Codeforces Round #279 (Div. 2) B. Queue
2016-07-10 17:39
471 查看
B. Queue
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
During the lunch break all n Berland State University students lined up in the food court. However, it turned out that the food court, too, has a lunch break and it temporarily stopped working.
Standing in a queue that isn't being served is so boring! So, each of the students wrote down the number of the student ID of the student that stands in line directly in front of him, and the student that stands in line directly behind him. If no one stands before or after a student (that is, he is the first one or the last one), then he writes down number 0 instead (in Berland State University student IDs are numerated from 1).
After that, all the students went about their business. When they returned, they found out that restoring the queue is not such an easy task.
Help the students to restore the state of the queue by the numbers of the student ID's of their neighbors in the queue.
Input
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of students in the queue.
Then n lines follow, i-th line contains the pair of integers ai, bi (0 ≤ ai, bi ≤ 106), where ai is the ID number of a person in front of a student and bi is the ID number of a person behind a student. The lines are given in the arbitrary order. Value 0 is given instead of a neighbor's ID number if the neighbor doesn't exist.
The ID numbers of all students are distinct. It is guaranteed that the records correspond too the queue where all the students stand in some order.
Output
Print a sequence of n integers x1, x2, ..., xn — the sequence of ID numbers of all the students in the order they go in the queue from the first student to the last one.
Examples
input
output
Note
The picture illustrates the queue for the first sample.
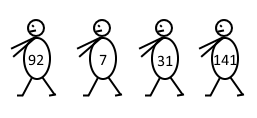
题意:告诉你前驱和后继,求原序列;
思路:两个数位置相差2;
找到前后的起点,两个方向扫一遍;
B. Queue
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
During the lunch break all n Berland State University students lined up in the food court. However, it turned out that the food court, too, has a lunch break and it temporarily stopped working.
Standing in a queue that isn't being served is so boring! So, each of the students wrote down the number of the student ID of the student that stands in line directly in front of him, and the student that stands in line directly behind him. If no one stands before or after a student (that is, he is the first one or the last one), then he writes down number 0 instead (in Berland State University student IDs are numerated from 1).
After that, all the students went about their business. When they returned, they found out that restoring the queue is not such an easy task.
Help the students to restore the state of the queue by the numbers of the student ID's of their neighbors in the queue.
Input
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of students in the queue.
Then n lines follow, i-th line contains the pair of integers ai, bi (0 ≤ ai, bi ≤ 106), where ai is the ID number of a person in front of a student and bi is the ID number of a person behind a student. The lines are given in the arbitrary order. Value 0 is given instead of a neighbor's ID number if the neighbor doesn't exist.
The ID numbers of all students are distinct. It is guaranteed that the records correspond too the queue where all the students stand in some order.
Output
Print a sequence of n integers x1, x2, ..., xn — the sequence of ID numbers of all the students in the order they go in the queue from the first student to the last one.
Examples
input
output
Note
The picture illustrates the queue for the first sample.
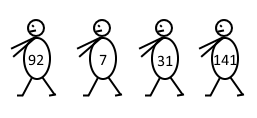
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
During the lunch break all n Berland State University students lined up in the food court. However, it turned out that the food court, too, has a lunch break and it temporarily stopped working.
Standing in a queue that isn't being served is so boring! So, each of the students wrote down the number of the student ID of the student that stands in line directly in front of him, and the student that stands in line directly behind him. If no one stands before or after a student (that is, he is the first one or the last one), then he writes down number 0 instead (in Berland State University student IDs are numerated from 1).
After that, all the students went about their business. When they returned, they found out that restoring the queue is not such an easy task.
Help the students to restore the state of the queue by the numbers of the student ID's of their neighbors in the queue.
Input
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of students in the queue.
Then n lines follow, i-th line contains the pair of integers ai, bi (0 ≤ ai, bi ≤ 106), where ai is the ID number of a person in front of a student and bi is the ID number of a person behind a student. The lines are given in the arbitrary order. Value 0 is given instead of a neighbor's ID number if the neighbor doesn't exist.
The ID numbers of all students are distinct. It is guaranteed that the records correspond too the queue where all the students stand in some order.
Output
Print a sequence of n integers x1, x2, ..., xn — the sequence of ID numbers of all the students in the order they go in the queue from the first student to the last one.
