php标准库SPL
2016-08-29 23:52
387 查看
简介
SPL是Standard PHP Library(PHP标准库)的缩写。The Standard PHP Library (SPL) is a collection of interfaces and classes that are meant to solve common problems.
官网说,SPL是用来解决典型问题(common problems)的一组接口与类的集合。
那么,什么是common problems呢?
数据结构
解决数据怎么存储问题
元素遍历
数据怎么查看
常用方法的统一调用
数组、集合大小
自定义遍历
类自动加载
spl_autoload_register
包含哪些内容?
- 数据结构
- 基础接口
- 基础函数
- 迭代器
- 异常
- 其它
SPL接口
Iterator迭代器接口
SPL规定,所有实现了Iterator接口的class,都可以用在foreach Loop中。Iterator接口中包含5个必须实现的方法:interface Iterator extends Traversable{
//返回当前元素
public mixed current ( void );
//返回当前元素的键
public scalar key ( void );
//向前移动到下一个元素
public void next ( void );
//返回到迭代器的第一个元素
public void rewind ( void );
//检查当前位置是否有效
public boolean valid ( void );
}class Employee{
private $_name;
function __construct($name){
$this->_name = $name;
}
function getName(){
return $this->_name;
}
}
对该对象做一个迭代器
class Department implements Iterator{
private $_name;
private $_employees;
private $_position = 0;
function __constructi($name){
$this->_name = $name;
$this->_employees = array();
$this->_position = 0;
}
function addEmployee(Employee $e){
$this->_employee = $e;
echo “<p>{$e->getName()} has been added to {$this->_name} department</p>”;
}
function key(){
return $this->_position();
}
function current(){
return $this->_employee[$this->_position];
}
function next(){
$this->_position ++;
}
function rewind(){
$this->_position = 0;
}
function valid(){//判断后面是否还有元素,是否已经到了数组的末尾
return isset(($this->_employee[$this->_position]));
}
}
进行迭代:
$e1 = new Employee(‘em1’); $e2 = new Employee(‘em2’);
$iter = new Department(‘Human’); $iter->addEmployee($e1);$iter->addEmployee($e2);
foreach($iter as $e){
echo "<p>{$e->getName}</p>”;
}拓展 :实现Countable接口的count()方法,可以使用count()得到迭代器里数据项的个数。
class a implements Iterator,Countable{
function count(){
return count($this->_employee);
}
}
echo count($iter);ArrayAccess 数组式访问接口
实现ArrayAccess接口,可以使得object像array那样操作。ArrayAccess接口包含四个必须实现的方法:interface ArrayAccess {
//检查一个偏移位置是否存在
public mixed offsetExists ( mixed $offset );
//获取一个偏移位置的值
public mixed offsetGet( mixed $offset );
//设置一个偏移位置的值
public mixed offsetSet ( mixed $offset );
//复位一个偏移位置的值
public mixed offsetUnset ( mixed $offset );
}示例:
<?php
class obj implements arrayaccess {
private $container = array();
public function __construct() {
1fff8
$this->container = array(
"one" => 1,
"two" => 2,
"three" => 3,
);
}
public function offsetSet($offset, $value) {
if (is_null($offset)) {
$this->container[] = $value;
} else {
$this->container[$offset] = $value;
}
}
public function offsetExists($offset) {
return isset($this->container[$offset]);
}
public function offsetUnset($offset) {
unset($this->container[$offset]);
}
public function offsetGet($offset) {
return isset($this->container[$offset]) ? $this->container[$offset] : null;
}
}
$obj = new obj;
var_dump(isset($obj["two"]));
var_dump($obj["two"]);
unset($obj["two"]);
var_dump(isset($obj["two"]));
$obj["two"] = "A value";
var_dump($obj["two"]);
$obj[] = 'Append 1';
$obj[] = 'Append 2';
$obj[] = 'Append 3';
print_r($obj);
?>
<?php
class ArrayAndObjectAccess implements ArrayAccess {
private $data = [];
