linux2.6内核SD Card Driver详细解析
2017-08-11 14:59
405 查看
***************************************************************************************************************************
作者:EasyWave 时间:2012.03.18
类别:linux驱动开发 声明:转载,请保留链接
***************************************************************************************************************************
一:MMC/SD/SDIO的概念
MMC:(Multi Media Card)由西门子公司和首推CF的SanDisk于1997年推出的多媒体记忆卡标准。
SD:(Secure Digital Memory Card)由日本松下、东芝及美国SanDisk公司于1999年8月共同开发研制的新一代记忆卡标准,已完全兼容MMC标准。
SDIO:(Secure Digital Input and Output Card)安全数字输入输出卡。SDIO是在SD标准上定义了一种外设接口,通过SD的I/O接脚来连接外围设备,并且通过SD上的 I/O数据接位与这些外围设备进行数据传输。是目前较热门的技术,如下图中的一些设备:GPS、相机、Wi-Fi、调频广播、条形码读卡器、蓝牙等。
工作模式:工作模式是针对主机控制器来说的。SDI控制器可以在符合MMC的标准下工作,或者可以在符合SD的标准下工作,或者可以在符合SDIO的标准下工作。故就分别简称为:MMC模式、SD模式和SDIO模式。
传输模式:传输模式也是针对主机控制器来说的,指控制器与卡之间数据的传输模式,或者说是总线类型。SDI控制器可支持SPI、1位和4位的三种传输模式(总线类型)。至于1位和4位又是什么意思呢?他们是指传输数据总线的线宽,具体参考数据手册。
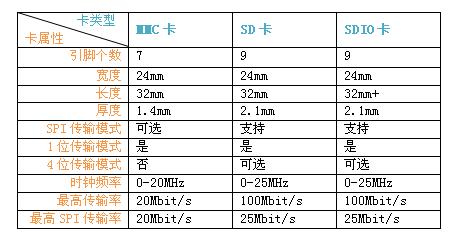
下面使用表格列出了MMC、SD、SDIO的电气特性及性能和不同工作模式下支持的传输模式情况:
二:MMC/SD协议
根据协议,MMC/SD卡的驱动被分为:卡识别阶段和数据传输阶段。在卡识别阶段通过命令使MMC/SD处于:空闲(idle)、准备(ready)、识别(ident)、等待(stby)、不活动(ina)几种不同的状态;而在数据传输阶段通过命令使MMC/SD处于:发送(data)、传输(tran)、接收(rcv)、程序(prg)、断开连接(dis)几种不同的状态。所以可以总结MMC/SD在工作的整个过程中分为两个阶段和十种状态。下面使用图形来描述一下在两个阶段中这十种状态之间的转换关系。
卡识别阶段,如下图:
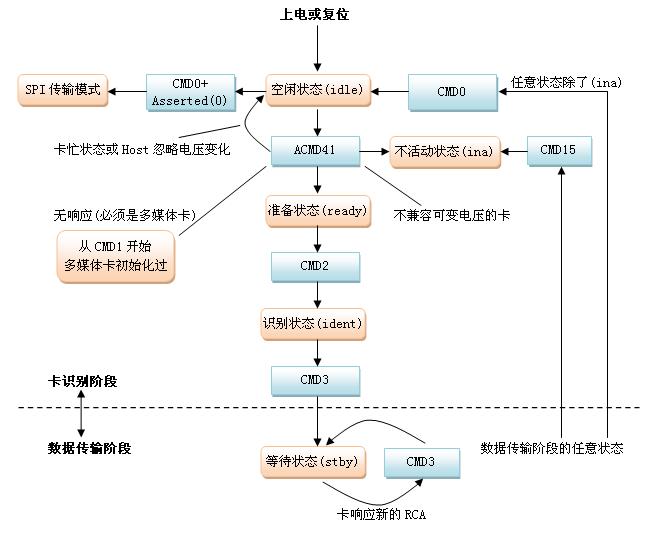
【图是从网络上抓取】
数据传输阶段,如下图:
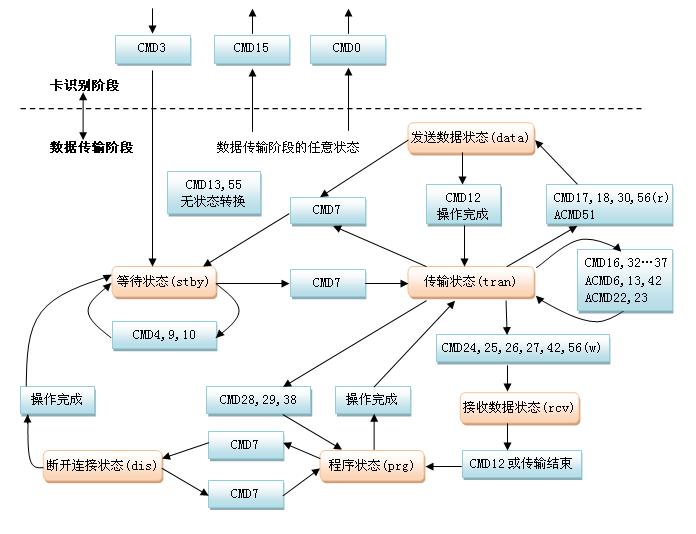
【图是从网络上抓取】
MMC/SD设备驱动代码在Linux源码中的位置/linux-2.6.35.4/drivers/mmc/,分别有card、core和host三个文件夹,他们都是MMC/SD卡的驱动。在实际驱动开发中,只需要在host文件夹下实现你具体的MMC/SD设备驱动部分代码,也就是控制器(支持对MMC/SD卡的控制,俗称MMC/SD主机控制器)和SDI控制器与MMC/SD卡的硬件接口电路。同时card、core和host这三层的关系,我们用一幅图来进行描述,图如下:

【图是从网络上抓取】
从图中的关系可以看出,整个MMC/SD模块中最重要的部分是Core核心层,他提供了一系列的接口函数,对上提供了将主机驱动注册到系统,给应用程序提供设备访问接口,对下提供了对主机控制器控制的方法及块设备请求的支持。
三:分析MMC/SD卡设备驱动程序
MMC/SD卡驱动程序的重要数据结构mmc_host,该结构位于Core核心层,主要用于核心层与主机驱动层的数据交换处理。定义在/include/linux/mmc/host.h中:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
struct mmc_host {
struct device *parent;
struct device class_dev;
int index;
const struct mmc_host_ops *ops;
unsigned int f_min;
unsigned int f_max;
u32 ocr_avail;
#define MMC_VDD_165_195 0x00000080 /* VDD voltage 1.65 - 1.95 */
#define MMC_VDD_20_21 0x00000100 /* VDD voltage 2.0 ~ 2.1 */
#define MMC_VDD_21_22 0x00000200 /* VDD voltage 2.1 ~ 2.2 */
#define MMC_VDD_22_23 0x00000400 /* VDD voltage 2.2 ~ 2.3 */
#define MMC_VDD_23_24 0x00000800 /* VDD voltage 2.3 ~ 2.4 */
#define MMC_VDD_24_25 0x00001000 /* VDD voltage 2.4 ~ 2.5 */
#define MMC_VDD_25_26 0x00002000 /* VDD voltage 2.5 ~ 2.6 */
#define MMC_VDD_26_27 0x00004000 /* VDD voltage 2.6 ~ 2.7 */
#define MMC_VDD_27_28 0x00008000 /* VDD voltage 2.7 ~ 2.8 */
#define MMC_VDD_28_29 0x00010000 /* VDD voltage 2.8 ~ 2.9 */
#define MMC_VDD_29_30 0x00020000 /* VDD voltage 2.9 ~ 3.0 */
#define MMC_VDD_30_31 0x00040000 /* VDD voltage 3.0 ~ 3.1 */
#define MMC_VDD_31_32 0x00080000 /* VDD voltage 3.1 ~ 3.2 */
#define MMC_VDD_32_33 0x00100000 /* VDD voltage 3.2 ~ 3.3 */
#define MMC_VDD_33_34 0x00200000 /* VDD voltage 3.3 ~ 3.4 */
#define MMC_VDD_34_35 0x00400000 /* VDD voltage 3.4 ~ 3.5 */
#define MMC_VDD_35_36 0x00800000 /* VDD voltage 3.5 ~ 3.6 */
unsigned long caps; /* Host capabilities */
#define MMC_CAP_4_BIT_DATA (1 << 0) /* Can the host do 4 bit transfers */
#define MMC_CAP_MMC_HIGHSPEED (1 << 1) /* Can do MMC high-speed timing */
#define MMC_CAP_SD_HIGHSPEED (1 << 2) /* Can do SD high-speed timing */
