Arduino—舵机控制
2016-10-22 19:53
686 查看
舵机是一种位置伺服的驱动器,主要是由外壳、电路板、无核心马达、齿轮与位置检测器所构成。
工作原理是由接收机或者单片机发出信号给舵机,其内部有一个基准电路,产生周期为20ms,宽度为1.5ms 的基准信号,将获得的直流偏置电压与电位器的电压比较,获得电压差输出。经由电路板上的IC 判断转动方向,再驱动无核心马达开始转动,透过减速齿轮将动力传至摆臂,同时由位置检测器送回信号,判断是否已经到达定位。适用于那些需要角度不断变化并可以保持的控制系统。当电机转速一定时,通过级联减速齿轮带动电位器旋转,使得电压差为0,电机停止转动。一般舵机旋转的角度范围是0 度到180 度。

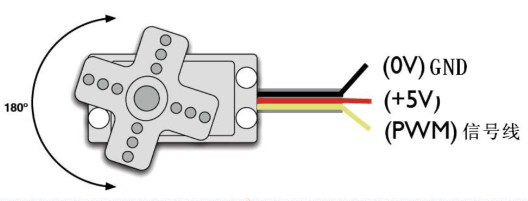
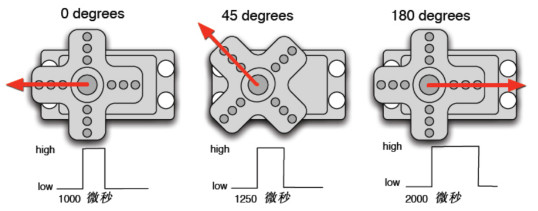
舵机的转动的角度是通过调节PWM(脉冲宽度调制)信号的占空比来实现的,标准PWM(脉冲宽度调制)信号的周期固定为20ms(50Hz),理论上脉宽分布应在1ms到2ms 之间,但是,事实上脉宽可由0.5ms 到2.5ms 之间,脉宽和舵机的转角0°~180°相对应。
有一点值得注意的地方,由于舵机牌子不同,对于同一信号,不同牌子的舵机旋转的角度也会有所不同。
Arduino 控制舵机的方法有两种:
第一种是通过Arduino 的普通数字传感器接口产生占空比不同的方波,模拟产生PWM 信号进行舵机定位,
第二种是直接利用Arduino 自带的Servo 函数进行舵机的控制,这种控制方法的优点在于程序编写,缺点是只能控制2 路舵机,因为Arduino 自带函数只能利用数字9、10 接口。Arduino 的驱动能力有限,所以当需要控制1 个以上的舵机时需要外接电源。
编写程序:
转动舵机到用户输入数字所对应的角度数的位置,并将角度打印显示到屏幕上。
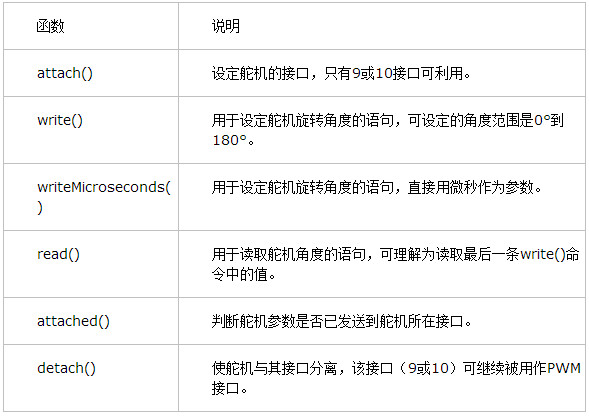
Arduino自带舵机类库文件Servo.h:
servo.cpp源码:
工作原理是由接收机或者单片机发出信号给舵机,其内部有一个基准电路,产生周期为20ms,宽度为1.5ms 的基准信号,将获得的直流偏置电压与电位器的电压比较,获得电压差输出。经由电路板上的IC 判断转动方向,再驱动无核心马达开始转动,透过减速齿轮将动力传至摆臂,同时由位置检测器送回信号,判断是否已经到达定位。适用于那些需要角度不断变化并可以保持的控制系统。当电机转速一定时,通过级联减速齿轮带动电位器旋转,使得电压差为0,电机停止转动。一般舵机旋转的角度范围是0 度到180 度。


舵机的转动的角度是通过调节PWM(脉冲宽度调制)信号的占空比来实现的,标准PWM(脉冲宽度调制)信号的周期固定为20ms(50Hz),理论上脉宽分布应在1ms到2ms 之间,但是,事实上脉宽可由0.5ms 到2.5ms 之间,脉宽和舵机的转角0°~180°相对应。
有一点值得注意的地方,由于舵机牌子不同,对于同一信号,不同牌子的舵机旋转的角度也会有所不同。

