胜者树与败者树
2014-12-21 22:34
274 查看
http://blog.csdn.net/whz_zb/article/details/7425152
胜者树与败者树
胜者树和败者树都是完全二叉树,是树形选择排序的一种变型。每个叶子结点相当于一个选手,每个中间结点相当于一场比赛,每一层相当于一轮比赛。
不同的是,胜者树的中间结点记录的是胜者的标号;而败者树的中间结点记录的败者的标号。
胜者树与败者树可以在log(n)的时间内找到最值。任何一个叶子结点的值改变后,利用中间结点的信息,还是能够快速地找到最值。在k路归并排序中经常用到。
一、胜者树
胜者树的一个优点是,如果一个选手的值改变了,可以很容易地修改这棵胜者树。只需要沿着从该结点到根结点的路径修改这棵二叉树,而不必改变其他比赛的结果。
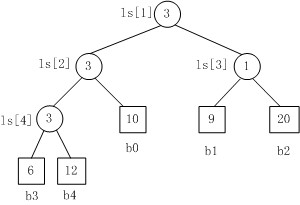
Fig. 1
Fig.1是一个胜者树的示例。规定数值小者胜。
1. b3 PK b4,b3胜b4负,内部结点ls[4]的值为3;
2. b3 PK b0,b3胜b0负,内部结点ls[2]的值为3;
3. b1 PK b2,b1胜b2负,内部结点ls[3]的值为1;
4. b3 PK b1,b3胜b1负,内部结点ls[1]的值为3。.
当Fig. 1中叶子结点b3的值变为11时,重构的胜者树如Fig. 2所示。
1. b3 PK b4,b3胜b4负,内部结点ls[4]的值为3;
2. b3 PK b0,b0胜b3负,内部结点ls[2]的值为0;
3. b1 PK b2,b1胜b2负,内部结点ls[3]的值为1;
4. b0 PK b1,b1胜b0负,内部结点ls[1]的值为1。.
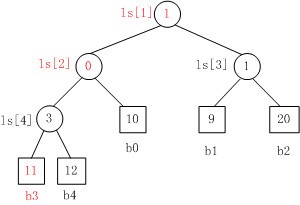
Fig. 2
二、败者树
败者树是胜者树的一种变体。在败者树中,用父结点记录其左右子结点进行比赛的败者,而让胜者参加下一轮的比赛。败者树的根结点记录的是败者,需要加一个结点来记录整个比赛的胜利者。采用败者树可以简化重构的过程。
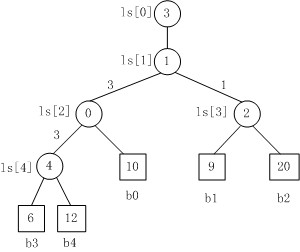
Fig. 3
Fig. 3是一棵败者树。规定数大者败。
1. b3 PK b4,b3胜b4负,内部结点ls[4]的值为4;
2. b3 PK b0,b3胜b0负,内部结点ls[2]的值为0;
3. b1 PK b2,b1胜b2负,内部结点ls[3]的值为2;
4. b3 PK b1,b3胜b1负,内部结点ls[1]的值为1;
5. 在根结点ls[1]上又加了一个结点ls[0]=3,记录的最后的胜者。
败者树重构过程如下:
· 将新进入选择树的结点与其父结点进行比赛:将败者存放在父结点中;而胜者再与上一级的父结点比较。
· 比赛沿着到根结点的路径不断进行,直到ls[1]处。把败者存放在结点ls[1]中,胜者存放在ls[0]中。
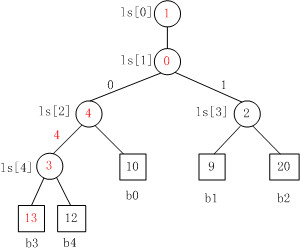
Fig. 4
Fig. 4是当b3变为13时,败者树的重构图。
注意,败者树的重构跟胜者树是不一样的,败者树的重构只需要与其父结点比较。对照Fig. 3来看,b3与结点ls[4]的原值比较,ls[4]中存放的原值是结点4,即b3与b4比较,b3负b4胜,则修改ls[4]的值为结点3。同理,以此类推,沿着根结点不断比赛,直至结束。
由上可知,败者树简化了重构。败者树的重构只是与该结点的父结点的记录有关,而胜者树的重构还与该结点的兄弟结点有关。
一 外部排序的基本思路
假设有一个72KB的文件,其中存储了18K个整数,磁盘中物理块的大小为4KB,将文件分成18组,每组刚好4KB。
首先通过18次内部排序,把18组数据排好序,得到初始的18个归并段R1~R18,每个归并段有1024个整数。
然后对这18个归并段使用4路平衡归并排序:
第1次归并:产生5个归并段
R11 R12 R13 R14 R15
其中
R11是由{R1,R2,R3,R4}中的数据合并而来
R12是由{R5,R6,R7,R8}中的数据合并而来
R13是由{R9,R10,R11,R12}中的数据合并而来
R14是由{R13,R14,R15,R16}中的数据合并而来
R15是由{R17,R18}中的数据合并而来
把这5个归并段的数据写入5个文件:
foo_1.dat foo_2.dat foo_3.dat foo_4.dat foo_5.dat
第2次归并:从第1次归并产生的5个文件中读取数据,合并,产生2个归并段
R21 R22
其中R21是由{R11,R12,R13,R14}中的数据合并而来
其中R22是由{R15}中的数据合并而来
把这2个归并段写入2个文件
bar_1.dat bar_2.dat
第3次归并:从第2次归并产生的2个文件中读取数据,合并,产生1个归并段
R31
R31是由{R21,R22}中的数据合并而来
把这个文件写入1个文件
foo_1.dat
此即为最终排序好的文件。
二 使用败者树加快合并排序
外部排序最耗时间的操作时磁盘读写,对于有m个初始归并段,k路平衡的归并排序,磁盘读写次数为
|logkm|,可见增大k的值可以减少磁盘读写的次数,但增大k的值也会带来负面效应,即进行k路合并
的时候会增加算法复杂度,来看一个例子。
把n个整数分成k组,每组整数都已排序好,现在要把k组数据合并成1组排好序的整数,求算法复杂度
u1: xxxxxxxx
u2: xxxxxxxx
u3: xxxxxxxx
.......
uk: xxxxxxxx
算法的步骤是:每次从k个组中的首元素中选一个最小的数,加入到新组,这样每次都要比较k-1次,故
算法复杂度为O((n-1)*(k-1)),而如果使用败者树,可以在O(logk)的复杂度下得到最小的数,算法复杂
度将为O((n-1)*logk), 对于外部排序这种数据量超大的排序来说,这是一个不小的提高。
关于败者树的创建和调整,可以参考清华大学《数据结构-C语言版》
三 产生二进制测试数据
打开Linux终端,输入命令
dd if=/dev/urandom of=random.dat bs=1M count=512
这样在当前目录下产生一个512M大的二进制文件,文件内的数据是随机的,读取文件,每4个字节
看成1个整数,相当于得到128M个随机整数。
四 程序实现
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
#include <assert.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define MAX_INT ~(1<<31)
#define MIN_INT 1<<31
//#define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
#define debug(...) debug( __VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...)
#endif
#define MAX_WAYS 100
typedef struct run_t {
