一文掌握 YUV 图像 1000 的基本处理
 YUV 图片
YUV 图片
YUV 的由来
YUV 是一种色彩编码模型,也叫做 YCbCr,其中 “Y” 表示明亮度(Luminance),“U” 和 “V” 分别表示色度(Chrominance)和浓度(Chroma)。
YUV 色彩编码模型,其设计初衷为了解决彩色电视机与黑白电视的兼容问题,利用了人类眼睛的生理特性(对亮度敏感,对色度不敏感),允许降低色度的带宽,降低了传输带宽。
在计算机系统中应用尤为广泛,利用 YUV 色彩编码模型可以降低图片数据的内存占用,提高数据处理效率。
另外,YUV 编码模型的图像数据一般不能直接用于显示,还需要将其转换为 RGB(RGBA) 编码模型,才能够正常显示图像。
YUV 几种常见采样方式
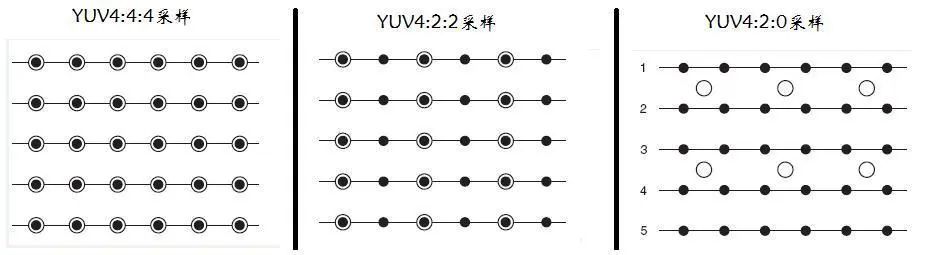 YUV 几种常见采样方式
YUV 几种常见采样方式
YUV 图像主流的采样方式有三种:
YUV 4:4:4,每一个 Y 分量对于一对 UV 分量,每像素占用 (Y + U + V = 8 + 8 + 1000 8 = 24bits)3 字节;
YUV 4:2:2,每两个 Y 分量共用一对 UV 分量,每像素占用 (Y + 0.5U + 0.5V = 8 + 4 + 4 = 16bits)2 字节;
YUV 4:2:0,每四个 Y 分量共用一对 UV 分量,每像素占用 (Y + 0.25U + 0.25V = 8 + 2 + 2 = 12bits)1.5 字节。
其中最常用的采样方式是 YUV422 和 YUV420 。
YUV 格式也可按照 YUV 三个分量的组织方式分为打包(Packed)格式和平面格式(Planar)。
打包(Packed)格式:每个像素点的 YUV 分量是连续交叉存储的,如 YUYV 、NV21 格式;
平面格式(Planar):YUV 图像数据的三个分量分别存放在不同的矩阵中,这种格式适用于采样,如 YV12、YU12 格式。
YUV 几种常用的格式
对 YUV 图像处理中,YUYV 、YU12(I420)、NV21 和 NV12 最为常用,下面介绍下这几种格式的存储方式。
以一幅分辨率为 4x4 的 YUV 图为例,说明在不同 YUV 格式下的存储方式(括号内范围表示内存地址索引范围,默认以下不同格式图片存储使用的都是连续内存)。
YUYV (YU 518 V422 采样方式)
YUYV 是 2 个Y 分量共用一对 UV 分量,YUYV 格式的存储格式:
(0 ~ 7) Y00 U00 Y01 V00 Y02 U01 Y03 V01
(8 ~ 15) Y10 U10 Y11 V10 Y12 U11 Y13 V11
(16 ~ 23) Y20 U20 Y21 V20 Y22 U21 Y23 V21
(24 ~ 31
ffa
) Y30 U30 Y31 V30 Y32 U31 Y33 V31
一幅 720P (1280x720分辨率) 的图片,使用 YUV422 采样时占用存储大小为:
Y 分量:1280 * 720 = 921600 字节
U 分量:1280 * 720 * 0.5 = 460800 字节
V 分量:1280 * 720 * 0.5 = 460800 字节
总大小:Y 分量 + U 分量 + V 分量 = (1280 * 720 + 1280 * 720 * 0.5 * 2) / 1024 / 1024 = 1.76 MB
由上面计算可以看出 YUV422 采样的图像比 RGB 模型图像节省了 1/3 的存储空间。,在传输时占用的带宽也会随之减小。
YV12/YU12 (YUV420 采样方式)
YV12/YU12 也属于 YUV420P ,即 YUV420 采样方式的平面模式,YUV 三个分量分别存储于 3 个不同的矩阵(平面)。
 YUV420P 存储方式图
YUV420P 存储方式图
YV12 格式的存储方式
(0 ~ 3) Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03
(4 ~ 7) Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13
(8 ~ 11) Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23
(12 ~ 15) Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33
(16 ~ 17) V00 V01
(18 ~ 19) V10 V11
(20 ~ 21) U00 U01
(22 ~ 23) U10 U11
YU12(也称 I420) 格式的存储方式
(0 ~ 3) Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03
(4 ~ 7) Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13
(8 ~ 11) Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23
(12 ~ 15) Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33
(16 ~ 17) U00 U01
(18 ~ 19) U10 U11
(20 ~ 21) V00 V01
(22 ~ 23) V10 V11
一幅 720P (1280x720分辨率) 的图片,使用 YUV420 采样时(格式 YV12/YU12 )占用存储大小为:
Y 分量:1280 * 720 = 921600 字节
U 分量:1280 * 720 * (1/4) = 230400 字节
V 分量:1280 * 720 * (1/4) = 230400 字节
总大小:Y 分量 + U 分量 + V 分量 = (1280 * 720 + 1280 * 720 * (1/4)* 2) / 1024 / 1024 = 1.32 MB
