Android新特性之RecyclerView的简单使用
2015-09-29 17:51
627 查看
Android新特性之RecyclerView的简单使用
RecyclerView是安卓5.0版本中的一个新控件,目的是来取代使用多年的ListView。RecyclerView的灵活性远超ListView,所以RecyclerView扩展性非常高,下面就让我们一起来看看RecyclerView的简单使用。简介
RecyclerView的设计非常灵活,它通过LayoutManager、ItemDecoration、ItemAnimator这三个类进行所有的布局控制,绑定数据依旧是使用Adapter进行绑定。所以我们只需要掌握这三个类的使用即可。环境配置
RecyclerView是android系统提供的新控件,自然按照谷歌的一贯作风,我们需要下载一个支持库。android.support.v7。所以使用该控件,我们需要添加v7包的引用。v7下载地址。下载完成后,我们需要在开发环境中添加该包的引用。简要介绍在Eclipse和Android Studio中的引用方式。
Eclipse添加V7包
1、在eclipse的工作控件将v7包导入到我们的工程中。注意:此时应将我们下载好的v7包放到我们工程目录下,不然后面导入后会出问题。
2、选中我们的项目,右键properties属性,进入如下图,我们点击add,系统就会在我们的工作目录下,找到Library类库,供我们添加,我们选择v7即可。这样我们就可以使用RecyclerView了。
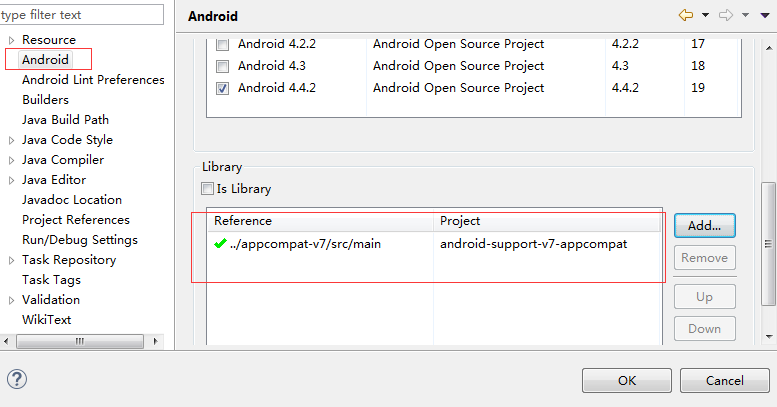
注意:如果你添加到v7包到eclipse了,但是找不到该library,你选中v7包工程右键属性选择Library,然后勾选上图中的isLibrary,点击确定即可。
AndroidStudio中添加v7包
1、要确保已经将Android Support Libraries升级到最新。
2、打开我们的module对应的build.gradle文件,在dependencies中添加
compile 'com.android.support:recyclerview-v7:21.0.+'
3、重新Build一下工程即可。
相关类介绍
一、RecyclerView我们打开源码,看到
public class RecyclerView extends ViewGroup
所以这也就是我们常见的自定义ViewGroup,只不过这个玩意比较牛逼罢了。通过源码,我们看到这玩意有很多方法,但是我们仅仅挑选几个常用的来说说。
1、public void setAdapter(Adapter adapter)
根据我们使用的经验,显然这个方法是让我们绑定数据的,只不过这个Adapter是
public static abstract class Adapter<VH extends ViewHolder>
类型的。
2、 public void setLayoutManager(LayoutManager layout)
看到layout开头,显然是跟布局有关,又有manager,所以这个LayoutManager肯定就是负责RecyclerView的布局的类。
3、public void addItemDecoration(ItemDecoration decor, int index)
为每个item附加的子视图,这个方法可用于添加分割线,这点和我们使用ListView的setDivider()有点类似,此时,我们只要传入一个ItemDecoration对象。
4、 public void setItemAnimator(ItemAnimator animator)
这个方法很牛逼,可以设置动画。先来看看官方文档对此方法的注释。
* Sets the {@link ItemAnimator} that will handle animations involving changes
* to the items in this RecyclerView. By default, RecyclerView instantiates and
* uses an instance of {@link DefaultItemAnimator}. Whether item animations are
* enabled for the RecyclerView depends on the ItemAnimator and whether
* the LayoutManager {@link LayoutManager#supportsPredictiveItemAnimations()
* supports item animations}.
