用Python研究了三千套房子,告诉你究竟是什么抬高了房价?(python实战)
2018-01-25 10:06
686 查看
https://www.tuicool.com/articles/FBvaM3f
关于房价,一直都是全民热议的话题,毕竟不少人终其一生都在为之奋斗。
房地产的泡沫究竟有多大不得而知?今天我们抛开泡沫,回归房屋最本质的内容,来分析一下房价的影响因素究竟是什么?
1、导入数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sn
import missingno as msno
%matplotlib inline
train = pd.read_csv('train.csv',index_col=0)
#导入训练集
test = pd.read_csv('test.csv',index_col=0)
#导入测试集
train.head(3)
print('train训练集缺失数据分布图')
msno.matrix(train)
print('test测试集缺失数据分布图')
msno.matrix(test)
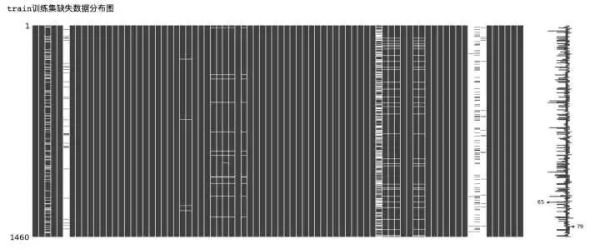
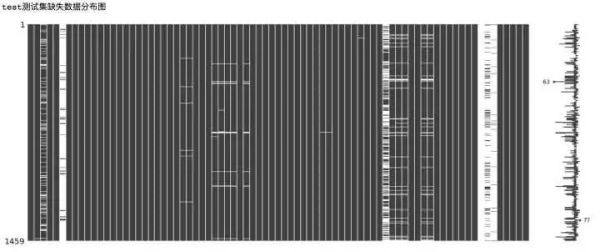
从上面的数据缺失可视化图中可以看出,部分特征的数据缺失十分严重,下面我们来对特征的缺失数量进行统计。
2、目标Y值分析
##分割Y和X数据
y=train['SalePrice']
#看一下y的值分布
prices = pd.DataFrame({'price':y,'log(price+1)':np.log1p(y)})
prices.hist()
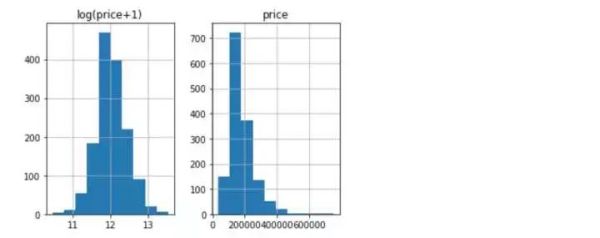
观察目标变量y的分布和取对数后的分布看,取完对数后更倾向于符合正太分布,故我们对y进行对数转化。
y = np.log1p(y) #+1的目的是防止对数转化后的值无意义
3、合并数据 缺失处理
#合并训练特征和测试集
all_df = pd.concat((X,test),axis=0)
print('all_df缺失数据图')
msno.matrix(all_df)
#定义缺失统计函数
def show_missing(feature):
missing = feature.columns[feature.isnull().any()].tolist()
return missing
print('缺失特征的数据缺失量统计:')
all_df[show_missing(all_df)].isnull().sum()
#先处理numeric数值型数据
#挨个儿看一下分布
fig,axs = plt.subplots(3,2,figsize=(16,9))
all_df['BsmtFinSF1'].hist(ax = axs[0,0])#众数填充
all_df['BsmtFinSF2'].hist(ax = axs[0,1])#众数
all_df['BsmtUnfSF'].hist(ax = axs[1,0])#中位数
all_df['TotalBsmtSF'].hist(ax = axs[1,1])#均值填充
all_df['BsmtFullBath'].hist(ax = axs[2,0])#众数
all_df['BsmtHalfBath'].hist(ax = axs[2,1])#众数
#lotfrontage用均值填充
mean_lotfrontage = all_df.LotFrontage.mean()
all_df.LotFrontage.hist()
print('用均值填充:')
cat_input(all_df,'LotFrontage',mean_lotfrontage)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtFinSF1',0.0)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtFinSF2',0.0)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtFullBath',0.0)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtHalfBath',0.0)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtUnfSF',467.00)
cat_input(all_df,'TotalBsmtSF',1051.78)
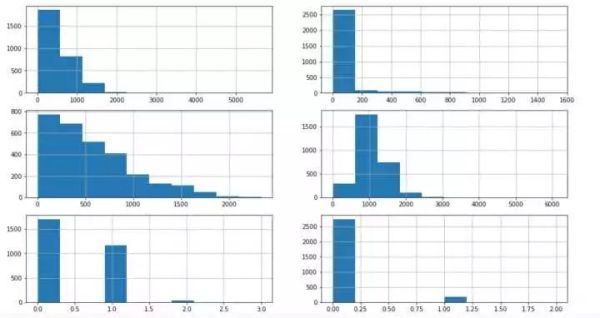
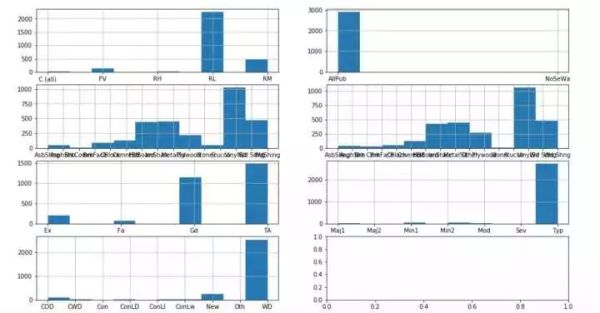
#在处理字符型,同样,挨个看下分布
fig,axs = plt.subplots(4,2,figsize=(16,9))
all_df['MSZoning'].hist(ax = axs[0,0])#众数填充
all_df['Utilities'].hist(ax = axs[0,1])#众数
all_df['Exterior1st'].hist(ax = axs[1,0])#众数
all_df['Exterior2nd'].hist(ax = axs[1,1])#众数填充
all_df['KitchenQual'].hist(ax = axs[2,0])#众数
all_df['Functional'].hist(ax = axs[2,1])#众数
all_df['SaleType'].hist(ax = axs[3,0])#众数
cat_input(all_df,'MSZoning','RL')
cat_input(all_df,'Utilities','AllPub')
cat_input(all_df,'Exterior1st','VinylSd')
cat_input(all_df,'Exterior2nd','VinylSd')
cat_input(all_df,'KitchenQual','TA')
cat_input(all_df,'Functional','Typ')
cat_input(all_df,'SaleType','WD')
#再看一下缺失分布
msno.matrix(all_df)