#define MMC_CAP_SDIO_IRQ (1 << 3) /* Can signal pending SDIO IRQs */
#define MMC_CAP_SPI (1 << 4) /* Talks only SPI protocols */
#define MMC_CAP_NEEDS_POLL (1 << 5) /* Needs polling for card-detection */
#define MMC_CAP_8_BIT_DATA (1 << 6) /* Can the host do 8 bit transfers */
#define MMC_CAP_DISABLE (1 << 7) /* Can the host be disabled */
#define MMC_CAP_NONREMOVABLE (1 << 8) /* Nonremovable e.g. eMMC */
#define MMC_CAP_WAIT_WHILE_BUSY (1 << 9) /* Waits while card is busy */
mmc_pm_flag_t pm_caps; /* supported pm features */
/* host specific block data */
unsigned int max_seg_size; /* see blk_queue_max_segment_size */
unsigned short max_hw_segs; /* see blk_queue_max_hw_segments */
unsigned short max_phys_segs; /* see blk_queue_max_phys_segments */
unsigned short unused;
unsigned int max_req_size; /* maximum number of bytes in one req */
unsigned int max_blk_size; /* maximum size of one mmc block */
unsigned int max_blk_count; /* maximum number of blocks in one req */
/* private data */
spinlock_t lock; /* lock for claim and bus ops */
struct mmc_ios ios; /* current io bus settings */
u32 ocr; /* the current OCR setting */
/* group bitfields together to minimize padding */
unsigned int use_spi_crc:1;
unsigned int claimed:1; /* host exclusively claimed */
unsigned int bus_dead:1; /* bus has been released */
#ifdef CONFIG_MMC_DEBUG
unsigned int removed:1; /* host is being removed */
#endif
/* Only used with MMC_CAP_DISABLE */
int enabled; /* host is enabled */
int nesting_cnt; /* "enable" nesting count */
int en_dis_recurs; /* detect recursion */
unsigned int disable_delay; /* disable delay in msecs */
struct delayed_work disable; /* disabling work */
struct mmc_card *card; /* device attached to this host */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
struct task_struct *claimer; /* task that has host claimed */
int claim_cnt; /* "claim" nesting count */
struct delayed_work detect;
const struct mmc_bus_ops *bus_ops; /* current bus driver */
unsigned int bus_refs; /* reference counter */
unsigned int sdio_irqs;
struct task_struct *sdio_irq_thread;
atomic_t sdio_irq_thread_abort;
mmc_pm_flag_t pm_flags; /* requested pm features */
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
struct led_trigger *led; /* activity led */
#endif
struct dentry *debugfs_root;
unsigned long private[0] ____cacheline_aligned;
};
MMC/SD卡驱动程序的重要数据结构mmc_host_ops,主要用于HOST端命令请求,直接跟芯片中SD卡寄存器打交道,定义在/include/linux/mmc/host.h中:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
struct mmc_host_ops {
/*
* Hosts that support power saving can use the 'enable' and 'disable'
* methods to exit and enter power saving states. 'enable' is called
* when the host is claimed and 'disable' is called (or scheduled with
* a delay) when the host is released. The 'disable' is scheduled if
* the disable delay set by 'mmc_set_disable_delay()' is non-zero,
* otherwise 'disable' is called immediately. 'disable' may be
* scheduled repeatedly, to permit ever greater power saving at the
* expense of ever greater latency to re-enable. Rescheduling is
* determined by the return value of the 'disable' method. A positive
* value gives the delay in milliseconds.
*
* In the case where a host function (like set_ios) may be called
* with or without the host claimed, enabling and disabling can be