int *buf; /* 输入缓冲区 */
int length; /* 缓冲区当前有多少个数 */
int offset; /* 缓冲区读到了文件的哪个位置 */
int idx; /* 缓冲区的指针 */
} run_t;
static unsigned int K; /* K路合并 */
static unsigned int BUF_PAGES; /* 缓冲区有多少个page */
static unsigned int PAGE_SIZE; /* page的大小 */
static unsigned int BUF_SIZE; /* 缓冲区的大小, BUF_SIZE = BUF_PAGES*PAGE_SIZE */
static int *buffer; /* 输出缓冲区 */
static char input_prefix[] = "foo_";
static char output_prefix[] = "bar_";
static int ls[MAX_WAYS]; /* loser tree */
void swap(int *p, int *q);
int partition(int *a, int s, int t);
void quick_sort(int *a, int s, int t);
void adjust(run_t ** runs, int n, int s);
void create_loser_tree(run_t **runs, int n);
long get_time_usecs();
void k_merge(run_t** runs, char* input_prefix, int num_runs, int base, int n_merge);
void usage();
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char filename[100];
unsigned int data_size;
unsigned int num_runs; /* 这轮迭代时有多少个归并段 */
unsigned int num_merges; /* 这轮迭代后产生多少个归并段 num_merges = num_runs/K */
unsigned int run_length; /* 归并段的长度,指数级增长 */
unsigned int num_runs_in_merge; /* 一般每个merge由K个runs合并而来,但最后一个merge可能少于K个runs */
int fd, rv, i, j, bytes;
struct stat sbuf;
if (argc != 3) {
usage();
return 0;
}
long start_usecs = get_time_usecs();
strcpy(filename, argv[1]);
fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("can't open file %s\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
rv = fstat(fd, &sbuf);
data_size = sbuf.st_size;
K = atoi(argv[2]);
PAGE_SIZE = 4096; /* page = 4KB */
BUF_PAGES = 32;
BUF_SIZE = PAGE_SIZE*BUF_PAGES;
num_runs = data_size / PAGE_SIZE; /* 初始时的归并段数量,每个归并段有4096 byte, 即1024个整数 */
buffer = (int *)malloc(BUF_SIZE);
run_length = 1;
run_t **runs = (run_t **)malloc(sizeof(run_t *)*(K+1));
for (i = 0; i < K; i++) {
runs[i] = (run_t *)malloc(sizeof(run_t));
runs[i]->buf = (int *)calloc(1, BUF_SIZE+4);
}
while (num_runs > 1) {
num_merges = num_runs / K;
int left_runs = num_runs % K;
if(left_runs > 0) num_merges++;
for (i = 0; i < num_merges; i++) {
num_runs_in_merge = K;
if ((i+1) == num_merges && left_runs > 0) {
num_runs_in_merge = left_runs;
}
int base = 0;
printf("Merge %d of %d,%d ways\n", i, num_merges, num_runs_in_merge);
for (j = 0; j < num_runs_in_merge; j++) {
if (run_length == 1) {
base = 1;
bytes = read(fd, runs[j]->buf, PAGE_SIZE);
runs[j]->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
quick_sort(runs[j]->buf, 0, runs[j]->length-1);
} else {
snprintf(filename, 20, "%s%d.dat", input_prefix, i*K+j);
int infd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
bytes = read(infd, runs[j]->buf, BUF_SIZE);
runs[j]->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
close(infd);
}
runs[j]->idx = 0;
runs[j]->offset = bytes;
}
k_merge(runs, input_prefix, num_runs_in_merge, base, i);
}
strcpy(filename, output_prefix);
strcpy(output_prefix, input_prefix);
strcpy(input_prefix, filename);
run_length *= K;
num_runs = num_merges;
}
for (i = 0; i < K; i++) {
free(runs[i]->buf);
free(runs[i]);
}
free(runs);
free(buffer);
close(fd);
long end_usecs = get_time_usecs();
double secs = (double)(end_usecs - start_usecs) / (double)1000000;