*/这段话的大概意思就是通过此方法设置ItemAnimator对象来实现RecyclerView的item的动画,默认情况下,使用DefaultItemAnimator动画。动画是否有效取决于ItemAnimator和LayoutManager的类对象。
以上就是众多方法中比较常用的四个,这四个方法的灵活性很高,所以也铸就了RecyclerView的高度灵活性,看了上面的四个方法,我们可以肯定RecyclerView类的内部肯定有对应的四个类对象来处理所需的效果。
二、LayoutManager
上面也分析了,这个LayoutManager就是我们的布局管理器。我们下来看看一张类的组织结构图。
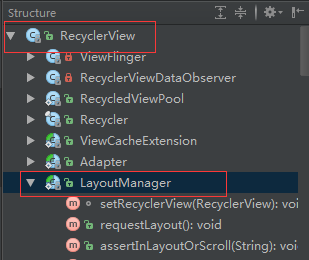
我们先来看看该类的定义源码来一睹风采。
public static abstract class LayoutManager
看到源码,吓了一跳,原来是一个抽象类,那我们setLayoutManager(LayoutManager layout)时难道要我们自定义一个LayoutManager对象么?哈哈!不会的,如果真是那样,我估计RecyclerView就变的极其复杂了,为什么?且看源码对该类的注释。
/** * A <code>LayoutManager</code> is responsible for measuring and positioning item views * within a <code>RecyclerView</code> as well as determining the policy for when to recycle * item views that are no longer visible to the user. By changing the <code>LayoutManager</code> * a <code>RecyclerView</code> can be used to implement a standard vertically scrolling list, * a uniform grid, staggered grids, horizontally scrolling collections and more. Several stock * layout managers are provided for general use. */
意思就是:LayoutManager负责RecyclerView中item的测量以及放置,同时也管理着item的回收。通过改变LayoutManager可以让RecyclerView形成垂直滚动的效果(ListView),统一网格效果(GridView)、交错网格效果(瀑布流)、横向滚动效果(HorizontalListView)等等。
所以说,这么复杂的东西怎么能让开发者完全实现呢?安卓肯定会给我们提供几个实现好的类。
LinearLayoutManager:线性布局管理器,支持横向和纵向形式。
GridLayoutManager: 网格布局管理器。
StaggeredGridLayoutManager:瀑布就式布局管理器
所以在实际开发中,我们可以根据实际需要进行使用,一般情况下,这三个子类能完全满足我们的需求,更高需求,请自定义LayoutManager对象。
三、ItemDecoration
为每个item附加的子视图,这个类可用于我们设置分割线,同样也是RecyclerView类的内部类,那么我们看看它的定义形式:
public static abstract class ItemDecoration
又是一个抽象类,所以注定了它是不平凡的,即我们需要自定义它的子类来实现绚丽的分割效果,官方现在好像还没有吧!以后估计可能有。
四、ItemAnimator
一看,跟Animator沾边,八成就是搞动画的出身。同样该类也是RecyclerView类的内部类,我们看看它的定义吧!
public static abstract class ItemAnimator
所以注定了不平凡有不平凡的伟大,我们需要自定义子类来实现动画,系统也提供默认的。
关于RecyclerView的基本要素,我们简要说了下,总体来说,功能很强大,能玩多6全看自身水平多高,涉及的方面比较多,上手比较容易,想精通这个控件,还是需要下很大功夫的。下面就开始学习使用这个控件了。
RecyclerView的使用
1、基本使用步骤:View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_linear_layout_manager, container, false); //RecyclerView的初始化 mRecyclerView = (RecyclerView)view.findViewById(R.id.recycler_view); //创建现行LinearLayoutManager mLayoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(getActivity()); //设置LayoutMananger mRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(mLayoutManager); //设置item的动画,可以不设置 mRecyclerView.setItemAnimator(new DefaultItemAnimator()); MyAdapter adapter = new MyAdapter(initDate()); //设置Adapter mRecyclerView.setAdapter(adapter);
以上就是使用的几个步骤,很简单,所以我们就开始学习使用。由于演示功能较多,所以我们采用在Fragment中进行。
ListView效果
1、首先我们创建名称为LinearLayoutManagerFragment的Fragment,用于展示线性的布局,然后创建对应的xml布局。在AndroidStudio中我们创建该fragment时系统已经默认帮我们创建好了,Eclipse中就不会。我们直接看xml布局中的RecyclerView的使用吧!
