Python 实现决策树 ID3 C4.5 悲观剪枝
2016-10-01 20:34
525 查看
#!/usr/bin/python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import math import random import operator ''' zys 2016-10-01 本程序实现的是C4.5(包含ID3的实现) 参考: http://blog.csdn.net/lulei1217/article/details/49583357 过程: 1、创建决策树 1)通过计算增量熵查找第一个最优特征分类 2)根据分类的特征如(0,1)分别去除掉数据中已经确定的分类数据 3)通过计算新数据增量熵查找下一个最优特征 4)返回导第二步骤,直到符合循环终止条件 条件一:其当前分类特征全部相同 条件二:所有特征都已经分类 2、进行悲观剪枝 3、使用决策树进行测试分类 ''' def createTree(traindata, labels): '''创建决策树''' classList = [item[-1] for item in traindata] ''' 当前特征分类的labels全部相同的时候停止分类,直接返回任意一个label 例如:当badrecord(不良记录) = 1时候,offer全部都为0 这时候直接返回0 ''' if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): return classList[0] if len(traindata[0]) == 1: return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeature = chooseBestFeature(traindata) # 获取最优分类特征 bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeature] tree = {bestFeatLabel: {}} featureList = [example[bestFeature] for example in traindata] uniqueVals = set(featureList) '''' 循环对后续特征分类 去除掉已经选择的特征和数据 ''' del(labels[bestFeature]) for feature in uniqueVals: A = getLablesByfeature(traindata, bestFeature, feature) tree[bestFeatLabel][feature] = createTree(A, labels[:]) return tree def majorityCnt(classList): '''当对最后一个特征进行分类时候,直接返回当前出现最多的labels''' classCount = {} for vote in classList: classCount[vote] = classCount.get(vote, 0) + 1 # key=operator.itemgetter(1) 定义函数key,获取对象的第1个域的值 sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1), reverse=True) return sortedClassCount[0][0] def chooseBestFeature(traindata): ''' 选择最优特征 在ID3中获取信息熵的增益:Gain(S,A) = Entropy(S) - ∑(|A| / |S|) * Entropy(A) 在C4.5中获取的是信息熵的增益率: SplitInfo(A) = - ∑(|A| / |S|) * log2(|A| / |S|) GainRate(S,A) = Gain(S,A) / SplitInfo(A) Entropy(S) 指总集合S的信息信息熵 A 是S中的某个属性的子集 |S| 指集合S的样例数data ''' size = len(traindata[0]) - 1 # 获取特征的数量 Entropy = calculateEntropy(traindata) # 计算总集合的信息熵 Entropy(S) GainRate = 0.0 bestFeature = -1 for i in range(size): ''' 获取当前特征的子集,例如: school 对应着[0,0,0,0,1,1,1,1] ''' featureList = [example[i] for example in traindata] ''' 获取当前特征的分类,例如 school 对应着[0,1] 名校、不是名校 ''' uniqueVals = set(featureList) newEntropy = 0.0 splitInfo = 0.0 for feature in uniqueVals: A = getLablesByfeature(traindata, i, feature) prob = float(len(A)) / len(traindata) # 计算特征子集的信息熵 Entropy(A) newEntropy += prob * calculateEntropy(A) info = 0.0 if(prob != 0): info = math.log(prob, 2) splitInfo -= prob * info newGain = Entropy - newEntropy # 计算信息增益 if (splitInfo == 0): # 修复溢出错误 splitinfo = -0.99 * math.log(0.99, 2) - 0.01 * math.log(0.01, 2) newGain = newGain / splitInfo if (newGain > GainRate): GainRate = newGain bestFeature = i return bestFeature ''' ID3 中的代码: def chooseBestFeature(traindata): size = len(traindata[0]) - 1 Entropy = calculateEntropy(traindata) Gain = 0.0 bestFeature = -1 for i in range(size): uniqueVals = set(featureList) newEntropy = 0.0 for feature in uniqueVals: A = getLablesByfeature(traindata, i, feature) prob = float(len(A)) / len(traindata) newEntropy += prob * calculateEntropy(A) newGain = Entropy - newEntropy if (newGain > Gain): Gain = newGain bestFeature = i return bestFeature ''' def getLablesByfeature(traindata, index, feature): ''' 