printf("Sorting took %.02f seconds.\n", secs);
printf("sorting result saved in %s%d.dat.\n", input_prefix, 0);
return 0;
}
void k_merge(run_t** runs, char* input_prefix, int num_runs, int base, int n_merge)
{
int bp, bytes, output_fd;
int live_runs = num_runs;
run_t *mr;
char filename[20];
bp = 0;
create_loser_tree(runs, num_runs);
snprintf(filename, 100, "%s%d.dat", output_prefix, n_merge);
output_fd = open(filename, O_CREAT|O_WRONLY|O_TRUNC,
S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG);
if (output_fd < 0) {
printf("create file %s fail\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
while (live_runs > 0) {
mr = runs[ls[0]];
buffer[bp++] = mr->buf[mr->idx++];
// 输出缓冲区已满
if (bp*4 == BUF_SIZE) {
bytes = write(output_fd, buffer, BUF_SIZE);
bp = 0;
}
// mr的输入缓冲区用完
if (mr->idx == mr->length) {
snprintf(filename, 20, "%s%d.dat", input_prefix, ls[0]+n_merge*K);
if (base) {
mr->buf[mr->idx] = MAX_INT;
live_runs--;
} else {
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
lseek(fd, mr->offset, SEEK_SET);
bytes = read(fd, mr->buf, BUF_SIZE);
close(fd);
if (bytes == 0) {
mr->buf[mr->idx] = MAX_INT;
live_runs--;
}
else {
mr->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
mr->offset += bytes;
mr->idx = 0;
}
}
}
adjust(runs, num_runs, ls[0]);
}
bytes = write(output_fd, buffer, bp*4);
if (bytes != bp*4) {
printf("!!!!!! Write Error !!!!!!!!!\n");
exit(0);
}
close(output_fd);
}
long get_time_usecs()
{
struct timeval time;
struct timezone tz;
memset(&tz, '\0', sizeof(struct timezone));
gettimeofday(&time, &tz);
long usecs = time.tv_sec*1000000 + time.tv_usec;
return usecs;
}
void swap(int *p, int *q)
{
int tmp;
tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
}
int partition(int *a, int s, int t)
{
int i, j; /* i用来遍历a[s]...a[t-1], j指向大于x部分的第一个元素 */
for (i = j = s; i < t; i++) {
if (a[i] < a[t]) {
swap(a+i, a+j);
j++;
}
}
swap(a+j, a+t);
return j;
}
void quick_sort(int *a, int s, int t)
{
int p;
if (s < t) {
p = partition(a, s, t);
quick_sort(a, s, p-1);
quick_sort(a, p+1, t);
}
}
void adjust(run_t ** runs, int n, int s)
{
int t, tmp;
t = (s+n)/2;
while (t > 0) {
if (s == -1) {
break;
}
if (ls[t] == -1 || runs[s]->buf[runs[s]->idx] > runs[ls[t]]->buf[runs[ls[t]]->idx]) {
tmp = s;
s = ls[t];
ls[t] = tmp;
}
t >>= 1;
}
ls[0] = s;
}
void create_loser_tree(run_t **runs, int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ls[i] = -1;
}
for (i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjust(runs, n, i);
}
}
void usage()
{
printf("sort <filename> <K-ways>\n");
printf("\tfilename: filename of file to be sorted\n");
printf("\tK-ways: how many ways to merge\n");
exit(1);
}
五 编译运行
gcc sort.c -o sort -g
./sort random.dat 64
以64路平衡归并对random.dat内的数据进行外部排序。在I5处理器,4G内存的硬件环境下,实验结果如下
文件大小 耗时
128M 14.72 秒
256M 30.89 秒
512M 71.65 秒
1G 169.18秒
六 读取二进制文件,查看排序结
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
#include <assert.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char *filename = argv[1];
int *buffer = (int *)malloc(1<<20);
struct stat sbuf;
int rv, data_size, i, bytes, fd;
fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("%s not found!\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
rv = fstat(fd, &sbuf);
data_size = sbuf.st_size;
bytes = read(fd, buffer, data_size);
for (i = 0; i < bytes/4; i++) {
printf("%d ", buffer[i]);
if ((i+1) % 10 == 0) {
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("\n");
close(fd);
free(buffer);
return 0;
}
http://blog.csdn.net/whz_zb/article/details/7425152
胜者树与败者树
胜者树和败者树都是完全二叉树,是树形选择排序的一种变型。每个叶子结点相当于一个选手,每个中间结点相当于一场比赛,每一层相当于一轮比赛。
不同的是,胜者树的中间结点记录的是胜者的标号;而败者树的中间结点记录的败者的标号。
胜者树与败者树可以在log(n)的时间内找到最值。任何一个叶子结点的值改变后,利用中间结点的信息,还是能够快速地找到最值。在k路归并排序中经常用到。
一、胜者树
胜者树的一个优点是,如果一个选手的值改变了,可以很容易地修改这棵胜者树。只需要沿着从该结点到根结点的路径修改这棵二叉树,而不必改变其他比赛的结果。

Fig. 1
Fig.1是一个胜者树的示例。规定数值小者胜。
1. b3 PK b4,b3胜b4负,内部结点ls[4]的值为3;
2. b3 PK b0,b3胜b0负,内部结点ls[2]的值为3;
3. b1 PK b2,b1胜b2负,内部结点ls[3]的值为1;
4. b3 PK b1,b3胜b1负,内部结点ls[1]的值为3。.
当Fig. 1中叶子结点b3的值变为11时,重构的胜者树如Fig. 2所示。
1. b3 PK b4,b3胜b4负,内部结点ls[4]的值为3;
2. b3 PK b0,b0胜b3负,内部结点ls[2]的值为0;
3. b1 PK b2,b1胜b2负,内部结点ls[3]的值为1;
4. b0 PK b1,b1胜b0负,内部结点ls[1]的值为1。.

Fig. 2
二、败者树
败者树是胜者树的一种变体。在败者树中,用父结点记录其左右子结点进行比赛的败者,而让胜者参加下一轮的比赛。败者树的根结点记录的是败者,需要加一个结点来记录整个比赛的胜利者。采用败者树可以简化重构的过程。

Fig. 3
Fig. 3是一棵败者树。规定数大者败。
1. b3 PK b4,b3胜b4负,内部结点ls[4]的值为4;
2. b3 PK b0,b3胜b0负,内部结点ls[2]的值为0;
3. b1 PK b2,b1胜b2负,内部结点ls[3]的值为2;
4. b3 PK b1,b3胜b1负,内部结点ls[1]的值为1;
5. 在根结点ls[1]上又加了一个结点ls[0]=3,记录的最后的胜者。
败者树重构过程如下:
· 将新进入选择树的结点与其父结点进行比赛:将败者存放在父结点中;而胜者再与上一级的父结点比较。
· 比赛沿着到根结点的路径不断进行,直到ls[1]处。把败者存放在结点ls[1]中,胜者存放在ls[0]中。

Fig. 4
Fig. 4是当b3变为13时,败者树的重构图。
注意,败者树的重构跟胜者树是不一样的,败者树的重构只需要与其父结点比较。对照Fig. 3来看,b3与结点ls[4]的原值比较,ls[4]中存放的原值是结点4,即b3与b4比较,b3负b4胜,则修改ls[4]的值为结点3。同理,以此类推,沿着根结点不断比赛,直至结束。
由上可知,败者树简化了重构。败者树的重构只是与该结点的父结点的记录有关,而胜者树的重构还与该结点的兄弟结点有关。
败者树 多路平衡归并外部排序
一 外部排序的基本思路假设有一个72KB的文件,其中存储了18K个整数,磁盘中物理块的大小为4KB,将文件分成18组,每组刚好4KB。
首先通过18次内部排序,把18组数据排好序,得到初始的18个归并段R1~R18,每个归并段有1024个整数。
然后对这18个归并段使用4路平衡归并排序:
第1次归并:产生5个归并段
R11 R12 R13 R14 R15
其中
R11是由{R1,R2,R3,R4}中的数据合并而来
R12是由{R5,R6,R7,R8}中的数据合并而来
R13是由{R9,R10,R11,R12}中的数据合并而来
R14是由{R13,R14,R15,R16}中的数据合并而来
R15是由{R17,R18}中的数据合并而来
把这5个归并段的数据写入5个文件:
foo_1.dat foo_2.dat foo_3.dat foo_4.dat foo_5.dat
第2次归并:从第1次归并产生的5个文件中读取数据,合并,产生2个归并段
R21 R22
其中R21是由{R11,R12,R13,R14}中的数据合并而来
其中R22是由{R15}中的数据合并而来
把这2个归并段写入2个文件
bar_1.dat bar_2.dat
第3次归并:从第2次归并产生的2个文件中读取数据,合并,产生1个归并段
R31
R31是由{R21,R22}中的数据合并而来
把这个文件写入1个文件
foo_1.dat
此即为最终排序好的文件。
二 使用败者树加快合并排序
外部排序最耗时间的操作时磁盘读写,对于有m个初始归并段,k路平衡的归并排序,磁盘读写次数为
|logkm|,可见增大k的值可以减少磁盘读写的次数,但增大k的值也会带来负面效应,即进行k路合并
的时候会增加算法复杂度,来看一个例子。
把n个整数分成k组,每组整数都已排序好,现在要把k组数据合并成1组排好序的整数,求算法复杂度
u1: xxxxxxxx
u2: xxxxxxxx
u3: xxxxxxxx
.......
uk: xxxxxxxx
算法的步骤是:每次从k个组中的首元素中选一个最小的数,加入到新组,这样每次都要比较k-1次,故
算法复杂度为O((n-1)*(k-1)),而如果使用败者树,可以在O(logk)的复杂度下得到最小的数,算法复杂
度将为O((n-1)*logk), 对于外部排序这种数据量超大的排序来说,这是一个不小的提高。
关于败者树的创建和调整,可以参考清华大学《数据结构-C语言版》
三 产生二进制测试数据
打开Linux终端,输入命令
dd if=/dev/urandom of=random.dat bs=1M count=512
这样在当前目录下产生一个512M大的二进制文件,文件内的数据是随机的,读取文件,每4个字节
看成1个整数,相当于得到128M个随机整数。
四 程序实现
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
#include <assert.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define MAX_INT ~(1<<31)
#define MIN_INT 1<<31
