剑指Offer----面试题22:栈的压入、弹出序列
2016-06-05 13:48
615 查看
题目:
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1/2/3/4/5是某栈的压入序列,序列4/5/3/2/1是该栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但是4/3/5/1/2就不是该压栈序列的弹出序列。分析:
建立一个辅助栈,将一个序列中的数字依次压入栈,依次弹出并和第二个序列中的栈相比较。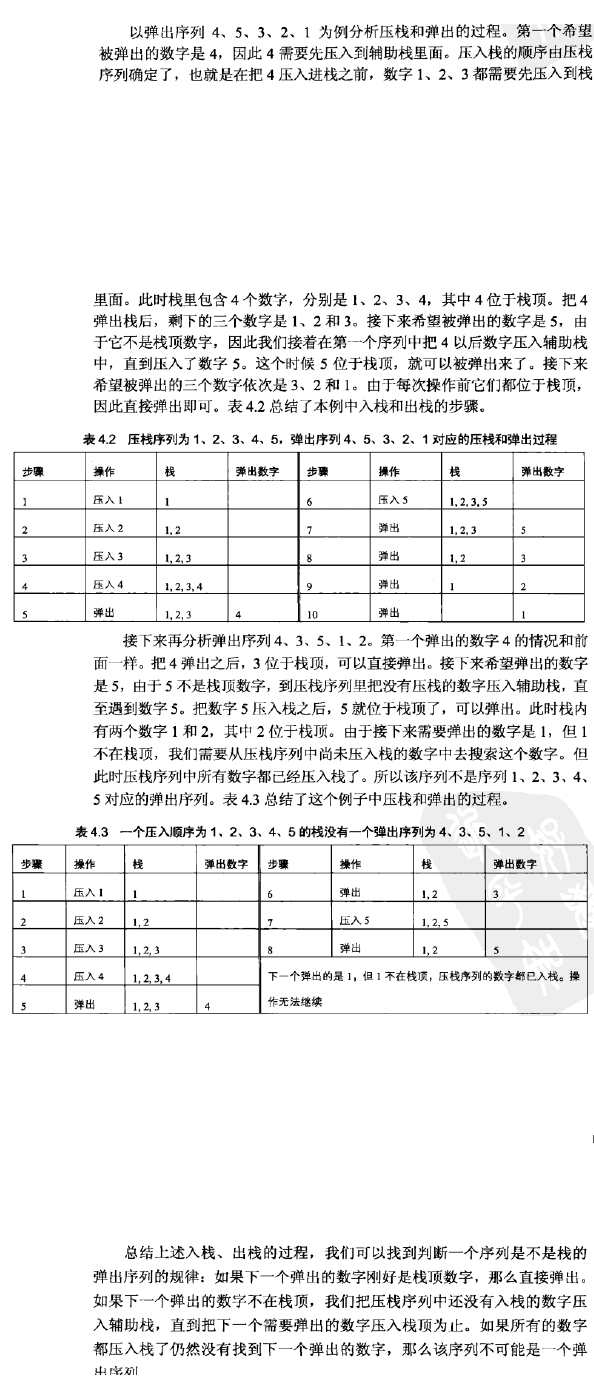
源代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::cin;
using std::stack;
using std::vector;
bool judge(const vector<int> &vec1, const vector<int> &vec2)
{
if (vec1.empty())
return false;
if (vec2.empty())
return false;
if (vec1.size() != vec2.size())
return false;
stack<int> stk;
auto it1 = vec1.begin();
auto it2 = vec2.begin();
while (it1 != vec1.end() && it2 != vec2.end())
{
//依次判断第一个序列和第二个序列相应位置上的值,若不相等,第一个序列该位置上的值压入栈并取下一个值
if (*it1 != *it2)
{
stk.push(*it1);
++it1;
}
else
{
//如果两个数相等,同时取下一个值
++it1;
++it2;
}
}
//如果两个序列中的值都相等,返回false
if ((it1 == vec1.end()) && (it2 == vec2.end()))
return true;
//如果都不想等,返回false
if ((it1 == vec1.end()) && (it2 == vec2.begin()))
return false;
//已经将第一个序列中和第二个序列相应位置上不相同数全部压入栈中,依次取得栈中的数值和序列二种的数相比较
while (!stk.empty() && (it2 != vec2.end()))
{
if (stk.top() == *it2)
{
//如果栈顶元素和序列二种的数相同,弹出栈中该元素且序列二前进一位
++it2;
stk.pop();
}
else//否则,返回false
return false;
}
//栈中的元素全部弹出且序列二也到底尾部,返回true
if (stk.empty() && (it2 == vec2.end()))
return true;
}
void test11()
{
cout << "\t===========第二个序列是栈的弹出序列=========" << endl;
vector<int> vec1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
vector<int> vec2 = { 4, 5, 3, 2, 1 };
bool result = judge(vec1, vec2);
if (result)
cout << "第二个序列是第该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
else
cout << "第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
}
void test12()
{
cout << "\t===========第二个序列bu是栈的弹出序列=========" << endl;
vector<int> vec1 = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
vector<int> vec2 = { 4, 3, 5, 2, 1 };
bool result = judge(vec1, vec2);
if (result)
cout << "第二个序列是第该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
else
cout << "第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
}
void test13()
{
cout << "\t===========第一个序列为空,第二个序列不为空=========" << endl;
vector<int> vec1;
vector<int> vec2 = { 4, 3, 5, 2, 1 };
bool result = judge(vec1, vec2);
if (result)
cout << "第二个序列是第该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
else
cout << "第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
}
void test14()
{
cout << "\t===========两个序列都为空=========" << endl;
vector<int> vec1;
vector<int> vec2;
bool result = judge(vec1, vec2);
if (result)
cout << "第二个序列是第该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
else
cout << "第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
}
void test15()
{
cout << "\t===========第一个序列不为空,第二个序列为空=========" << endl;
vector<int> vec1 = { 1,2, 3, 4, 5 };
vector<int> vec2;
bool result = judge(vec1, vec2);
if (result)
cout << "第二个序列是第该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
else
cout << "第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列" << endl;
}
int main()
{
test11();
cout << endl;
test12();
cout << endl;
test13();
cout << endl;
test14();
cout << endl;
test15();
cout << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果如下:
===========第二个序列是栈的弹出序列========= 第二个序列是第该栈的弹出序列 ===========第二个序列bu是栈的弹出序列========= 第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列 ===========第一个序列为空,第二个序列不为空========= 第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列 ===========两个序列都为空========= 第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列 ===========第一个序列不为空,第二个序列为空========= 第二个序列bu是该栈的弹出序列 请按任意键继续. . .
改进版核心代码:
bool judge2(const int *arrA, const int *arrB, int length)
{
if (arrA == nullptr || arrB == nullptr || length <= 0)
return false;
bool result = true;
stack<int> stk;
const int *tempA = arrA;
const int *tempB = arrB;
for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i)
{
if (*(tempA + i) != *(tempB))
stk.push(*(tempA + i));
else
tempB++;
}
while (!stk.empty())
{
if (stk.top() == (*tempB))
{
stk.pop();
++tempB;
}
else
{
result = false;
break;
}
}
return result;
}官方源代码:
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<stack>
bool IsPopOrder(const int* pPush, const int* pPop, int nLength)
{
bool bPossible = false;
if (pPush != NULL && pPop != NULL && nLength > 0)
{
const int* pNextPush = pPush;
const int* pNextPop = pPop;
std::stack<int> stackData;
while (pNextPop - pPop < nLength)
{
// 当辅助栈的栈顶元素不是要弹出的元素
// 先压入一些数字入栈
while (stackData.empty() || stackData.top() != *pNextPop)
{
// 如果所有数字都压入辅助栈了,退出循环
if (pNextPush - pPush == nLength)
break;
stackData.push(*pNextPush);
pNextPush++;
}
if (stackData.top() != *pNextPop)
break;
stackData.pop();
pNextPop++;
}
if (stackData.empty() && pNextPop - pPop == nLength)
bPossible = true;
}
return bPossible;
}
// ====================测试代码====================
void Test(char* testName, const int* pPush, const int* pPop, int nLength, bool expected)
{
if (testName != NULL)
printf("%s begins: ", testName);
if (IsPopOrder(pPush, pPop, nLength) == expected)
printf("Passed.\n");
else
printf("failed.\n");
}
void Test1()
{
const int nLength = 5;
int push[nLength] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int pop[nLength] = { 4, 5, 3, 2, 1 };
Test("Test1", push, pop, nLength, true);
}
void Test2()
{
const int nLength = 5;
int push[nLength] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int pop[nLength] = { 3, 5, 4, 2, 1 };
Test("Test2", push, pop, nLength, true);
}
void Test3()
{
const int nLength = 5;
int push[nLength] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int pop[nLength] = { 4, 3, 5, 1, 2 };
Test("Test3", push, pop, nLength, false);
}
void Test4()
{
const int nLength = 5;
int push[nLength] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int pop[nLength] = { 3, 5, 4, 1, 2 };
Test("Test4", push, pop, nLength, false);
}
// push和pop序列只有一个数字
void Test5()
{
const int nLength = 1;
int push[nLength] = { 1 };
int pop[nLength] = { 2 };
Test("Test5", push, pop, nLength, false);
}
void Test6()
{
const int nLength = 1;
int push[nLength] = { 1 };
int pop[nLength] = { 1 };
Test("Test6", push, pop, nLength, true);
}
void Test7()
{
Test("Test7", NULL, NULL, 0, false);
}
int main()
{
Test1();
Test2();
Test3();
Test4();
Test5();
Test6();
Test7();
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果:
Test1 begins: Passed. Test2 begins: Passed. Test3 begins: Passed. Test4 begins: Passed. Test5 begins: Passed. Test6 begins: Passed. Test7 begins: Passed. 请按任意键继续. . .
相关文章推荐