* done directly and will nest correctly. Call 'mmc_host_enable()' and
* 'mmc_host_lazy_disable()' for this purpose, but note that these
* functions must be paired.
*
* Alternatively, 'mmc_host_enable()' may be paired with
* 'mmc_host_disable()' which calls 'disable' immediately. In this
* case the 'disable' method will be called with 'lazy' set to 0.
* This is mainly useful for error paths.
*
* Because lazy disable may be called from a work queue, the 'disable'
* method must claim the host when 'lazy' != 0, which will work
* correctly because recursion is detected and handled.
*/
int (*enable)(struct mmc_host *host);
int (*disable)(struct mmc_host *host, int lazy);
void (*request)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req);
/*
* Avoid calling these three functions too often or in a "fast path",
* since underlaying controller might implement them in an expensive
* and/or slow way.
*
* Also note that these functions might sleep, so don't call them
* in the atomic contexts!
*
* Return values for the get_ro callback should be:
* 0 for a read/write card
* 1 for a read-only card
* -ENOSYS when not supported (equal to NULL callback)
* or a negative errno value when something bad happened
*
* Return values for the get_cd callback should be:
* 0 for a absent card
* 1 for a present card
* -ENOSYS when not supported (equal to NULL callback)
* or a negative errno value when something bad happened
*/
void (*set_ios)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
int (*get_ro)(struct mmc_host *host);
int (*get_cd)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*enable_sdio_irq)(struct mmc_host *host, int enable);
/* optional callback for HC quirks */
void (*init_card)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_card *card);
};
对于mmc_host_ops需要重点讲一下:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
void (*request)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req);
这个函数主要用于SD卡命令的传输,比如发送和接收命令,CMD0,CMD8,ACMD41诸如此类的都是在这个函数去实现。
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
void (*set_ios)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
这个函数主要用于设置SD卡的CLK,MMC_POWER_OFF,MMC_POWER_ON的一些初始化。
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
int (*get_ro)(struct mmc_host *host);
这个函数主要用于检测SD卡的写保护是否打开。
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
int (*get_cd)(struct mmc_host *host);
这个函数主要用于SD卡的检测,是否有卡插入和弹出。
MMC/SD卡驱动程序的重要函数mmc_alloc_host,用于分配mmc_host结构体指针的内存空间大小,定义在host.c中:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
struct mmc_host *mmc_alloc_host(int extra, struct device *dev)
{
int err;
struct mmc_host *host;
if (!idr_pre_get(&mmc_host_idr, GFP_KERNEL))
return NULL;
host = kzalloc(sizeof(struct mmc_host) + extra, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!host)
return NULL;
spin_lock(&mmc_host_lock);
err = idr_get_new(&mmc_host_idr, host, &host->index);
spin_unlock(&mmc_host_lock);
if (err)
goto free;
dev_set_name(&host->class_dev, "mmc%d", host->index);
host->parent = dev;
host->class_dev.parent = dev;
host->class_dev.class = &mmc_host_class;
device_initialize(&host->class_dev);
spin_lock_init(&host->lock);
init_waitqueue_head(&host->wq);
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&host->detect, mmc_rescan);
INIT_DELAYED_WORK_DEFERRABLE(&host->disable, mmc_host_deeper_disable);
/*
* By default, hosts do not support SGIO or large requests.
