Python数据挖掘-支持向量机SVM
2018-02-14 11:33
507 查看
本文章内容来自麦子学院课程-机器学习,特此申明。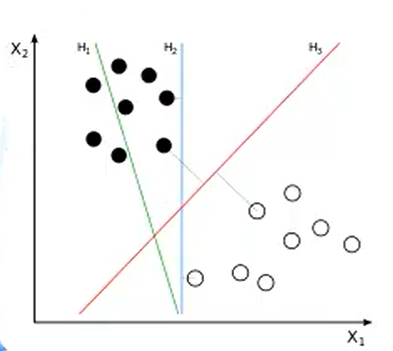 3.2 SVM寻找区分两类的超平面(hyper plane), 使边际(margin)最大
3.2 SVM寻找区分两类的超平面(hyper plane), 使边际(margin)最大 总共可以有多少个可能的超平面?无数条 如何选取使边际(margin)最大的超平面 (Max Margin Hyperplane)? 超平面到一侧最近点的距离等于到另一侧最近点的距离,两侧的两个超平面平行3. 线性可区分(linear separable) 和 线性不可区分 (linear inseparable)
总共可以有多少个可能的超平面?无数条 如何选取使边际(margin)最大的超平面 (Max Margin Hyperplane)? 超平面到一侧最近点的距离等于到另一侧最近点的距离,两侧的两个超平面平行3. 线性可区分(linear separable) 和 线性不可区分 (linear inseparable) 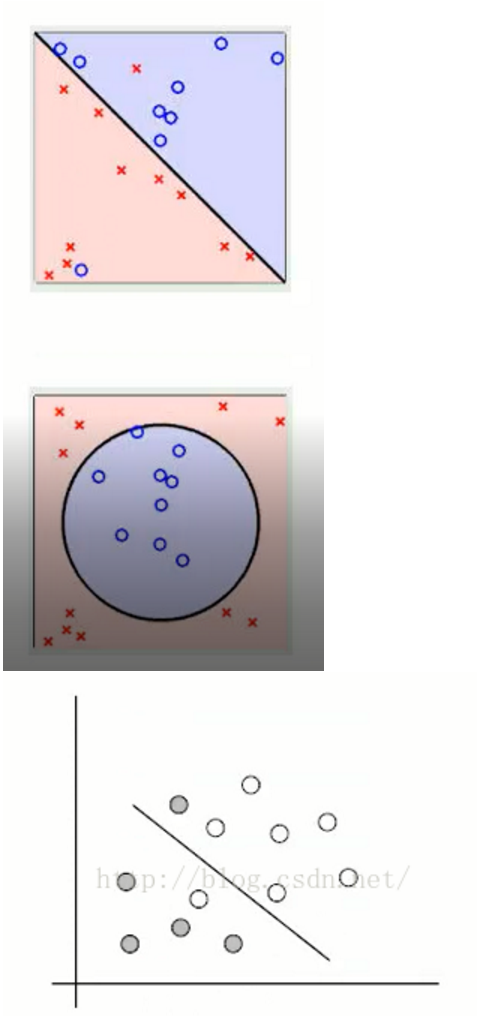 4. 定义与公式建立 超平面可以定义为:
4. 定义与公式建立 超平面可以定义为:  W: weight vectot,n是特征值的个数 X: 训练实例 b: bias 4.1 假设2维特征向量:X = (x1, X2)
W: weight vectot,n是特征值的个数 X: 训练实例 b: bias 4.1 假设2维特征向量:X = (x1, X2) 

 其中,
其中, 5.2 对于任何测试(要归类的)实例,带入以上公式,得出的符号是正还是负决定例题1:
5.2 对于任何测试(要归类的)实例,带入以上公式,得出的符号是正还是负决定例题1: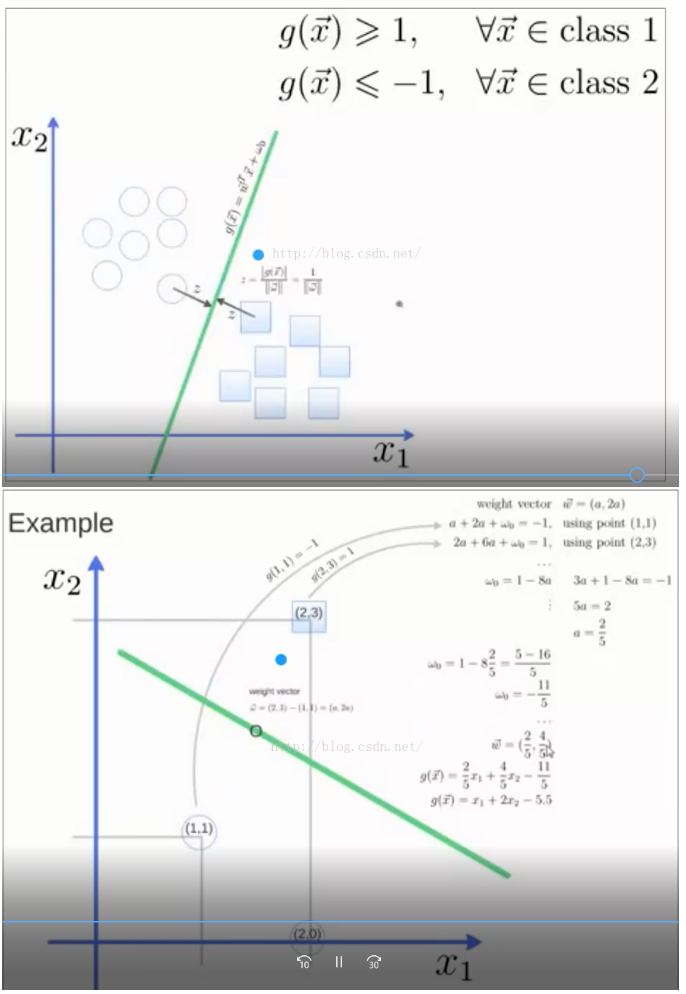 代码:
代码: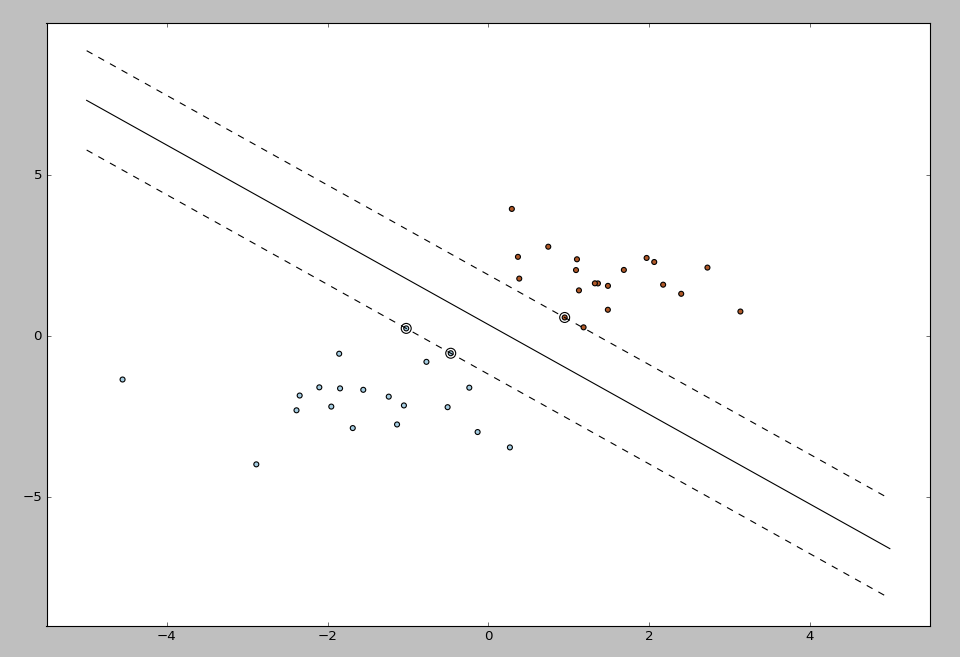 结果数据:w: [ 0.90230696 0.64821811]a: -1.39198047626support_vectors_: [[-1.02126202 0.2408932 ] [-0.46722079 -0.53064123] [ 0.95144703 0.57998206]]clf.coef_: [[ 0.90230696 0.64821811]]
结果数据:w: [ 0.90230696 0.64821811]a: -1.39198047626support_vectors_: [[-1.02126202 0.2408932 ] [-0.46722079 -0.53064123] [ 0.95144703 0.57998206]]clf.coef_: [[ 0.90230696 0.64821811]]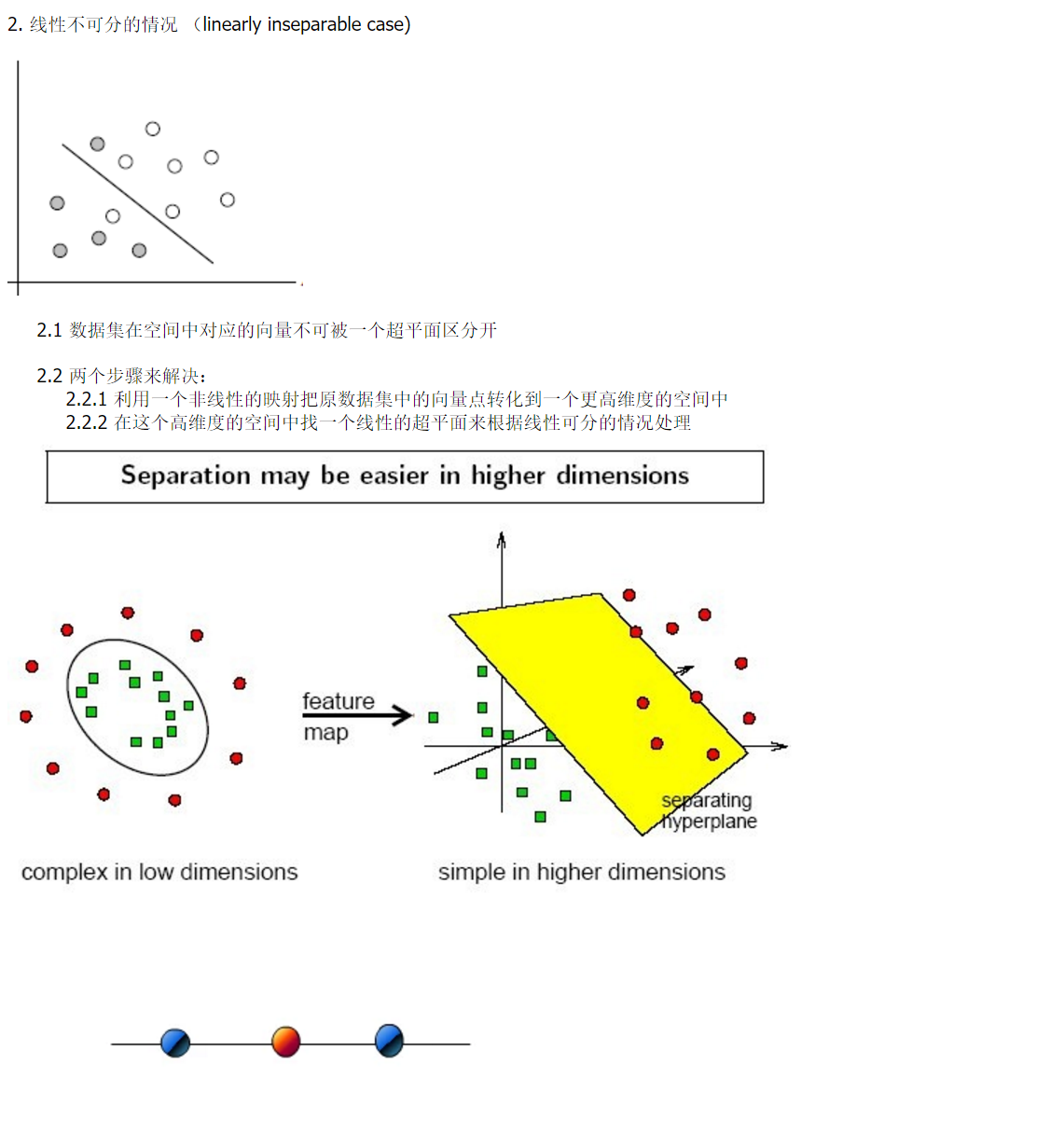

 例子:以下为人脸识别的算法实现from __future__ import print_functionfrom time import time #有此步骤要计时,看花了多少时间import logging #打印进展信息import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #最后需要把我们识别出来的人脸,用图来绘制出来#以下为sklearn包from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_peoplefrom sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCVfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_reportfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixfrom sklearn.decomposition import RandomizedPCAfrom sklearn.svm import SVC# 显示进度和错误信息,basicConfig:把程序中的进展的参数打印出来logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')################################################################################fetch_lfw_people用于下载名人的人脸库的,下载的数据集地址:http://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/lfw/index.htmllfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4)# 转换为数组n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape #n_samples=1288为多少个实例,h=50,w=37,即1288*50*37# 对于机器学习,我们直接使用2个数据(由于该模型忽略了相对像素位置信息) X每行是实例,每列为特征值。