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView android:id="@+id/recycler_view" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:scrollbars="vertical" /> </FrameLayout>
使用很简单,下面看看我们在Fragment中的使用代码:
public class LinearLayoutManagerFragment extends Fragment {
private RecyclerView mRecyclerView;
private RecyclerView.LayoutManager mLayoutManager;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_linear_layout_manager, container, false);
//RecyclerView的初始化
mRecyclerView = (RecyclerView)view.findViewById(R.id.recycler_view);
//创建现行LinearLayoutManager
mLayoutManager = new LinearLayoutManager(getActivity());
//设置LayoutMananger
mRecyclerView.setLayoutManager(mLayoutManager);
//设置item的动画,可以不设置
mRecyclerView.setItemAnimator(new DefaultItemAnimator());
MyAdapter adapter = new MyAdapter(initDate());
//设置Adapter
mRecyclerView.setAdapter(adapter);
return view;
}
private List<String> initDate(){
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0;i<50;i++){
list.add("测试用例:" + i);
}
return list;
}
class MyAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<MyAdapter.ViewHolder>{
private List<String> items;
public MyAdapter(List<String> items) {
this.items = items;
}
/**
* 创建ViewHolder的布局
* @param parent
* @param viewType
* @return
*/
@Override
public MyAdapter.ViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext()).inflate(R.layout.item,parent,false);
return new ViewHolder(view);
}
/**
* 通过ViewHolder将数据绑定到界面上进行显示
* @param holder
* @param position
*/
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(MyAdapter.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
holder.mTextView.setText(items.get(position));
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return items.size();
}
public class ViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder{
public TextView mTextView;
public ViewHolder(View itemView) {
super(itemView);
mTextView = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.textView);
}
}
}
}item的布局,仅仅包含一个TextView用于展示。
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:padding="20dp" android:background="#7fa87f" android:textColor="#ffffff" android:gravity="center_horizontal"/> </LinearLayout>
使用步骤与我们开篇说的一样,其实和ListView的使用差异不大,初始化控件,然后设置控件的相关属性,接着绑定数据,只不Recyclerview的属性设置有些复杂罢了。比较明显的变化就数Adapter的变化了。以前在使用ListView时,我们继承BaseAdapter来自定义Adatper适配器,然后使用ViewHolder进行复用Item。现在我们在看看RecyclerView.Adapter。
public static abstract class Adapter<VH extends ViewHolder>
看到这个类的定义确实吓一跳,Adapter里面都是ViewHolder类型,难道系统有ViewHolder,猜对了,系统中已经带了ViewHolder类型,
public static abstract class ViewHolder
所以我们我们要继承此ViewHolder来自定义我们的ViewHolder。就有了上面的写法,来发效果图!

ok,简单的使用已经完成,我们前面也分析了,RecyclerView可以实现横向的ListView,那么我们来看看效果,我们创建名为HorrizontalManagerFragment的fragment。内容可以完全复制LinearLayoutManagerFragment的内容,只需要做以下几点修改:
private LinearLayoutManager mLayoutManager; mLayoutManager.setOrientation(LinearLayoutManager.HORIZONTAL);
即可。效果图:

上面的效果实现了,但是感觉是不是很别扭,少了点什么。就是分割线,下面我们来给我们的RecyclerView添加分割线。当我们调用mRecyclerView.addItemDecoration()方法添加decoration的时候,RecyclerView在绘制的时候,去会绘制decorator,即调用该类的onDraw和onDrawOver方法,
onDraw方法先于drawChildren
onDrawOver在drawChildren之后,一般我们选择复写其中一个即可。
getItemOffsets 可以通过outRect.set()为每个Item设置一定的偏移量,主要用于绘制Decorator。
我们建一个包用来放我们的ItemDecoration,我们先找一个现成的例子,来试试。
