【bzoj4431】[Nwerc2015]Hole in One一杆进洞
2016-04-10 16:30
239 查看
Problem
Description
Janine recently went to her local game store and bought “Hole in One”, a new mini-golf game for her computer. As indicated by the name, the objective of the game is to shoot a ball into a hole using just one shot. The game also borrows elements from brick breaker style games: in the playing field, several walls are placed that will be destroyed upon being hit by the ball. The score of a successful shot depends on the number of destroyed walls, so Janine wonders: what is the maximum number of walls that can be hit while performing a “Hole in One”?For the purposes of this problem you can think of the playing field as a cartesian plane with the initial position of the ball at the origin. The walls are non-intersecting axis-parallel line segments in this plane (i.e., parallel to either the x axis or the y axis). The diameter of the ball is negligible so it is represented as a single point.
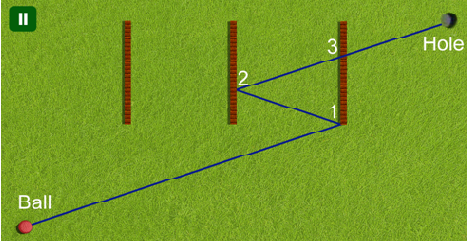
Figure H.1: Illustration of the first sample input: The ball first bounces off two walls at points 1 and 2. When it passes point 3 the wall has already vanished.
Whenever the ball hits a wall, two things happen:
The direction of the ball changes in the usual way: the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection.
The wall that the ball touched is destroyed. Following common video game logic, no rubble of the wall remains; it will be as though it vanished.
The behaviour of the ball is also affected by the power of the shot. In particular, an optimal shot may need to first roll over the hole, then hit some more walls, and only later drop into the hole.
Input
The input consists of:one line with one integer n (0 ≤ n ≤ 8), the number of walls;
one line with two integers x and y, the coordinates of the hole;
n lines each with four integers x1,y1,x2 and y2 (either x1=x2 , or y1=y2 , but not both), representing a wall with end points (x1,y1) and (x2,y2).
The hole is not at the origin and not on a wall. The walls do not touch or intersect each other.
No wall lies completely on the x axis or the y axis. All coordinates in the input are integers with
absolute value at most 1 000.
Output
If there is no way to shoot the ball such that it reaches the hole, print “impossible”. Otherwise, print the maximum number of walls that can be destroyed in a single “Hole in One” shot.Sample Input
Sample Input 13
4 2
1 1 1 2
2 1 2 2
3 1 3 2
Sample Input 2
1
2 0
1 -1 1 1
Sample Input 3
2
-2 4
2 4 2 2
0 6 -2 6
Sample Output
Sample Output 12
Sample Output 2
Impossible
Sample Output 3
2
Source
NWERC 2015 Problem HSolution

枚举所有可能的撞击墙壁的方案,包括撞击哪些墙,和撞击的顺序
从目标点T开始,计算小球每一次弹射的目标点(也就是按逆序对每堵墙取轴对称点)
从原点开始,按顺序弹向下一目标点,找到线段与对应墙的交点作为反射点,判断是否合法
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define rep(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i <= (b); i++)
#define red(i, a, b) for(int i = (a); i >= (b); i--)
#define ll long long
#define y1 yy1
#define abs Abs
#define Vector Point
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar();
while(!isdigit(c)) { if (c == '-') f = -1; c = getchar(); }
while(isdigit(c)) { x = x * 10 + c - '0'; c = getchar(); }
return x * f;
}
template<typename tn> void cmax(tn& a, tn b) { if (b > a) a = b; }
template<typename tn> void cmin(tn& a, tn b) { if (b < a) a = b; }
template<typename tn> tn abs(tn x) { return x < 0 ? -x : x; }