X = lfw_people.datan_features = X.shape[1] #每个人可以获得多少个特征值 n_features=1850# 预测的标签是该人的身份y = lfw_people.target #每个实例对应的人名,即标记,1288维target_names = lfw_people.target_names #返回所有人的名字,7*1维tuplen_classes = target_names.shape[0] #看有多少个人?即多少类?n_classes=7print("Total dataset size:")print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples)print("n_features: %d" % n_features)print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes)################################################################################ 分为训练集和使用分层k折的测试集# 分为训练集和测试集,X_train为训练集的特征向量, y_train为训练集的标记,train_target:所要划分的样本结果X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25) #966*1850 322*1850 966*1 322*1################################################################################ 在面部数据集上计算PCA(特征面)(被视为未标记的数据集):无监督特征提取/维数降低,因为1850列数据维度太高,所以降为150维n_components = 150print("Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces"% (n_components, X_train.shape[0]))#Extracting the top 150 eigenfaces(特征脸) from 966 faces
例子:以下为人脸识别的算法实现from __future__ import print_functionfrom time import time #有此步骤要计时,看花了多少时间import logging #打印进展信息import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #最后需要把我们识别出来的人脸,用图来绘制出来#以下为sklearn包from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_peoplefrom sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCVfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_reportfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixfrom sklearn.decomposition import RandomizedPCAfrom sklearn.svm import SVC# 显示进度和错误信息,basicConfig:把程序中的进展的参数打印出来logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')################################################################################fetch_lfw_people用于下载名人的人脸库的,下载的数据集地址:http://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/lfw/index.htmllfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4)# 转换为数组n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape #n_samples=1288为多少个实例,h=50,w=37,即1288*50*37# 对于机器学习,我们直接使用2个数据(由于该模型忽略了相对像素位置信息) X每行是实例,每列为特征值。