由上面计算可以看出 YUV420 采样(格式 YV12/YU12 )的图像比 RGB 模型图像节省了 1/2 的存储空间。
NV21/NV12 (YUV420 采样方式)
NV21/NV12 属于 YUV420SP ,YUV420SP 格式有 2 个平面,Y 分量存储于一个平面,UV 分量交错存储于另一个平面。
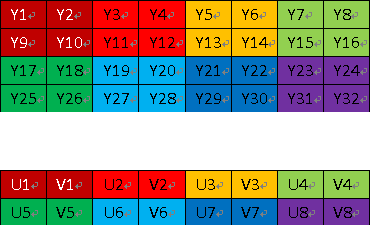 YUV420SP 存储方式图
YUV420SP 存储方式图
NV21 格式的存储方式
(0 ~ 3) Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03 &n
1000
bsp;
(4 ~ 7) Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13
(8 ~ 11) Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23
(12 ~ 15) Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33
(16 ~ 19) V00 U00 V01 U01
(20 ~ 23) V10 U10 V11 U11
NV12 格式的存储方式
(0 ~ 3) Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03
(4 ~ 7) Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13
(8 ~ 11) Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23
(12 ~ 15) Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33
(16 ~ 19) U00 V00 U01 V01
(20 ~ 23) U10 V10 U11 V11
NV21 与 NV12 格式的区别仅在于 UV 分量排列的先后顺序不同。
一幅 720P (1280x720分辨率) 的图片,使用 YUV420 采样时(格式 NV21/NV12 )占用存储大小为:
Y 分量:1280 * 720 = 921600 字节
UV 分量:1280 * 720 * (1/2) = 460800 字节
总大小:Y 分量 + UV 分量 = (1280 * 720 + 1280 * 720 * (1/2)) / 1024 / 1024 = 1.32 MB
由上面计算可以看出 YUV420 采样(格式 NV21/NV12 )的图像比 RGB 模型图像也节省了 1/2 的存储空间。
YUV 图像的基本操作
下面以最常用的 NV21 图为例介绍其旋转、缩放和剪切的基本方法。
YUV 图片的定义、加载、保存及内存释放。
//YUV420SP NV21 or NV12
typedef struct
{
int width; // 图片宽
int height; // 图片高
unsigned char *yPlane; // Y 平面指针
unsigned char *uvPlane; // UV 平面指针
} YUVImage;
void LoadYUVImage(const char *filePath, YUVImage *pImage)
{
FILE *fpData = fopen(filePath, "rb+");
if (fpData != NULL)
{
fseek(fpData, 0, SEEK_END);
int len = ftell(fpData);
pImage->yPlane = malloc(len);
fseek(fpData, 0, SEEK_SET);
fread(pImage->yPlane, 1, len, fpData);
fclose(fpData);
fpData = NULL;
}
pImage->uvPlane = pImage->yPlane + pImage->width * pImage->height;
}
void SaveYUVImage(const char *filePath, YUVImage *pImage)
{
FILE *fp = fopen(filePath, "wb+");
if (fp)
{
fwrite(pImage->yPlane, pImage->width * pImage->height, 1, fp);
fwrite(pImage->uvPlane, pImage->width * (pImage->height >> 1), 1, fp);
}
}
void ReleaseYUVImage(YUVImage *pImage)
{
if (pImage->yPlane)
{
free(pImage->yPlane);
pImage->yPlane = NULL;
pImage->uvPlane = NULL;
}
}
NV21 图片旋转
以顺时针旋转 90 度为例,Y 和 UV 两个平面分别从平面左下角进行纵向拷贝,需要注意的是一对 UV 分量作为一个整体进行拷贝。
以此类比,顺时针旋转 180 度时从平面右下角进行横向拷贝,顺时针旋转 270 度时从平面右上角进行纵向拷贝。
 Y 平面旋转 90 度
Y 平面旋转 90 度
 UV 平面旋转 90 度
UV 平面旋转 90 度
存储空间表示:
Y00 Y01 Y02 Y03
1000
; Y30 Y20 Y10 Y00
Y10 Y11 Y12 Y13 旋转90度 Y31 Y21 Y11 Y01
Y20 Y21 Y22 Y23 -----> Y32 Y22 Y12 Y02
Y30 Y31 Y32 Y33 Y33 Y23 Y13 Y03
旋转90度
V00 U00 V01 U01 -----> V10 U10 V00 U00
V10 U10 V11 U11 V11 U11 V01 U01
代码实现:
//angle 90, 270, 180
