人数共为:" << persons << endl;
}
delete[] num;
num = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
int HanXinCount(int *num)
{
int persons = -1;
for (int i = 10; i <= 100;i++)
{
if ( i%3==num[0] && i%5==num[1] && i%7==num[2])
{
persons = i;
}
}
return persons;
}
练习26,组合数
描述找出从自然数1、2、... 、n(0<n<10)中任取r(0<r<=n)个数的所有组合。
输入输入n、r。
输出按特定顺序输出所有组合。
特定顺序:每一个组合中的值从大到小排列,组合之间按逆字典序排列。
样例输入
5 3
样例输出
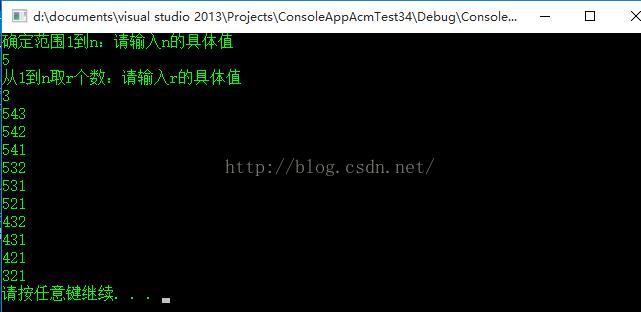
543 542 541 532 531 521 432 431 421 321
难度3,第32题
方法:
DFS法,深度遍历型程序设计
“组合数”代码实现如下:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
// ConsoleAppAcmTest32.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int a[11];
bool visit[11];//存放数据被访问否
void DFSCombiNum1(int n,int cur, int r);
void printNum(int *w, int r);
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
system("color 0A");
int n = 5;
int r = 3;
cout << "确定范围1到n:请输入n的具体值"<<endl;
cin >> n;
while (n>10)
{
cout << "重新确定范围1到n:请输入n的具体值" << endl;
cin >> n;
}
cout << "从1到n取r个数:请输入r的具体值" << endl;
cin >> r;
while (r > n)
{
cout << "重新输入r" << endl;
cin >> r;
}
memset(visit, false, sizeof(visit));//初始化
DFSCombiNum1(n,1, r);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
//递归法DFS
void DFSCombiNum1(int n, int cur, int r) //入口、当前层、总层数
{
if (cur > r) //结束条件
return;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--)//从n遍历到1,
{
if (!visit[i])//当前这个数没有被访问过,则访问他
{
visit[i] = true;
a[cur] = i;//记录要输出的数字
if (cur == r)//每次当cur增加到r时就输出放在a中的数
{
printNum(a, r);
}
DFSCombiNum1(i - 1, cur + 1, r);
visit[i] = false;
}
}
}
void printNum(int *a, int r)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= r; i++)
{
cout << a[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
练习27,计算超大数相乘:
编写两个超大数相乘,不用考虑负数[html]
view plain
copy
print?
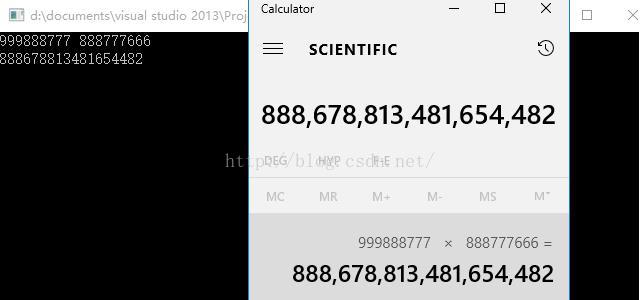
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void Multiply(const string &a, const string &b, vector<int> &ansStr);
int main()
{
string bigNum1, bigNum2; // 初始状态用string来存储大数
while (cin >> bigNum1 >> bigNum2)
{
vector<int> ans(bigNum1.size() + bigNum2.size(), 0);//接收答案,这里必须给予ans大小,否则传递参数时out of range
Multiply(bigNum1, bigNum2, ans);
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < ans.size(); i++)
cout << ans[i];
cout << endl;
ans.clear();
}
return 0;
}
void Multiply(const string &a, const string &b, vector<int> &ans)
{
int lena = a.length(),lenb = b.length();
for (int i = 0; i < lena; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < lenb; j++)
{//25,a[0]=2,a[1]=5,31,b[0]=3,b[1]=1;推出==》ans[1]=6,ans[2]=17,ans[3]=5,(ans[0]=0)
ans[i + j + 1] += (a[i] - '0')*(b[j] - '0');
}}
for (int i = lena + lenb - 1; i >= 0; i--)// 这里实现进位操作
{
if (ans[i] >= 10)
{
ans[i - 1] += ans[i] / 10;//让高位获得来自低位的进位值,注意ans[i]相对ans[i-1]是低位
ans[i] %= 10;//低位自裁,只保留当前数的个位即可,比如223,只保留3,22给高位
}}}
练习28,单词的部分逆置
举例;“I am Chinese.”逆置后为”Chinese. am I“
参考代码:
[html]
view plain
copy
print?