public class DividerItemDecoration extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration{
private static final int[] ATTRS = new int[]{
android.R.attr.listDivider
};
public static final int HORIZONTAL_LIST = LinearLayoutManager.HORIZONTAL;
public static final int VERTICAL_LIST = LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL;
private Drawable mDivider;
private int mOrientation;
public DividerItemDecoration(Context context, int orientation) {
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(ATTRS);
mDivider = a.getDrawable(0);
a.recycle();
setOrientation(orientation);
}
public void setOrientation(int orientation) {
if (orientation != HORIZONTAL_LIST && orientation != VERTICAL_LIST) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid orientation");
}
mOrientation = orientation;
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent) {
Log.v("recyclerview - itemdecoration", "onDraw()");
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL_LIST) {
drawVertical(c, parent);
} else {
drawHorizontal(c, parent);
}
}
public void drawVertical(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent) {
final int left = parent.getPaddingLeft();
final int right = parent.getWidth() - parent.getPaddingRight();
final int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView v = new android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView(parent.getContext());
final RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
final int top = child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin;
final int bottom = top + mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight();
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
public void drawHorizontal(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent) {
final int top = parent.getPaddingTop();
final int bottom = parent.getHeight() - parent.getPaddingBottom();
final int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
final View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
final RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
final int left = child.getRight() + params.rightMargin;
final int right = left + mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight();
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, int itemPosition, RecyclerView parent) {
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL_LIST) {
outRect.set(0, 0, 0, mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight());
} else {
outRect.set(0, 0, mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth(), 0);
}
}
}在Fragment中只需增加
mRecyclerView.addItemDecoration(new DividerItemDecoration(getActivity(),LinearLayoutManager.VERTICAL));
来看看效果图:

通过上面的实例,线条已经画出来了,我们只需要改变Draw的实例就可以了,所以这个玩的空间就比较大了。比如:
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:shape="rectangle" > <solid android:color="#00ff00"/> <corners android:radius="20dp"/> <size android:height="4dp"/> </shape>
效果图:

总之不单单添加分割线,其它用处也很多,样式更加随心所欲。
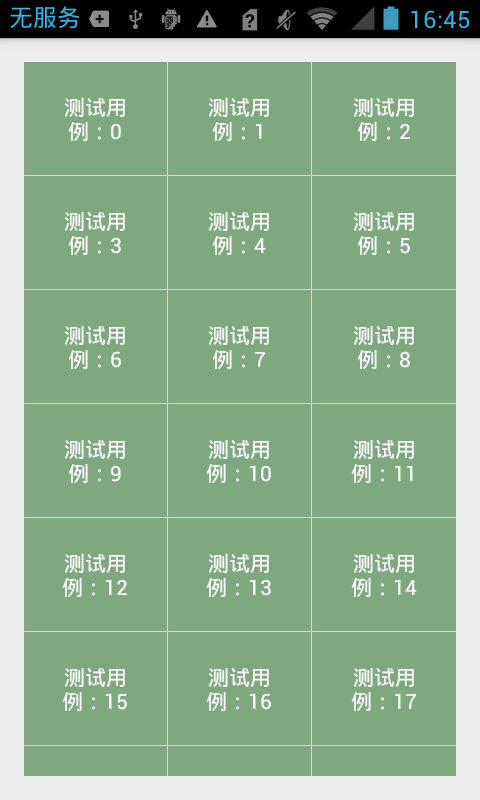
GridView效果
步骤如上,我们只需要更改LayoutManager所指向的对象即可。
mLayoutManager = new GridLayoutManager(getActivity(),4);
这样就能实现一个GridView效果,我们要处理的就是ItemDecrator的处理。
下面引自张鸿洋写的一个效果:
/**
*
* @author zhy
*
*/