public function &__get ($key) {
return $this->data[$key];
}
public function __set($key,$value) {
$this->data[$key] = $value;
}
public function __isset ($key) {
return isset($this->data[$key]);
}
public function __unset($key) {
unset($this->data[$key]);
}
public function offsetSet($offset,$value) {
if (is_null($offset)) {
$this->data[] = $value;
} else {
$this->data[$offset] = $value;
}
}
public function offsetExists($offset) {
return isset($this->data[$offset]);
}
public function offsetUnset($offset) {
if ($this->offsetExists($offset)) {
unset($this->data[$offset]);
}
}
public function offsetGet($offset) {
return $this->offsetExists($offset) ? $this->data[$offset] : null;
}
}
$foo = new ArrayAndObjectAccess();
// Set data as array and object
$foo->fname = 'Yousef';
$foo->lname = 'Ismaeil';
// Call as object
echo 'fname as object '.$foo->fname."\n";
// Call as array
echo 'lname as array '.$foo['lname']."\n";
// Reset as array
$foo['fname'] = 'Cliprz';
echo $foo['fname']."\n";
/** Outputs
fname as object Yousef
lname as array Ismaeil
Cliprz
*/
?>IteratorAggregate 聚合式迭代器接口
假设对象A实现了上面的ArrayAccess接口,这时候虽然可以像数组那样操作,却无法使用foreach遍历,除非实现了前面提到的Iterator接口。另一个解决方法是,有时会需要将数据和遍历部分分开,这时就可以实现IteratorAggregate接口。它规定了一个getIterator()方法,返回一个使用Iterator接口的object。
IteratorAggregate extends Traversable {
/* 获取一个外部迭代器 */
abstract public Traversable getIterator ( void )
}示例:
<?php
class myData implements IteratorAggregate {
public $property1 = "Public property one";
public $property2 = "Public property two";
public $property3 = "Public property three";
public function __construct() {
$this->property4 = "last property";
}
public function getIterator() {
return new ArrayIterator($this);
}
}
$obj = new myData;
foreach($obj as $key => $value) {
var_dump($key, $value);
echo "\n";
}
?>注意:
虽然都继承自Traversable,但这是一个无法在 PHP 脚本中实现的内部引擎接口。我们直接使用IteratorAggregate 或 Iterator 接口来代替它。
RecursiveIterator
这个接口用于遍历多层数据,它继承了Iterator接口,因而也具有标准的current()、key()、next()、 rewind()和valid()方法。同时,它自己还规定了getChildren()和hasChildren()方法。The getChildren() method must return an object that implements RecursiveIterator。接口摘要:
RecursiveIterator extends Iterator {
/* 方法 */
public RecursiveIterator getChildren ( void )
public bool hasChildren ( void )
/* 继承的方法 */
abstract public mixed Iterator::current ( void )
abstract public scalar Iterator::key ( void )
abstract public void Iterator::next ( void )
abstract public void Iterator::rewind ( void )
abstract public boolean Iterator::valid ( void )
}示例:
<?php
class MyRecursiveIterator implements RecursiveIterator
{
private $_data;
private $_position = 0;
public function __construct(array $data) {
$this->_data = $data;
}
public function valid() {
return isset($this->_data[$this->_position]);
}
public function hasChildren() {
return is_array($this->_data[$this->_position]);
}
public function next() {
$this->_position++;
}
public function current() {
return $this->_data[$this->_position];
}
public function getChildren() {
echo '<pre>';
print_r($this->_data[$this->_position]);
echo '</pre>';
}
public function rewind() {
$this->_position = 0;
}
public function key() {
