【keras】函数式(Functional)模型学习以LSTM为例构建多输入和多输出模型及完整实例(二)
2018-01-12 11:39
836 查看
多输入和多输出模型:使用函数式模型的一个典型场景是搭建多输入、多输出的模型。
考虑这样一个模型。我们希望预测Twitter上一条新闻会被转发和点赞多少次。模型的主要输入是新闻本身,也就是一个词语的序列。但我们还可以拥有额外的输入,如新闻发布的日期等。这个模型的损失函数将由两部分组成,辅助的损失函数评估仅仅基于新闻本身做出预测的情况,主损失函数评估基于新闻和额外信息的预测的情况,即使来自主损失函数的梯度发生弥散,来自辅助损失函数的信息也能够训练Embeddding和LSTM层。在模型中早点使用主要的损失函数是对于深度网络的一个良好的正则方法。总而言之,该模型框图如下:
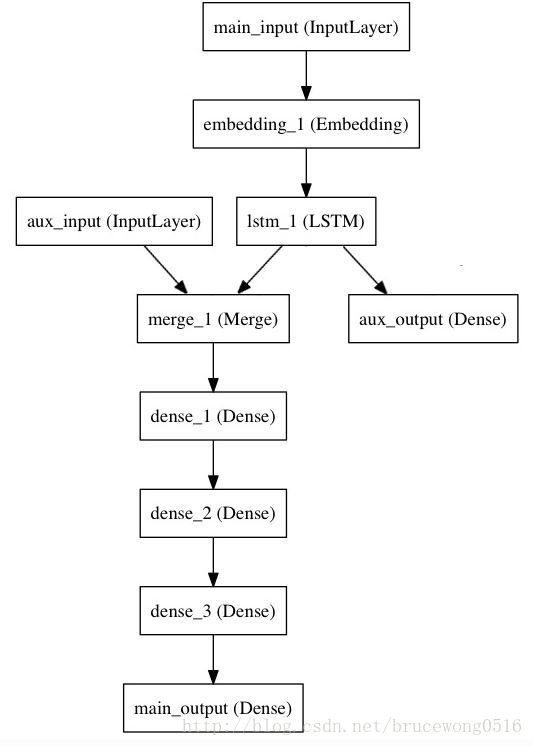
用函数式模型来实现这个框图
主要的输入接收新闻本身,即一个整数的序列(每个整数编码了一个词)。这些整数位于1到10,000之间(即我们的字典有10,000个词)。这个序列有100个单词。
然后,我们插入一个额外的损失,使得即使在主损失很
cffb
高的情况下,LSTM和Embedding层也可以平滑的训练。
再然后,我们将LSTM与额外的输入数据串联起来组成输入,送入模型中:
构建整个2输入,2输出的模型:
模型定义完毕,下一步编译模型。我们给额外的损失赋0.2的权重。我们可以通过关键字参数loss_weights或loss来为不同的输出设置不同的损失函数或权值。这两个参数均可为Python的列表或字典。这里我们给loss传递单个损失函数,这个损失函数会被应用于所有输出上。
编译完成后,我们通过传递训练数据和目标值训练该模型:
当然,因为之前已经定了了名称,所以可以更加全面的进行编译和训练模型:
完整实例:
考虑这样一个模型。我们希望预测Twitter上一条新闻会被转发和点赞多少次。模型的主要输入是新闻本身,也就是一个词语的序列。但我们还可以拥有额外的输入,如新闻发布的日期等。这个模型的损失函数将由两部分组成,辅助的损失函数评估仅仅基于新闻本身做出预测的情况,主损失函数评估基于新闻和额外信息的预测的情况,即使来自主损失函数的梯度发生弥散,来自辅助损失函数的信息也能够训练Embeddding和LSTM层。在模型中早点使用主要的损失函数是对于深度网络的一个良好的正则方法。总而言之,该模型框图如下:

用函数式模型来实现这个框图
主要的输入接收新闻本身,即一个整数的序列(每个整数编码了一个词)。这些整数位于1到10,000之间(即我们的字典有10,000个词)。这个序列有100个单词。
from keras.layers import Input, Embedding, LSTM, Dense from keras.models import Model # 设定主要输入的张量,并命名main_input # Headline input: meant to receive sequences of 100 integers, between 1 and 10000. # Note that we can name any layer by passing it a "name" argument. main_input = Input(shape=(100,), dtype='int32', name='main_input') # 嵌入生成512列维度的张量 # This embedding layer will encode the input sequence # into a sequence of dense 512-dimensional vectors. x = Embedding(output_dim=512, input_dim=10000, input_length=100)(main_input) #使用LSTM模型 # A LSTM will transform the vector sequence into a single vector, # containing information about the entire sequence lstm_out = LSTM(32)(x)
然后,我们插入一个额外的损失,使得即使在主损失很
cffb
高的情况下,LSTM和Embedding层也可以平滑的训练。
auxiliary_output = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid', name='aux_output')(lstm_out)
再然后,我们将LSTM与额外的输入数据串联起来组成输入,送入模型中:
#额外的输入数据 auxiliary_input = Input(shape=(5,), name='aux_input') #将LSTM得到的张量与额外输入的数据串联起来 x = keras.layers.concatenate([lstm_out, auxiliary_input]) #建立一个深层连接的网络 # We stack a deep densely-connected network on top x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x) x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x) x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x) #得到输出的张量 # And finally we add the main logistic regression layer main_output = Dense(1, activation='sigmoid', name='main_output')(x)
构建整个2输入,2输出的模型:
model = Model(inputs=[main_input, auxiliary_input], outputs=[main_output, auxiliary_output])
模型定义完毕,下一步编译模型。我们给额外的损失赋0.2的权重。我们可以通过关键字参数loss_weights或loss来为不同的输出设置不同的损失函数或权值。这两个参数均可为Python的列表或字典。这里我们给loss传递单个损失函数,这个损失函数会被应用于所有输出上。
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy',loss_weights=[1., 0.2])
编译完成后,我们通过传递训练数据和目标值训练该模型:
model.fit([headline_data, additional_data], [labels, labels],epochs=50, batch_size=32)
当然,因为之前已经定了了名称,所以可以更加全面的进行编译和训练模型:
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',
loss={'main_output': 'binary_crossentropy', 'aux_output': 'binary_crossentropy'},
loss_weights={'main_output': 1., 'aux_output': 0.2})
# And trained it via:
model.fit({'main_input': headline_data, 'aux_input': additional_data},
{'main_output': labels, 'aux_output': labels},