#include "string"
#include "vector"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str;
while (getline(cin,str))
{
//以此为例 "I am Chinese."
int i = 0, j = str.size() - 1;
char temp;
//逆置字符串,"esenihC. ma I"
while (j > i)
{
temp = str[i];
str[i] = str[j];
str[j] = temp;
i++; j--;
}
//部分反转,"Chinese. am I"
int begin = 0, end = 0;
int ii = 0;
while (ii < str.size())
{
if (str[ii] != ' ')//寻找空格前的子串
{
begin = ii;
while (str[ii] != ' '&& ii < str.size())//这里考虑了在计数最后一个字符时的情况
{
ii++;
}
ii--;
end = ii;
}
while (end > begin)
{
temp = str[begin];
str[begin++] = str[end];
str[end--] = temp;
}
ii++;
}
cout << str << endl;
}
return 0;
}
练习29,二分查找法存在的问题
PS:有的东西表面看上去公正、全面,实际可能走向极端的分立思维,许多客观事物不能简单均分,可能其内在具有复杂的联系,一旦坚持平分,结果倒失去了客观、全面的基础。时间复杂度
折半搜索每次把搜索区域减少一半,时间复杂度为
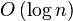
。(n代表集合中元素的个数)
空间复杂度
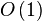
。虽以递归形式定义,但是尾递归,可改写为循环
维基百科告诉我们要这样写:为什么呢?
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size:12px;">//递归版本
int binary_search( const int arr[], int low, int high, int key)
{
int mid = low+(high-low)/2; // 别用 (low+high)/2 ,因为可能引起溢出问题。
if(low>high)
return -1;
else
{
if(arr[mid]==key)
return mid;
else if(arr[mid]>key)
return binary_search(arr,low,mid-1,key);
else
return binary_search(arr,mid+1,high,key);
}
}</span>
开始分析
一般二分法这样写:
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?
<span style="font-size:12px;">int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int h, int key)
{
while (l <= h)
{
// find index of middle element
int m = (l+h)/2;
// Check if key is present at mid
if (arr[m] == key) return m;
// If key greater, ignore left half
if (arr[m] < key) l = m + 1;
// If key is smaller, ignore right half
else h = m - 1;
}
// if we reach here, then element was not present
return -1;
}</span>
以上看起来没事,除了一个很微妙的东西,表达“m =(l+r)/ 2″。它不能用于l和r特别大的时候,如果l和r的总和大于最大正int值(2的31次方–1)。将溢出为负值,即求和之后成了负值时,再除以2也是负值。这将导致索引超出范围和不可预知的结果。
所以解决这个问题的方法就是:
mid = ((unsigned int)low + (unsigned int)high)) >> 1 ;
或者
mid = low+(high-low)/2;
练习30,显式的调用析构器和构造器
构造函数是一个很特殊的成员函数,当一个对象被创建时他将会自动被调用。析构器也是一个很特殊的成员函数,当对象在作用域结束时会被自动的隐式调用。当动态分配内存和销毁时也会调用这两个特殊的函数,即new和delete操作符!进入正题,显式调用这两个特殊的函数:
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
Test() { cout << "Constructor is executed\n"; }
~Test() { cout << "Destructor is executed\n"; }
};
int main()
{
Test(); // 显式调用构造器
Test t; // 创建本地对象
t.~Test(); // 显式调用析构器
return 0;
}
///输出:
Constructor is executed (Test()显式调用产生的,同时会产生一个临时对象,并立刻销毁)
Destructor is executed (临时对象造成的,此时析构器被调用)
Constructor is executed (创建本地对象产生的)
Destructor is executed (显式调用析构器产生的,但是并不意味着对象被销毁)
Destructor is executed (main结束时,析构函数在对象t作用域的末尾调用,起到释放资源的作用)
当构造器被显式调用时,编译器立刻创建了一个未命名的临时对象,同时它也被立刻销毁,这也是为什么输出中的第二行会是“析构器被执行”特别注意,如果对象时动态分配的内存,千万别显式调用析构器,因为delete会调用析构器。
类的成员函数也能调用析构器和构造器
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
Test() { cout << "Constructor is executed\n"; }
~Test() { cout << "Destructor is executed\n"; }
void show() { Test(); this->Test::~Test(); }
};
int main()
{
Test t;
t.show();
return 0;
}
输出:
Constructor is executed
Constructor is executed
Destructor is executed
Destructor is executed
Destructor is executed
最后再来分析一段程序:
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
Test() { cout << "+++"; }
~Test() { cout << "---"; }
friend void fun(Test t);
};
void fun(Test t)
{
Test();//析构器和构造器均会被调用
t.~Test();//显式调用析构器............然后就完了吗?对象t在这个函数的末尾被自动在调用一次析构器!!!