return $this->_position;
}
}
$arr = array(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 => array(10, 20, 30), 6, 7, 8, 9 => array(1, 2, 3));
$mri = new MyRecursiveIterator($arr);
foreach ($mri as $c => $v) {
if ($mri->hasChildren()) {
echo "$c has children: <br />";
$mri->getChildren();
} else {
echo "$v <br />";
}
}
?>
Result:
0
1
2
3
4
5 has children:
Array
(
[0] => 10
[1] => 20
[2] => 30
)
6
7
8
9 has children:
Array
(
[0] => 1
[1] => 2
[2] => 3
)SeekableIterator
SeekableIterator接口也是Iterator接口的延伸,除了Iterator的5个方法以外,还规定了seek()方法,参数是元素的位置,返回该元素。如果该位置不存在,则抛出OutOfBoundsException。接口摘要 :
SeekableIterator extends Iterator {
/* 方法 */
abstract public void seek ( int $position )
/* 继承的方法 */
abstract public mixed Iterator::current ( void )
abstract public scalar Iterator::key ( void )
abstract public void Iterator::next ( void )
abstract public void Iterator::rewind ( void )
abstract public boolean Iterator::valid ( void )
}示例:
<?php
class MySeekableIterator implements SeekableIterator {
private $position;
private $array = array(
"first element",
"second element",
"third element",
"fourth element"
);
/* Method required for SeekableIterator interface */
public function seek($position) {
if (!isset($this->array[$position])) {
throw new OutOfBoundsException("invalid seek position ($position)");
}
$this->position = $position;
}
/* Methods required for Iterator interface */
public function rewind() {
$this->position = 0;
}
public function current() {
return $this->array[$this->position];
}
public function key() {
return $this->position;
}
public function next() {
++$this->position;
}
public function valid() {
return isset($this->array[$this->position]);
}
}
try {
$it = new MySeekableIterator;
echo $it->current(), "\n";
$it->seek(2);
echo $it->current(), "\n";
$it->seek(1);
echo $it->current(), "\n";
$it->seek(10);
} catch (OutOfBoundsException $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
?>
以上例程的输出类似于:
first element
third element
second element
invalid seek position (10)Countable
这个接口规定了一个count()方法,返回结果集的数量。class a implements Iterator,Countable{
function count(){
return count($this->_employee);
}
}
echo count($iter);SPL数据结构
数据结构是计算机存储、组织数据的方式。SPL提供了双向链表、堆栈、队列、堆、降序堆、升序堆、优先级队列、定长数组、对象容器。
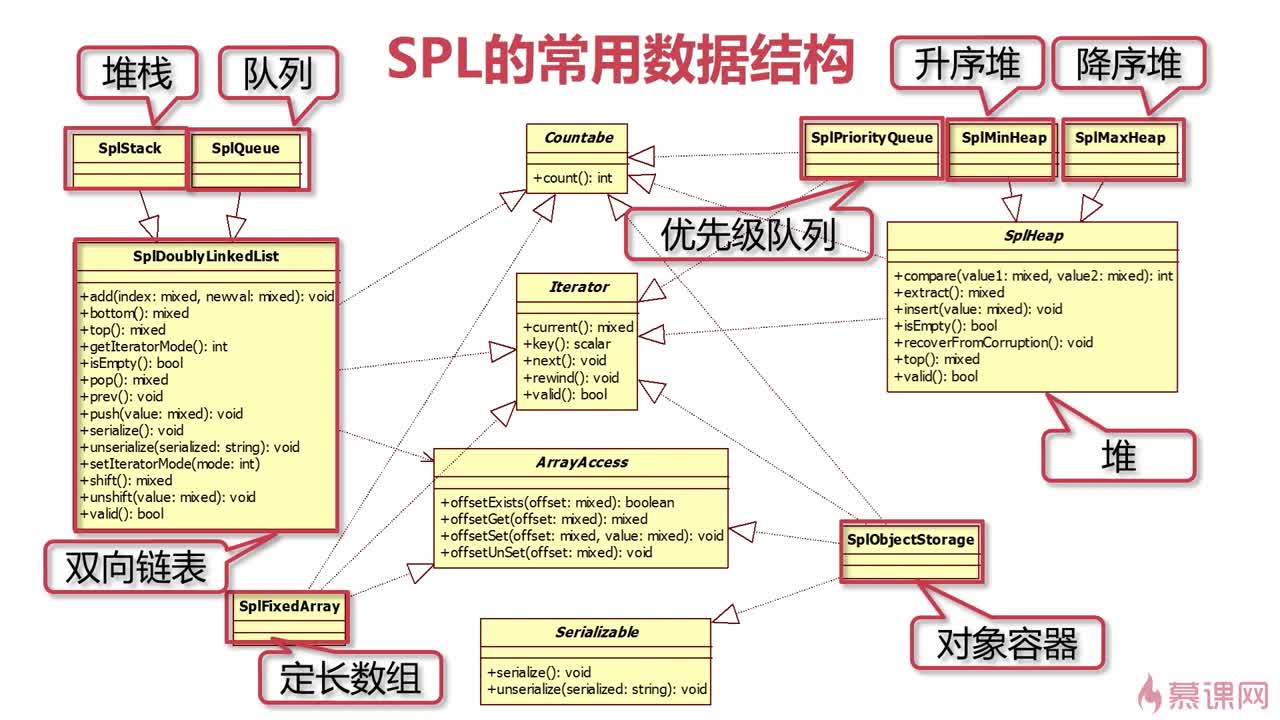
基本概念
Bottom:节点,第一个节点称Bottom;Top:最后添加的链表的节点称Top;
当前节点(Current):链表指针指向的节点称为当前节点;
SplDoublyLinkedList双向链表
SplDoublyLinkedList 实现了Iterator , ArrayAccess , Countable接口。类摘要
SplDoublyLinkedList implements Iterator , ArrayAccess , Countable {
/* 方法 */
public __construct ( void )
public void add ( mixed $index , mixed $newval )
public mixed bottom ( void )
public int count ( void )
public mixed current ( void )
public int getIteratorMode ( void )
public bool isEmpty ( void )
public mixed key ( void )
public void next ( void )
public bool offsetExists ( mixed $index )
public mixed offsetGet ( mixed $index )
public void offsetSet ( mixed $index , mixed $newval )
public void offsetUnset ( mixed $index )
public mixed pop ( void )
public void prev ( void )
public void push ( mixed $value )
public void rewind ( void )
public string serialize ( void )
