Rational Krylov Method(克雷洛夫法)求解特征值问题matlab代码示例(和Arnoldi方法比较)
2017-07-27 22:23
489 查看
最基本的特征值问题分为三类:
1、标准的线性特征值问题:
Ax=λx,A∈Cn∗n
2、普遍的线性特征值问题:
Ax=λBx,A、B∈Cn∗n
3、普遍的艾米特正定线性特征值问题:
Ax=λBx,A、B∈Cn∗n
A∗=A,B∗=B>0∈Cn∗n
不妨做一个程序将RKM方法和Arnoldi方法做一个比较。
用到的一些子函数就一起列在下面了:
1、标准的线性特征值问题:
Ax=λx,A∈Cn∗n
2、普遍的线性特征值问题:
Ax=λBx,A、B∈Cn∗n
3、普遍的艾米特正定线性特征值问题:
Ax=λBx,A、B∈Cn∗n
A∗=A,B∗=B>0∈Cn∗n
不妨做一个程序将RKM方法和Arnoldi方法做一个比较。
% demo routine for Rational Krylov vs Arnoldi with shift-invert
clc
clear
n = 1000;
m = 40; % subspace size
A = diag([1:1:n]); % testing matrix A of eigenvalues 1, 2, .., n
% shifts: define more shift as you like
sigma1 = 101.5;
sigma2 = 121.5;
% -- Rational Krylov with shifts SIGMA
m1 = floor(m/2); m2 = m-m1;
SIGMA = [repmat(sigma1, m1, 1); repmat(sigma2, m2, 1)];
%SIGMA = repmat([sigma1; sigma2], m/2, 1); % even number m
[Q1, K, L] = rarnoldi(A, SIGMA, m);
[V1, E1] = eig(L(1:m,:), K(1:m,:));
% pick eig of relative residual norm < tol
tol = 1.0E-6;
nA = norm(A,1);
e1 = [];
for i = 1:m
lam = E1(i,i);
v = Q1*(K*V1(:, i));
res = norm(A*v-lam*v)/norm(v)/nA;
if res<tol, e1 = [e1, lam]; end
end
% -- shift invert Arnoldi with shift sigma1
sigma = sigma1;
[LL, UU, PP] = lu(A-sigma*speye(n));
Afun = @(x) UU \ (LL \ (PP*x));
[Q2, H] = arnoldi(Afun, n, m);
[V2, E2] = eig(H(1:m,:)); E2 = 1./E2 + sigma;
% pick eig of relative residual norm < tol
tol = 1.0E-6;
nA = norm(A,1);
e2 = [];
for i = 1:m
lam = E2(i,i);
v = Q2(:,1:m)*V2(:, i);
res = norm(A*v-lam*v)/norm(v)/nA;
if res<tol, e2 = [e2, lam]; end
end
% -- display results
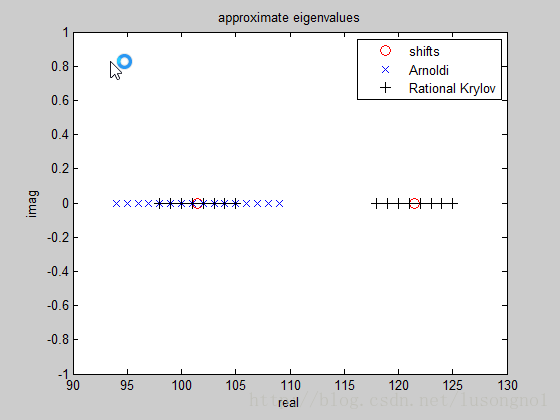
figure
plot(real([sigma1, sigma2]), imag([sigma1, sigma2]), 'or', 'DisplayName', 'shifts', 'MarkerSize', 8)
hold on;
plot(real(e2), imag(e2), 'xb', 'DisplayName', 'Arnoldi', 'MarkerSize', 8);
plot(real(e1), imag(e1), '+k', 'DisplayName', 'Rational Krylov', 'MarkerSize', 8);
legend show
xlabel('real'); ylabel('imag')
title('approximate eigenvalues')
% END
用到的一些子函数就一起列在下面了:
function [V, H] = arnoldi(Afun, n, m) % function [V, H] = arnoldi(Afun, n, m) produce an Arnoldi decomposition % of order m for a square matri A. % Afun(v) = A*v % n = dim of A % v = randn(n,1); v = v / norm(v); V = v; H = zeros(m+1, m); for i = 1:m w = Afun(v); h = V'*w; w = w - V*h; gamma = norm(w); if gamma==0 return end v = w/gamma; V = [V, v]; H(1:i,i) = h; H(1+i, i) = gamma; end function [V, K, L] = rarnoldi(A, SIGMA, m) % function [V, K, L] = rarnoldi(Afun, n, m) produce an rational Krylov % decomposition of order m for a square matri A. % SIGMA: length m vector containing shifts % n = size(A,1); v = randn(n,1); v = v / norm(v); V = v; K = zeros(m+1, m); L = zeros(m+1, m); for i = 1:m sigma = SIGMA(i); if sigma ~= inf w = (A-sigma*speye(n))\v; h = V'*w; w = w - V*h; gamma = norm(w); v = w/gamma; V = [V, v]; K(1:i, i) = h; K(i+1, i) = gamma; L(1:i+1, i) = sigma*K(1:i+1, i); L(i, i) = L(i, i) + 1; else w = A*v; h = V'*w; w = w - V*h; gamma = norm(w); v = w/gamma; V = [V, v]; K(i, i) = 1; L(1:i, i) = h; L(i+1, i) = gamma; end % breakdown case L(i+1, i) = K(i+1,i) = 0 is not treated. end
相关文章推荐
- Matlab遗传算法优化问题求解的示例代码
- Arnoldi方法求特征值:matlab中eigs函数的一个使用示例
- 遗传算法 求解旅行商 TSP 问题,matlab代码
- 《Thinking in Java》RMI远程方法示例代码运行是可能遇到的问题及解决方法
- 遗传算法求解带非线性约束的单目标问题,matlab代码,基于K Deb的论文
- 聚类方法:DBSCAN算法研究(3)--C++代码实现及与matlab实例结果比较
- matlab实现蒙特卡洛方法求解线性规划问题
- 使用MATLAB自带函数求解二次特征值问题
- 数值计算方法 求解初值问题(伪代码 c/c++ python)
- 字符串包含问题的求解(最简单的方法——只有两行代码)
- 遗传算法求解迷宫问题的matlab代码——greatji_1994
- 背包问题,动态规划求解,matlab代码,c++代码
- MATLAB实现多分类问题,使用libsvm,1-vs-rest和1-vs-1两种方法代码
- Matlab遗传算法优化问题求解的演示样例代码
- 用非递归方法实现 求解字符串组合的问题 JAVA代码
- 关于“未指定的错误”的问题 的比较正解的解决方法
- VC++.NET 2005 几个比较难缠的问题及其解决方法(转)
- C# 冒泡排序法示例代码(包含泛型方法)
- C#.NET示例读写xml所有节点的代码实现方法和读取xml节点的数据总结
- 《Programming Ruby 中文版第二版》P577页singleton_method_undefined方法说明有点问题