X = lfw_people.datan_features = X.shape[1] #每个人可以获得多少个特征值 n_features=1850# 预测的标签是该人的身份y = lfw_people.target #每个实例对应的人名,即标记,1288维target_names = lfw_people.target_names #返回所有人的名字,7*1维tuplen_classes = target_names.shape[0] #看有多少个人?即多少类?n_classes=7print("Total dataset size:")print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples)print("n_features: %d" % n_features)print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes)################################################################################ 分为训练集和使用分层k折的测试集# 分为训练集和测试集,X_train为训练集的特征向量, y_train为训练集的标记,train_target:所要划分的样本结果X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25) #966*1850 322*1850 966*1 322*1################################################################################ 在面部数据集上计算PCA(特征面)(被视为未标记的数据集):无监督特征提取/维数降低,因为1850列数据维度太高,所以降为150维n_components = 150print("Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces"% (n_components, X_train.shape[0]))#Extracting the top 150 eigenfaces(特征脸) from 966 faces
Part One:线性可分的SVM
1. SVM 背景 1.1 最早是由 Vladimir N. Vapnik 和 Alexey Ya. Chervonenkis 在1963年提出 1.2 目前的版本(soft margin)是由Corinna Cortes 和 Vapnik在1993年提出,并在1995年发表 1.3 深度学习(2012)出现之前,SVM被认为机器学习中近十几年来最成功,表现最好的算法2. 机器学习的一般框架: 训练集 => 提取特征向量 => 结合一定的算法(分类器:比如决策树,KNN)=>得到结果 3.1 例子: 3. 介绍: 两类?哪条线最好? 3.2 SVM寻找区分两类的超平面(hyper plane), 使边际(margin)最大
3.2 SVM寻找区分两类的超平面(hyper plane), 使边际(margin)最大 总共可以有多少个可能的超平面?无数条 如何选取使边际(margin)最大的超平面 (Max Margin Hyperplane)? 超平面到一侧最近点的距离等于到另一侧最近点的距离,两侧的两个超平面平行3. 线性可区分(linear separable) 和 线性不可区分 (linear inseparable)
总共可以有多少个可能的超平面?无数条 如何选取使边际(margin)最大的超平面 (Max Margin Hyperplane)? 超平面到一侧最近点的距离等于到另一侧最近点的距离,两侧的两个超平面平行3. 线性可区分(linear separable) 和 线性不可区分 (linear inseparable)  4. 定义与公式建立 超平面可以定义为:
4. 定义与公式建立 超平面可以定义为:  W: weight vectot,n是特征值的个数 X: 训练实例 b: bias 4.1 假设2维特征向量:X = (x1, X2)
W: weight vectot,n是特征值的个数 X: 训练实例 b: bias 4.1 假设2维特征向量:X = (x1, X2) 

 其中,
其中, 5.2 对于任何测试(要归类的)实例,带入以上公式,得出的符号是正还是负决定例题1:
5.2 对于任何测试(要归类的)实例,带入以上公式,得出的符号是正还是负决定例题1: 代码:
代码:from sklearn import svm X = [[2, 0], [1, 1], [2,3]] y = [0, 0, 1] clf = svm.SVC(kernel = 'linear') clf.fit(X, y) print clf # get support vectors print clf.support_vectors_ # get indices of support vectors print clf.support_ # get number of support vectors for each class print clf.n_support_例题2:print(__doc__)import numpy as npimport pylab as plfrom sklearn import svm# we create 40 separable pointsnp.random.seed(0)X = np.r_[np.random.randn(20, 2) - [2, 2], np.random.randn(20, 2) + [2, 2]]Y = [0] * 20 + [1] * 20# fit the modelclf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear')clf.fit(X, Y)# get the separating hyperplanew = clf.coef_[0]a = -w[0] / w[1]xx = np.linspace(-5, 5)yy = a * xx - (clf.intercept_[0]) / w[1]# plot the parallels to the separating hyperplane that pass through the# support vectorsb = clf.support_vectors_[0]yy_down = a * xx + (b[1] - a * b[0])b = clf.support_vectors_[-1]yy_up = a * xx + (b[1] - a * b[0])print("w: ", w)print("a: ", a)# print " xx: ", xx# print " yy: ", yyprint("support_vectors_: ", clf.support_vectors_)print("clf.coef_: ", clf.coef_)# In scikit-learn coef_ attribute holds the vectors of the separating hyperplanes for linear models. It has shape (n_classes, n_features) if n_classes > 1 (multi-class one-vs-all) and (1, n_features) for binary classification.## In this toy binary classification example, n_features == 2, hence w = coef_[0] is the vector orthogonal to the hyperplane (the hyperplane is fully defined by it + the intercept).## To plot this hyperplane in the 2D case (any hyperplane of a 2D plane is a 1D line), we want to find a f as in y = f(x) = a.x + b. In this case a is the slope of the line and can be computed by a = -w[0] / w[1].# plot the line, the points, and the nearest vectors to the planepl.plot(xx, yy, 'k-')pl.plot(xx, yy_down, 'k--')pl.plot(xx, yy_up, 'k--')pl.scatter(clf.support_vectors_[:, 0], clf.support_vectors_[:, 1],s=80, facecolors='none')pl.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=Y, cmap=pl.cm.Paired)pl.axis('tight')pl.show()运行结果图如下:
 结果数据:w: [ 0.90230696 0.64821811]a: -1.39198047626support_vectors_: [[-1.02126202 0.2408932 ] [-0.46722079 -0.53064123] [ 0.95144703 0.57998206]]clf.coef_: [[ 0.90230696 0.64821811]]
结果数据:w: [ 0.90230696 0.64821811]a: -1.39198047626support_vectors_: [[-1.02126202 0.2408932 ] [-0.46722079 -0.53064123] [ 0.95144703 0.57998206]]clf.coef_: [[ 0.90230696 0.64821811]]Part Two:线性不可分的SVM