* They have to set these according to their abilities.
*/
host->max_hw_segs = 1;
host->max_phys_segs = 1;
host->max_seg_size = PAGE_CACHE_SIZE;
host->max_req_size = PAGE_CACHE_SIZE;
host->max_blk_size = 512;
host->max_blk_count = PAGE_CACHE_SIZE / 512;
return host;
free:
kfree(host);
return NULL;
而在mmc_alloc_host函数中被调用的mmc_rescan函数,这个是需要重点关注的,因为SD卡协议中的检测,以及卡识别等都是在此函数中实现,具体的代码如下:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
void mmc_rescan(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct mmc_host *host =
container_of(work, struct mmc_host, detect.work);
u32 ocr;
int err;
mmc_bus_get(host);
/* if there is a card registered, check whether it is still present */
if ((host->bus_ops != NULL) && host->bus_ops->detect && !host->bus_dead)
host->bus_ops->detect(host);
mmc_bus_put(host);
mmc_bus_get(host);
/* if there still is a card present, stop here */
if (host->bus_ops != NULL) {
mmc_bus_put(host);
goto out;
}
/* detect a newly inserted card */
/*
* Only we can add a new handler, so it's safe to
* release the lock here.
*/
mmc_bus_put(host);
if (host->ops->get_cd && host->ops->get_cd(host) == 0)
goto out;
mmc_claim_host(host);
mmc_power_up(host);
sdio_reset(host);
mmc_go_idle(host); //让SD卡处于IDL_STATUS
mmc_send_if_cond(host, host->ocr_avail); //检测SD卡是否支持SD2.0
/*
* First we search for SDIO...
*/
err = mmc_send_io_op_cond(host, 0, &ocr); //检测是否是支持SDIO的卡,比如:SDIO WIFI等.
if (!err) {
if (mmc_attach_sdio(host, ocr))
mmc_power_off(host);
goto out;
}
/*
* ...then normal SD...
*/
err = mmc_send_app_op_cond(host, 0, &ocr); //检测是否是支持标准的SD卡.
if (!err) {
if (mmc_attach_sd(host, ocr))
mmc_power_off(host);
goto out;
}
/*
* ...and finally MMC.
*/
err = mmc_send_op_cond(host, 0, &ocr); //最后才是检测是否是支持MMC的卡
if (!err) {
if (mmc_attach_mmc(host, ocr))
mmc_power_off(host);
goto out;
}
mmc_release_host(host);
mmc_power_off(host);
out:
if (host->caps & MMC_CAP_NEEDS_POLL)
mmc_schedule_delayed_work(&host->detect, HZ);
}
MMC/SD卡驱动程序的重要函数mmc_add_host,用于挂载一个mmc_host到内核,定义在host.c中:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
int mmc_add_host(struct mmc_host *host)
{
int err;
WARN_ON((host->caps & MMC_CAP_SDIO_IRQ) &&
!host->ops->enable_sdio_irq);
led_trigger_register_simple(dev_name(&host->class_dev), &host->led);
err = device_add(&host->class_dev);
if (err)
return err;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
mmc_add_host_debugfs(host);
#endif
mmc_start_host(host);
return 0;
}
可以从SD卡平台驱动看到上面函数的调用情况:
static int __devinit s3cmci_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3cmci_host *host;
//实例一个名为mmc的结构体指针,用于与Core核心层中的mmc_host结构体指针相关联
struct mmc_host *mmc;
int ret;
spin_lock_init(&host->complete_lock);
//分配mmc_host结构体指针的内存空间大小,该函数在host.c中实现,这里要注意一点,为什么参数
//是s3cmci_host结构体的大小,到host.c中看,实际这里分配的是mmc_host加s3cmci_host的大小。
mmc = mmc_alloc_host(sizeof(struct s3cmci_host), &pdev->dev);
if (!mmc)
{
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto probe_out;
}
//调用mmc_priv函数将mmc_host和s3cmci_host结构体的对象关联起来,mmc_priv定义在host.h中
host = mmc_priv(mmc);
//下面就开始初始化s3cmci_host结构体的各成员
host->mmc = mmc;
host->pdev = pdev;
host->pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data;
..................................
..................................
..................................