//#define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
#define debug(...) debug( __VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...)
#endif
#define MAX_WAYS 100
typedef struct run_t {
int *buf; /* 输入缓冲区 */
int length; /* 缓冲区当前有多少个数 */
int offset; /* 缓冲区读到了文件的哪个位置 */
int idx; /* 缓冲区的指针 */
} run_t;
static unsigned int K; /* K路合并 */
static unsigned int BUF_PAGES; /* 缓冲区有多少个page */
static unsigned int PAGE_SIZE; /* page的大小 */
static unsigned int BUF_SIZE; /* 缓冲区的大小, BUF_SIZE = BUF_PAGES*PAGE_SIZE */
static int *buffer; /* 输出缓冲区 */
static char input_prefix[] = "foo_";
static char output_prefix[] = "bar_";
static int ls[MAX_WAYS]; /* loser tree */
void swap(int *p, int *q);
int partition(int *a, int s, int t);
void quick_sort(int *a, int s, int t);
void adjust(run_t ** runs, int n, int s);
void create_loser_tree(run_t **runs, int n);
long get_time_usecs();
void k_merge(run_t** runs, char* input_prefix, int num_runs, int base, int n_merge);
void usage();
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char filename[100];
unsigned int data_size;
unsigned int num_runs; /* 这轮迭代时有多少个归并段 */
unsigned int num_merges; /* 这轮迭代后产生多少个归并段 num_merges = num_runs/K */
unsigned int run_length; /* 归并段的长度,指数级增长 */
unsigned int num_runs_in_merge; /* 一般每个merge由K个runs合并而来,但最后一个merge可能少于K个runs */
int fd, rv, i, j, bytes;
struct stat sbuf;
if (argc != 3) {
usage();
return 0;
}
long start_usecs = get_time_usecs();
strcpy(filename, argv[1]);
fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("can't open file %s\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
rv = fstat(fd, &sbuf);
data_size = sbuf.st_size;
K = atoi(argv[2]);
PAGE_SIZE = 4096; /* page = 4KB */
BUF_PAGES = 32;
BUF_SIZE = PAGE_SIZE*BUF_PAGES;
num_runs = data_size / PAGE_SIZE; /* 初始时的归并段数量,每个归并段有4096 byte, 即1024个整数 */
buffer = (int *)malloc(BUF_SIZE);
run_length = 1;
run_t **runs = (run_t **)malloc(sizeof(run_t *)*(K+1));
for (i = 0; i < K; i++) {
runs[i] = (run_t *)malloc(sizeof(run_t));
runs[i]->buf = (int *)calloc(1, BUF_SIZE+4);
}
while (num_runs > 1) {
num_merges = num_runs / K;
int left_runs = num_runs % K;
if(left_runs > 0) num_merges++;
for (i = 0; i < num_merges; i++) {
num_runs_in_merge = K;
if ((i+1) == num_merges && left_runs > 0) {
num_runs_in_merge = left_runs;
}
int base = 0;
printf("Merge %d of %d,%d ways\n", i, num_merges, num_runs_in_merge);
for (j = 0; j < num_runs_in_merge; j++) {
if (run_length == 1) {
base = 1;
bytes = read(fd, runs[j]->buf, PAGE_SIZE);
runs[j]->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
quick_sort(runs[j]->buf, 0, runs[j]->length-1);
} else {
snprintf(filename, 20, "%s%d.dat", input_prefix, i*K+j);
int infd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
bytes = read(infd, runs[j]->buf, BUF_SIZE);
runs[j]->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
close(infd);
}
runs[j]->idx = 0;
runs[j]->offset = bytes;
}
k_merge(runs, input_prefix, num_runs_in_merge, base, i);
}
strcpy(filename, output_prefix);
strcpy(output_prefix, input_prefix);
strcpy(input_prefix, filename);
run_length *= K;
num_runs = num_merges;
}