public void setIteratorMode ( int $mode )
public mixed shift ( void )
public mixed top ( void )
public void unserialize ( string $serialized )
public void unshift ( mixed $value )
public bool valid ( void )
}注意:
SplDoublyLinkedList:: setIteratorMode用来设置迭代遍历的方向和行为。
当前节点操作:
- rewind:将链表的当前指针指向第一个元素
- current:链表当前指针,当节点被删除后,会指向空节点
- prev:上一个
- next:下一个
增加节点操作:
- push 在双向链表的结尾处将元素压入
- unshift 前置双链表元素,预备值在双链表的开始
删除节点操作:
- pop 从双向链表的结尾弹出一个节点,不会改变指针位置
- shift从双向链表的开头弹出一个节点,不会改变指针位置
定位操作:
- bottom 返回当前双向链表的第一个节点的值,当前指针不变
- top返回当前双向链表的最后一个节点的值,当前指针不变
特定节点操作:
- offsetExists 理解为key是否存在
- offsetGet将key节点拿出来
- offsetSet把数据刷新
- offsetUnset删除
There are two orthogonal sets of modes that can be set: 1. The direction of the iteration (either one or the other): SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_LIFO (Stack style) //在遍历元素时,像栈一样,后入先出 SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_FIFO (Queue style) //在遍历时,像队列一样,先入先出 2. The behavior of the iterator (either one or the other): SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_DELETE (Elements are deleted by the iterator) // 该元素被遍历到之后就删除 SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_KEEP (Elements are traversed by the iterator) //// 该元素被遍历到之后不受影响 The default mode is: SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_FIFO | SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_KEEP
FIFO and LIFO in SplDoublyLinkedList
$list = new SplDoublyLinkedList();
$list->push('a');
$list->push('b');
$list->push('c');
$list->push('d');
echo "FIFO (First In First Out) :\n";
$list->setIteratorMode(SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_FIFO);
for ($list->rewind(); $list->valid(); $list->next()) {
echo $list->current()."\n";
}
Result :
// FIFO (First In First Out):
// a
// b
// c
// d
echo "LIFO (Last In First Out) :\n";
$list->setIteratorMode(SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_LIFO);
for ($list->rewind(); $list->valid(); $list->next()) {
echo $list->current()."\n";
}
Result :
// LIFO (Last In First Out):
// d
// c
// b
// a<?php
$doubly=new SplDoublyLinkedList();
$doubly->push(array('name'=>'Naruto'));
$doubly->push(array('name'=>'Sakura'));
$doubly->push(array('name'=>'Neji'));
$doubly->push(array('name'=>'Sasuke'));
var_dump($doubly);
echo '<br/>LIFO Traversing - Keep mode <br/>';
$doubly->setIteratorMode(SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_LIFO | SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_KEEP);
$doubly->rewind();
foreach($doubly as $key=>$value)
{
echo '<br/>Traversed:'.$key.' '.$value['name'];
}
echo '<br/>LIFO Traversing - Delete mode <br/>';
$doubly->setIteratorMode(SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_LIFO | SplDoublyLinkedList::IT_MODE_DELETE);
$doubly->rewind();
foreach($doubly as $key=>$value)
{
if($key == 2) break;
echo '<br/>Traversed:'.$key.' '.$value['name']; //将a[3]删除,然后不再往下遍历
}
var_dump($doubly);
?>
//output
object(SplDoublyLinkedList)#1 (2) {
["flags":"SplDoublyLinkedList":private]=>
int(0)
["dllist":"SplDoublyLinkedList":private]=>
array(4) {
[0]=>
array(1) {
["name"]=>
string(6) "Naruto"
}
[1]=>