const int N = 20;
const double eps = 1e-8;
struct LINE{
double x1, y1, x2, y2; int tag;
}w
;
struct Point{
double x, y;
Point(double x = 0, double y = 0):x(x),y(y) { }
}p
;
int n, flag = 0, line
, l
, vis
, used
;
double xs, ys, xt, yt;
Vector operator + (Vector A, Vector B) { return Vector(A.x + B.x, A.y + B.y); }
Vector operator - (Point A, Point B) { return Vector(A.x - B.x, A.y - B.y); }
int dcmp(double x) {
if (fabs(x) < eps) return 0;
else return x < 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
bool operator == (const Point& A, const Point& B) {
return dcmp(A.x - B.x) == 0 && dcmp(A.y - B.y) == 0;
}
double dot(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x * B.x + A.y * B.y; }
double cross(Vector A, Vector B) { return A.x * B.y - A.y * B.x; }
Point Get_Inter(Point p, Vector v, LINE w) {
double xt, yt;
if (w.tag) {
yt = w.y1;
xt = (yt - p.y) * v.x / v.y + p.x;
}else {
xt = w.x1;
yt = (xt - p.x) * v.y / v.x + p.y;
}
return Point(xt, yt);
}
bool On_Wall(Point p, LINE w) {
if (w.tag) return (p.x >= w.x1 && p.x <= w.x2);
else return (p.y >= w.y1 && p.y <= w.y2);
}
bool On_Seg(Point p, Point a1, Point a2) { return dcmp(dot(a1 - p, a2 - p)) <= 0; }
void solve(int m) {
memset(used, 0, sizeof(used));
double X = xt, Y = yt;
rep(i, 1, m) l[i] = line[i]; l[m + 1] = 0;
red(i, m, 1) {
if (w[l[i]].tag) Y = 2 * w[l[i]].y1 - Y;
else X = 2 * w[l[i]].x1 - X;
p[i] = Point(X, Y);
}
p[++m] = Point(xt, yt);
Point now = Point(0, 0);
rep(i, 1, m) {
Vector dir = p[i] - now;
Point rev_p;
if (i != m) {
if (w[l[i]].tag == 1 && dcmp(dir.y) == 0) return;
if (w[l[i]].tag == 0 && dcmp(dir.x) == 0) return;
rev_p = Get_Inter(now, dir, w[l[i]]);
if (!On_Seg(rev_p, now, p[i])) return;
if (!On_Wall(rev_p, w[l[i]])) return;
}else rev_p = p[m];
rep(j, 1, n) {
if (used[j] || j == l[i]) continue;
if (w[j].tag == 1 && dcmp(dir.y) == 0) continue;
if (w[j].tag == 0 && dcmp(dir.x) == 0) continue;
Point tmp = Get_Inter(now, dir, w[j]);
if (!On_Wall(tmp, w[j])) continue;
if (On_Seg(tmp, now, rev_p)) return;
}
now = rev_p; used[l[i]] = 1;
}
flag = 1;
return;
}
void dfs1(int lim, int dep) {
if (dep > lim) { solve(lim); return; }
rep(i, 1, n) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
line[dep] = i; vis[i] = 1;
dfs1(lim, dep + 1);
if (flag) return;
vis[i] = 0;
}
}
int main() {
freopen("H.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("H.out", "w", stdout);
n = read();
if (n == 0) { printf("0\n"); return 0; }
xs = ys = 0;
xt = (double)read(); yt = (double)read();
rep(i, 1, n) {
int x1 = read(), y1 = read(), x2 = read(), y2 = read();
if (x1 > x2) swap(x1, x2);
if (y1 > y2) swap(y1, y2);
w[i].x1 = (double)x1; w[i].y1 = (double)y1;
w[i].x2 = (double)x2; w[i].y2 = (double)y2;
w[i].tag = dcmp(x1 - x2) != 0;
}
red(num, n, 0) {
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
dfs1(num, 1);
if (flag) { printf("%d\n", num); break; }
}
if (!flag) printf("impossible\n");
return 0;
}尾声
判断合法状态真的很蛋疼。。炸到只有三十分,后来发现是没有判断南辕北辙的情况,也就是这样|| × –> ×
是不是很像一个表情。。
End.
相关文章推荐
- vs2012快捷键
- 使用Spring RestTemplate解析RESTful服务
- Java异常机制
- 分享一些互联网公司j2ee面试题
- 【POJ1021】Intervals (最短路解差分约束)
- SDAU 搜索专题 25 推箱子
- 常用正则表达式
- uva548
- LeetCode *** 204. Count Primes
- 遥感图像
- quartz的JDBC JobStoreTX的配置使用
- android 绘图之Path与Paint详解
- Linux内核分析第七周学习笔记——Linux内核如何装载和启动一个可执行程序
- 小组团队介绍
- 数据结构之二叉树
- MYSQL 中的常见问题(包括数据筛选)
- Intent 的Flag属性(Activity在栈位置的主宰者)
- 栈的压入与弹出
- vmvare 安装centos,把原来的eth0和eth1找回来
- java基础(二),hello word
