第三章 LinkedList源码解析
2016-12-29 00:00
381 查看
一、对于LinkedList需要掌握的八点内容
LinkedList的创建:即构造器
往LinkedList中添加对象:即add(E)方法
获取LinkedList中的单个对象:即get(int index)方法
修改LinkedList中的指定索引的节点的数据set(int index, E element)
删除LinkedList中的对象:即remove(E),remove(int index)方法
遍历LinkedList中的对象:即iterator,在实际中更常用的是增强型的for循环去做遍历
判断对象是否存在于LinkedList中:contain(E)
LinkedList中对象的排序:主要取决于所采取的排序算法(以后讲)
二、源码分析
2.1、[b]LinkedList的创建[/b]
实现方式:
源代码:在读源代码之前,首先要知道什么是环形双向链表,参考《算法导论(第二版)》P207
Entry是LinkedList的一个内部类:
执行完上述的无参构造器后:形成的空环形双向链表如下:
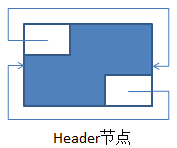
其中,左上角为previous,右下角为next
2.2、往LinkedList中添加对象(add(E e))
实现方式:
源代码:
在添加一个元素后的新环形双向链表如下:
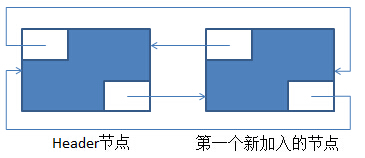
在上述的基础上,再调用一次add(E)后,新的环形双向链表如下:
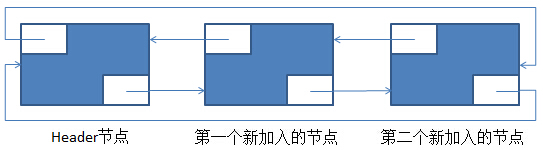
这里,结合着代码注释与图片去看add(E)的源代码就好。
注意:在添加元素方面LinkedList不需要考虑数组扩容和数组复制,只需要新建一个对象,但是需要修改前后两个对象的属性。
[b][b]2.3、获取LinkedList中的单个对象(get(int index))[/b][/b]
实现方式:
源代码:
注意:
链表节点的按索引查找,需要遍历链表;而数组不需要。
header节点既是头节点也是尾节点
双向链表的查找,先去判断索引值index是否小于size/2,若小于,从header节点开始,从前往后找;若大于等于,从header节点开始,从后往前找
size>>1,右移一位等于除以2;左移一位等于乘以2
2.4、修改[b][b][b]LinkedList中[/b][/b]指定索引的节点的数据:set(int index, E element)[/b]
使用方式:
源代码:
注意:entry(int index)查看上边
2.5、删除[b][b][b]LinkedList[/b][/b]中的对象[/b]
2.5.1、remove(Object o)
使用方式:
源代码:
注意:
header节点不可删除
2.5.2、remove(int index)
使用方式:
源代码:
注意:
remove(entry(index))见上边
remove(Object o)需要遍历链表,remove(int index)也需要
2.6、判断对象是否存在于LinkedList中([b]contains(E))[/b]
源代码:
注意:
indexOf(Object o)返回第一个出现的元素o的索引
2.7、遍历[b]LinkedList中的对象(iterator())[/b]
使用方式:
源代码:iterator()方法是在父类AbstractSequentialList中实现的,
listIterator()方法是在父类AbstractList中实现的,
listIterator(int index)方法是在父类AbstractList中实现的,
该方法返回AbstractList的一个内部类ListItr对象
ListItr:
上边这个类并不完整,它继承了内部类Itr,还扩展了一些其他方法(eg.向前查找方法hasPrevious()等),至于hasNext()/next()等方法还是来自于Itr的。
Itr:
注:
上述的Itr我去掉了一个此时用不到的方法和属性。
这里的get(int index)方法参照2.3所示。
三、总结
LinkedList基于环形双向链表方式实现,无容量的限制
添加元素时不用扩容(直接创建新节点,调整插入节点的前后节点的指针属性的指向即可)
线程不安全
get(int index):需要遍历链表
remove(Object o)需要遍历链表
remove(int index)需要遍历链表
contains(E)需要遍历链表
LinkedList的创建:即构造器
往LinkedList中添加对象:即add(E)方法
获取LinkedList中的单个对象:即get(int index)方法
修改LinkedList中的指定索引的节点的数据set(int index, E element)
删除LinkedList中的对象:即remove(E),remove(int index)方法
遍历LinkedList中的对象:即iterator,在实际中更常用的是增强型的for循环去做遍历
判断对象是否存在于LinkedList中:contain(E)
LinkedList中对象的排序:主要取决于所采取的排序算法(以后讲)
二、源码分析
2.1、[b]LinkedList的创建[/b]
实现方式:
List<String> strList0 = new LinkedList<String>();
源代码:在读源代码之前,首先要知道什么是环形双向链表,参考《算法导论(第二版)》P207
private transient Entry<E> header = new Entry<E>(null, null, null);//底层是双向链表,这时先初始化一个空的header节点
private transient int size = 0;//链表中的所存储的元素个数
/** * 构造环形双向链表 */
public LinkedList() { header.next = header.previous = header;//形成环形双向链表
}Entry是LinkedList的一个内部类:
/** * 链表节点 */
private static class Entry<E> { E element; //链表节点所存储的数据
Entry<E> next; //当前链表节点的下一节点
Entry<E> previous; //当前链表节点的前一个节点
Entry(E element, Entry<E> next, Entry<E> previous) { this.element = element; this.next = next; this.previous = previous; } }执行完上述的无参构造器后:形成的空环形双向链表如下:

其中,左上角为previous,右下角为next
2.2、往LinkedList中添加对象(add(E e))
实现方式:
strList0.add("hello");源代码:
/** * 在链表尾部增加新节点,新节点封装的数据为e */
public boolean add(E e) { addBefore(e, header);//在链表尾部增加新节点,新节点封装的数据为e
return true; }/* * 在链表指定节点entry后增加新节点,新节点封装的数据为e */
private Entry<E> addBefore(E e, Entry<E> entry) { Entry<E> newEntry = new Entry<E>(e, entry, entry.previous); newEntry.previous.next = newEntry;//新节点的前一个节点的下一节点为该新节点
newEntry.next.previous = newEntry;//新节点的下一个节点的前一节点为该新节点
size++; //链表中元素个数+1
modCount++; //与ArrayList相同,用于在遍历时查看是否发生了add和remove操作
return newEntry; }在添加一个元素后的新环形双向链表如下:

在上述的基础上,再调用一次add(E)后,新的环形双向链表如下:

这里,结合着代码注释与图片去看add(E)的源代码就好。
注意:在添加元素方面LinkedList不需要考虑数组扩容和数组复制,只需要新建一个对象,但是需要修改前后两个对象的属性。
[b][b]2.3、获取LinkedList中的单个对象(get(int index))[/b][/b]
实现方式:
strList.get(0);//注意:下标从0开始
源代码:
/** * 返回索引值为index节点的数据,index从0开始计算 */
public E get(int index) { return entry(index).element; }/** * 获取指定index索引位置的节点(需要遍历链表) */
private Entry<E> entry(int index) { //index:0~size-1
if (index < 0 || index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index:"+index+", Size:"+size); Entry<E> e = header;//头节点:既作为头节点也作为尾节点
if (index < (size >> 1)) {//index<size/2,则说明index在前半个链表中,从前往后找
for (int i = 0; i <= index; i++) e = e.next; } else {//index>=size/2,则说明index在后半个链表中,从后往前找
for (int i = size; i > index; i--) e = e.previous; } return e; }注意:
链表节点的按索引查找,需要遍历链表;而数组不需要。
header节点既是头节点也是尾节点
双向链表的查找,先去判断索引值index是否小于size/2,若小于,从header节点开始,从前往后找;若大于等于,从header节点开始,从后往前找
size>>1,右移一位等于除以2;左移一位等于乘以2
2.4、修改[b][b][b]LinkedList中[/b][/b]指定索引的节点的数据:set(int index, E element)[/b]
使用方式:
strList.set(0, "world");
源代码:
/** * 修改指定索引位置index上的节点的数据为element */
public E set(int index, E element) { Entry<E> e = entry(index);//查找index位置的节点
E oldVal = e.element;//获取该节点的旧值
e.element = element;//将新值赋给该节点的element属性
return oldVal;//返回旧值
}注意:entry(int index)查看上边
2.5、删除[b][b][b]LinkedList[/b][/b]中的对象[/b]
2.5.1、remove(Object o)
使用方式:
strList.remove("world")源代码:
/** * 删除第一个出现的指定元数据为o的节点 */
public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) {//从前往后删除第一个null //遍历链表
for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { if (e.element == null) { remove(e); return true; } } } else { for (Entry<E> e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { if (o.equals(e.element)) { remove(e); return true; } } } return false; }/* * 删除节点e */
private E remove(Entry<E> e) { //header节点不可删除
if (e == header) throw new NoSuchElementException(); E result = e.element; //调整要删除节点的前后节点的指针指向
e.previous.next = e.next; e.next.previous = e.previous; //将要删除元素的三个属性置空
e.next = e.previous = null; e.element = null; size--;//size-1
modCount++; return result; }注意:
header节点不可删除
2.5.2、remove(int index)
使用方式:
strList.remove(0);
源代码:
/** * 删除指定索引的节点 */
public E remove(int index) { return remove(entry(index)); }注意:
remove(entry(index))见上边
remove(Object o)需要遍历链表,remove(int index)也需要