//下面对mmc_host进行初始化
mmc->ops = &s3cmci_ops; //SDI主机控制器操作结构体
mmc->ocr_avail = MMC_VDD_32_33 | MMC_VDD_33_34; //设置工作电压范围
mmc->caps = MMC_CAP_4_BIT_DATA; //设置总线宽度为4位
mmc->f_min = host->clk_rate / (host->clk_div * 256); //设置最小工作频率
mmc->f_max = host->clk_rate / host->clk_div; //设置最大工作频率
mmc->max_blk_count = 4095;
mmc->max_blk_size = 4095;
mmc->max_req_size = 4095 * 512;
mmc->max_seg_size = mmc->max_req_size;
mmc->max_phys_segs = 128;
mmc->max_hw_segs = 128;
//将SDI host设备注册到系统中
ret = mmc_add_host(mmc);
if (ret)
{
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to add mmc host./n");
goto free_cpufreq;
}
//将SDI host设备的数据赋值给系统平台设备
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, mmc);
return 0;
..................................
..................................
..................................
probe_free_host:
mmc_free_host(mmc);
probe_out:
return ret;
}
http://blog.csdn.net/wavemcu/article/details/7366852
作者:EasyWave 时间:2012.03.18
类别:linux驱动开发 声明:转载,请保留链接
***************************************************************************************************************************
一:MMC/SD/SDIO的概念
MMC:(Multi Media Card)由西门子公司和首推CF的SanDisk于1997年推出的多媒体记忆卡标准。
SD:(Secure Digital Memory Card)由日本松下、东芝及美国SanDisk公司于1999年8月共同开发研制的新一代记忆卡标准,已完全兼容MMC标准。
SDIO:(Secure Digital Input and Output Card)安全数字输入输出卡。SDIO是在SD标准上定义了一种外设接口,通过SD的I/O接脚来连接外围设备,并且通过SD上的 I/O数据接位与这些外围设备进行数据传输。是目前较热门的技术,如下图中的一些设备:GPS、相机、Wi-Fi、调频广播、条形码读卡器、蓝牙等。
工作模式:工作模式是针对主机控制器来说的。SDI控制器可以在符合MMC的标准下工作,或者可以在符合SD的标准下工作,或者可以在符合SDIO的标准下工作。故就分别简称为:MMC模式、SD模式和SDIO模式。
传输模式:传输模式也是针对主机控制器来说的,指控制器与卡之间数据的传输模式,或者说是总线类型。SDI控制器可支持SPI、1位和4位的三种传输模式(总线类型)。至于1位和4位又是什么意思呢?他们是指传输数据总线的线宽,具体参考数据手册。
下面使用表格列出了MMC、SD、SDIO的电气特性及性能和不同工作模式下支持的传输模式情况:

二:MMC/SD协议
根据协议,MMC/SD卡的驱动被分为:卡识别阶段和数据传输阶段。在卡识别阶段通过命令使MMC/SD处于:空闲(idle)、准备(ready)、识别(ident)、等待(stby)、不活动(ina)几种不同的状态;而在数据传输阶段通过命令使MMC/SD处于:发送(data)、传输(tran)、接收(rcv)、程序(prg)、断开连接(dis)几种不同的状态。所以可以总结MMC/SD在工作的整个过程中分为两个阶段和十种状态。下面使用图形来描述一下在两个阶段中这十种状态之间的转换关系。
卡识别阶段,如下图:

【图是从网络上抓取】
数据传输阶段,如下图:

【图是从网络上抓取】
MMC/SD设备驱动代码在Linux源码中的位置/linux-2.6.35.4/drivers/mmc/,分别有card、core和host三个文件夹,他们都是MMC/SD卡的驱动。在实际驱动开发中,只需要在host文件夹下实现你具体的MMC/SD设备驱动部分代码,也就是控制器(支持对MMC/SD卡的控制,俗称MMC/SD主机控制器)和SDI控制器与MMC/SD卡的硬件接口电路。同时card、core和host这三层的关系,我们用一幅图来进行描述,图如下:

【图是从网络上抓取】
从图中的关系可以看出,整个MMC/SD模块中最重要的部分是Core核心层,他提供了一系列的接口函数,对上提供了将主机驱动注册到系统,给应用程序提供设备访问接口,对下提供了对主机控制器控制的方法及块设备请求的支持。
三:分析MMC/SD卡设备驱动程序
MMC/SD卡驱动程序的重要数据结构mmc_host,该结构位于Core核心层,主要用于核心层与主机驱动层的数据交换处理。定义在/include/linux/mmc/host.h中:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
struct mmc_host {
struct device *parent;
struct device class_dev;
int index;
const struct mmc_host_ops *ops;
unsigned int f_min;
unsigned int f_max;
u32 ocr_avail;
#define MMC_VDD_165_195 0x00000080 /* VDD voltage 1.65 - 1.95 */
#define MMC_VDD_20_21 0x00000100 /* VDD voltage 2.0 ~ 2.1 */
#define MMC_VDD_21_22 0x00000200 /* VDD voltage 2.1 ~ 2.2 */
#define MMC_VDD_22_23 0x00000400 /* VDD voltage 2.2 ~ 2.3 */
#define MMC_VDD_23_24 0x00000800 /* VDD voltage 2.3 ~ 2.4 */
#define MMC_VDD_24_25 0x00001000 /* VDD voltage 2.4 ~ 2.5 */
#define MMC_VDD_25_26 0x00002000 /* VDD voltage 2.5 ~ 2.6 */
#define MMC_VDD_26_27 0x00004000 /* VDD voltage 2.6 ~ 2.7 */
#define MMC_VDD_27_28 0x00008000 /* VDD voltage 2.7 ~ 2.8 */
#define MMC_VDD_28_29 0x00010000 /* VDD voltage 2.8 ~ 2.9 */
#define MMC_VDD_29_30 0x00020000 /* VDD voltage 2.9 ~ 3.0 */
#define MMC_VDD_30_31 0x00040000 /* VDD voltage 3.0 ~ 3.1 */
#define MMC_VDD_31_32 0x00080000 /* VDD voltage 3.1 ~ 3.2 */
#define MMC_VDD_32_33 0x00100000 /* VDD voltage 3.2 ~ 3.3 */