binggo,数据干净啦!下面开始处理特征,经过上述略微复杂的处理,数据集中所有的缺失数据都已处理完毕,可以开始接下来的工作啦!
缺失处理总结:在本篇文章所使用的数据集中存在比较多的缺失,缺失数据包括数值型和字符型,处理原则主要有两个:
一、根据绘制数据分布直方图,观察数据分布的状态,采取合适的方式填充缺失数据;
二、非常重要的特征描述,认真阅读,按照特征描述填充可以解决大部分问题。
4、特征处理
让我们在重新仔细审视一下数据有没有问题?仔细观察发现MSSubClass特征实际上是分类特征,但是数据显示是int类型,这个需要改成str。
#观察特征属性发现,MSSubClass是分类特征,但是数据给的是数值型,需要对其做转换
all_df['MSSubClass']=all_df['MSSubClass'].astype(str)
#将分类变量转变成数值变量
all_df = pd.get_dummies(all_df)
print('分类变量转换完成后有{}行{}列'.format(*all_df.shape))
分类变量转换完成后有2919行316列
#标准化处理
numeric_cols = all_df.columns[all_df.dtypes !='uint8']
#x-mean(x)/std(x)
numeric_mean = all_df.loc[:,numeric_cols].mean()
numeric_std = all_df.loc[:,numeric_cols].std()
all_df.loc[:,numeric_cols] = (all_df.loc[:,numeric_cols]-numeric_mean)/numeric_std
再把数据拆分到训练集和测试集
train_df = all_df.ix[0:1460]#训练集
test_df = all_df.ix[1461:]#测试集
5、构建基准模型
from sklearn import cross_validation
from sklearn import linear_model
from sklearn.learning_curve import learning_curve
from sklearn.metrics import explained_variance_score
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
y = y.values #转换成array数组
X = train_df.values #转换成array数组
cv = cross_validation.ShuffleSplit(len(X),n_iter=3,test_size=0.2)
print('岭回归交叉验证结果:')
for train_index,test_index in cv:
ridge = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=1).fit(X,y)
print('train_score:{0:.3f},test_score:{1:.3f}\n'.format(ridge.score(X[train_index],y[train_index]), ridge.score(X[test_index],y[test_index])))
print('随机森林交叉验证结果:')
for train_index,test_index in cv:
rf = RandomForestRegressor().fit(X,y)
print('train_score:{0:.3f},test_score:{1:.3f}\n'.format(rf.score(X[train_index],y[train_index]), rf.score(X[test_index],y[test_index])))