array(1) {
["name"]=>
string(6) "Sakura"
}
[2]=>
array(1) {
["name"]=>
string(4) "Neji"
}
[3]=>
array(1) {
["name"]=>
string(6) "Sasuke"
}
}
}
LIFO Traversing - Keep mode :
Traversed:3 Sasuke
Traversed:2 Neji
Traversed:1 Sakura
Traversed:0 Naruto
LIFO Traversing - Delete mode :
Traversed:3 Sasuke
object(SplDoublyLinkedList)#1 (2) {
["flags":"SplDoublyLinkedList":private]=>
int(3)
["dllist":"SplDoublyLinkedList":private]=>
array(3) {
[0]=>
array(1) {
["name"]=>
string(6) "Naruto"
}
[1]=>
array(1) {
["name"]=>
string(6) "Sakura"
}
[2]=>
array(1) {
["name"]=>
string(4) "Neji"
}
}
}示例:SplDoublyLinkedList.php <?php /** *SplDoublyLinkedList 类学习 */ $obj = new SplDoublyLinkedList(); $obj -> push(1);//把新的节点添加到链表的顶部top $obj -> push(2); $obj -> push(3); $obj -> unshift(10);//把新节点添加到链表底部bottom print_r($obj); $obj ->rewind();//rewind操作用于把节点指针指向Bottom所在节点 $obj -> prev();//使指针指向上一个节点,靠近Bottom方向 echo 'next node :'.$obj->current().PHP_EOL; $obj -> next(); $obj -> next(); echo 'next node :'.$obj->current().PHP_EOL; $obj -> next(); if($obj -> current()) echo 'current node valid'.PHP_EOL; else echo 'current node invalid'.PHP_EOL; $obj ->rewind(); //如果当前节点是有效节点,valid返回true if($obj->valid()) echo 'valid list'.PHP_EOL; else echo 'invalid list'.PHP_EOL; print_r($obj); echo 'pop value :'.$obj -> pop().PHP_EOL; print_r($obj); echo 'next node :'.$obj ->current().PHP_EOL; $obj ->next();//1 $obj ->next();//2 $obj -> pop();//把top位置的节点从链表中删除,并返回,如果current正好指>向top位置,那么调用pop之后current()会失效 echo 'next node:'.$obj -> current().PHP_EOL; print_r($obj); $obj ->shift();//把bottom位置的节点从链表中删除,并返回 print_r($obj);
SplStack 栈
栈(Stack)是一种特殊的线性表,因为它只能在线性表的一端进行插入或删除元素(即进栈和出栈)。栈是一种后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构。
SplStack 继承自 双向链表 SplDoublyLinkedList。
示例:
<?php
$stack = new SplStack();
$stack->push(1);
$stack->push(2);
$stack->push(3);
echo 'bottom:'.$stack -> bottom().PHP_EOL;
echo "top:".$stack->top().PHP_EOL;
//堆栈的offset=0,是top所在位置(即栈的末尾)
$stack -> offsetSet(0, 10);
echo "top:".$stack->top().'<br/>';
//堆栈的rewind和双向链表的rewind相反,堆栈的rewind使得当前指针指向top所在位置,而双向链表调用之后指向bottom所在位置
$stack -> rewind();
echo 'current:'.$stack->current().'<br/>';
$stack ->next();//堆栈的next操作使指针指向靠近bottom位置的下一个节点,而双向链表是靠近top的下一个节点
echo 'current:'.$stack ->current().'<br/>';
//遍历堆栈
$stack -> rewind();
while ($stack->valid()) {
echo $stack->key().'=>'.$stack->current().PHP_EOL;
$stack->next();//不从链表中删除元素
}
echo '<br/>';
echo $stack->pop() .'--';
echo $stack->pop() .'--';
echo $stack->pop() .'--';
输出:
bottom:1 top:3 top:10
current:10
current:2
2=>10 1=>2 0=>1
10--2--1--SplQueue 队列
队列是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构。使用队列时插入在一端进行而删除在另一端进行。SplQueue 也是继承自 双向链表 SplDoublyLinkedList,并有自己的方法:
/* 方法 */
__construct ( void )
mixed dequeue ( void )
void enqueue ( mixed $value )
void setIteratorMode ( int $mode )
示例1:
<?php
$queue = new SplQueue();
$queue->enqueue(1);
$queue->enqueue(2);
echo $queue->dequeue() .'--';
echo $queue->dequeue() .'--';
//1--2--
示例2:
<?php
$obj = new SplQueue();
$obj -> enqueue('a');
$obj -> enqueue('b');
$obj -> enqueue('c');
echo 'bottom:'.$obj -> bottom().PHP_EOL;