#define MMC_VDD_33_34 0x00200000 /* VDD voltage 3.3 ~ 3.4 */
#define MMC_VDD_34_35 0x00400000 /* VDD voltage 3.4 ~ 3.5 */
#define MMC_VDD_35_36 0x00800000 /* VDD voltage 3.5 ~ 3.6 */
unsigned long caps; /* Host capabilities */
#define MMC_CAP_4_BIT_DATA (1 << 0) /* Can the host do 4 bit transfers */
#define MMC_CAP_MMC_HIGHSPEED (1 << 1) /* Can do MMC high-speed timing */
#define MMC_CAP_SD_HIGHSPEED (1 << 2) /* Can do SD high-speed timing */
#define MMC_CAP_SDIO_IRQ (1 << 3) /* Can signal pending SDIO IRQs */
#define MMC_CAP_SPI (1 << 4) /* Talks only SPI protocols */
#define MMC_CAP_NEEDS_POLL (1 << 5) /* Needs polling for card-detection */
#define MMC_CAP_8_BIT_DATA (1 << 6) /* Can the host do 8 bit transfers */
#define MMC_CAP_DISABLE (1 << 7) /* Can the host be disabled */
#define MMC_CAP_NONREMOVABLE (1 << 8) /* Nonremovable e.g. eMMC */
#define MMC_CAP_WAIT_WHILE_BUSY (1 << 9) /* Waits while card is busy */
mmc_pm_flag_t pm_caps; /* supported pm features */
/* host specific block data */
unsigned int max_seg_size; /* see blk_queue_max_segment_size */
unsigned short max_hw_segs; /* see blk_queue_max_hw_segments */
unsigned short max_phys_segs; /* see blk_queue_max_phys_segments */
unsigned short unused;
unsigned int max_req_size; /* maximum number of bytes in one req */
unsigned int max_blk_size; /* maximum size of one mmc block */
unsigned int max_blk_count; /* maximum number of blocks in one req */
/* private data */
spinlock_t lock; /* lock for claim and bus ops */
struct mmc_ios ios; /* current io bus settings */
u32 ocr; /* the current OCR setting */
/* group bitfields together to minimize padding */
unsigned int use_spi_crc:1;
unsigned int claimed:1; /* host exclusively claimed */
unsigned int bus_dead:1; /* bus has been released */
#ifdef CONFIG_MMC_DEBUG
unsigned int removed:1; /* host is being removed */
#endif
/* Only used with MMC_CAP_DISABLE */
int enabled; /* host is enabled */
int nesting_cnt; /* "enable" nesting count */
int en_dis_recurs; /* detect recursion */
unsigned int disable_delay; /* disable delay in msecs */
struct delayed_work disable; /* disabling work */
struct mmc_card *card; /* device attached to this host */
wait_queue_head_t wq;
struct task_struct *claimer; /* task that has host claimed */
int claim_cnt; /* "claim" nesting count */
struct delayed_work detect;
const struct mmc_bus_ops *bus_ops; /* current bus driver */
unsigned int bus_refs; /* reference counter */
unsigned int sdio_irqs;
struct task_struct *sdio_irq_thread;
atomic_t sdio_irq_thread_abort;
mmc_pm_flag_t pm_flags; /* requested pm features */
#ifdef CONFIG_LEDS_TRIGGERS
struct led_trigger *led; /* activity led */
#endif
struct dentry *debugfs_root;
unsigned long private[0] ____cacheline_aligned;
};
MMC/SD卡驱动程序的重要数据结构mmc_host_ops,主要用于HOST端命令请求,直接跟芯片中SD卡寄存器打交道,定义在/include/linux/mmc/host.h中:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
struct mmc_host_ops {
/*
* Hosts that support power saving can use the 'enable' and 'disable'
* methods to exit and enter power saving states. 'enable' is called
* when the host is claimed and 'disable' is called (or scheduled with
* a delay) when the host is released. The 'disable' is scheduled if
* the disable delay set by 'mmc_set_disable_delay()' is non-zero,
* otherwise 'disable' is called immediately. 'disable' may be
* scheduled repeatedly, to permit ever greater power saving at the
* expense of ever greater latency to re-enable. Rescheduling is
* determined by the return value of the 'disable' method. A positive
* value gives the delay in milliseconds.