void RotateYUVImage(YUVImage *pSrcImg, YUVImage *pDstImg, int angle)
{
int yIndex = 0;
int uvIndex = 0;
switch (angle)
&
1000
nbsp; {
case 90:
{
// y plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->width; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->height; j++) {
*(pDstImg->yPlane + yIndex) = *(pSrcImg->yPlane + (pSrcImg->height - j - 1) * pSrcImg->width + i);
yIndex++;
}
}
//uv plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->width; i += 2) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->height / 2; j++) {
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + uvIndex) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + (pSrcImg->height / 2 - j - 1) * pSrcImg->width + i);
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + uvIndex + 1) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + (pSrcImg->height / 2 - j - 1) * pSrcImg->width + i + 1);
uvIndex += 2;
}
}
}
break;
case 180:
{
// y plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->height; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->width; j++)&nbs
ff8
p;{
*(pDstImg->yPlane + yIndex) = *(pSrcImg->yPlane + (pSrcImg->height - 1 - i) * pSrcImg->width + pSrcImg->width - 1 - j);
yIndex++;
}
}
//uv plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->height / 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->width; j += 2) {
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + uvIndex) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + (pSrcImg->height / 2 - 1 - i) * pSrcImg->width + pSrcImg->width - 2 - j);
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + uvIndex + 1) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + (pSrcImg->height / 2 - 1 - i) * pSrcImg->width + pSrcImg->width - 1 - j);
uvIndex += 2;
}
}
}
break;
case 270:
{
// y plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->width; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->height; j++) {
*(pDstImg->yPlane + yIndex) = *(pSrcImg->yPlane + j * pSrcImg->width + (pSrcImg->width - i - 1));
yIndex++;
}
}
//uv plane
for (int i = 0; i < pSrcImg->width; i += 2) {
for (int j = 0; j < pSrcImg->height / 2; j++) {
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + uvIndex + 1) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + j * pSrcImg->width + (pSrcImg->width - i - 1));
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + uvIndex) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + j * pSrcImg->width + (pSrcImg->width - i - 2));
uvIndex += 2;
}
}
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
NV21 图片缩放
将 2x2 的 NV21 图缩放成 4x4 的 NV21 图,原图横向每个像素的 Y 分量向右拷贝 1(放大倍数-1)次,纵向每列元素以列为单位向下拷贝 1(放大倍数-1)次.