通过特征来获取对应的Lables,例如: 获取school=0,多对应的Lables [0,0,1,0] ''' A = [] for item in traindata: if item[index] == feature: temp = item[:index] # 抽取除index特征外的所有的记录的内容 temp.extend(item[index + 1:]) A.append(temp) return A def calculateEntropy(data): ''' 计算信息熵 Entropy=-∑P(ui)*log(P(ui)) P(ui)是类别ui出现概率 ''' labelCount = {} for item < 4000 span class="hljs-keyword">in data: lable = item[-1] labelCount[lable] = labelCount.get(lable, 0) + 1 entropy = 0.0 for key in labelCount: p = float(labelCount[key]) / len(data) entropy -= p * math.log(p, 2) return entropy def classify(tree, lables, item): ''' 测试 tree.keys()找出所有的key,在获取对应的key值时候需要将其改变为list类型 ''' root = list(tree.keys())[0] nextNode = tree[root] index = lables.index(root) key = item[index] val = nextNode[key] ''' 判断valueOfFeat是否是dict类型 如果是说明其还有子节 不是则表示没有子节点,返回的值就是其对应的分类 ''' if(isinstance(val, dict)): classLabel = classify(val, lables, item) else: classLabel = val return classLabel def getCount(tree, data, lables, count): root = list(tree.keys())[0] nextNode = tree[root] index = lables.index(root) del(lables[index]) for key in nextNode.keys(): rightcount = 0 wrongcount = 0 A = getLablesByfeature(data, index, key) # 判断是否是叶子节点,不是则迭代进入下一层 if(isinstance(nextNode[key], dict)): getCount(nextNode[key], A, lables[:], count) else: for item in A: # 判断数组给定的分类是否与叶子节点的值相同 if(str(item[-1]) == str(nextNode[key])): rightcount += 1 else: wrongcount += 1 count.append([rightcount, wrongcount]) def cutBranch(tree, data, lables): ''' 悲观剪枝 参考:http://www.jianshu.com/p/794d08199e5e old = errorNum + o.5 * L errorNum:叶子节点错误分类的个数,L:叶子节点个数 p = old / N N:数据样本总个数 new = errorNum + o.5 S = math.sqrt(N * p * (1 - p)) if new <= old - S then 剪枝 注:都是自己理解的,如果有不对的地方欢迎指出 ''' root = list(tree.keys())[0] nextNode = tree[root] index = lables.index(root) newTree = {root: {}} del(lables[index]) for key in nextNode.keys(): # 如果子节点不是叶子节点就判断其是否满足剪枝 if(isinstance(nextNode[key], dict)): A = getLablesByfeature(data, index, key) count = [] # 获取每个叶子节点的(正确分类数,错误分类数) getCount(nextNode[key], A, lables[:], count) allnum = 0 errornum = 0 for i in count: allnum += i[0] + i[1] errornum += i[1] if(errornum == 0): # 当该子树不存在错误分类的时候,不对该树进行剪枝操作 # 进行下个循环 newTree[root][key] = nextNode[key] continue old = errornum + len(count) * 0.5 new = errornum + 0.5 p = old / allnum S = math.sqrt(allnum * p * (1 - p)) if(new <= old - S): # 用当前分类时出现最多的lables代替该子树 classList = [item[-1] for item in A] newTree[root][key] = majorityCnt(classList) else: # 不满足剪枝则进入其子树内部继续进行剪枝操作 newTree[root][key] = cutBranch(nextNode[key], A, lables[:]) else: newTree[root][key] = nextNode[key] return newTree if(__name__ == "__main__"): ''' -----------------------------开始----------------------------- 公司校园招聘 名校 技术能力 不良记录 是否录取 是(1) 厉害(1) 有(1) 录取(1) 否(0) 一般(0) 无(0) 不录取(0) data = [[0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 0, 1], [0, 1, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1, 0]] lables = ["school", "ability", "badrecord", "offer"] ''' # data = [['youth', 'high', 'no', 'fair', 'no'], # ['youth', 'high', 'no', 'excellent', 'no'], # ['middle_aged', 'high', 'no', 'fair', 'yes'], # ['senior', 'medium', 'no', 'fair', 'yes'], # ['senior', 'low', 