*
* In the case where a host function (like set_ios) may be called
* with or without the host claimed, enabling and disabling can be
* done directly and will nest correctly. Call 'mmc_host_enable()' and
* 'mmc_host_lazy_disable()' for this purpose, but note that these
* functions must be paired.
*
* Alternatively, 'mmc_host_enable()' may be paired with
* 'mmc_host_disable()' which calls 'disable' immediately. In this
* case the 'disable' method will be called with 'lazy' set to 0.
* This is mainly useful for error paths.
*
* Because lazy disable may be called from a work queue, the 'disable'
* method must claim the host when 'lazy' != 0, which will work
* correctly because recursion is detected and handled.
*/
int (*enable)(struct mmc_host *host);
int (*disable)(struct mmc_host *host, int lazy);
void (*request)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req);
/*
* Avoid calling these three functions too often or in a "fast path",
* since underlaying controller might implement them in an expensive
* and/or slow way.
*
* Also note that these functions might sleep, so don't call them
* in the atomic contexts!
*
* Return values for the get_ro callback should be:
* 0 for a read/write card
* 1 for a read-only card
* -ENOSYS when not supported (equal to NULL callback)
* or a negative errno value when something bad happened
*
* Return values for the get_cd callback should be:
* 0 for a absent card
* 1 for a present card
* -ENOSYS when not supported (equal to NULL callback)
* or a negative errno value when something bad happened
*/
void (*set_ios)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
int (*get_ro)(struct mmc_host *host);
int (*get_cd)(struct mmc_host *host);
void (*enable_sdio_irq)(struct mmc_host *host, int enable);
/* optional callback for HC quirks */
void (*init_card)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_card *card);
};
对于mmc_host_ops需要重点讲一下:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
void (*request)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_request *req);
这个函数主要用于SD卡命令的传输,比如发送和接收命令,CMD0,CMD8,ACMD41诸如此类的都是在这个函数去实现。
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
void (*set_ios)(struct mmc_host *host, struct mmc_ios *ios);
这个函数主要用于设置SD卡的CLK,MMC_POWER_OFF,MMC_POWER_ON的一些初始化。
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
int (*get_ro)(struct mmc_host *host);
这个函数主要用于检测SD卡的写保护是否打开。
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
int (*get_cd)(struct mmc_host *host);
这个函数主要用于SD卡的检测,是否有卡插入和弹出。
MMC/SD卡驱动程序的重要函数mmc_alloc_host,用于分配mmc_host结构体指针的内存空间大小,定义在host.c中:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
struct mmc_host *mmc_alloc_host(int extra, struct device *dev)
{
int err;
struct mmc_host *host;
if (!idr_pre_get(&mmc_host_idr, GFP_KERNEL))
return NULL;
host = kzalloc(sizeof(struct mmc_host) + extra, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!host)
return NULL;
spin_lock(&mmc_host_lock);
err = idr_get_new(&mmc_host_idr, host, &host->index);
spin_unlock(&mmc_host_lock);
if (err)
goto free;
dev_set_name(&host->class_dev, "mmc%d", host->index);
host->parent = dev;
host->class_dev.parent = dev;
host->class_dev.class = &mmc_host_class;
device_initialize(&host->class_dev);
spin_lock_init(&host->lock);
init_waitqueue_head(&host->wq);
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&host->detect, mmc_rescan);
INIT_DELAYED_WORK_DEFERRABLE(&host->disable, mmc_host_deeper_disable);
/*
* By default, hosts do not support SGIO or large requests.
* They have to set these according to their abilities.
*/
host->max_hw_segs = 1;
host->max_phys_segs = 1;
host->max_seg_size = PAGE_CACHE_SIZE;
host->max_req_size = PAGE_CACHE_SIZE;
host->max_blk_size = 512;
host->max_blk_count = PAGE_CACHE_SIZE / 512;
return host;
free:
kfree(host);
return NULL;
而在mmc_alloc_host函数中被调用的mmc_rescan函数,这个是需要重点关注的,因为SD卡协议中的检测,以及卡识别等都是在此函数中实现,具体的代码如下:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
void mmc_rescan(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct mmc_host *host =
container_of(work, struct mmc_host, detect.work);
u32 ocr;
int err;
mmc_bus_get(host);
/* if there is a card registered, check whether it is still present */
if ((host->bus_ops != NULL) && host->bus_ops->detect && !host->bus_dead)
host->bus_ops->detect(host);
mmc_bus_put(host);
mmc_bus_get(host);
/* if there still is a card present, stop here */
if (host->bus_ops != NULL) {
mmc_bus_put(host);
goto out;
}
/* detect a newly inserted card */
/*
* Only we can add a new handler, so it's safe to
* release the lock here.