Arduino 控制舵机的方法有两种:
第一种是通过Arduino 的普通数字传感器接口产生占空比不同的方波,模拟产生PWM 信号进行舵机定位,
第二种是直接利用Arduino 自带的Servo 函数进行舵机的控制,这种控制方法的优点在于程序编写,缺点是只能控制2 路舵机,因为Arduino 自带函数只能利用数字9、10 接口。Arduino 的驱动能力有限,所以当需要控制1 个以上的舵机时需要外接电源。
编写程序:
转动舵机到用户输入数字所对应的角度数的位置,并将角度打印显示到屏幕上。
int servopin=11;//定义数字接口9 连接伺服舵机信号线
int myangle;//定义角度变量0-180
int pulsewidth;//定义脉宽变量
int val; //0-9
void servopulse(int servopin,int myangle)//定义一个脉冲函数
{
pulsewidth=(myangle*11)+500;//将角度转化为500-2480 的脉宽值
digitalWrite(servopin,HIGH);//将舵机接口电平至高
delayMicroseconds(pulsewidth);//延时脉宽值的微秒数weimiao
digitalWrite(servopin,LOW);//将舵机接口电平至低
delay(20-pulsewidth/1000);
}
void setup()
{
pinMode(servopin,OUTPUT);//设定舵机接口为输出接口
Serial.begin(9600);//连接到串行端口,波特率为9600
Serial.println("servo=o_seral_simple ready" ) ;
}
void loop()//将0 到9 的数转化为0 到180 角度,并让LED 闪烁相应数的次数
{
val=Serial.read();//读取串行端口的值
if(val>'0'&&val<='9')
{
val=val-'0';//将特征量转化为数值变量
val=val*(180/9);//将数字转化为角度
Serial.print("moving servo to ");
//DEC:十进制形式输出 b 的 ASCII 编码值,并同时跟随一个回车和换行符
Serial.print(val,DEC);
Serial.println();
for(int i=0;i<=50;i++) //给予舵机足够的时间让它转到指定角度
{
servopulse(servopin,val);//引用脉冲函数
}
}
}Arduino自带舵机类库文件Servo.h:

#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
// a maximum of eight servo objects can be created
int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position
void setup()
{
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop()
{
for(pos = 0; pos < 180; pos += 1) // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees
{ // in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
for(pos = 180; pos>=1; pos-=1) // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees
{
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach th
4000
e position
}
}servo.cpp源码:
uint8_t Servo::attach(int pin)
{
return this->attach(pin, MIN_PULSE_WIDTH, MAX_PULSE_WIDTH);
}
uint8_t Servo::attach(int pin, int min, int max)
{
if(this->servoIndex < MAX_SERVOS ) {
pinMode( pin, OUTPUT) ; // set servo pin to output
servos[this->servoIndex].Pin.nbr = pin;
// todo min/max check: abs(min - MIN_PULSE_WIDTH) /4 < 128
this->min = (MIN_PULSE_WIDTH - min)/4; //resolution of min/max is 4 uS
this->max = (MAX_PULSE_WIDTH - max)/4;
// initialize the timer if it has not already been initialized
timer16_Sequence_t timer = SERVO_INDEX_TO_TIMER(servoIndex);
if(isTimerActive(timer) == false)
initISR(timer);
servos[this->servoIndex].Pin.isActive = true; // this must be set after the check for isTimerActive
}
return this->servoIndex ;
}
void Servo::detach()
{
servos[this->servoIndex].Pin.isActive = false;
timer16_Sequence_t timer = SERVO_INDEX_TO_TIMER(servoIndex);
if(isTimerActive(timer) == false) {
finISR(timer);
}
}
void Servo::write(int value)
{
if(value < MIN_PULSE_WIDTH)
{ // treat values less than 544 as angles in degrees (valid values in microseconds are handled as microseconds)
if(value < 0) value = 0;
if(value > 180) value = 180;
value = map(value, 0, 180, SERVO_MIN(), SERVO_MAX());
}
this->writeMicroseconds(value);
}
void Servo::writeMicroseconds(int value)
{
// calculate and store the values for the given channel
byte channel = this->servoIndex;
if( (channel < MAX_SERVOS) ) // ensure channel is valid
{
if( value < SERVO_MIN() ) // ensure pulse width is valid
value = SERVO_MIN();
else if( value > SERVO_MAX() )
value = SERVO_MAX();
value = value - TRIM_DURATION;
value = usToTicks(value); // convert to ticks after compensating for interrupt overhead - 12 Aug 2009
uint8_t oldSREG = SREG;
cli();
servos[channel].ticks = value;
SREG = oldSREG;
}
}
int Servo::read() // return the value as degrees
{
return map( this->readMicroseconds()+1, SERVO_MIN(), SERVO_MAX(), 0, 180);
}
int Servo::readMicroseconds()
{
unsigned int pulsewidth;
if( this->servoIndex != INVALID_SERVO )
pulsewidth = ticksToUs(servos[this->servoIndex].ticks) + TRIM_DURATION ; // 12 aug 2009
else
pulsewidth = 0;
return pulsewidth;
}
bool Servo::attached()
{
return servos[this->servoIndex].Pin.isActive ;
}
相关文章推荐
- Arduino控制步进电机和舵机机器臂
- Arduino控制舵机和无刷电机(ESC)
- Arduino教程 模拟输入输出以及电机和舵机控制
- Arduino 摇杆控制 舵机
- 【Arduino入门教程之二】控制舵机转动
- 利用arduino 控制舵机转动
- (升级版)arduino uno + dht11 + 舵机 +w5100网络模块 温度 网络控制舵机
- Arduino对舵机的控制
- Arduino学习之二——舵机控制2
- Arduino舵机控制1
- 15自由度机器人课程日志(四)arduino控制舵机控制器
- Arduino之舵机控制
- arduino uno + 舵机 + dht11 + 杜邦线 + usb + 面包板 测温度 控制舵机运动
- C#串口控制舵机、arduino源码 及C#源码及界面
- Arduino 舵机控制
- 树莓派与arduino结合控制舵机实现灵活监控
- Arduino控制360度旋转舵机
- Arduino系列教程-017 舵机控制
- Arduino通过串口控制舵机角度实验
- 关于Arduino 用Servo库控制舵机出现抖动的问题