 将 2x2 的 NV21 图缩放成 4x4 的 NV21 图
将 2x2 的 NV21 图缩放成 4x4 的 NV21 图
将 4x4 的 NV21 图缩放成 2x2 的 NV21 图,实际上就是进行采样。
 将 4x4 的 NV21 图缩放成 2x2 的 NV21 图
将 4x4 的 NV21 图缩放成 2x2 的 NV21 图
代码实现:
void ResizeYUVImage(YUVImage *pSrcImg, YUVImage *pDstImg)
{
if (pSrcImg->width > pDstImg->width)
{
//缩小
int x_scale = pSrcImg->width / pDstImg->width;
int y_scale = pSrcImg->height / pDstImg->height;
for
fea
(size_t i = 0; i < pDstImg->height; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < pDstImg->width; j++)
{
*(pDstImg->yPlane + i*pDstImg->width + j) = *(pSrcImg->yPlane + i * y_scale *pSrcImg->width + j * x_scale);
}
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < pDstImg->height / 2; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < pDstImg->width; j += 2)
{
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + i*pDstImg->width + j) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + i * y_scale *pSrcImg->width + j * x_scale);
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + i*pDstImg->width + j + 1) = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + i * y_scale *pSrcImg->width + j * x_scale + 1);
}
}
}
else
{
// 放大
int x_scale = pDstImg->width / pSrcImg->width;
int y_scale = pDstImg->height / pSrcImg->height;
for (size_t i = 0; i < pSrcImg->height; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < pSrcImg->width; j++)
{
int yValue = *(pSrcImg->yPlane + i *pSrcImg->width + j);
for (size_t k = 0; k < x_scale; k++)
{
*(pDstImg->yPlane + i * y_scale * pDstImg->width + j * x_scale + k) = yValue;
}
}
unsigned char *pSrcRow = pDstImg->yPlane + i * y_scale * pDstImg->width;
unsigned char *pDstRow = NULL;
for (size_t l = 1; l < y_scale; l++)
{
pDstRow = (pDstImg->yPlane + (i * y_scale + l)* pDstImg->width);
memcpy(pDstRow, pSrcRow, pDstImg->width * sizeof(unsigned char ));
}
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < pSrcImg->height / 2; i++)
{
for (si
ff8
ze_t j = 0; j < pSrcImg->width; j += 2)
{
int vValue = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + i *pSrcImg->width + j);
int uValue = *(pSrcImg->uvPlane + i *pSrcImg->width + j + 1);
for (size_t k = 0; k < x_scale * 2; k += 2)
{