echo 'top:'.$obj -> top();
echo '<br/>';
//队列里的offset=0是指向bottom位置
$obj -> offsetSet(0,'A');
echo 'bottom:'.$obj -> bottom();
echo '<br/>';
//队列里的rewind使得指针指向bottom所在位置的节点
$obj -> rewind();
echo 'current:'.$obj->current();
echo '<br/>';
while ($obj ->valid()) {
echo $obj ->key().'=>'.$obj->current().PHP_EOL;
$obj->next();//
}
echo '<br/>';
//dequeue操作从队列中提取bottom位置的节点,并返回,同时从队列里面删除该元素
echo 'dequeue obj:'.$obj->dequeue();
echo '<br/>';
echo 'bottom:'.$obj -> bottom().PHP_EOL;
输出:
bottom:a top:c
bottom:A
current:A
0=>A 1=>b 2=>c
dequeue obj:A
bottom:bSplHeap 堆
堆(Heap)就是为了实现优先队列而设计的一种数据结构,它是通过构造二叉堆(二叉树的一种)实现。根节点最大的堆叫做最大堆或大根堆,根节点最小的堆叫做最小堆或小根堆。二叉堆还常用于排序(堆排序)。
SplHeap 是一个抽象类,实现了Iterator , Countable接口。最大堆(SplMaxHeap)和最小堆(SplMinHeap)就是继承它实现的。最大堆和最小堆并没有额外的方法。
如皋要使用SplHeap类,需要实现其抽象方法int compare ( mixed value1,mixedvalue2 )。
类摘要:
abstract SplHeap implements Iterator , Countable {
/* 方法 */
public __construct ( void )
abstract protected int compare ( mixed $value1 , mixed $value2 )
public int count ( void )
public mixed current ( void )
public mixed extract ( void )
public void insert ( mixed $value )
public bool isEmpty ( void )
public mixed key ( void )
public void next ( void )
public void recoverFromCorruption ( void )
public void rewind ( void )
public mixed top ( void )
public bool valid ( void )
}示例:
<?php
class MySimpleHeap extends SplHeap
{
//compare()方法用来比较两个元素的大小,绝对他们在堆中的位置
public function compare( $value1, $value2 ) {
return ( $value1 - $value2 );
}
}
$obj = new MySimpleHeap();
$obj->insert( 4 );
$obj->insert( 8 );
$obj->insert( 1 );
$obj->insert( 0 );
echo $obj->top(); //8
echo $obj->count(); //4
echo '<br/>';
foreach( $obj as $number ) {
echo $number.PHP_EOL;
}
输出:
84
8 4 1 0SplMaxHeap 最大堆
最大堆(SplMaxHeap)继承自抽象类SplHeap实现的。最大堆并没有额外的方法。SplMinHeap 最小堆
最小堆(SplMinxHeap)继承自抽象类SplHeap实现的。最小堆并没有额外的方法。示例:
<?php $obj = new SplMinHeap(); $obj->insert(4); $obj->insert(8); //提取 echo $obj->extract(). PHP_EOL; echo $obj->extract(); //4 8 SplPriorityQueue 优先级队列 优先级队列SplPriorityQueue是基于堆实现的。和堆一样,也有int compare ( mixed $priority1 , mixed $priority2 )方法。
SplPriorityQueue优先级队列
优先级队列SplPriorityQueue是基于堆实现的。和堆一样,也有int compare ( mixed priority1,mixedpriority2 )方法。SplPriorityQueue 实现了Iterator , Countable 接口。
示例:
$pq = new SplPriorityQueue();
$pq->insert('a', 10);
$pq->insert('b', 1);
$pq->insert('c', 8);
echo $pq->count() .PHP_EOL; //3
echo $pq->current() . PHP_EOL; //a
/**
* 设置元素出队模式
* SplPriorityQueue::EXTR_DATA 仅提取值
* SplPriorityQueue::EXTR_PRIORITY 仅提取优先级
* SplPriorityQueue::EXTR_BOTH 提取数组包含值和优先级
*/
$pq->setExtractFlags(SplPriorityQueue::EXTR_DATA);
while($pq->valid()) {
print_r($pq->current()); //a c b
$pq->next();
}SplFixedArray 定长数组
SplFixedArray 实现了Iterator , ArrayAccess , Countable 接口。和普通数组不一样,定长数组规定了数组的长度。优势就是比普通的数组处理更快。
<?php $arr = new SplFixedArray(5); $arr[0] = 1; $arr[1] = 2; $arr[2] = 3; print_r($arr); //SplFixedArray Object ( [0] => 1 [1] => 2 [2] => 3 [3] => [4] => )
SplObjectStorage 对象容器
SplObjectStorage是用来存储一组对象的,特别是当你需要唯一标识对象的时候。该类实现了Countable ,Iterator ,Serializable ,ArrayAccess四个接口。可实现统计、迭代、序列化、数组式访问等功能。示例:
class A {
public $i;
public function __construct($i) {