epochs=50, batch_size=32)完整实例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Jan 12 10:28:27 2018
函数模型之多输入与多输出模型
@author: BruceWong
"""
import keras
from keras.layers import Input, Embedding, LSTM, Dense
from keras.models import Model
import numpy as np
#generate data
#main_data
#这里构建数据集:主数据集为10000*100的二维数组,意味着100个特征
#标签为10000*1的二维数组,共有10种输出结果
main_x = np.random.random((10000,100))
main_y = keras.utils.to_categorical(np.random.randint(10,size = (10000,1)))
#additional_data
'''
All input arrays (x) should have the same number of samples. Got array shapes:
主数据集和额外的数据集的输入的特征张量的数据集个数相等,也就是行数相等;
'''
add_x = np.random.random((10000,10))
add_y = keras.utils.to_categorical(np.random.randint(10,size = (10000,1)))
# 设定主要输入的张量,并命名main_input
# Headline input: meant to receive sequences of 100 integers, between 1 and 10000.
# Note that we can name any layer by passing it a "name" argument.
'''
所有的input里面的shape的维度均是特征个数维度,列的个数;shape=(特征个数,)
'''
main_input = Input(shape=(100,), dtype='int32', name='main_input')
# 嵌入生成512列维度的张量
# This embedding layer will encode the input sequence
# into a sequence of dense 512-dimensional vectors.
x = Embedding(output_dim=512, input_dim=10000, input_length=100)(main_input)
#print(x.shape)
#使用LSTM模型
# A LSTM will transform the vector sequence into a single vector,
# containing information about the entire sequence
lstm_out = LSTM(32)(x)
auxiliary_output = Dense(10, activation='sigmoid', name='aux_output')(lstm_out)
#额外的输入数据
'''
所有的input里面的shape的维度均是特征个数维度,列的个数;shape=(特征个数,)
'''
auxiliary_input = Input(shape=(10,), name='aux_input')
'''
#将LSTM得到的张量与额外输入的数据串联起来,这里是横向连接
'''
x = keras.layers.concatenate([lstm_out, auxiliary_input])
#建立一个深层连接的网络
# We stack a deep densely-connected network on top
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
#得到主数据集输出的张量,10与输入的主数据集标签数据集的标签类相等
# And finally we add the main logistic regression layer
main_output = Dense(10, activation='sigmoid', name='main_output')(x)
#生成模型
model = Model(inputs=[main_input, auxiliary_input], outputs=[main_output, auxiliary_output])
#编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='binary_crossentropy',loss_weights=[1., 0.2])
#训练模型
model.fit([main_x, add_x], [main_y, main_y],epochs=10, batch_size=128)
#model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop',loss={'main_output': 'binary_crossentropy', 'aux_output': 'binary_crossentropy'},loss_weights={'main_output': 1., 'aux_output': 0.2})
# And trained it via:
#model.fit({'main_input': headline_data, 'aux_input': additional_data},{'main_output': labels, 'aux_output': labels},epochs=50, batch_size=32)
相关文章推荐
- [转]深度学习与爬虫实例教学--深度学习模型构建和训练
- 【keras】序贯Sequential模型实例之使用LSTM的序列分类
- 【keras】序贯Sequential模型实例之用于序列分类的栈式LSTM
- Unix学习笔记------书本例题编程实例------从标注输入读入然后从标准输出输出
- 如何为LSTM重新构建输入数据(Keras)
- keras: 在构建LSTM模型时,使用变长序列的方法
- keras搬砖系列-keras多输入多输出模型
- keras:2)函数式(Functional)模型
- Python中用Keras构建LSTM模型进行时间序列预测
- keras在构建LSTM模型时对变长序列的处理
- 深度学习与爬虫实例教学--深度学习模型构建和训练
- 【Keras初学】keras构建两种特征输入,两个输出同时训练
- 使用深度学习检测DGA(域名生成算法)——LSTM的输入数据本质上还是词袋模型
- python学习之 输入 输出
- Python 学习笔记之八——输入和输出
- Problem Description 求n个数的最小公倍数。 Input 输入包含多个测试实例,每个测试实例的开始是一个正整数n,然后是n个正整数。 Output 为每组测试数据输出它们的最小公倍数,每个测试实例的输出占一行。你可以假设最后的输出是一个32位的整数。 Sample
- Keras中的三输入模型的损失函数Triplet Loss
- MyBatis框架的学习(四)——Mapper.xml文件中的输入和输出映射以及动态sql
- [webGL学习]基于three.js构建WebGL实例第一讲
- 【fis3学习】中大型项目构建发布实例