哇!好意外啊,这两个模型的结果表现都不错,但是随机森林的结果似乎更好,下面来看看学习曲线情况。
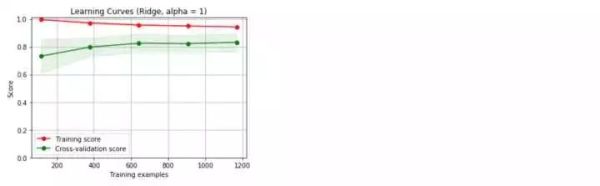
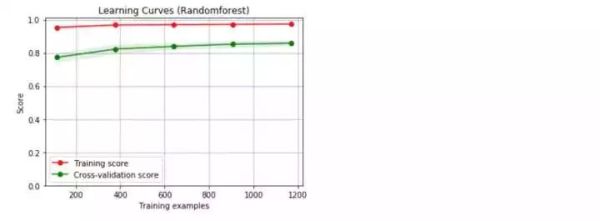
我们采用的是默认的参数,没有调优处理,得到的两个基准模型都存在过拟合现象。下面,我们开始着手参数的调整,希望能够改善模型的过拟合现象。
6、参数调优
岭回归正则项缩放系数alpha调整
alphas =[0.01,0.1,1,10,20,50,100,300]
test_scores = []
for alp in alphas:
clf = linear_model.Ridge(alp)
test_score = -cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
test_scores.append(np.mean(test_score))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.plot(alphas,test_scores)
plt.title('alpha vs test_score')
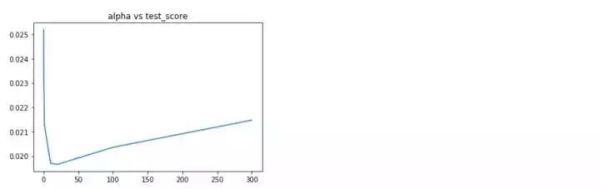
alpha在10-20附近均方误差最小
随机森林参数调优
随机森林算法,本篇中主要调整三个参数:maxfeatures,maxdepth,n_estimators
#随机森林的深度参数
max_depth=[2,4,6,8,10]
test_scores_depth = []
for depth in max_depth:
clf = RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=depth)
test_score_depth = -cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
test_scores_depth.append(np.mean(test_score_depth))
#随机森林的特征个数参数
max_features =[.1, .3, .5, .7, .9, .99]
test_scores_feature = []
for feature in max_features:
clf = RandomForestRegressor(max_features=feature)
test_score_feature = -cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
test_scores_feature.append(np.mean(test_score_feature))
#随机森林的估计器个位数参数
n_estimators =[10,50,100,200,500]
test_scores_n = []
for n in n_estimators:
clf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=n)
test_score_n = -cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
test_scores_n.append(np.mean(test_score_n))
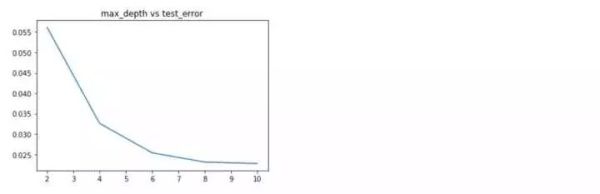
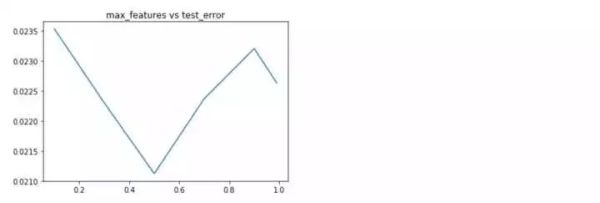
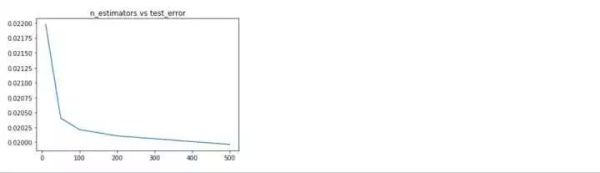
随机森林的各项参数来看,深度位于8,选择特征个数比例为0.5,估计器个数为500时,效果最好。下面分别利用上述得到的最优参数分别重新训练,看一下学习曲线,过拟合现象是否得到缓解?
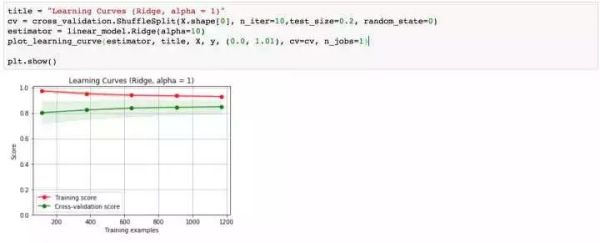
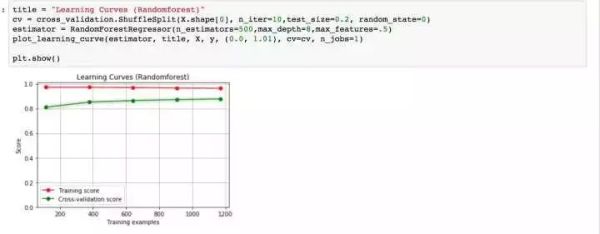
再回想一下,我们最初的基线模型学习曲线的形状,是不是得到了一定程度的缓解?OK,下面我们采用模型融合技术,对数据进行预测。
#预测
ridge = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=10).fit(X,y)
rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=500,max_depth=8,max_features=.5).fit(X,y)
y_ridge = np.expm1(ridge.predict(test_df.values))
y_rf = np.expm1(rf.predict(test_df.values))
y_final = (y_ridge + y_rf)/2

