POJ 2417 Discrete Logging 离散对数
2014-08-04 17:04
465 查看
链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2417
题意:
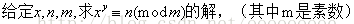
思路:求离散对数,Baby Step Giant Step算法基本应用。
以下转载自:AekdyCoin
【普通Baby Step Giant Step】
【问题模型】
求解
A^x = B (mod C) 中 0 <= x < C 的解,C 为素数
【思路】
我们可以做一个等价
x = i * m + j ( 0 <= i < m, 0 <=j < m) m = Ceil ( sqrt( C) )
而这么分解的目的无非是为了转化为:
(A^i)^m * A^j = B ( mod C)
之后做少许暴力的工作就可以解决问题:
(1) for i = 0 -> m, 插入Hash (i, A^i mod C)
(2) 枚举 i ,对于每一个枚举到的i,令 AA = (A^m)^i mod C
我们有
AA * A^j = B (mod C)
显然AA,B,C均已知,而由于C为素数,那么(AA,C)无条件为1
于是对于这个模方程解的个数唯一(可以利用扩展欧几里得或 欧拉定理来求解)
那么对于得到的唯一解X,在Hash表中寻找,如果找到,则返回 i * m + j
注意:由于i从小到大的枚举,而Hash表中存在的j必然是对于某个剩余系内的元素X 是最小的(就是指标)
所以显然此时就可以得到最小解
如果需要得到 x > 0的解,那么只需要在上面的步骤中判断 当 i * m + j > 0 的时候才返回
(转载结束)
本题只是最基础的应用,复杂度是

代码:
题意:
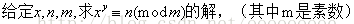
思路:求离散对数,Baby Step Giant Step算法基本应用。
以下转载自:AekdyCoin
【普通Baby Step Giant Step】
【问题模型】
求解
A^x = B (mod C) 中 0 <= x < C 的解,C 为素数
【思路】
我们可以做一个等价
x = i * m + j ( 0 <= i < m, 0 <=j < m) m = Ceil ( sqrt( C) )
而这么分解的目的无非是为了转化为:
(A^i)^m * A^j = B ( mod C)
之后做少许暴力的工作就可以解决问题:
(1) for i = 0 -> m, 插入Hash (i, A^i mod C)
(2) 枚举 i ,对于每一个枚举到的i,令 AA = (A^m)^i mod C
我们有
AA * A^j = B (mod C)
显然AA,B,C均已知,而由于C为素数,那么(AA,C)无条件为1
于是对于这个模方程解的个数唯一(可以利用扩展欧几里得或 欧拉定理来求解)
那么对于得到的唯一解X,在Hash表中寻找,如果找到,则返回 i * m + j
注意:由于i从小到大的枚举,而Hash表中存在的j必然是对于某个剩余系内的元素X 是最小的(就是指标)
所以显然此时就可以得到最小解
如果需要得到 x > 0的解,那么只需要在上面的步骤中判断 当 i * m + j > 0 的时候才返回
(转载结束)
本题只是最基础的应用,复杂度是

代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
#define maxn 10005
#define INF 0x7fffffff
#define eps 1e-8
typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
using namespace std;
LL pow_mod(LL aa,LL ii,LL nn)
{
if(ii==0)
return 1%nn;
LL temp=pow_mod(aa,ii>>1,nn);
temp=temp*temp%nn;
if(ii&1)
temp=temp*aa%nn;
return temp;
}
struct b_step
{
int i,m;
} bb[100005];
bool cmp(b_step a,b_step b)
{
return a.m==b.m?a.i<b.i:a.m<b.m;
}
int BiSearch(int m,LL num)
{
int low=0,high=m,mid;
while(low<=high)
{
mid=(low+high)>>1;
if(bb[mid].m==num)
return bb[mid].i;
if(bb[mid].m<num)
low=mid+1;
else
high=mid-1;
}
return -1;
}
void giant_step_baby_step(LL b,LL n,LL p)
{
int m=(int)ceil(sqrt((double)p));
bb[0].i=0,bb[0].m=1;
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
{
bb[i].i=i;
bb[i].m=bb[i-1].m*b%p;
}
sort(bb,bb+m,cmp);
int top=0;
for(int i=1; i<m; i++)
if(bb[i].m!=bb[top].m)
bb[++top]=bb[i];
LL bm=pow_mod(pow_mod(b,p-2,p),m,p);
LL ans=-1;
LL tmp=n;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
int pos=BiSearch(top,tmp);
if(~pos)
{
ans=m*i+pos;
break;
}
tmp=((LL)tmp*bm)%p;
}
if(!~ans)
puts("no solution");
else
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
int main()
{
LL p,b,n;
while(~scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&p,&b,&n))
{
giant_step_baby_step(b,n,p);
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging 离散对数/BabyStep_GiantStep
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging 离散对数
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging (求解模方程a^x≡b(mod n))
- [poj 2417]Discrete Logging 数论 BSGS
- poj 2417 Discrete Logging 求解模方程a^x=b(mod n),n为素数+模板题(baby_step giant_step)
- poj 2417 Discrete Logging
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging (BSGS)
- POJ 2417/BZOJ 3239(Discrete Logging-BSGS)[Template:数论]
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging
- poj 2417 Discrete Logging ---高次同余第一种类型。babystep_gaint_step
- 【POJ 3243-Clever Y】 与【POJ 2417-Discrete Logging】(解高次同余方程 Baby-Step-Gaint-Step)
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging (Baby-Step Giant-Step)
- [POJ 2417]Discrete Logging
- poj 2417 Discrete Logging 数论baby_step,giant_step算法
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging【大步小步
- POJ 2417:Discrete Logging——Baby Step, Giant Step
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging (Baby-Step-Gaint-Step)
- POJ 2417 Discrete Logging 笔记
- BSGS算法+逆元 POJ 2417 Discrete Logging