根据前面的内容我们测试的是线性可分的SVM,以下为线性不可分的SVM实现原理及例程:1. SVM算法特性: 1.1 训练好的模型的算法复杂度是由支持向量的个数决定的,而不是由数据的维度决定的。所以SVM不太容易产生overfitting 1.2 SVM训练出来的模型完全依赖于支持向量(Support Vectors), 即使训练集里面所有非支持向量的点都被去除,重复训练过程,结果仍然会得到完全一样的模型。 1.3 一个SVM如果训练得出的支持向量个数比较小,SVM训练出的模型比较容易被泛化。

 例子:以下为人脸识别的算法实现from __future__ import print_functionfrom time import time #有此步骤要计时,看花了多少时间import logging #打印进展信息import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #最后需要把我们识别出来的人脸,用图来绘制出来#以下为sklearn包from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_peoplefrom sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCVfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_reportfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixfrom sklearn.decomposition import RandomizedPCAfrom sklearn.svm import SVC# 显示进度和错误信息,basicConfig:把程序中的进展的参数打印出来logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')################################################################################fetch_lfw_people用于下载名人的人脸库的,下载的数据集地址:http://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/lfw/index.htmllfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4)# 转换为数组n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape #n_samples=1288为多少个实例,h=50,w=37,即1288*50*37# 对于机器学习,我们直接使用2个数据(由于该模型忽略了相对像素位置信息) X每行是实例,每列为特征值。X = lfw_people.datan_features = X.shape[1] #每个人可以获得多少个特征值 n_features=1850# 预测的标签是该人的身份y = lfw_people.target #每个实例对应的人名,即标记,1288维target_names = lfw_people.target_names #返回所有人的名字,7*1维tuplen_classes = target_names.shape[0] #看有多少个人?即多少类?n_classes=7print("Total dataset size:")print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples)print("n_features: %d" % n_features)print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes)################################################################################ 分为训练集和使用分层k折的测试集# 分为训练集和测试集,X_train为训练集的特征向量, y_train为训练集的标记,train_target:所要划分的样本结果X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25) #966*1850 322*1850 966*1 322*1################################################################################ 在面部数据集上计算PCA(特征面)(被视为未标记的数据集):无监督特征提取/维数降低,因为1850列数据维度太高,所以降为150维n_components = 150print("Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces"% (n_components, X_train.shape[0]))#Extracting the top 150 eigenfaces(特征脸) from 966 faces
