图像处理------颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient) 分类: 视频图像处理 2015-07-24 09:23 27人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
2015-07-24 09:23
633 查看
有过UI设计经验的一定对2D图形渲染中的Color Gradient 或多或少有些接触,很多编程
语言也提供了Gradient的接口,但是想知道它是怎么实现的嘛?
本文介绍三种简单的颜色梯度变化算法,就可以很容易实现常见的梯度变化算法
三种都要求提供两个参数即起始颜色RGB值, 最终颜色RGB的值。
垂直梯度颜色变化,效果如下:
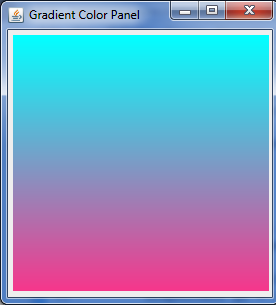
水平梯度颜色变化,效果如下:
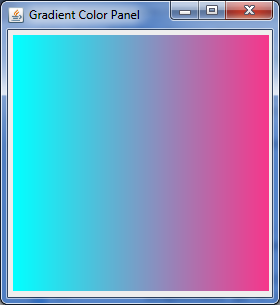
水平与垂直两个方向叠加梯度变化效果如下:
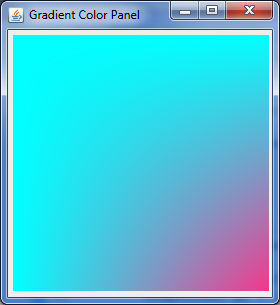
算法代码及其解释
计算起始颜色和终点颜色RGB之间差值代码如下:
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0];
float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1];
float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2];
实现垂直梯度变化的代码如下:
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f);
实现水平梯度变化代码如下:
// set gradient color valuefor each pixel
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)col/255.0f) +0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)col/255.0f) +0.5f);
实现水平和垂直两个方向上Gradient叠加代码如下:
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f);
程序对上面三种Gradient方法分别放在三个不同的方法中,根据参数调用。
程序的完全Java源代码如下:
[java] view plaincopyimport java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.RenderingHints;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import javax.swing.JComponent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class ColorGradientDemo extends JComponent {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4134440495899912869L;
private BufferedImage image = null;
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
g2.drawImage(getImage(4), 5, 5, image.getWidth(), image.getHeight(), null);
}
public BufferedImage getImage(int type) {
if(image == null) {
image = new BufferedImage(256, 256, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB);
int[] rgbData = new int[256*256];
if(type == 1) {
generateVGradientImage(rgbData);
} else if(type == 2) {
generateHGradientImage(rgbData);
} else {
generateHVGradientImage(rgbData);
}
setRGB(image, 0, 0, 256, 256, rgbData);
}
return image;
}
private void generateVGradientImage(int[] rgbData) {
int[] startColor = getStartColor();
int[] endColor = getEndColor();
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0];
float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1];
float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2];
int a=255;
int r=0, g=0, b=0;
int index = 0;
for(int row=0; row<256; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<256; col++) {
// set random color value for each pixel
// set gradient color value for each pixel
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f);
rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) |
((r & 0xff) << 16) |
((g & 0xff) << 8) |
((b & 0xff));
index++;
}
}
}
private void generateHGradientImage(int[] rgbData) {
int[] startColor = getStartColor();
int[] endColor = getEndColor();
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0];
float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1];
float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2];
int a=255;
int r=0, g=0, b=0;
int index = 0;
for(int row=0; row<256; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<256; col++) {
// set gradient color value for each pixel
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f);
rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) |
((r & 0xff) << 16) |
((g & 0xff) << 8) |
((b & 0xff));
index++;
}
}
}
private void generateHVGradientImage(int[] rgbData) {
int[] startColor = getStartColor();
int[] endColor = getEndColor();
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0];
float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1];
float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2];
int a=255;
int r=0, g=0, b=0;
int index = 0;
float size = (float)Math.pow(255.0d, 2.0);
for(int row=0; row<256; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<256; col++) {
// set random color value for each pixel
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f);
rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) |
((r & 0xff) << 16) |
((g & 0xff) << 8) |
((b & 0xff));
index++;
}
}
}
public int[] getStartColor() {
return new int[]{246,53,138};
}
public int[] getEndColor() {
return new int[]{0,255,255};
}
public void setRGB( BufferedImage image, int x, int y, int width, int height, int[] pixels ) {
int type = image.getType();
if ( type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB || type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB )
image.getRaster().setDataElements( x, y, width, height, pixels );
else
image.setRGB( x, y, width, height, pixels, 0, width );
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Gradient Color Panel");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.getContentPane().setLayout(new BorderLayout());
// Display the window.
frame.getContentPane().add(new ColorGradientDemo(), BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(280,305));
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
语言也提供了Gradient的接口,但是想知道它是怎么实现的嘛?
本文介绍三种简单的颜色梯度变化算法,就可以很容易实现常见的梯度变化算法
三种都要求提供两个参数即起始颜色RGB值, 最终颜色RGB的值。
垂直梯度颜色变化,效果如下:

水平梯度颜色变化,效果如下:

水平与垂直两个方向叠加梯度变化效果如下:

算法代码及其解释
计算起始颜色和终点颜色RGB之间差值代码如下:
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0];
float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1];
float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2];
实现垂直梯度变化的代码如下:
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f);
实现水平梯度变化代码如下:
// set gradient color valuefor each pixel
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)col/255.0f) +0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)col/255.0f) +0.5f);
实现水平和垂直两个方向上Gradient叠加代码如下:
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f);
程序对上面三种Gradient方法分别放在三个不同的方法中,根据参数调用。
程序的完全Java源代码如下:
[java] view plaincopyimport java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.RenderingHints;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import javax.swing.JComponent;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class ColorGradientDemo extends JComponent {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4134440495899912869L;
private BufferedImage image = null;
protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) {
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D)g;
g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
g2.drawImage(getImage(4), 5, 5, image.getWidth(), image.getHeight(), null);
}
public BufferedImage getImage(int type) {
if(image == null) {
image = new BufferedImage(256, 256, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB);
int[] rgbData = new int[256*256];
if(type == 1) {
generateVGradientImage(rgbData);
} else if(type == 2) {
generateHGradientImage(rgbData);
} else {
generateHVGradientImage(rgbData);
}
setRGB(image, 0, 0, 256, 256, rgbData);
}
return image;
}
private void generateVGradientImage(int[] rgbData) {
int[] startColor = getStartColor();
int[] endColor = getEndColor();
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0];
float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1];
float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2];
int a=255;
int r=0, g=0, b=0;
int index = 0;
for(int row=0; row<256; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<256; col++) {
// set random color value for each pixel
// set gradient color value for each pixel
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f);
rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) |
((r & 0xff) << 16) |
((g & 0xff) << 8) |
((b & 0xff));
index++;
}
}
}
private void generateHGradientImage(int[] rgbData) {
int[] startColor = getStartColor();
int[] endColor = getEndColor();
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0];
float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1];
float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2];
int a=255;
int r=0, g=0, b=0;
int index = 0;
for(int row=0; row<256; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<256; col++) {
// set gradient color value for each pixel
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f);
rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) |
((r & 0xff) << 16) |
((g & 0xff) << 8) |
((b & 0xff));
index++;
}
}
}
private void generateHVGradientImage(int[] rgbData) {
int[] startColor = getStartColor();
int[] endColor = getEndColor();
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0];
float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1];
float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2];
int a=255;
int r=0, g=0, b=0;
int index = 0;
float size = (float)Math.pow(255.0d, 2.0);
for(int row=0; row<256; row++) {
for(int col=0; col<256; col++) {
// set random color value for each pixel
r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f);
g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f);
b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f);
rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) |
((r & 0xff) << 16) |
((g & 0xff) << 8) |
((b & 0xff));
index++;
}
}
}
public int[] getStartColor() {
return new int[]{246,53,138};
}
public int[] getEndColor() {
return new int[]{0,255,255};
}
public void setRGB( BufferedImage image, int x, int y, int width, int height, int[] pixels ) {
int type = image.getType();
if ( type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB || type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB )
image.getRaster().setDataElements( x, y, width, height, pixels );
else
image.setRGB( x, y, width, height, pixels, 0, width );
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame frame = new JFrame("Gradient Color Panel");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.getContentPane().setLayout(new BorderLayout());
// Display the window.
frame.getContentPane().add(new ColorGradientDemo(), BorderLayout.CENTER);
frame.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(280,305));
frame.pack();
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
相关文章推荐
- spark资料下载
- UITableViewCell 分割线左对齐
- iOS 集成银联支付(绕过文档的坑,快速集成)
- html 上下左右都居中
- 图像处理------噪声之美 - 随机噪声产生
- 图像处理------噪声之美 - 随机噪声产生
- 修改端口
- 产品编辑
- Android:太多东西显示不完?用ScrollView吧
- 对RadioButton和CheckBox的一些总结
- 四季歌吉他谱
- 图像处理------噪声之美 - 随机噪声产生
- 获取linux系统的cup信息,内存信息c代码
- sendmail笔记
- 什么是文件的共享,试简述用文件路径名加快文件查找的两种方法。
- 图像处理------噪声之美 - 随机噪声产生 分类: 视频图像处理 2015-07-24 09:22 26人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
- HDU 5303 Delicious Apples (2015多校第二场 贪心 + 枚举)
- 图像处理------透明混合 - Alpha Blending效果
- 图像处理------透明混合 - Alpha Blending效果
- product_category