本篇房价预测的模型搭建已经完成。同样,再梳理一边思路:
一、本篇用到的房价数据集存在比较多的数据缺失,且分类变量十分多。在预处理阶段需要将训练集和测试集合并,进行缺失填充和one-hot独热变量处理,保证数据处理过程的一致性,在数据缺失填充过程中,需要综合考虑特征的实际描述和数据的分布,选择合适的填充方式填充;
二、为防止数据变量不统一带来的模型准确率下降,将数值型特征进行标准化处理,数据处理完成后,按照数据合并的方式,再还原到训练集和测试集;
三、先构建岭回归和随机森林基准模型,进行三折交叉验证,绘制学习曲线,存在明显的过拟合现象;
四、接下来分别对两个基准模型进行参数调优,获得使得均方误差最小的参数,返回到训练集进行训练;
五、采用并行模型融合的方式,计算两个模型预测结果的均值作为测试集的预测结果。
关于房价,一直都是全民热议的话题,毕竟不少人终其一生都在为之奋斗。
房地产的泡沫究竟有多大不得而知?今天我们抛开泡沫,回归房屋最本质的内容,来分析一下房价的影响因素究竟是什么?
1、导入数据
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sn
import missingno as msno
%matplotlib inline
train = pd.read_csv('train.csv',index_col=0)
#导入训练集
test = pd.read_csv('test.csv',index_col=0)
#导入测试集
train.head(3)
print('train训练集缺失数据分布图')
msno.matrix(train)
print('test测试集缺失数据分布图')
msno.matrix(test)



从上面的数据缺失可视化图中可以看出,部分特征的数据缺失十分严重,下面我们来对特征的缺失数量进行统计。
2、目标Y值分析
##分割Y和X数据
y=train['SalePrice']
#看一下y的值分布
prices = pd.DataFrame({'price':y,'log(price+1)':np.log1p(y)})
prices.hist()