例子:以下为人脸识别的算法实现from __future__ import print_functionfrom time import time #有此步骤要计时,看花了多少时间import logging #打印进展信息import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #最后需要把我们识别出来的人脸,用图来绘制出来#以下为sklearn包from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.datasets import fetch_lfw_peoplefrom sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCVfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_reportfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixfrom sklearn.decomposition import RandomizedPCAfrom sklearn.svm import SVC# 显示进度和错误信息,basicConfig:把程序中的进展的参数打印出来logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s %(message)s')################################################################################fetch_lfw_people用于下载名人的人脸库的,下载的数据集地址:http://vis-www.cs.umass.edu/lfw/index.htmllfw_people = fetch_lfw_people(min_faces_per_person=70, resize=0.4)# 转换为数组n_samples, h, w = lfw_people.images.shape #n_samples=1288为多少个实例,h=50,w=37,即1288*50*37# 对于机器学习,我们直接使用2个数据(由于该模型忽略了相对像素位置信息) X每行是实例,每列为特征值。X = lfw_people.datan_features = X.shape[1] #每个人可以获得多少个特征值 n_features=1850# 预测的标签是该人的身份y = lfw_people.target #每个实例对应的人名,即标记,1288维target_names = lfw_people.target_names #返回所有人的名字,7*1维tuplen_classes = target_names.shape[0] #看有多少个人?即多少类?n_classes=7print("Total dataset size:")print("n_samples: %d" % n_samples)print("n_features: %d" % n_features)print("n_classes: %d" % n_classes)################################################################################ 分为训练集和使用分层k折的测试集# 分为训练集和测试集,X_train为训练集的特征向量, y_train为训练集的标记,train_target:所要划分的样本结果X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25) #966*1850 322*1850 966*1 322*1################################################################################ 在面部数据集上计算PCA(特征面)(被视为未标记的数据集):无监督特征提取/维数降低,因为1850列数据维度太高,所以降为150维n_components = 150print("Extracting the top %d eigenfaces from %d faces"% (n_components, X_train.shape[0]))#Extracting the top 150 eigenfaces(特征脸) from 966 facest0 = time()
pca = RandomizedPCA(n_components=n_components, whiten=True).fit(X_train)