$this->i = $i;
}
}
$a1 = new A(1);
$a2 = new A(2);
$a3 = new A(3);
$a4 = new A(4);
$container = new SplObjectStorage();
//SplObjectStorage::attach 添加对象到Storage中
$container->attach($a1);
$container->attach($a2);
$container->attach($a3);
//SplObjectStorage::detach 将对象从Storage中移除
$container->detach($a2);
//SplObjectStorage::contains用于检查对象是否存在Storage中
var_dump($container->contains($a1)); //true
var_dump($container->contains($a4)); //false
//遍历
$container->rewind();
while($container->valid()) {
var_dump($container->current());
$container->next();
}SPL类
SPL的内置类
SPL除了定义一系列Interfaces以外,还提供一系列的内置类,它们对应不同的任务,大大简化了编程。查看所有的内置类,可以使用下面的代码:
<?php
// a simple foreach() to traverse the SPL class names
foreach(spl_classes() as $key=>$value)
{
echo $key.' -> '.$value.'<br />';
}
?>SplFileInfo
PHP SPL中提供了SplFileInfo和SplFileObject两个类来处理文件操作。SplFileInfo用来获取文件详细信息:
$file = new SplFileInfo('foo-bar.txt');
print_r(array(
'getATime' => $file->getATime(), //最后访问时间
'getBasename' => $file->getBasename(), //获取无路径的basename
'getCTime' => $file->getCTime(), //获取inode修改时间
'getExtension' => $file->getExtension(), //文件扩展名
'getFilename' => $file->getFilename(), //获取文件名
'getGroup' => $file->getGroup(), //获取文件组
'getInode' => $file->getInode(), //获取文件inode
'getLinkTarget' => $file->getLinkTarget(), //获取文件链接目标文件
'getMTime' => $file->getMTime(), //获取最后修改时间
'getOwner' => $file->getOwner(), //文件拥有者
'getPath' => $file->getPath(), //不带文件名的文件路径
'getPathInfo' => $file->getPathInfo(), //上级路径的SplFileInfo对象
'getPathname' => $file->getPathname(), //全路径
'getPerms' => $file->getPerms(), //文件权限
'getRealPath' => $file->getRealPath(), //文件绝对路径
'getSize' => $file->getSize(),//文件大小,单位字节
'getType' => $file->getType(),//文件类型 file dir link
'isDir' => $file->isDir(), //是否是目录
'isFile' => $file->isFile(), //是否是文件
'isLink' => $file->isLink(), //是否是快捷链接
'isExecutable' => $file->isExecutable(), //是否可执行
'isReadable' => $file->isReadable(), //是否可读
'isWritable' => $file->isWritable(), //是否可写
));SplFileObject
SplFileObject继承SplFileInfo并实现RecursiveIterator、 SeekableIterator接口 ,用于对文件遍历、查找、操作遍历:try {
foreach(new SplFileObject('foo-bar.txt') as $line) {
echo $line;
}
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
查找指定行:
try {
$file = new SplFileObject('foo-bar.txt');
$file->seek(2);
echo $file->current();
} catch (Exception $e) {
echo $e->getMessage();
}
写入csv文件:
$list = array (
array( 'aaa' , 'bbb' , 'ccc' , 'dddd' ),
array( '123' , '456' , '7891' )
);
$file = new SplFileObject ( 'file.csv' , 'w' );
foreach ( $list as $fields ) {
$file -> fputcsv ( $fields );
}DirectoryIterator
该类继承自SplFileInfo并实现SeekableIterator接口。这个类用来查看一个目录中的所有文件和子目录:
<?php
try{
/*** class create new DirectoryIterator Object ***/
foreach ( new DirectoryIterator('./') as $Item )
{
echo $Item.'<br />';
}
}
/*** if an exception is thrown, catch it here ***/
catch(Exception $e){
echo 'No files Found!<br />';
}
?>ArrayObject
该类实现了ArrayAccess ,Countable, IteratorAggregate, Serializable接口。这个类可以将Array转化为object。
<?php
/*** a simple array ***/
$array = array('koala', 'kangaroo', 'wombat', 'wallaby', 'emu', 'kiwi', 'kookaburra', 'platypus');
/*** create the array object ***/