}
int main()
{
Test();//输出+++,然后---
Test t;//输出+++
fun(t);//输出+++,---,---,---
return 0;//输出---
}
所以输出为:
[cpp] view
plaincopyprint?
+++
---
+++
+++
---
---
---
---
有时候显示调用析构器是有用的,微软告诉我们:
很少需要显式调用析构函数。 但是,对置于绝对地址的对象进行清理会很有用。 这些对象通常使用采用位置参数的用户定义的 new 运算符进行分配。 delete 运算符不能释放该内存,因为它不是从自由存储区分配的(有关详细信息,请参阅 new
和 delete 运算符)。 但是,对析构函数的调用可以执行相应的清理。 若要显式调用 String 类的对象 s 的析构函数,请使用下列语句之一:
s.String::~String(); // Nonvirtual call ps->String::~String(); // Nonvirtual call s.~String(); // Virtual call ps->~String(); // Virtual call
可以使用对前面显示的析构函数的显式调用的表示法,无论类型是否定义了析构函数。 这允许您进行此类显式调用,而无需了解是否为此类型定义了析构函数。 显式调用析构函数,其中未定义的析构函数无效。
练习31,调整数组结构
模拟小波变换中LL,HL,LH,HH系数调整[html]
view plain
copy
print?
#include "iostream"
#include "windows.h"
#include "fstream"
#include "algorithm"
using namespace wavelet;
using namespace std;
bool AdjustData(
double *pDetCoef,
const int height,
const int width
)
{
if (pDetCoef == NULL)
return false;
double *ptmpdet = new double[height / 2 * width];
for (int i = 0; i < height / 2 * width; i++)
ptmpdet[i] = pDetCoef[i];
int pos1 = 0;
int pos2 = height / 2 * width / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < height / 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
if (j < width / 2)
pDetCoef[pos1++] = ptmpdet[i*width + j];
else
pDetCoef[pos2++] = ptmpdet[i*width + j];
}
}
delete[] ptmpdet;
ptmpdet = NULL;
return true;
}
bool IAdjustData(
double *pDetCoef,
const int height,
const int width
)
{
if (pDetCoef == NULL)
return false;
double *ptmpdet = new double[height / 2 * width];
for (int i = 0; i < height / 2 * width; i++)
ptmpdet[i] = pDetCoef[i];
int pos1 = 0;
int pos2 = height / 2 * width / 2;
for (int i = 0; i < height / 2; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
if (j < width / 2)
pDetCoef[i*width + j] = ptmpdet[pos1++];
else
pDetCoef[i*width + j] = ptmpdet[pos2++];
}
}
delete[] ptmpdet;
ptmpdet = NULL;
return true;
}
int main()
{
system("color 0A");
double s[30] = {1,2,3,4,5,6, 2,3,4,5,6,7, 3,4,5,6,7,8, 4,5,6,7,8,9, 5,6,7,8,9,10};
int height = 5;
int width = 6;
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
cout << s[i*width + j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl; cout << endl;
AdjustData(s,height,width);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
cout << s[i*width + j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
IAdjustData(s, height, width);
cout << endl; cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
cout << s[i*width + j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
题源参考
【1】《编程之美》【2】《C++算法,妙趣横生》
【3】南阳理工OJ
【4】九度OJ
【5】维基百科
【6】C++primer
相关文章推荐
- 算法设计几个经典思维题目
- 若干经典基础算法题目练习
- Uva 算法入门经典(数据结构基础)线性表题目
- 【索引】算法竞赛入门经典-第5章 基础题目选解
- 算法竞赛入门经典:第五章 基础题目选解 5.9 Cantor数
- 算法竞赛入门经典:第五章 基础题目选解 5.3 周期串
- 算法竞赛入门经典:第五章 基础题目选解 5.11果园里的树
- 经典算法题目——最长公共子序列问题
- 两个基础的算法题目
- 两个基础的算法题目
- 分享:C语言的学习基础,100个经典的算法
- java经典的基础题目
- PHP写的几个基础算法
- 几个算法题目
- Java面试中遇到的一些经典算法题目
- 终于把dp算法几个经典题目ac了
- 分享Java面试中遇到的一些经典算法题目 (转)
- 两个基础的算法题目
- PHP写的几个基础算法 (转载)
- 两个基础的算法题目