#n_components:这个参数可以帮我们指定希望PCA降维后的特征维度数目;whiten :判断是否进行白化。所谓白化,就是对降维后的数据的每个特征进行归一化,让方差都为1.对于PCA降维本身来说,一般不需要白化。如果你PCA降维后有后续的数据处理动作,可以考虑白化。
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
eigenfaces = pca.components_.reshape((n_components, h, w)) #eigenfaces为150*50*37
print("Projecting the input data on the eigenfaces orthonormal basis")
t0 = time()
X_train_pca = pca.transform(X_train) #用X来训练PCA模型,同时返回降维后的数据。 tuple:966*150
X_test_pca = pca.transform(X_test) #用X来训练PCA模型,同时返回降维后的数据。 tuple:966*150
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))###############################################################################
# 训练SVM分类模型
print("Fitting the classifier to the training set")
t0 = time()
param_grid = {'C': [1e3, 5e3, 1e4, 5e4, 1e5], 'gamma': [0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001, 0.005, 0.01, 0.1], }
#生成一个字典param_grid,用于SVC方法的两个参数(c-惩罚因子与gamma-Kenel函数因子)的选择,看哪一对值能产生最好的结果(准确率),进行多对量的尝试
clf = GridSearchCV(SVC(kernel='rbf', class_weight='auto'), param_grid) #GridSearchCV:当我们调用SVC函数时,将我们前面的组合进行多次计算尝试,返回最好的结果。
#因为是对图形的SVC,所以建议用rbf核函数;权重选择自动的; param_grid为参数矩阵
clf = clf.fit(X_train_pca, y_train) #进行建模
print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))
print("Best estimator found by grid search:")
print(clf.best_estimator_)
############################################此步骤打印如下:##########
# Best estimator found by grid search:#SVC(C=1000.0, cache_size=200, class_weight='auto', coef0=0.0, # decision_function_shape=None, degree=3, gamma=0.001, kernel='rbf', # max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True, # tol=0.001, verbose=False)################################################################################ 测试集上的模型质量的定量评估print("Predicting people's names on the test set")t0 = time()y_pred = clf.predict(X_test_pca)print("done in %0.3fs" % (time() - t0))print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, target_names=target_names))print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred, labels=range(n_classes)))#########此步骤打印信息如下#########Predicting people's names on the test set#done in 4.283s# precision recall f1-score support# Ariel Sharon 0.69 0.58 0.63 19# Colin Powell 0.72 0.75 