$arrayObj = new ArrayObject($array);
/*** iterate over the array ***/
for($iterator = $arrayObj->getIterator();
/*** check if valid ***/
$iterator->valid();
/*** move to the next array member ***/
$iterator->next())
{
/*** output the key and current array value ***/
echo $iterator->key() . ' => ' . $iterator->current() . '<br />';
}
?>对元素排序:
$arrayObj->natcasesort();
显示元素的数量:
echo $arrayObj->count();
删除一个元素:
$arrayObj->offsetUnset(5);
某一个元素是否存在:
if ($arrayObj->offsetExists(3))
{
echo 'Offset Exists<br />';
}更改某个位置的元素值:
$arrayObj->offsetSet(5, "galah");
显示某个位置的元素值:
echo $arrayObj->offsetGet(4);
ArrayIterator
该类实现了ArrayAccess, Countable , SeekableIterator , Serializable 接口。这个类实际上是对ArrayObject类的补充,为后者提供遍历功能。
<?php
/*** a simple array ***/
$array = array('koala', 'kangaroo', 'wombat', 'wallaby', 'emu', 'kiwi', 'kookaburra', 'platypus');
try {
$object = new ArrayIterator($array);
foreach($object as $key=>$value)
{
echo $key.' => '.$value.'<br />';
}
}
catch (Exception $e)
{
echo $e->getMessage();
}
?>ArrayIterator类也支持offset类方法和count()方法:
<ul>
<?php
/*** a simple array ***/
$array = array('koala', 'kangaroo', 'wombat', 'wallaby', 'emu', 'kiwi', 'kookaburra', 'platypus');
try {
$object = new ArrayIterator($array);
/*** check for the existence of the offset 2 ***/
if($object->offSetExists(2))
{
/*** set the offset of 2 to a new value ***/
$object->offSetSet(2, 'Goanna');
}
/*** unset the kiwi ***/
foreach($object as $key=>$value)
{
/*** check the value of the key ***/
if($object->offSetGet($key) === 'kiwi')
{
/*** unset the current key ***/
$object->offSetUnset($key);
}
echo '<li>'.$key.' - '.$value.'</li>'."\n";
}
}
catch (Exception $e)
{
echo $e->getMessage();
}
?>
</ul>RecursiveArrayIterator类和RecursiveIteratorIterator类
ArrayIterator类和ArrayObject类,只支持遍历一维数组。如果要遍历多维数组,必须先用RecursiveArrayIterator生成一个Iterator,然后再对这个Iterator使用RecursiveIteratorIterator。<?php
$array = array(
array('name'=>'butch', 'sex'=>'m', 'breed'=>'boxer'),
array('name'=>'fido', 'sex'=>'m', 'breed'=>'doberman'),
array('name'=>'girly','sex'=>'f', 'breed'=>'poodle')
);
foreach(new RecursiveIteratorIterator(new RecursiveArrayIterator($array)) as $key=>$value)
{
echo $key.' -- '.$value.'<br />';
}
?>参考: 1. 飞鸿影~ :PHP标准库 (SPL) 笔记 http://www.cnblogs.com/52fhy/p/5573757.html 2. PHP SPL笔记 - 阮一峰的网络日志 http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2008/07/php_spl_notes.html 3. PHP: SPL - Manual http://php.net/manual/zh/book.spl.php[/code]
相关文章推荐
- php标准库函数功能(SPL)
- 解析PHP SPL标准库的用法(遍历目录,查找固定条件的文件)
- PHP SPL标准库之文件操作(SplFileInfo和SplFileObject)
- PHP SPL标准库之SplFixedArray使用实例
- PHP SPL标准库之接口(Interface)详解
- PHP SPL标准库的用法(遍历目录,查找固定条件的文件)
- PHP SPL标准库之数据结构栈(SplStack)介绍
- PHP SPL标准库之接口(Interface)
- PHP SPL标准库之数据结构堆(SplHeap)、最大堆(SplMaxHeap)、最小堆(SplMinHeap)
- PHP SPL标准库之数据结构堆(SplHeap)简单使用实例
- PHP标准库SPL
- 使用php标准库spl在实现观察者模式
- PHP SPL 标准库
- PHP SPL标准库相关函数介绍
- PHP SPL标准库之数据结构队列(SplQueue)和优先队列(SplPriorityQueue)
- 解析PHP SPL标准库的用法(遍历目录,查找固定条件的文件)
- SPL(PHP标准库)-----------------------个人笔记
- PHP SPL标准库之数据结构双链表(SplDoublyLinkedList)
- PHP SPL标准库之文件操作(SplFileInfo和SplFileObject)实例
- PHP SPL标准库之数据结构堆(SplHeap)简单使用实例