Examples
input
4 92 31 0 7 31 0 7 141
output
92 7 31 141
Note
The picture illustrates the queue for the first sample.
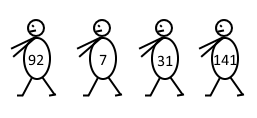
题意:告诉你前驱和后继,求原序列;
思路:两个数位置相差2;
找到前后的起点,两个方向扫一遍;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define esp 0.00000000001
const int N=3e5+10,M=1e6+10,inf=1e9,mod=1e9+7;
int a[M];
int b[M];
int ans[M];
int flag[M];
int main()
{
int x,y,z,i,t;
scanf("%d",&x);
for(i=0;i<x;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&y,&z);
a[y]=z;
b[z]=y;
flag[y]++;
flag[z]++;
}
int st=0;
int ji=0;
while(a[st])
{
ans[ji+2]=a[st];
flag[a[st]]=0;
st=a[st];
ji+=2;
}
if(x&1)
{
int en=0;
for(i=1;i<=M;i++)
if(flag[i]&&!a[i])
en=i;
int ji=x;
while(en)
{
ans[ji]=en;
en=b[en];
ji-=2;
}
}
else
{
int ji=x-1;
int en=0;
while(b[en])
{
ans[ji]=b[en];
en=b[en];
ji-=2;
}
}
for(i=1;i<=x;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
return 0;
}B. Queue
time limit per test
2 seconds
memory limit per test
256 megabytes
input
standard input
output
standard output
During the lunch break all n Berland State University students lined up in the food court. However, it turned out that the food court, too, has a lunch break and it temporarily stopped working.
Standing in a queue that isn't being served is so boring! So, each of the students wrote down the number of the student ID of the student that stands in line directly in front of him, and the student that stands in line directly behind him. If no one stands before or after a student (that is, he is the first one or the last one), then he writes down number 0 instead (in Berland State University student IDs are numerated from 1).
After that, all the students went about their business. When they returned, they found out that restoring the queue is not such an easy task.
Help the students to restore the state of the queue by the numbers of the student ID's of their neighbors in the queue.
Input
The first line contains integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 2·105) — the number of students in the queue.
Then n lines follow, i-th line contains the pair of integers ai, bi (0 ≤ ai, bi ≤ 106), where ai is the ID number of a person in front of a student and bi is the ID number of a person behind a student. The lines are given in the arbitrary order. Value 0 is given instead of a neighbor's ID number if the neighbor doesn't exist.
The ID numbers of all students are distinct. It is guaranteed that the records correspond too the queue where all the students stand in some order.
Output
Print a sequence of n integers x1, x2, ..., xn — the sequence of ID numbers of all the students in the order they go in the queue from the first student to the last one.
Examples
input
4 92 31 0 7 31 0 7 141
output
92 7 31 141
Note
The picture illustrates the queue for the first sample.
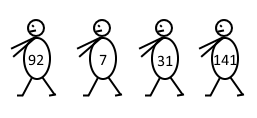
相关文章推荐
- leetcode60. Permutation Sequence
- php实现简单的SQL Builder
- 【荐】如何正确理解PHP之include,include_once,require,require_once等包含作用域
- map按key和value排序
- HDOJ/HDU 1242 Rescue(经典BFS深搜-优先队列)
- HDOJ/HDU 1242 Rescue(经典BFS深搜-优先队列)
- 数据库交互 query
- leetcode357. Count Numbers with Unique Digits
- 特殊权限-SUID,SGID,Sticky 学习笔记
- Mysql插入数据里有中文字符出现Incorrect string value的错误
- $_SERVER["SCRIPT_NAME"]、$_SERVER["PHP_SELF"]、$_SERVER["QUERY_STRING"]、$_SERVER["REQUEST_URI"]
- TI BIOS MCSDK 2.0 User Guide
- CSS链接四种状态注意顺序、UI伪类选择器的顺序
- UIView的layoutSubviews和drawRect
- 前景检测算法(十二)--基于模糊Choquet积分
- HDU 286 Data Handler <deque 双向队列>
- QML UI布局管理
- java中String类、StringBuilder类和StringBuffer类详解
- SoapUI 笔记13 JDBC请求
- leetcode:Top K Frequent Elements