for (i = 0; i < K; i++) {
free(runs[i]->buf);
free(runs[i]);
}
free(runs);
free(buffer);
close(fd);
long end_usecs = get_time_usecs();
double secs = (double)(end_usecs - start_usecs) / (double)1000000;
printf("Sorting took %.02f seconds.\n", secs);
printf("sorting result saved in %s%d.dat.\n", input_prefix, 0);
return 0;
}
void k_merge(run_t** runs, char* input_prefix, int num_runs, int base, int n_merge)
{
int bp, bytes, output_fd;
int live_runs = num_runs;
run_t *mr;
char filename[20];
bp = 0;
create_loser_tree(runs, num_runs);
snprintf(filename, 100, "%s%d.dat", output_prefix, n_merge);
output_fd = open(filename, O_CREAT|O_WRONLY|O_TRUNC,
S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG);
if (output_fd < 0) {
printf("create file %s fail\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
while (live_runs > 0) {
mr = runs[ls[0]];
buffer[bp++] = mr->buf[mr->idx++];
// 输出缓冲区已满
if (bp*4 == BUF_SIZE) {
bytes = write(output_fd, buffer, BUF_SIZE);
bp = 0;
}
// mr的输入缓冲区用完
if (mr->idx == mr->length) {
snprintf(filename, 20, "%s%d.dat", input_prefix, ls[0]+n_merge*K);
if (base) {
mr->buf[mr->idx] = MAX_INT;
live_runs--;
} else {
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
lseek(fd, mr->offset, SEEK_SET);
bytes = read(fd, mr->buf, BUF_SIZE);
close(fd);
if (bytes == 0) {
mr->buf[mr->idx] = MAX_INT;
live_runs--;
}
else {
mr->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
mr->offset += bytes;
mr->idx = 0;
}
}
}
adjust(runs, num_runs, ls[0]);
}
bytes = write(output_fd, buffer, bp*4);
if (bytes != bp*4) {
printf("!!!!!! Write Error !!!!!!!!!\n");
exit(0);
}
close(output_fd);
}
long get_time_usecs()
{
struct timeval time;
struct timezone tz;
memset(&tz, '\0', sizeof(struct timezone));
gettimeofday(&time, &tz);
long usecs = time.tv_sec*1000000 + time.tv_usec;
return usecs;
}
void swap(int *p, int *q)
{
int tmp;
tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
}
int partition(int *a, int s, int t)
{
int i, j; /* i用来遍历a[s]...a[t-1], j指向大于x部分的第一个元素 */
for (i = j = s; i < t; i++) {
if (a[i] < a[t]) {
swap(a+i, a+j);
j++;
}
}
swap(a+j, a+t);
return j;
}
void quick_sort(int *a, int s, int t)
{
int p;
if (s < t) {
p = partition(a, s, t);
quick_sort(a, s, p-1);
quick_sort(a, p+1, t);
}
}
void adjust(run_t ** runs, int n, int s)
{
int t, tmp;
t = (s+n)/2;
while (t > 0) {
if (s == -1) {
break;
}
if (ls[t] == -1 || runs[s]->buf[runs[s]->idx] > runs[ls[t]]->buf[runs[ls[t]]->idx]) {
tmp = s;
s = ls[t];
ls[t] = tmp;
}
t >>= 1;
}
ls[0] = s;
}
void create_loser_tree(run_t **runs, int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ls[i] = -1;
}
for (i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjust(runs, n, i);
}
}
void usage()
{
printf("sort <filename> <K-ways>\n");
printf("\tfilename: filename of file to be sorted\n");
printf("\tK-ways: how many ways to merge\n");
exit(1);
}
#include <assert.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#define MAX_INT ~(1<<31)
#define MIN_INT 1<<31
//#define DEBUG
#ifdef DEBUG
#define debug(...) debug( __VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define debug(...)
