head first python 第二章代码
2017-02-17 22:13
369 查看
第二章代码
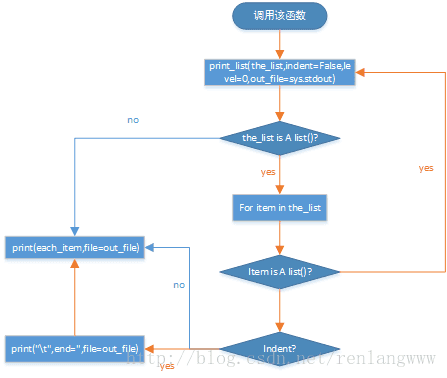
print_list(the_list,indent=False,level=0,out_file=sys.stdout)
这是一个递归方法,用为输出the_list 中的数据
the_list 输入要打印的数据类型,可以为任意
indent=False 是否打印缩进
level 打印缩进的级别,如the_list元素的缩进为0,the_list的自己元素中的list的元素缩进就为+1 就为1;如此递加
out_file=sys.stdout默认值为stdout,即输出在console窗口中。
流程图如下:
-
range 是一个类。
range(10)返回的是0..<10的一个range实例,可以用for in遍历。
range(0,10,2)返回0..10并且以2为增量的一个range实例。
其中有两个函数
第一个函数统计某一个值在range中出现的次数,不在时返回0,有是返回数字。既然是range为什么会出现两次…有什么意义?
第二个函数返回value对应的索引位值,如果value不在range会抛出 ValueError异常,x is not in range
end=”可以输出将多个值输出在一行
sys.stdout默认输出在console中
print_list(the_list,indent=False,level=0,out_file=sys.stdout)
这是一个递归方法,用为输出the_list 中的数据
the_list 输入要打印的数据类型,可以为任意
indent=False 是否打印缩进
level 打印缩进的级别,如the_list元素的缩进为0,the_list的自己元素中的list的元素缩进就为+1 就为1;如此递加
out_file=sys.stdout默认值为stdout,即输出在console窗口中。
流程图如下:

import sys
def print_list(the_list,indent=False,level=0,out_file=sys.stdout):
if(isinstance(the_list,list)):
#isinstance 运行时识别,判断变量“the_list”是否为一个list类型。
for each_item in the_list:
#this funciton takes one positional argument called "the list",which is any Python list()
if(isinstance(each_item,list)):
print_list(each_item,indent,level+1,out_file)
#判断each_item是否为list,如果是进行递归调用,并在‘t’后加+1
else:
if(indent):
for tab_stop in range(level):
print("\t",end='',file=out_file)
print(each_item,file=out_file)
else:
if(indent):
for tab_stop in range(level):
print("\t",end='',file=out_file)
print(the_list,file=out_file)-
一 isinstance()
>>> help(isinstance) Help on built-in function isinstance in module builtins: isinstance(obj, class_or_tuple, /) Return whether an object is an instance of a class or of a subclass thereof. A tuple, as in ``isinstance(x, (A, B, ...))``, may be given as the target to check against. This is equivalent to ``isinstance(x, A) or isinstance(x, B) or ...`` etc.
二 range()
class range(object) | range(stop) -> range object | range(start, stop[, step]) -> range object | | Return an object that produces a sequence of integers from start (inclusive) | to stop (exclusive) by step. range(i, j) produces i, i+1, i+2, ..., j-1. | start defaults to 0, and stop is omitted! range(4) produces 0, 1, 2, 3. | These are exactly the valid indices for a list of 4 elements. | When step is given, it specifies the increment (or decrement). | start | | step | | stop
range 是一个类。
range(10)返回的是0..<10的一个range实例,可以用for in遍历。
range(0,10,2)返回0..10并且以2为增量的一个range实例。
其中有两个函数
| count(...) | rangeobject.count(value) -> integer -- return number of occurrences of value | | index(...) | rangeobject.index(value, [start, [stop]]) -> integer -- return index of value. | Raise ValueError if the value is not present.
第一个函数统计某一个值在range中出现的次数,不在时返回0,有是返回数字。既然是range为什么会出现两次…有什么意义?
第二个函数返回value对应的索引位值,如果value不在range会抛出 ValueError异常,x is not in range
>>> item = range(2,10,2) >>> index=item.index(9) Traceback (most recent call last): File "<pyshell#25>", line 1, in <module> index=item.index(9) ValueError: 9 is not in range >>> index=item.index(8) >>> >>> print(index) 3
三 print
print(...) print(value, ..., sep=' ', end='\n', file=sys.stdout, flush=False) Prints the values to a stream, or to sys.stdout by default. Optional keyword arguments: file: a file-like object (stream); defaults to the current sys.stdout. sep: string inserted between values, default a space. end: string appended after the last value, default a newline. flush: whether to forcibly flush the stream.
end=”可以输出将多个值输出在一行
sys.stdout默认输出在console中
相关文章推荐
- Python初入门(二) 可共享的函数模板(Head First Python 第二章 共享你的代码)
- Head_first_python 第二章共享你的代码 函数模块
- Head First Python---------(一)第一章(初识Python__人人都爱列表)、第二章(共享你的代码__函数模块)、第三章(文件与异常__处理错误)
- head.First.python:注册pypi、上传代码、更新代码
- 笔记:HeadFirstPython(2)共享你的代码
- 《head first python》— 函数定义、模块与发布、共享代码
- 【head first python】2.共享你的代码 函数模块
- Head First Python Notes Chapter II 第二章
- 《HeadFirst Python》第二章学习笔记
- [Head First Python]6. 定制数据对象:打包代码与数据
- Head First Python(如何向PYPI发布你的代码)学习笔记
- HeadFirstPython---------(四)第六章(定制数据对象__打包代码与数据)
- Head First Python代码实践(第六章)有注释
- 《HeadFirst Python》第二章学习笔记
- Head First Python 第二章 函数模块&第三章 文件与异常&第四章 持久存储&第五章 处理数据
- Head First Python(分享你的代码)
- 《Head First Python》笔记 第二章
- Python初入门(六)(Head First Python 第六章 打包代码与数据 ,字典,类与继承)
- Head First C# 中文版 图文皆译 第二章 page67
- Head First C# 中文版 图文皆译 第二章 page73