观察目标变量y的分布和取对数后的分布看,取完对数后更倾向于符合正太分布,故我们对y进行对数转化。
y = np.log1p(y) #+1的目的是防止对数转化后的值无意义
3、合并数据 缺失处理
#合并训练特征和测试集
all_df = pd.concat((X,test),axis=0)
print('all_df缺失数据图')
msno.matrix(all_df)
#定义缺失统计函数
def show_missing(feature):
missing = feature.columns[feature.isnull().any()].tolist()
return missing
print('缺失特征的数据缺失量统计:')
all_df[show_missing(all_df)].isnull().sum()
#先处理numeric数值型数据
#挨个儿看一下分布
fig,axs = plt.subplots(3,2,figsize=(16,9))
all_df['BsmtFinSF1'].hist(ax = axs[0,0])#众数填充
all_df['BsmtFinSF2'].hist(ax = axs[0,1])#众数
all_df['BsmtUnfSF'].hist(ax = axs[1,0])#中位数
all_df['TotalBsmtSF'].hist(ax = axs[1,1])#均值填充
all_df['BsmtFullBath'].hist(ax = axs[2,0])#众数
all_df['BsmtHalfBath'].hist(ax = axs[2,1])#众数
#lotfrontage用均值填充
mean_lotfrontage = all_df.LotFrontage.mean()
all_df.LotFrontage.hist()
print('用均值填充:')
cat_input(all_df,'LotFrontage',mean_lotfrontage)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtFinSF1',0.0)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtFinSF2',0.0)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtFullBath',0.0)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtHalfBath',0.0)
cat_input(all_df,'BsmtUnfSF',467.00)
cat_input(all_df,'TotalBsmtSF',1051.78)
#在处理字符型,同样,挨个看下分布
fig,axs = plt.subplots(4,2,figsize=(16,9))
all_df['MSZoning'].hist(ax = axs[0,0])#众数填充
all_df['Utilities'].hist(ax = axs[0,1])#众数
all_df['Exterior1st'].hist(ax = axs[1,0])#众数
all_df['Exterior2nd'].hist(ax = axs[1,1])#众数填充
all_df['KitchenQual'].hist(ax = axs[2,0])#众数
all_df['Functional'].hist(ax = axs[2,1])#众数
all_df['SaleType'].hist(ax = axs[3,0])#众数
cat_input(all_df,'MSZoning','RL')
cat_input(all_df,'Utilities','AllPub')
cat_input(all_df,'Exterior1st','VinylSd')
cat_input(all_df,'Exterior2nd','VinylSd')
cat_input(all_df,'KitchenQual','TA')
cat_input(all_df,'Functional','Typ')
cat_input(all_df,'SaleType','WD')
#再看一下缺失分布
msno.matrix(all_df)





binggo,数据干净啦!下面开始处理特征,经过上述略微复杂的处理,数据集中所有的缺失数据都已处理完毕,可以开始接下来的工作啦!
缺失处理总结:在本篇文章所使用的数据集中存在比较多的缺失,缺失数据包括数值型和字符型,处理原则主要有两个:
一、根据绘制数据分布直方图,观察数据分布的状态,采取合适的方式填充缺失数据;
二、非常重要的特征描述,认真阅读,按照特征描述填充可以解决大部分问题。
4、特征处理
让我们在重新仔细审视一下数据有没有问题?仔细观察发现MSSubClass特征实际上是分类特征,但是数据显示是int类型,这个需要改成str。
#观察特征属性发现,MSSubClass是分类特征,但是数据给的是数值型,需要对其做转换
all_df['MSSubClass']=all_df['MSSubClass'].astype(str)
#将分类变量转变成数值变量
all_df = pd.get_dummies(all_df)
print('分类变量转换完成后有{}行{}列'.format(*all_df.shape))
分类变量转换完成后有2919行316列
#标准化处理
numeric_cols = all_df.columns[all_df.dtypes !='uint8']
#x-mean(x)/std(x)
numeric_mean = all_df.loc[:,numeric_cols].mean()
numeric_std = all_df.loc[:,numeric_cols].std()
all_df.loc[:,numeric_cols] = (all_df.loc[:,numeric_cols]-numeric_mean)/numeric_std
再把数据拆分到训练集和测试集
train_df = all_df.ix[0:1460]#训练集
test_df = all_df.ix[1461:]#测试集
5、构建基准模型
from sklearn import cross_validation
from sklearn import linear_model
from sklearn.learning_curve import learning_curve
from sklearn.metrics import explained_variance_score
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
y = y.values #转换成array数组
X = train_df.values #转换成array数组
cv = cross_validation.ShuffleSplit(len(X),n_iter=3,test_size=0.2)
print('岭回归交叉验证结果:')
for train_index,test_index in cv:
ridge = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=1).fit(X,y)
print('train_score:{0:.3f},test_score:{1:.3f}\n'.format(ridge.score(X[train_index],y[train_index]), ridge.score(X[test_index],y[test_index])))
print('随机森林交叉验证结果:')
for train_index,test_index in cv:
rf = RandomForestRegressor().fit(X,y)
print('train_score:{0:.3f},test_score:{1:.3f}\n'.format(rf.score(X[train_index],y[train_index]), rf.score(X[test_index],y[test_index])))