'yes', 'fair', 'yes'], # ['senior', 'low', 'yes', 'excellent', 'no'], # ['middle_aged', 'low', 'yes', 'excellent', 'yes'], # ['youth', 'medium', 'no', 'fair', 'no'], # ['youth', 'low', 'yes', 'fair', 'yes'], # ['senior', 'medium', 'yes', 'fair', 'yes'], # ['youth', 'medium', 'yes', 'excellent', 'yes'], # ['middle_aged', 'medium', 'no', 'excellent', 'yes'], # ['middle_aged', 'high', 'yes', 'fair', 'yes'], # ['senior', 'medium', 'no', 'excellent', 'no']] # lables = ['age', 'income', 'student', 'credit_rating'] data = [['dark_green', 'curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'distinct', 'sinking', 'hard_smooth', 1], ['black', 'curl_up', 'heavily', 'distinct', 'sinking', 'hard_smooth', 1], ['black', 'curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'distinct', 'sinking', 'hard_smooth', 1], ['dark_green', 'little_curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'distinct', 'little_sinking', 'soft_stick', 1], ['black', 'little_curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'little_blur', 'little_sinking', 'soft_stick', 1], ['dark_green', 'stiff', 'clear', 'distinct', 'even', 'soft_stick', 0], ['light_white', 'little_curl_up', 'heavily', 'little_blur', 'sinking', 'hard_smooth', 0], ['black', 'little_curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'distinct', 'little_sinking', 'soft_stick', 0], ['light_white', 'curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'blur', 'even', 'hard_smooth', 0], ['dark_green', 'curl_up', 'heavily', 'little_blur', 'little_sinking', 'hard_smooth', 0], ['dark_green', 'curl_up', 'heavily', 'distinct', 'sinking', 'hard_smooth', 1], ['light_white', 'curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'distinct', 'sinking', 'hard_smooth', 1], ['black', 'little_curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'distinct', 'little_sinking', 'hard_smooth', 1], ['black', 'little_curl_up', 'heavily', 'little_blur', 'little_sinking', 'hard_smooth', 0], ['light_white', 'stiff', 'clear', 'blur', 'even', 'hard_smooth', 0], ['light_white', 'curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'blur', 'even', 'soft_stick', 0], ['dark_green', 'little_curl_up', 'little_heavily', 'little_blur', 'sinking', 'hard_smooth', 0]] lables = ['color', 'root', 'knocks', 'texture', 'navel', 'touch'] ''' 传入的是data和lables的复制,因为在函数中会改变该值。 而python传参传递的是一个地址,因此会改变原本的数据 ''' decisiontree = createTree(data[:], lables[:]) createPlot(decisiontree) decisiontree = cutBranch(decisiontree, data, lables[:]) k = 0 for item in data: if(classify(decisiontree, lables[:], item) == item[-1]): k += 1 print(float(k) / len(data)) createPlot(decisiontree)
使用matplotlib画出决策树
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ''' 使用matplotlib的annotate画出决策树 参考: http://matplotlib.org/api/pyplot_api.html#matplotlib.pyplot.annotate matplotlib.pyplot.annotate(text,xy,xytext,xycoords,textcoords,arrowprops) text:注解的内容 xy:箭头指向的坐标 xytext:注解内容的坐标,如果没有默认xy xycoords:给定xy一个坐标系统 textcoords:给定xytext一个坐标系统 arrowprops:箭头的格式 ''' decisionNode = dict(boxstyle="round4", color='#3366FF') # 定义判断结点形态 leafNode = dict(boxstyle="circle", color='#FF6633') # 定义叶结点形态 arrow_args = dict(arrowstyle="<-", color='g') # 