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + i * y_scale * pDstImg->width + j * x_scale + k) = vValue;
*(pDstImg->uvPlane + i * y_scale * pDstImg->width + j * x_scale + k + 1) = uValue;
}
}
unsigned char *pSrcRow = pDstImg->uvPlane + i * y_scale * pDstImg->width;
unsigned char *pDstRow = NULL;
for (size_t l = 1; l < y_scale; l++)
{
pDstRow = (pDstImg->uvPlane + (i * y_scale + l)* pDstImg->width);
memcpy(pDstRow, pSrcRow, pDstImg->width * sizeof(unsigned char ));
}
}
}
}
NV21 图片裁剪
图例中将 6x6 的 NV21 图按照横纵坐标偏移量为(2,2)裁剪成 4x4 的 NV21 图。
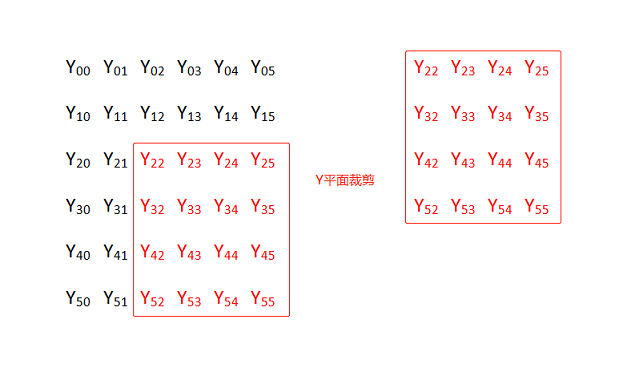 对 Y 平面裁剪
对 Y 平面裁剪
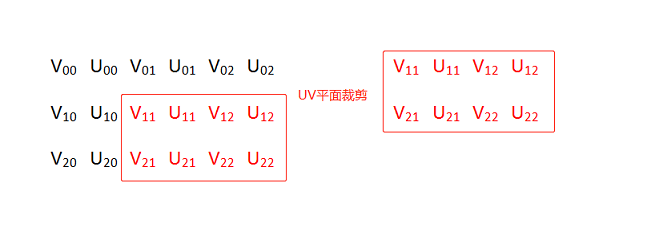 对 UV 平面裁剪
对 UV 平面裁剪
代码实现:
// x_offSet ,y_offSet % 2 == 0
void CropYUVImage(YUVImage *pSrcImg, int x_offSet, int y_offSet, YUVImage *pDstImg)
{
// 确保裁剪区域不存在内存越界
int cropWidth = pSrcImg->width - x_offSet;
cropWidth = cropWidth > pDstImg->width ? pDstImg->width : cropWidth;
int cropHeight = pSrcImg->height - y_offSet;
cropHeight = cropHeight > pDstImg->height ? pDstImg->height : cropHeight;
unsigned char *pSrcCursor = NULL;
unsigned char *pDstCursor = NULL;
//crop yPlane
for (size_t i = 0; i < cropHeight; i++)
{
pSrcCursor = pSrcImg->yPlane + (y_offSet + i) * pSrcImg->width + x_offSet;
pDstCursor = pDstImg->yPlane + i * pDstImg->width;
memcpy(pDstCursor, pSrcCursor, sizeof(unsigned char ) * cropWidth);
}
//crop uvPlane
for (size_t i = 0; i < cropHeight / 2; i++)
{
pSrcCursor = pSrcImg->uvPlane + (y_offSet / 2 + i) * pSrcImg->width + x_offSet;
pDstCursor = pDstImg->uvPlane + i * pDstImg->width;
memcpy(pDstCursor, pSrcCursor, sizeof(unsigned char ) * cropWidth);
}
}
测试原图
 IMG_840x1074 原图(图片用于显示都已转成 PNG)
IMG_840x1074 原图(图片用于显示都已转成 PNG)
测试代码
void main()
{
YUVImage srcImg = { 0 };
srcImg.width = 840;
srcImg.height = 1074;
LoadYUVImage("IMG_840x1074.NV21", &srcImg);
YUVImage rotateDstImg = { 0 };
rotateDstImg.width = 1074;
rotateDstImg.height = 840;
rotateDstImg.yPlane = malloc(rotateDstImg.width * rotateDstImg.height*1.5);
rotateDstImg.uvPlane = rotateDstImg.yPlane + rotateDstImg.width * rotateDstImg.height;
RotateYUVImage(&srcImg, &rotateDstImg, 270);
SaveYUVImage("D:\\material\\IMG_1074x840_270.NV21", &rotateDstImg);
RotateYUVImage(&srcImg, &rotateDstImg, 90);
