Trapping Rain Water II
2017-05-04 11:33
246 查看
Trapping Rain Water II
Given an
a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
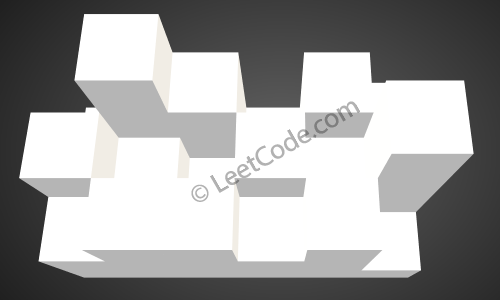
The above image represents the elevation map
the rain.
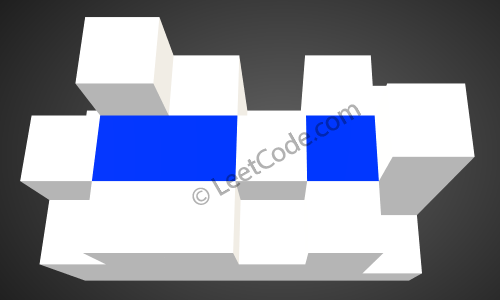
After the rain, water are trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
解析:
从四周开始从低处上升水平面
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> que;
if (heightMap.empty()) return 0;
int rows=heightMap.size();
int cols=heightMap[0].size();
int ans=0;
vector<vector<int>>vis(rows,vector<int>(cols,0));
for (int i=0; i<rows; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<cols; j++)
{
if (i==0||i==(rows-1)||j==0||j==(cols-1))
{
int pos=i*cols+j;
que.push(make_pair(heightMap[i][j],pos));
vis[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
int dx[4]={0,1,0,-1};
int dy[4]={-1,0,1,0};
int height=INT_MIN;
while(!que.empty())
{
pair<int,int>cur=que.top();
que.pop();
int curheight=cur.first;
int currow=cur.second/cols;
int curcol=cur.second%cols;
height=max(height,curheight);
for (int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
int temprow=currow+dy[i];
int tempcol=curcol+dx[i];
if (temprow<0||temprow>=rows||tempcol<0||tempcol>=cols||vis[temprow][tempcol])
{
continue;
}
if (heightMap[temprow][tempcol]<height)
{
ans+=(height-heightMap[temprow][tempcol]);
}
vis[temprow][tempcol]=1;
que.push(make_pair(heightMap[temprow][tempcol],temprow*cols+tempcol));
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Given an
m x nmatrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in
a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map: [ [1,4,3,1,3,2], [3,2,1,3,2,4], [2,3,3,2,3,1] ] Return 4.

The above image represents the elevation map
[[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]]before
the rain.

After the rain, water are trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
解析:
从四周开始从低处上升水平面
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> que;
if (heightMap.empty()) return 0;
int rows=heightMap.size();
int cols=heightMap[0].size();
int ans=0;
vector<vector<int>>vis(rows,vector<int>(cols,0));
for (int i=0; i<rows; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<cols; j++)
{
if (i==0||i==(rows-1)||j==0||j==(cols-1))
{
int pos=i*cols+j;
que.push(make_pair(heightMap[i][j],pos));
vis[i][j]=1;
}
}
}
int dx[4]={0,1,0,-1};
int dy[4]={-1,0,1,0};
int height=INT_MIN;
while(!que.empty())
{
pair<int,int>cur=que.top();
que.pop();
int curheight=cur.first;
int currow=cur.second/cols;
int curcol=cur.second%cols;
height=max(height,curheight);
for (int i=0; i<4; i++)
{
int temprow=currow+dy[i];
int tempcol=curcol+dx[i];
if (temprow<0||temprow>=rows||tempcol<0||tempcol>=cols||vis[temprow][tempcol])
{
continue;
}
if (heightMap[temprow][tempcol]<height)
{
ans+=(height-heightMap[temprow][tempcol]);
}
vis[temprow][tempcol]=1;
que.push(make_pair(heightMap[temprow][tempcol],temprow*cols+tempcol));
}
}
return ans;
}
};
相关文章推荐
- [LeetCode] Trapping Rain Water II 收集雨水之二
- leetcode 407. Trapping Rain Water II
- 407. Trapping Rain Water II
- leetcode 407. Trapping Rain Water II
- 42. Trapping Rain Water 及类似题目 407. Trapping Rain Water II 11. Container With Most Water
- [Leetcode] 407. Trapping Rain Water II 解题报告
- Leetcode 407 Trapping Rain Water II
- Trapping Rain Water II
- LeetCode 407. Trapping Rain Water II
- LeetCode Trapping Rain Water II
- bfs-407. Trapping Rain Water II[Hard]
- (算法)Trapping Rain Water II
- LintCode 364 Trapping Rain Water II
- 407. Trapping Rain Water II
- [LeetCode]407. Trapping Rain Water II
- Leetcode 407. Trapping Rain Water II
- 407. Trapping Rain Water II
- [poj] The Wedding Juicer | [lintcode] Trapping Rain Water II
- Trapping Rain Water II
- [LintCode] Trapping rain water II