#endif
#define MAX_WAYS 100
typedef struct run_t {
int *buf; /* 输入缓冲区 */
int length; /* 缓冲区当前有多少个数 */
int offset; /* 缓冲区读到了文件的哪个位置 */
int idx; /* 缓冲区的指针 */
} run_t;
static unsigned int K; /* K路合并 */
static unsigned int BUF_PAGES; /* 缓冲区有多少个page */
static unsigned int PAGE_SIZE; /* page的大小 */
static unsigned int BUF_SIZE; /* 缓冲区的大小, BUF_SIZE = BUF_PAGES*PAGE_SIZE */
static int *buffer; /* 输出缓冲区 */
static char input_prefix[] = "foo_";
static char output_prefix[] = "bar_";
static int ls[MAX_WAYS]; /* loser tree */
void swap(int *p, int *q);
int partition(int *a, int s, int t);
void quick_sort(int *a, int s, int t);
void adjust(run_t ** runs, int n, int s);
void create_loser_tree(run_t **runs, int n);
long get_time_usecs();
void k_merge(run_t** runs, char* input_prefix, int num_runs, int base, int n_merge);
void usage();
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char filename[100];
unsigned int data_size;
unsigned int num_runs; /* 这轮迭代时有多少个归并段 */
unsigned int num_merges; /* 这轮迭代后产生多少个归并段 num_merges = num_runs/K */
unsigned int run_length; /* 归并段的长度,指数级增长 */
unsigned int num_runs_in_merge; /* 一般每个merge由K个runs合并而来,但最后一个merge可能少于K个runs */
int fd, rv, i, j, bytes;
struct stat sbuf;
if (argc != 3) {
usage();
return 0;
}
long start_usecs = get_time_usecs();
strcpy(filename, argv[1]);
fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("can't open file %s\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
rv = fstat(fd, &sbuf);
data_size = sbuf.st_size;
K = atoi(argv[2]);
PAGE_SIZE = 4096; /* page = 4KB */
BUF_PAGES = 32;
BUF_SIZE = PAGE_SIZE*BUF_PAGES;
num_runs = data_size / PAGE_SIZE; /* 初始时的归并段数量,每个归并段有4096 byte, 即1024个整数 */
buffer = (int *)malloc(BUF_SIZE);
run_length = 1;
run_t **runs = (run_t **)malloc(sizeof(run_t *)*(K+1));
for (i = 0; i < K; i++) {
runs[i] = (run_t *)malloc(sizeof(run_t));
runs[i]->buf = (int *)calloc(1, BUF_SIZE+4);
}
while (num_runs > 1) {
num_merges = num_runs / K;
int left_runs = num_runs % K;
if(left_runs > 0) num_merges++;
for (i = 0; i < num_merges; i++) {
num_runs_in_merge = K;
if ((i+1) == num_merges && left_runs > 0) {
num_runs_in_merge = left_runs;
}
int base = 0;
printf("Merge %d of %d,%d ways\n", i, num_merges, num_runs_in_merge);
for (j = 0; j < num_runs_in_merge; j++) {
if (run_length == 1) {
base = 1;
bytes = read(fd, runs[j]->buf, PAGE_SIZE);
runs[j]->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
quick_sort(runs[j]->buf, 0, runs[j]->length-1);
} else {
snprintf(filename, 20, "%s%d.dat", input_prefix, i*K+j);
int infd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
bytes = read(infd, runs[j]->buf, BUF_SIZE);
runs[j]->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
close(infd);
}
runs[j]->idx = 0;
runs[j]->offset = bytes;
}
k_merge(runs, input_prefix, num_runs_in_merge, base, i);
}
strcpy(filename, output_prefix);
strcpy(output_prefix, input_prefix);
strcpy(input_prefix, filename);
run_length *= K;
num_runs = num_merges;
}
for (i = 0; i < K; i++) {
free(runs[i]->buf);
free(runs[i]);
}
free(runs);
free(buffer);
close(fd);
long end_usecs = get_time_usecs();
double secs = (double)(end_usecs - start_usecs) / (double)1000000;
printf("Sorting took %.02f seconds.\n", secs);
printf("sorting result saved in %s%d.dat.\n", input_prefix, 0);