SaveYUVImage("D:\\material\\IMG_1074x840_90.NV21", &rotateDstImg);
rotateDstImg.width = 840;
rotateDstImg.height = 1074;
RotateYUVImage(&srcImg, &rotateDstImg, 180);
SaveYUVImage("D:\\material\\IMG_840x1074_180.NV21", &rotateDstImg);
YUVImage resizeDstImg = { 0 };
resizeDstImg.width = 420;
resizeDstImg.height = 536;
resizeDstImg.yPlane = malloc(resizeDstImg.width * resizeDstImg.height*1.5);
resizeDstImg.uvPlane = resizeDstImg.yPlane + resizeDstImg.width * resizeDstImg.height;
ResizeYUVImage(&srcImg, &resizeDstImg);
SaveYUVImage("D:\\material\\IMG_420x536_Resize.NV21", &resizeDstImg);
YUVImage cropDstImg = { 0 };
cropDstImg.width = 300;
cropDstImg.height = 300;
cropDstImg.yPlane = malloc(cropDstImg.width * cropDstImg.height*1.5);
cropDstImg.uvPlane = cropDstImg.yPlane + cropDstImg.width * cropDstImg.height;
CropYUVImage(&srcImg, 100, 500, &cropDstImg);
SaveYUVImage("D:\\material\\IMG_300x300_crop.NV21", &cropDstImg);
ReleaseYUVImage(&srcImg);
ReleaseYUVImage(&rotateDstImg);
ReleaseYUVImage(&resizeDstImg);
ReleaseYUVImage(&cropDstImg);
}
测试结果
 IMG_1074x840_270(旋转270度)
IMG_1074x840_270(旋转270度)
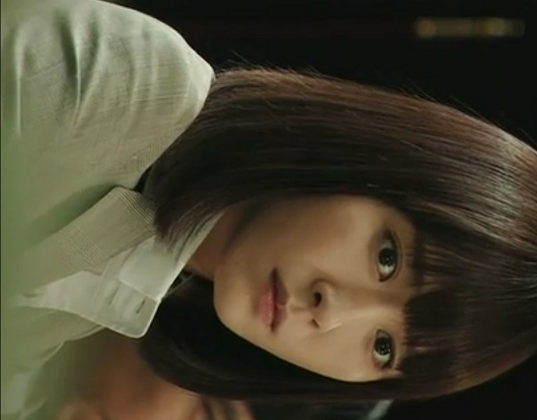 IMG_1074x840_90(旋转90度)
IMG_1074x840_90(旋转90度)
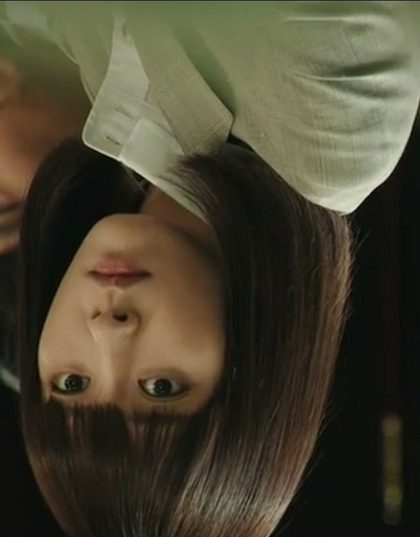 IMG_840x1074_180(旋转180度)
IMG_840x1074_180(旋转180度)
 IMG_420x536_Resize(缩放)
IMG_420x536_Resize(缩放)
 IMG_300x300_Crop(裁剪)
IMG_300x300_Crop(裁剪)
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/50534150
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1442041
-- 技术交流可以添加我的微信:Byte-Flow --

字节流动
推荐:
Android OpenGL ES 从入门到精通系统性学习教程
觉得不错,点个在看呗~
本文分享自微信公众号 - 字节流动(google_developer)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。
- Python图像处理库:PIL中Image,ImageDraw等基本模块介绍
- 图像处理基本算法 Hough变换
- 20200316.图像处理基本操作
- python图像处理库Pillow基本使用方法
- 从零开始学习数字图像处理——第一天(什么是数字图像处理,数字图像处理的基本步骤)
- 图形图像基本处理之——一个非常容易理解的图像求质心代码
- 三种图像处理的基本边缘检测法
- Matlab图像处理常用基本函数
- C#基本图像处理
- 基于标准C语言的数字图像处理基本框架
- 计算机视觉--基本的图像操作和处理
- Python-OpenCV 处理图像(一):基本操作
- Python3与OpenCV3.3 图像处理(二)--图像基本操作
- 图像处理基本概念——卷积,滤波,平滑(转载)
- 图像处理之图像基本变化(平移、缩放、旋转)(Octave实现)
- 图像处理基本算法-立体视觉
- OpenCV 教程(1) -- 基本图像处理
- 图像处理基本知识
- 图像处理基本概念——卷积,滤波,平滑
- Opencv学习笔记(三)--图像处理的基本操作

