分析奇数与偶数之间的关系
2017-04-22 12:52
239 查看
C. Mike and gcd problem
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Mike has a sequence A = [a1, a2, ..., an] of
length n. He considers the sequence B = [b1, b2, ..., bn] beautiful
if the gcd of all its elements is bigger than 1,
i.e.
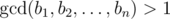
.
Mike wants to change his sequence in order to make it beautiful. In one move he can choose an index i (1 ≤ i < n),
delete numbers ai, ai + 1 and
put numbers ai - ai + 1, ai + ai + 1 in
their place instead, in this order. He wants perform as few operations as possible. Find the minimal number of operations to make sequence A beautiful
if it's possible, or tell him that it is impossible to do so.
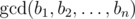
is
the biggest non-negative number d such that d divides bi for
every i (1 ≤ i ≤ n).
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000)
— length of sequence A.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109)
— elements of sequence A.
Output
Output on the first line "YES" (without quotes) if it is possible to make sequence A beautiful
by performing operations described above, and "NO" (without quotes) otherwise.
If the answer was "YES", output the minimal number of moves needed to make sequence A beautiful.
Examples
input
output
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first example you can simply make one move to obtain sequence [0, 2] with
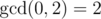
.
In the second example the gcd of the sequence is already greater than 1.
刚拿到这道题目简直就是全程懵逼,像这种一眼看上去就是数论的题我是无能为力。但这道题考的却不是艰难的数论知识,而是一种分析问题的能力,就像昨晚学长说的,我们不能只做水题,而是多做那种可以锻炼我们分析能力的题目,这是我们做题的目的。
我们可以发现,对a[i]和a[i+1]执行两遍之后,会变成-2*a[i+1],2*a[i],我们会发现,这两个都变成了偶数,而两个偶数的最大公约数是大于等于2的,符合题目要求。那么我们是不是让所有a[i]变成偶数不就可以了,但这只是我们根据自己的分析瞎想的解题方法。那我们就来验证一下这是不是最优解。因为a[i]和a[i+1]两个变成偶数只需要两步即可,那么要想有更好的方法就必须一步!就这个题目来说,很显然,不可能的。所以,这是最优的方案。代码自然就敲出来了。
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
Mike has a sequence A = [a1, a2, ..., an] of
length n. He considers the sequence B = [b1, b2, ..., bn] beautiful
if the gcd of all its elements is bigger than 1,
i.e.
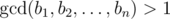
.
Mike wants to change his sequence in order to make it beautiful. In one move he can choose an index i (1 ≤ i < n),
delete numbers ai, ai + 1 and
put numbers ai - ai + 1, ai + ai + 1 in
their place instead, in this order. He wants perform as few operations as possible. Find the minimal number of operations to make sequence A beautiful
if it's possible, or tell him that it is impossible to do so.
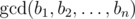
is
the biggest non-negative number d such that d divides bi for
every i (1 ≤ i ≤ n).
Input
The first line contains a single integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000)
— length of sequence A.
The second line contains n space-separated integers a1, a2, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109)
— elements of sequence A.
Output
Output on the first line "YES" (without quotes) if it is possible to make sequence A beautiful
by performing operations described above, and "NO" (without quotes) otherwise.
If the answer was "YES", output the minimal number of moves needed to make sequence A beautiful.
Examples
input
2 1 1
output
YES 1
input
3 6 2 4
output
YES 0
input
2 1 3
output
YES 1
Note
In the first example you can simply make one move to obtain sequence [0, 2] with
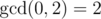
.
In the second example the gcd of the sequence is already greater than 1.
刚拿到这道题目简直就是全程懵逼,像这种一眼看上去就是数论的题我是无能为力。但这道题考的却不是艰难的数论知识,而是一种分析问题的能力,就像昨晚学长说的,我们不能只做水题,而是多做那种可以锻炼我们分析能力的题目,这是我们做题的目的。
我们可以发现,对a[i]和a[i+1]执行两遍之后,会变成-2*a[i+1],2*a[i],我们会发现,这两个都变成了偶数,而两个偶数的最大公约数是大于等于2的,符合题目要求。那么我们是不是让所有a[i]变成偶数不就可以了,但这只是我们根据自己的分析瞎想的解题方法。那我们就来验证一下这是不是最优解。因为a[i]和a[i+1]两个变成偶数只需要两步即可,那么要想有更好的方法就必须一步!就这个题目来说,很显然,不可能的。所以,这是最优的方案。代码自然就敲出来了。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int n;
int re[100005];
int gcd(int x,int y)
{
int a,b,c;
a=abs(x);
b=abs(y);
while(b)
{
c=a%b;
a=b;
b=c;
}
return a;
}
void solve(int x,int y)
{
int temp1=re[x]-re[y];
int temp2=re[x]+re[y];
re[x]=temp1;
re[y]=temp2;
}
int main()
{
cin>>n;
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>re[i];
int gcdcommen=gcd(re[1],re[2]);
for(i=3;i<=n;i++)
{
gcdcommen=gcd(gcdcommen,re[i]);
}
cout<<"YES"<<endl;
if(gcdcommen>1)
{
cout<<0<<endl;
return 0;
}
int step=0;
for(i=1;i<n;i++)
{
while(re[i]%2 != 0)
{
solve(i,i+1);
step++;
}
}
if(re
%2 != 0)
{
while(re
%2 != 0)
{
solve(n-1,n);
step++;
}
}
cout<<step<<endl;
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- php绝对路径与相对路径之间关系的的分析
- Nginx源码分析-4个重要结构之间的关系
- 需求分析、架构分析、领域分析和系统分析之间的关系和概念?
- Android Contact分析(一):Data, RawContact, Contact之间的关系
- Android Contact分析(一):Data, RawContact, Contact之间的关系
- Spring例子JPetStore分析---------3jpetstore的各层之间的关系部分分析
- 《火球——UML大战需求分析》(第3章 分析业务模型-类图)——3.3 类之间的关系
- Java中引用之间的关系及内存分析
- Android4.0.1 Activity的DecorView与SurfaceFlinger的Surface之间关系的建立过程分析
- live555 类之间的依属关系和功能分析
- 在做系统分析时,用到的几种对象之间的关系
- 项目过程之间的关系分析
- 纯技术分析阿里云OS和Android之间的关系(转)
- Nginx源码分析-4个重要结构之间的关系
- 应用程序调用dll组件,及dll组件之间的关系,dll中类及函数的导入导出;dll的导出方式和链接方式分析(一)
- java基础代码实例 求1-100之间的奇数和偶数
- Android Contact分析(一):Data, RawContact, Contact之间的关系