public class DividerGridItemDecoration extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration
{
private static final int[] ATTRS = new int[] { android.R.attr.listDivider };
private Drawable mDivider;
public DividerGridItemDecoration(Context context)
{
final TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(ATTRS);
mDivider = a.getDrawable(0);
a.recycle();
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent, State state)
{
drawHorizontal(c, parent);
drawVertical(c, parent);
}
private int getSpanCount(RecyclerView parent)
{
// 列数
int spanCount = -1;
LayoutManager layoutManager = parent.getLayoutManager();
if (layoutManager instanceof GridLayoutManager)
{
spanCount = ((GridLayoutManager) layoutManager).getSpanCount();
} else if (layoutManager instanceof StaggeredGridLayoutManager)
{
spanCount = ((StaggeredGridLayoutManager) layoutManager)
.getSpanCount();
}
return spanCount;
}
public void drawHorizontal(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent)
{
int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++)
{
final View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
final RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
final int left = child.getLeft() - params.leftMargin;
final int right = child.getRight() + params.rightMargin
+ mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth();
final int top = child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin;
final int bottom = top + mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight();
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
public void drawVertical(Canvas c, RecyclerView parent)
{
final int childCount = parent.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++)
{
final View child = parent.getChildAt(i);
final RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child
.getLayoutParams();
final int top = child.getTop() - params.topMargin;
final int bottom = child.getBottom() + params.bottomMargin;
final int left = child.getRight() + params.rightMargin;
final int right = left + mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth();
mDivider.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);
mDivider.draw(c);
}
}
private boolean isLastColum(RecyclerView parent, int pos, int spanCount,
int childCount)
{
LayoutManager layoutManager = parent.getLayoutManager();
if (layoutManager instanceof GridLayoutManager)
{
if ((pos + 1) % spanCount == 0)// 如果是最后一列,则不需要绘制右边
{
return true;
}
} else if (layoutManager instanceof StaggeredGridLayoutManager)
{
int orientation = ((StaggeredGridLayoutManager) layoutManager)
.getOrientation();
if (orientation == StaggeredGridLayoutManager.VERTICAL)
{
if ((pos + 1) % spanCount == 0)// 如果是最后一列,则不需要绘制右边
{
return true;
}
} else
{
childCount = childCount - childCount % spanCount;
if (pos >= childCount)// 如果是最后一列,则不需要绘制右边
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean isLastRaw(RecyclerView parent, int pos, int spanCount,
int childCount)
{
LayoutManager layoutManager = parent.getLayoutManager();
if (layoutManager instanceof GridLayoutManager)
{
childCount = childCount - childCount % spanCount;
if (pos >= childCount)// 如果是最后一行,则不需要绘制底部
return true;
} else if (layoutManager instanceof StaggeredGridLayoutManager)
