LeetCode113:Path Sum II
2016-12-06 09:42
323 查看
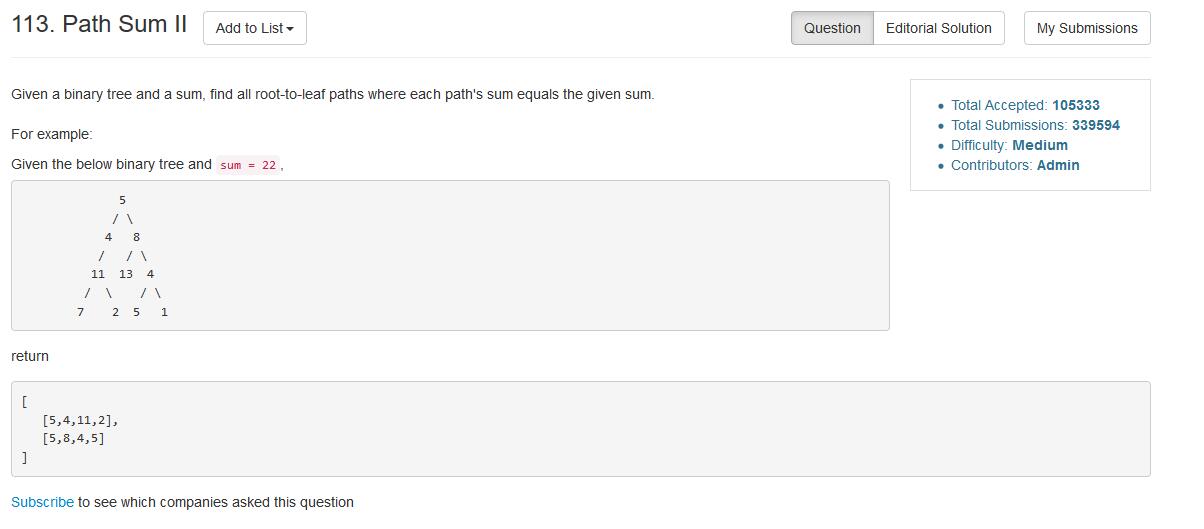
将当前节点加入到临时存储集中,若满足条件则加入到结果集,否则向下搜索左右子树,在搜索完左右子树后还原(回溯法)
1、概念
回溯算法实际上一个类似枚举的搜索尝试过程,主要是在搜索尝试过程中寻找问题的解,当发现已不满足求解条件时,就“回溯”返回,尝试别的路径。
回溯法是一种选优搜索法,按选优条件向前搜索,以达到目标。但当探索到某一步时,发现原先选择并不优或达不到目标,就退回一步重新选择,这种走不通就退回再走的技术为回溯法,而满足回溯条件的某个状态的点称为“回溯点”。
许多复杂的,规模较大的问题都可以使用回溯法,有“通用解题方法”的美称。
2、基本思想
在包含问题的所有解的解空间树中,按照深度优先搜索的策略,从根结点出发深度探索解空间树。当探索到某一结点时,要先判断该结点是否包含问题的解,如果包含,就从该结点出发继续探索下去,如果该结点不包含问题的解,则逐层向其祖先结点回溯。(其实回溯法就是对隐式图的深度优先搜索算法)。
若用回溯法求问题的所有解时,要回溯到根,且根结点的所有可行的子树都要已被搜索遍才结束。
而若使用回溯法求任一个解时,只要搜索到问题的一个解就可以结束。
3、用回溯法解题的一般步骤:
(1)针对所给问题,确定问题的解空间:
首先应明确定义问题的解空间,问题的解空间应至少包含问题的一个(最优)解。
(2)确定结点的扩展搜索规则
(3)以深度优先方式搜索解空间,并在搜索过程中用剪枝函数避免无效搜索。
public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public void robot(TreeNode root, int sum , List<Integer> tmp){
if(root==null) return;
tmp.add(root.val);
sum = sum-root.val;
if(root.left==null && root.right==null){ //叶子为空
if(sum==0){ //满足条件
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
}
}
else{ //叶子不为空
if(root.left!=null)
robot(root.left,sum,tmp);
if(root.right!=null)
robot(root.right,sum,tmp);
}
//回溯
sum-=root.val;
tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root==null) return ans;
//List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
ans.clear();
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
robot(root,sum,tmp);
return ans;
}
}public class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
public void robot(TreeNode root, int sum,int cur){
if(root==null) return;
tmp.add(root.val);
cur+=root.val;
if(root.left==null && root.right==null && sum==cur){ //叶子节点为空 并且满足当前满足条件
ans.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
}
robot(root.left,sum,cur);
robot(root.right,sum,cur);
//回溯
cur-=root.val;
tmp.remove(tmp.size()-1);
}
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
robot(root,sum,0);
return ans;
}
}参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/steven_oyj/archive/2010/05/22/1741376.html
相关文章推荐
- LeetCode113—Path Sum II
- LeetCode 113 Path Sum II
- [LeetCode]题解(python):113-Path Sum II
- leetcode113~Path Sum II
- 【LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现】【113-Path Sum II(路径和)】
- LeetCode题解-113-Path Sum II
- LeetCode 113 Path Sum II (DFS)
- LeetCode_113 Path Sum II
- leetcode[113]Path Sum II
- [leetcode 113] Path Sum II
- LeetCode(113) Path Sum II
- LeetCode 113:Path Sum II
- 【leetcode c++】113 Path Sum II
- Leetcode 113, Path Sum II
- Leetcode-113 Path Sum II
- [LeetCode]113 Path Sum II
- [leetcode-113]Path Sum II(java)
- Java for LeetCode 113 Path Sum II
- Leetcode 113 Path Sum II
- leetcode || 113、Path Sum II
