hdu 2845 Beans简单dp
2016-11-17 22:48
405 查看
Beans
[b]Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 4509 Accepted Submission(s): 2124
[/b]
[align=left]Problem Description[/align]
Bean-eating is an interesting game, everyone owns an M*N matrix, which is filled with different qualities beans. Meantime, there is only one bean in any 1*1 grid. Now you want to eat the beans and collect the qualities, but everyone
must obey by the following rules: if you eat the bean at the coordinate(x, y), you can’t eat the beans anyway at the coordinates listed (if exiting): (x, y-1), (x, y+1), and the both rows whose abscissas are x-1 and x+1.
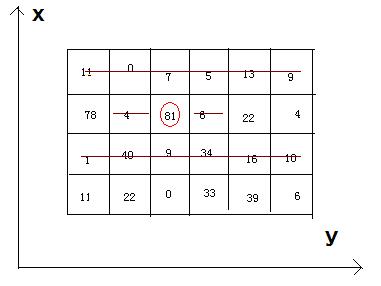
Now, how much qualities can you eat and then get ?
[align=left]Input[/align]
There are a few cases. In each case, there are two integer M (row number) and N (column number). The next M lines each contain N integers, representing the qualities of the beans. We can make sure that the quality of bean isn't beyond
1000, and 1<=M*N<=200000.
[align=left]Output[/align]
For each case, you just output the MAX qualities you can eat and then get.
[align=left]Sample Input[/align]
4 6
11 0 7 5 13 9
78 4 81 6 22 4
1 40 9 34 16 10
11 22 0 33 39 6
[align=left]Sample Output[/align]
242
题意:求最大qualities,选一个数后,不能再选这个数的左右相邻的数,也不能选与这个数相邻行的数。
这样就很简单了。
1.如果是开二维:dp[i][j]=max(dp[i-2][m],dp[i][j-2]);
2.如果是开一维:dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+a[i]),得出每一行最右边的最优情况,再以最右边列跑一遍dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+a[i]),即可得出结果了。
然而我的二维是T,不知为何(可能STL占据较大的时间),吃T代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#define eps 1e-8
#define zero(x) (((x>0?(x):-(x))-eps)
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define memmax(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a))
#define pfn printf("\n")
#define ll __int64
#define ull unsigned long long
#define sf(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define sf64(a) scanf("%I64d",&a)
#define sf264(a,b) scanf("%I64d%I64d",&a,&b)
#define sf364(a,b,c) scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&a,&b,&c)
#define sf2(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)
#define sf3(a,b,c) scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define sf4(a,b,c,d) scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d)
#define sff(a) scanf("%f",&a)
#define sfs(a) scanf("%s",a)
#define sfs2(a,b) scanf("%s%s",a,b)
#define sfs3(a,b,c) scanf("%s%s%s",a,b,c)
#define sfd(a) scanf("%lf",&a)
#define sfd2(a,b) scanf("%lf%lf",&a,&b)
#define sfd3(a,b,c) scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c)
#define sfd4(a,b,c,d) scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c,&d)
#define sfc(a) scanf("%c",&a)
#define ull unsigned long long
#define pp pair<int,int>
#define debug printf("***\n")
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double e = exp(1.0);
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;;
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; }
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) { return a < b ? a : b; }
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) { return a > b ? a : b; }
bool cmpbig(int a, int b){ return a>b; }
bool cmpsmall(int a, int b){ return a<b; }
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
int n,m;
while(~sf2(n,m))
{
map<int,map<int,int> >dp;
map<int,map<int,int> >a;
dp.clear();a.clear();
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
sf(a[i][j]);
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
dp[i][j]=max(a[i][j]+dp[i][j-2],max(a[i][j]+dp[i-2][m-1],a[i][j]+dp[i-2][m]));
}
int num=0;
num=max(max(dp[n-1][m-1],dp[n-1][m]),max(dp
[m-1],dp
[m]));
printf("%d\n",num);
}
return 0;
}AC代码:
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#define eps 1e-8
#define zero(x) (((x>0?(x):-(x))-eps)
#define mem(a,b) memset(a,b,sizeof(a))
#define memmax(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a))
#define pfn printf("\n")
#define ll __int64
#define ull unsigned long long
#define sf(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define sf64(a) scanf("%I64d",&a)
#define sf264(a,b) scanf("%I64d%I64d",&a,&b)
#define sf364(a,b,c) scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&a,&b,&c)
#define sf2(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)
#define sf3(a,b,c) scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define sf4(a,b,c,d) scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c,&d)
#define sff(a) scanf("%f",&a)
#define sfs(a) scanf("%s",a)
#define sfs2(a,b) scanf("%s%s",a,b)
#define sfs3(a,b,c) scanf("%s%s%s",a,b,c)
#define sfd(a) scanf("%lf",&a)
#define sfd2(a,b) scanf("%lf%lf",&a,&b)
#define sfd3(a,b,c) scanf("%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c)
#define sfd4(a,b,c,d) scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&a,&b,&c,&d)
#define sfc(a) scanf("%c",&a)
#define ull unsigned long long
#define pp pair<int,int>
#define debug printf("***\n")
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
const double e = exp(1.0);
const int INF = 0x7fffffff;;
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; }
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; }
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) { return a < b ? a : b; }
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) { return a > b ? a : b; }
bool cmpbig(int a, int b){ return a>b; }
bool cmpsmall(int a, int b){ return a<b; }
using namespace std;
#define MAX 200010
int a[MAX];
int dp[MAX];
int main()
{
//freopen("data.in","r",stdin);
int n,m;
while(~sf2(n,m))
{
int i;
mem(a,0);
mem(dp,0);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
//mem(b,0);
for(int j=2;j<=m+1;j++)
{
sf(a[j]);
a[j]=max(a[j-1],a[j-2]+a[j]);
}
dp[i]=a[m+1];
}
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
i>=2?dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+dp[i]):dp[i]=max(dp[i],dp[i-1]);
printf("%d\n",dp
);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- HDU-2845-Beans(简单DP)
- HDU-2845-Beans-简单dp
- hdu 2845 Beans(dp)
- HDU 2845 Beans (DP)
- HDU 2845 Beans(最大不连续子序列和 dp)
- HDU 2845 Beans (DP)
- HDU 2845 Beans (两次线性dp)
- HDU 2845 Beans (DP)
- hdu 2845 Beans--二维DP
- HDU 2845 Beans(DP,最大不连续和)
- HDU 2845 Beans (两次线性dp)
- hdu 2845 Beans(二次DP)
- HDU 2845 Beans(dp+求两次最达不连续子序列和)
- HDU 2845 Beans (DP)
- HDU 2845 Beans(dp)
- HDU 2845 Beans 行列dp
- hdu 2845——Beans——————【dp】
- hdu2845—Beans(dp)
- HDU 2845 Beans(dp)
- hdu 2845 Beans(dp)