{
int orientation = ((StaggeredGridLayoutManager) layoutManager)
.getOrientation();
// StaggeredGridLayoutManager 且纵向滚动
if (orientation == StaggeredGridLayoutManager.VERTICAL)
{
childCount = childCount - childCount % spanCount;
// 如果是最后一行,则不需要绘制底部
if (pos >= childCount)
return true;
} else
// StaggeredGridLayoutManager 且横向滚动
{
// 如果是最后一行,则不需要绘制底部
if ((pos + 1) % spanCount == 0)
{
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, int itemPosition,
RecyclerView parent)
{
int spanCount = getSpanCount(parent);
int childCount = parent.getAdapter().getItemCount();
if (isLastRaw(parent, itemPosition, spanCount, childCount))// 如果是最后一行,则不需要绘制底部
{
outRect.set(0, 0, mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth(), 0);
} else if (isLastColum(parent, itemPosition, spanCount, childCount))// 如果是最后一列,则不需要绘制右边
{
outRect.set(0, 0, 0, mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight());
} else
{
outRect.set(0, 0, mDivider.getIntrinsicWidth(),
mDivider.getIntrinsicHeight());
}
}
}效果图:
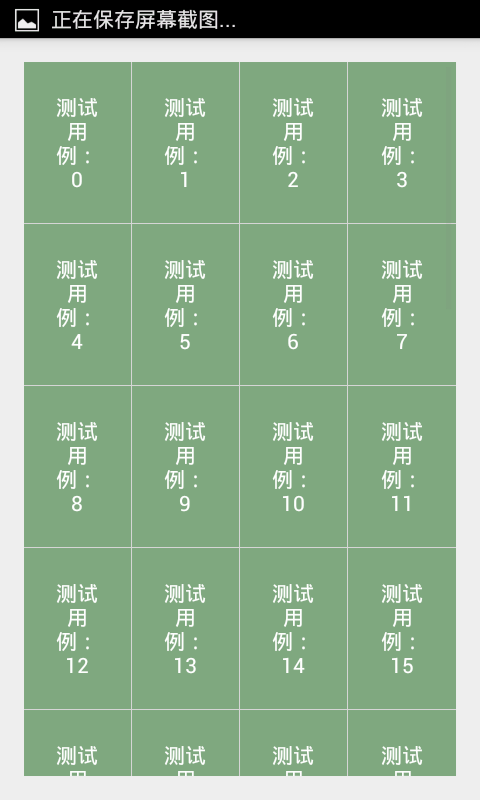
瀑布流效果
同样,我们只需要修改LayoutManager来实现效果:
mLayoutManager = new StaggeredGridLayoutManager(3, StaggeredGridLayoutManager.VERTICAL);
效果图:
我们发现,每个item都很整齐,但是瀑布流的效果不是这样的啊!那我们怎么搞,就是在onBindViewHolder方法中修改每个view的大小。
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(MyAdapter.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params= holder.mTextView.getLayoutParams();
params.height = (int) (100 + Math.random() * 400);
holder.mTextView.setLayoutParams(params);
holder.mTextView.setText(items.get(position));
}效果图:
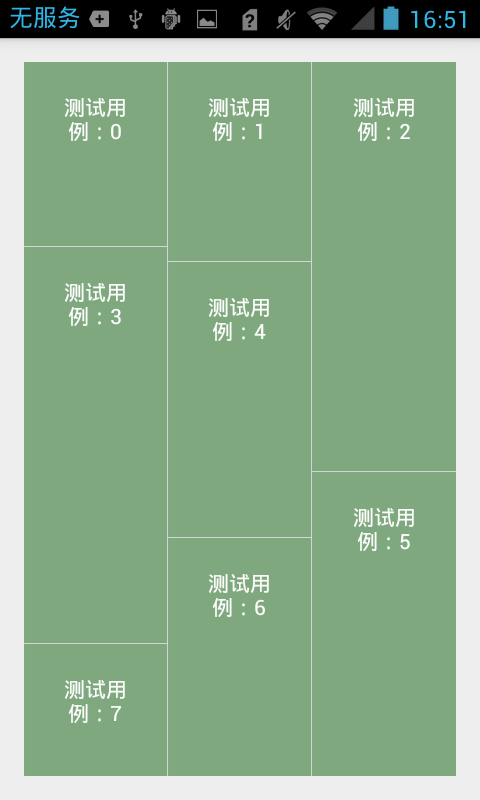
至此,所有的展示工作已经完成,那么我们进行点击事件处理。
点击效果处理
RecyclerView没有像ListView有setOnItemClick的事件,那么只有我们通过回调接口进行设置。
public interface OnItemClick {
public void onItemClick(int position);
}
public void setOnItemClick(OnItemClick onItemClick){
this.onItemClick = onItemClick;
}
public void onBindViewHolder(final MyAdapter.ViewHolder holder, int position) {
holder.mTextView.setText(items.get(position));
if(onItemClick != null){
holder.itemView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
onItemClick.onItemClick(holder.getPosition());
}
});
}
}这样我们就能进行点击事件的处理了。效果图:

至此,关于RecyclerView的基本用法讲解完毕,还是要多练习,比如分割线的处理以及动画的处理,这部分是个亮点也是难点。
源码下载地址
参考文档:
http://www.devstore.cn/new/newInfo/868.html
http://blog.jobbole.com/74208/
http://www.jcodecraeer.com/a/anzhuokaifa/androidkaifa/2014/1118/2004.html
http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/45059587
http://blog.csdn.net/guxiao1201/article/details/40399777
作者:mr_dsw 欢迎转载,与人分享是进步的源泉!
转载请保留地址:http://blog.csdn.net/mr_dsw
相关文章推荐
- Android新特性之RecyclerView的简单使用
- Android Material适配 为控件设置指定背景色和点击波纹效果
- 解决Android加载图片时内存溢出的问题
- Android混淆打包错误Conversion to Dalvik format failed with error 1
- Android Gallery画廊 图片展示控件
- 基于飞思卡尔imx6 sabrelite开发板的android lvds屏幕驱动调试
- 【Android】Activity切换动画效果
- 再回首【Android 自定义View (二) 进阶】
- 【Android开发经验】我们要友好的告诉用户,程序要崩溃了
- Android的自定义闹钟
- (转)Android 模仿淘宝滑动查看图片的效果 Gallery + ImageSwitcher
- android BaseAdapter中改变某个item的部分布局
- 如何自动获取android 安装APK成功后的状态
- Android5.0 Toolbar和Theme的使用
- Android系统【文件权限与类型】
- Android ListView两种长按弹出菜单方式
- android: 长按删除listview的item
- Android中的Activity生命周期详解
- android的简单wifi demo
- gradle配置.so文件存放目录