0.74 57# Donald Rumsfeld 0.67 0.71 0.69 34# George W Bush 0.86 0.87 0.86 135#Gerhard Schroeder 0.73 0.80 0.76 30# Hugo Chavez 0.91 0.62 0.74 16# Tony Blair 0.70 0.68 0.69 31# avg / total 0.78 0.78 0.78 322#confusion_matrix: 对角线上表示实际值与我们预测值是一样的#[[ 11 2 4 1 1 0 0]# [ 2 43 2 5 1 0 4]# [ 1 0 24 7 2 0 0]# [ 2 7 5 117 1 1 2]# [ 0 1 1 2 24 0 2]# [ 0 3 0 1 1 10 1]# [ 0 4 0 3 3 0 21]]
###############################################################################
# 使用matplotlib进行定性评估
def plot_gallery(images, titles, h, w, n_row=3, n_col=4):
"""Helper function to plot a gallery of portraits"""
plt.figure(figsize=(1.8 * n_col, 2.4 * n_row)) #画面布局
plt.subplots_adjust(bottom=0, left=.01, right=.99, top=.90, hspace=.35)
for i in range(n_row * n_col):
plt.subplot(n_row, n_col, i + 1)
plt.imshow(images[i].reshape((h, w)), cmap=plt.cm.gray)
plt.title(titles[i], size=12)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
# 在测试集的一部分绘制预测结果
def title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i):
pred_name = target_names[y_pred[i]].rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
true_name = target_names[y_test[i]].rsplit(' ', 1)[-1]
return 'predicted: %s\ntrue: %s' % (pred_name, true_name)
prediction_titles = [title(y_pred, y_test, target_names, i) for i in range(y_pred.shape[0])]
#prediction_titles为322*1维的名字
plot_gallery(X_test, prediction_titles, h, w) #传入的x_test为322幅图像数据,但我们在函数中只显示前12张。
# 绘制最有意义的特征面的画廊
eigenface_titles = ["eigenface %d" % i for i in range(eigenfaces.shape[0])]
plot_gallery(eigenfaces, eigenface_titles, h, w)
plt.show()运行结果:
相关文章推荐
- 数据挖掘(Python)——利用sklearn进行数据挖掘,实现算法:svm、knn、C5.0、NaiveBayes
- 在R中使用支持向量机(SVM)进行数据挖掘(下)
- 数据挖掘---分类算法之支持向量机SVM
- python 数据科学 - 【分类模型】 ☞ 稳健滴 SVM 支持向量机
- 数据挖掘10大算法(1)-支持向量机(SVM)(一)
- 数据挖掘-SVM(支持向量机)的matlab基础DEMO详细注解
- 数据挖掘--支持向量机(SVM)基础
- 数据挖掘笔记-分类-支持向量机SVM-1
- 利用R语言实现支持向量机(SVM)数据挖掘案例
- 数据挖掘---分类算法之支持向量机SVM
- 机器学习与数据挖掘-支持向量机(SVM)(一)
- 在R中使用支持向量机(SVM)进行数据挖掘(上)
- 数据挖掘学习------------------4-分类方法-7-支持向量机(SVM)
- 用Python 爬取淘宝商品数据挖掘分析实战
- 【Python数据挖掘课程】三.Kmeans聚类代码实现、作业及优化
- 数据挖掘笔记:分类和预测bayes,svm等
- python数据分析和数据挖掘笔记
- 数据挖掘回顾五:分类算法之 支撑向量机(SVM) 算法
- 关于python,数据挖掘,自然语言处理的一些学习资源
- python/pandas数据挖掘(十四)-groupby,聚合,分组级运算