哇!好意外啊,这两个模型的结果表现都不错,但是随机森林的结果似乎更好,下面来看看学习曲线情况。


我们采用的是默认的参数,没有调优处理,得到的两个基准模型都存在过拟合现象。下面,我们开始着手参数的调整,希望能够改善模型的过拟合现象。
6、参数调优
岭回归正则项缩放系数alpha调整
alphas =[0.01,0.1,1,10,20,50,100,300]
test_scores = []
for alp in alphas:
clf = linear_model.Ridge(alp)
test_score = -cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
test_scores.append(np.mean(test_score))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.plot(alphas,test_scores)
plt.title('alpha vs test_score')

alpha在10-20附近均方误差最小
随机森林参数调优
随机森林算法,本篇中主要调整三个参数:maxfeatures,maxdepth,n_estimators
#随机森林的深度参数
max_depth=[2,4,6,8,10]
test_scores_depth = []
for depth in max_depth:
clf = RandomForestRegressor(max_depth=depth)
test_score_depth = -cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
test_scores_depth.append(np.mean(test_score_depth))
#随机森林的特征个数参数
max_features =[.1, .3, .5, .7, .9, .99]
test_scores_feature = []
for feature in max_features:
clf = RandomForestRegressor(max_features=feature)
test_score_feature = -cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
test_scores_feature.append(np.mean(test_score_feature))
#随机森林的估计器个位数参数
n_estimators =[10,50,100,200,500]
test_scores_n = []
for n in n_estimators:
clf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=n)
test_score_n = -cross_val_score(clf,X,y,cv=10,scoring='neg_mean_squared_error')
test_scores_n.append(np.mean(test_score_n))



随机森林的各项参数来看,深度位于8,选择特征个数比例为0.5,估计器个数为500时,效果最好。下面分别利用上述得到的最优参数分别重新训练,看一下学习曲线,过拟合现象是否得到缓解?


再回想一下,我们最初的基线模型学习曲线的形状,是不是得到了一定程度的缓解?OK,下面我们采用模型融合技术,对数据进行预测。
#预测
ridge = linear_model.Ridge(alpha=10).fit(X,y)
rf = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=500,max_depth=8,max_features=.5).fit(X,y)
y_ridge = np.expm1(ridge.predict(test_df.values))
y_rf = np.expm1(rf.predict(test_df.values))
y_final = (y_ridge + y_rf)/2

本篇房价预测的模型搭建已经完成。同样,再梳理一边思路:
一、本篇用到的房价数据集存在比较多的数据缺失,且分类变量十分多。在预处理阶段需要将训练集和测试集合并,进行缺失填充和one-hot独热变量处理,保证数据处理过程的一致性,在数据缺失填充过程中,需要综合考虑特征的实际描述和数据的分布,选择合适的填充方式填充;
二、为防止数据变量不统一带来的模型准确率下降,将数值型特征进行标准化处理,数据处理完成后,按照数据合并的方式,再还原到训练集和测试集;
三、先构建岭回归和随机森林基准模型,进行三折交叉验证,绘制学习曲线,存在明显的过拟合现象;
四、接下来分别对两个基准模型进行参数调优,获得使得均方误差最小的参数,返回到训练集进行训练;
五、采用并行模型融合的方式,计算两个模型预测结果的均值作为测试集的预测结果。
相关文章推荐
- 用Python研究了三千套房子,告诉你究竟是什么抬高了房价?
- [高级]Android Launcher研究(二)-----------Launcher为何物,究竟是干什么的?
- Android Launcher研究(二)-----------Launcher为何物,究竟是干什么的?
- Android Launcher研究(二)-----------Launcher为何物,究竟是干什么的?
- Python tensorflow实战3.神经网络 - 理解到底什么是神经网络,编程原理
- Python爬虫实战之爬取链家广州房价_04链家的模拟登录(记录)
- Python实战:网络爬虫都能干什么?
- 一分钟告诉你究竟DevOps是什么鬼?
- Python爬虫实战之爬取链家广州房价_03存储
- [转载] Python的GIL是什么鬼,多线程性能究竟如何
- 几个故事告诉你,火热的区块链究竟是什么?
- Python的GIL是什么鬼,多线程性能究竟如何
- [置顶] Python的GIL是什么鬼,多线程性能究竟如何
- Android Launcher研究(二)-----------Launcher为何物,究竟是干什么的?
- Python的GIL是什么鬼,多线程性能究竟如何
- 几个故事告诉你,火热的区块链究竟是什么?
- Python 的 GIL 是什么鬼,多线程性能究竟如何
- 房价高得有多离谱 日本东京四环房子什么价?
- 【原创】Python处理海量数据的实战研究
- python实战二:查看某网页是用什么编码的