*/
mmc_bus_put(host);
if (host->ops->get_cd && host->ops->get_cd(host) == 0)
goto out;
mmc_claim_host(host);
mmc_power_up(host);
sdio_reset(host);
mmc_go_idle(host); //让SD卡处于IDL_STATUS
mmc_send_if_cond(host, host->ocr_avail); //检测SD卡是否支持SD2.0
/*
* First we search for SDIO...
*/
err = mmc_send_io_op_cond(host, 0, &ocr); //检测是否是支持SDIO的卡,比如:SDIO WIFI等.
if (!err) {
if (mmc_attach_sdio(host, ocr))
mmc_power_off(host);
goto out;
}
/*
* ...then normal SD...
*/
err = mmc_send_app_op_cond(host, 0, &ocr); //检测是否是支持标准的SD卡.
if (!err) {
if (mmc_attach_sd(host, ocr))
mmc_power_off(host);
goto out;
}
/*
* ...and finally MMC.
*/
err = mmc_send_op_cond(host, 0, &ocr); //最后才是检测是否是支持MMC的卡
if (!err) {
if (mmc_attach_mmc(host, ocr))
mmc_power_off(host);
goto out;
}
mmc_release_host(host);
mmc_power_off(host);
out:
if (host->caps & MMC_CAP_NEEDS_POLL)
mmc_schedule_delayed_work(&host->detect, HZ);
}
MMC/SD卡驱动程序的重要函数mmc_add_host,用于挂载一个mmc_host到内核,定义在host.c中:
[plain]
view plain
copy
print?
int mmc_add_host(struct mmc_host *host)
{
int err;
WARN_ON((host->caps & MMC_CAP_SDIO_IRQ) &&
!host->ops->enable_sdio_irq);
led_trigger_register_simple(dev_name(&host->class_dev), &host->led);
err = device_add(&host->class_dev);
if (err)
return err;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
mmc_add_host_debugfs(host);
#endif
mmc_start_host(host);
return 0;
}
可以从SD卡平台驱动看到上面函数的调用情况:
static int __devinit s3cmci_probe(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
struct s3cmci_host *host;
//实例一个名为mmc的结构体指针,用于与Core核心层中的mmc_host结构体指针相关联
struct mmc_host *mmc;
int ret;
spin_lock_init(&host->complete_lock);
//分配mmc_host结构体指针的内存空间大小,该函数在host.c中实现,这里要注意一点,为什么参数
//是s3cmci_host结构体的大小,到host.c中看,实际这里分配的是mmc_host加s3cmci_host的大小。
mmc = mmc_alloc_host(sizeof(struct s3cmci_host), &pdev->dev);
if (!mmc)
{
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto probe_out;
}
//调用mmc_priv函数将mmc_host和s3cmci_host结构体的对象关联起来,mmc_priv定义在host.h中
host = mmc_priv(mmc);
//下面就开始初始化s3cmci_host结构体的各成员
host->mmc = mmc;
host->pdev = pdev;
host->pdata = pdev->dev.platform_data;
..................................
..................................
..................................
//下面对mmc_host进行初始化
mmc->ops = &s3cmci_ops; //SDI主机控制器操作结构体
mmc->ocr_avail = MMC_VDD_32_33 | MMC_VDD_33_34; //设置工作电压范围
mmc->caps = MMC_CAP_4_BIT_DATA; //设置总线宽度为4位
mmc->f_min = host->clk_rate / (host->clk_div * 256); //设置最小工作频率
mmc->f_max = host->clk_rate / host->clk_div; //设置最大工作频率
mmc->max_blk_count = 4095;
mmc->max_blk_size = 4095;
mmc->max_req_size = 4095 * 512;
mmc->max_seg_size = mmc->max_req_size;
mmc->max_phys_segs = 128;
mmc->max_hw_segs = 128;
//将SDI host设备注册到系统中
ret = mmc_add_host(mmc);
if (ret)
{
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to add mmc host./n");
goto free_cpufreq;
}
//将SDI host设备的数据赋值给系统平台设备
platform_set_drvdata(pdev, mmc);
return 0;
..................................
..................................
..................................
probe_free_host:
mmc_free_host(mmc);
probe_out:
return ret;
}
http://blog.csdn.net/wavemcu/article/details/7366852
相关文章推荐
- linux2.6内核SD Card Driver详细解析之一
- linux2.6内核SD Card Driver详细解析之一
- linux2.6内核SD Card Driver详细解析之一
- linux2.6内核SD Card Driver详细解析之一
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- linux2.6内核initrd机制解析
- Linux操作系统内核启动参数详细解析 [转]
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- linux2.6内核initrd机制解析
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- linux2.6内核kthread 内核线程机制解析(自己写的额注释)
- LINUX SD card driver分析
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- Linux2.6 内核的 Initrd 机制解析
- Linux操作系统内核启动参数详细解析
- linux-2.6内核升级详细文档
