排序算法 之 插入排序InsertionSort
2016-07-30 17:01
405 查看
介绍
插入排序的工作原理是,对于每个未排序数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入。步骤
从第一个元素开始,该元素可以认为已经被排序取出下一个元素,在已经排序的元素序列中从后向前扫描
如果被扫描的元素(已排序)大于新元素,将该元素后移一位
重复步骤3,直到找到已排序的元素小于或者等于新元素的位置
将新元素插入到该位置后
重复步骤2~5
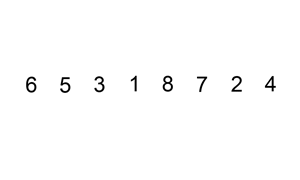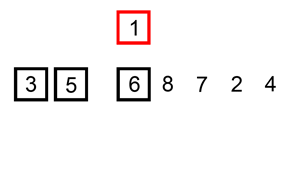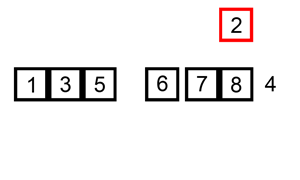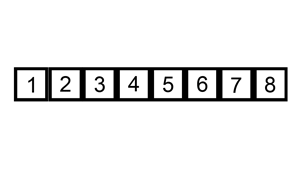
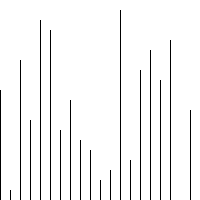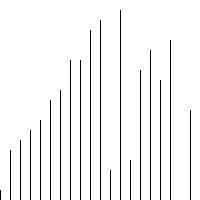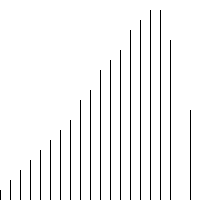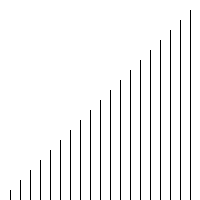
代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Wed Apr 27 10:41:00 2016 @author: zang """ from matplotlib import pyplot as plt import random def bubbleSort1(unsortedList):#采用递归 if len(unsortedList)<2: return unsortedList list_length=len(unsortedList) for i in range(list_length - 1): if unsortedList[i] > unsortedList[i + 1]: unsortedList[i],unsortedList[i + 1] = unsortedList[i + 1], unsortedList[i] max_num = unsortedList.pop() return bubbleSort1(unsortedList) + [max_num] def insertSort(unsortedList): n = len(unsortedList) for i in range(1,n): if unsortedList[i] < unsortedList[i-1]: temp = unsortedList[i] index = i #待插入的下标 for j in range(i-1,-1,-1): #从i-1 循环到 0 (包括0) if unsortedList[j] > temp : unsortedList[j+1] = unsortedList[j] index = j #记录待插入下标 else : break unsortedList[index] = temp return unsortedList def plotScatter(inputList): plt.scatter(range(len(inputList)),inputList) plt.show() if __name__ == "__main__": num_list = range(1000) unsortedList = random.sample(num_list, 30) print "unsortedList:" plotScatter(unsortedList) print unsortedList sortedList = insertSort(unsortedList) print "sortedList:" plotScatter(sortedList) print sortedList
测试
输入[544, 757, 514, 875, 371, 44, 538, 296, 155, 148, 612, 847, 352, 973, 654, 135, 956, 197, 655, 270, 280, 609, 175, 891, 450, 128, 75, 260, 248, 540]
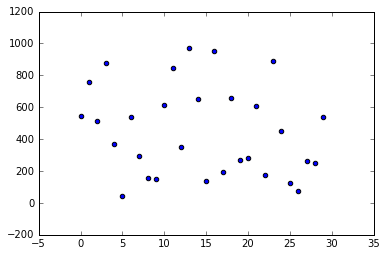
输出
[44, 75, 128, 135, 148, 155, 175, 197, 248, 260, 270, 280, 296, 352, 371, 450, 514, 538, 540, 544, 609, 612, 654, 655, 757, 847, 875, 891, 956, 973]
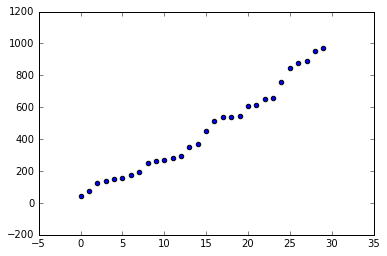
分析
| 情况 | 性能 |
|---|---|
| Worst case performance: | O(n2) |
| Best case performance: | O(n) |
| Average case performance: | O(n2) |
| Worst case space complexity: | O(1) |
参考
http://wuchong.me/blog/2014/02/09/algorithm-sort-summary/http://blog.jobbole.com/72850/
相关文章推荐
- 排序算法(一)—插入排序(Insertion sort)
- 基础排序算法 – 插入排序Insertion sort
- 经典排序算法 – 插入排序Insertion sort
- 排序算法——插入排序(Insertion Sort)
- 经典排序算法 – 插入排序Insertion sort
- 排序算法——插入排序(Insertion Sort)
- 排序算法--插入排序(Insertion Sort)_C#程序实现
- 排序算法总结之插入排序 Insertion Sort
- 经典算法(8)- 插入排序(Insertion Sort) 及三个基本排序算法的比较
- 基础排序算法 – 插入排序Insertion sort
- 排序算法---插入排序(Insertion Sort)
- 排序算法-插入排序 Insertion Sort Θ(n-n)
- 插入排序(insertion sort)算法实现
- [LeetCode147]Insertion Sort List(链表插入排序)
- 插入排序(1)InsertionSort
- insertion sort(插入排序)
- 经典排序算法 – 插入排序Insertion sort
- [C++]LeetCode: 126 Insertion Sort List (插入排序链表)
- 插入排序 insertion_sort
- 排序算法之插入排序<Insertion_Sort>及其C语言代码实现