定义箭头 # 绘制带箭头的注释 def plotNode(nodeTxt, centerPt, parentPt, nodeType): cr c715 eatePlot.ax1.annotate(nodeTxt, xy=parentPt, xycoords='axes fraction', xytext=centerPt, textcoords='axes fraction', va="center", ha="center", bbox=nodeType, arrowprops=arrow_args) # 计算叶结点数 def getNumLeafs(myTree): numLeafs = 0 firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] secondDict = myTree[firstStr] for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': numLeafs += getNumLeafs(secondDict[key]) else: numLeafs += 1 return numLeafs # 计算树的层数 def getTreeDepth(myTree): maxDepth = 0 firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] secondDict = myTree[firstStr] for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': thisDepth = 1 + getTreeDepth(secondDict[key]) else: thisDepth = 1 if thisDepth > maxDepth: maxDepth = thisDepth return maxDepth # 在父子结点间填充文本信息相同 def plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, txtString): xMid = (parentPt[0] - cntrPt[0]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[0] yMid = (parentPt[1] - cntrPt[1]) / 2.0 + cntrPt[1] createPlot.ax1.text(xMid, yMid, txtString, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30) def plotTree(myTree, parentPt, nodeTxt): numLeafs = getNumLeafs(myTree) depth = getTreeDepth(myTree) firstStr = list(myTree.keys())[0] cntrPt = (plotTree.xOff + (1.0 + float(numLeafs)) / 2.0 / plotTree.totalW, plotTree.yOff) plotMidText(cntrPt, parentPt, nodeTxt) # 在父子结点间填充文本信息 plotNode(firstStr, cntrPt, parentPt, decisionNode) # 绘制带箭头的注释 secondDict = myTree[firstStr] plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff - 1.0 / plotTree.totalD for key in secondDict.keys(): if type(secondDict[key]).__name__ == 'dict': plotTree(secondDict[key], cntrPt, str(key)) else: plotTree.xOff = plotTree.xOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalW plotNode(secondDict[key], (plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, leafNode) plotMidText((plotTree.xOff, plotTree.yOff), cntrPt, str(key)) plotTree.yOff = plotTree.yOff + 1.0 / plotTree.totalD def createPlot(inTree): fig = plt.figure(1, facecolor='white') fig.clf() axprops = dict(xticks=[], yticks=[]) createPlot.ax1 = plt.subplot(111, frameon=False, **axprops) plotTree.totalW = float(getNumLeafs(inTree)) plotTree.totalD = float(getTreeDepth(inTree)) plotTree.xOff = -0.5 / plotTree.totalW plotTree.yOff = 1.0 plotTree(inTree, (0.5, 1.0), '') plt.show()
效果图
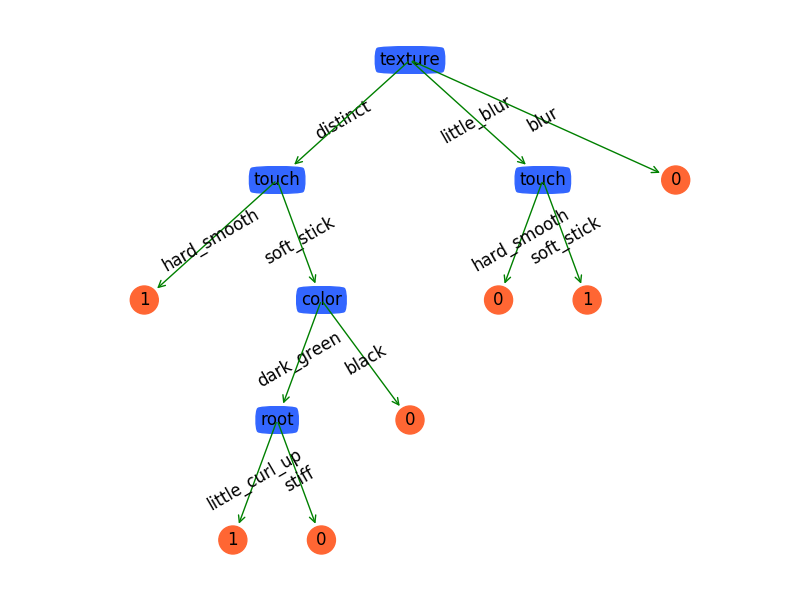
相关文章推荐
- 机器学习算法的Python实现 (3):CART决策树与剪枝处理
- Python实现决策树(ID3、C4.5)
- 决策树 (Decision Tree) 进阶应用 CART剪枝方法及Python实现方式
- 决策树ID3;C4.5详解和python实现与R语言实现比较
- 【Python学习系列十一】Python实现决策树实现C4.5(信息增益率)
- 机器学习算法的Python实现 (3):CART决策树与剪枝处理
- [置顶] 《统计学习方法》 决策树 ID3和C4.5 生成算法 Python实现
- 决策树剪枝简单python实现
- ID3 决策树 Python实现
- 决策树(ID3,C4.5)Python实现
- 用python实现c4.5算法,并进行悲观剪枝
- 【机器学习算法-python实现】决策树-Decision tree(1) 信息熵划分数据集
- 决策树的python实现方法
- Twitter的分布式自增ID算法Snowflake实现分析及其Java、Php和Python版
- 【机器学习算法-python实现】Adaboost的实现(1)-单层决策树(decision stump)
- 决策树的python实现方法
- 【机器学习算法-python实现】决策树-Decision tree(2) 决策树的实现
- 【机器学习】决策树-ID3算法的Python实现
- 【机器学习算法-python实现】决策树-Decision tree(1) 信息熵划分数据集
- 通过python调用adb命令实现用元素名称、id、class定位元素