2.6、判断对象是否存在于LinkedList中([b]contains(E))[/b]
源代码:
/** * 链表中是否包含指定数据o的节点 */
public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) != -1; }/** * 从header开始,查找第一个出现o的索引 */
public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) {//从header开始,查找第一个出现null的索引
for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { if (e.element == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Entry e = header.next; e != header; e = e.next) { if (o.equals(e.element)) return index; index++; } } return -1; }注意:
indexOf(Object o)返回第一个出现的元素o的索引
2.7、遍历[b]LinkedList中的对象(iterator())[/b]
使用方式:
List<String> strList = new LinkedList<String>(); strList.add("jigang"); strList.add("nana"); strList.add("nana2"); Iterator<String> it = strList.iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); }源代码:iterator()方法是在父类AbstractSequentialList中实现的,
public Iterator<E> iterator() { return listIterator(); }listIterator()方法是在父类AbstractList中实现的,
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() { return listIterator(0); }listIterator(int index)方法是在父类AbstractList中实现的,
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) { if (index < 0 || index > size()) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("Index: " + index); return new ListItr(index); }该方法返回AbstractList的一个内部类ListItr对象
ListItr:
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> { ListItr(int index) { cursor = index; }上边这个类并不完整,它继承了内部类Itr,还扩展了一些其他方法(eg.向前查找方法hasPrevious()等),至于hasNext()/next()等方法还是来自于Itr的。
Itr:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> { int cursor = 0;//标记位:标记遍历到哪一个元素 int expectedModCount = modCount;//标记位:用于判断是否在遍历的过程中,是否发生了add、remove操作 //检测对象数组是否还有元素 public boolean hasNext() { return cursor != size();//如果cursor==size,说明已经遍历完了,上一次遍历的是最后一个元素 } //获取元素 public E next() { checkForComodification();//检测在遍历的过程中,是否发生了add、remove操作 try { E next = get(cursor++); return next; } catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {//捕获get(cursor++)方法的IndexOutOfBoundsException checkForComodification(); throw new NoSuchElementException(); } } //检测在遍历的过程中,是否发生了add、remove等操作 final void checkForComodification() { if (modCount != expectedModCount)//发生了add、remove操作,这个我们可以查看add等的源代码,发现会出现modCount++ throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } }注:
上述的Itr我去掉了一个此时用不到的方法和属性。
这里的get(int index)方法参照2.3所示。
三、总结
LinkedList基于环形双向链表方式实现,无容量的限制
添加元素时不用扩容(直接创建新节点,调整插入节点的前后节点的指针属性的指向即可)
线程不安全
get(int index):需要遍历链表
remove(Object o)需要遍历链表
remove(int index)需要遍历链表
contains(E)需要遍历链表
相关文章推荐
- 第三章 LinkedList源码解析
- 第三章 3.4.1节练习
- [kernel 启动流程] (第三章)第一阶段之——proc info的获取
- 《VC++深入详解》第三章
- 《数学之美》第三章 统计语言模型
- 第三章—使用变量
- 数学一本通第三章总结
- 数据结构 第三章 栈和队列
- [置顶] 信息学奥赛一本通(C++版) 第三部分 数据结构 第三章 树
- 第三章 栈和队列 思维导图
- 第三章 RDD编程
- 编程珠玑第三章习题答案
- 用python学概率与统计(第三章)描述性统计:数值方法
- 第三章的知识点总结导图
- 《菜鸟反攻战》第三章 --- 嵌套循环
- 疯狂JAVA讲义第三章练习
- 算法竞赛入门经典第三章3-5 Puzzle UVA - 227
- JUnit in Action 2nd Edition 第三章 精通Junit(2)
- 软件工程复习——第三章
- 《Linux命令行与shell脚本编程大全》 第三章 学习笔记