return 0;
}
void k_merge(run_t** runs, char* input_prefix, int num_runs, int base, int n_merge)
{
int bp, bytes, output_fd;
int live_runs = num_runs;
run_t *mr;
char filename[20];
bp = 0;
create_loser_tree(runs, num_runs);
snprintf(filename, 100, "%s%d.dat", output_prefix, n_merge);
output_fd = open(filename, O_CREAT|O_WRONLY|O_TRUNC,
S_IRWXU|S_IRWXG);
if (output_fd < 0) {
printf("create file %s fail\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
while (live_runs > 0) {
mr = runs[ls[0]];
buffer[bp++] = mr->buf[mr->idx++];
// 输出缓冲区已满
if (bp*4 == BUF_SIZE) {
bytes = write(output_fd, buffer, BUF_SIZE);
bp = 0;
}
// mr的输入缓冲区用完
if (mr->idx == mr->length) {
snprintf(filename, 20, "%s%d.dat", input_prefix, ls[0]+n_merge*K);
if (base) {
mr->buf[mr->idx] = MAX_INT;
live_runs--;
} else {
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
lseek(fd, mr->offset, SEEK_SET);
bytes = read(fd, mr->buf, BUF_SIZE);
close(fd);
if (bytes == 0) {
mr->buf[mr->idx] = MAX_INT;
live_runs--;
}
else {
mr->length = bytes/sizeof(int);
mr->offset += bytes;
mr->idx = 0;
}
}
}
adjust(runs, num_runs, ls[0]);
}
bytes = write(output_fd, buffer, bp*4);
if (bytes != bp*4) {
printf("!!!!!! Write Error !!!!!!!!!\n");
exit(0);
}
close(output_fd);
}
long get_time_usecs()
{
struct timeval time;
struct timezone tz;
memset(&tz, '\0', sizeof(struct timezone));
gettimeofday(&time, &tz);
long usecs = time.tv_sec*1000000 + time.tv_usec;
return usecs;
}
void swap(int *p, int *q)
{
int tmp;
tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
}
int partition(int *a, int s, int t)
{
int i, j; /* i用来遍历a[s]...a[t-1], j指向大于x部分的第一个元素 */
for (i = j = s; i < t; i++) {
if (a[i] < a[t]) {
swap(a+i, a+j);
j++;
}
}
swap(a+j, a+t);
return j;
}
void quick_sort(int *a, int s, int t)
{
int p;
if (s < t) {
p = partition(a, s, t);
quick_sort(a, s, p-1);
quick_sort(a, p+1, t);
}
}
void adjust(run_t ** runs, int n, int s)
{
int t, tmp;
t = (s+n)/2;
while (t > 0) {
if (s == -1) {
break;
}
if (ls[t] == -1 || runs[s]->buf[runs[s]->idx] > runs[ls[t]]->buf[runs[ls[t]]->idx]) {
tmp = s;
s = ls[t];
ls[t] = tmp;
}
t >>= 1;
}
ls[0] = s;
}
void create_loser_tree(run_t **runs, int n)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ls[i] = -1;
}
for (i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
adjust(runs, n, i);
}
}
void usage()
{
printf("sort <filename> <K-ways>\n");
printf("\tfilename: filename of file to be sorted\n");
printf("\tK-ways: how many ways to merge\n");
exit(1);
}五 编译运行
gcc sort.c -o sort -g
./sort random.dat 64
以64路平衡归并对random.dat内的数据进行外部排序。在I5处理器,4G内存的硬件环境下,实验结果如下
文件大小 耗时
128M 14.72 秒
256M 30.89 秒
512M 71.65 秒
1G 169.18秒
六 读取二进制文件,查看排序结
[cpp]
view plaincopyprint?
#include <assert.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char *filename = argv[1];
int *buffer = (int *)malloc(1<<20);
struct stat sbuf;
int rv, data_size, i, bytes, fd;
fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
printf("%s not found!\n", filename);
exit(0);
}
rv = fstat(fd, &sbuf);
data_size = sbuf.st_size;
bytes = read(fd, buffer, data_size);
for (i = 0; i < bytes/4; i++) {
printf("%d ", buffer[i]);
if ((i+1) % 10 == 0) {
printf("\n");
}
}
printf("\n");
close(fd);
free(buffer);
return 0;
}
