Android4.2 G-Sensor工作流程
2013-06-07 10:11
246 查看
分类:
Android Framework
Android系统
Linux驱动 2013-06-07 10:11
1320人阅读 评论(4)
收藏
举报
目录(?)[+]
1. 简介
在了解Sensor工作流程以前,一直以为其事件是通过Event Hub来进行输送的,可是研究完Android4.0代码之后,才发现自己错了。其主要框架如下图所示:
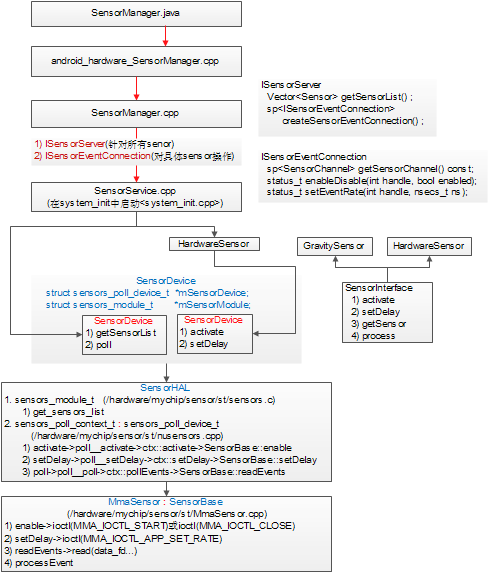
2.功能模块
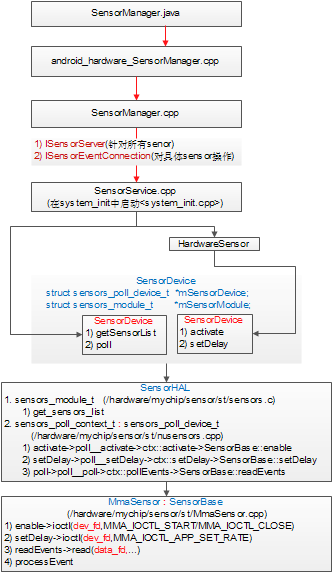
2.1 SensorManager.java
与下层接口功能:1) 在SensorManager函数中
(1) 调用native sensors_module_init初始化sensor list,即实例化native中的SensorManager
(2) 创建SensorThread线程
2) 在类SensorThread中
(1) 调用native sensors_create_queue创建队列
(2) 在线程中dead loop地调用native sensors_data_poll以从队列sQueue中获取事件(float[] values = new float[3];)
(3) 收到事件之后,报告sensor event给所有注册且关心此事件的listener
与上层的接口功能:
1) 在onPause时取消listener注册
2) 在onResume时注册listener
3) 把收到的事件报告给注册的listener
2.2 android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp
实现SensorManager.java中的native函数,它主要调用SenrsorManager.cpp和SensorEventQueue.cpp中的类来完成相关的工作。2.3 SensorManager.cpp
[cpp]view plaincopy
class SensorManager :
public ASensorManager,
public Singleton<SensorManager>
{
public:
SensorManager(); //调用assertStateLocked
~SensorManager();
//调用assertStateLocked,并返回mSensorList
ssize_t getSensorList(Sensor const* const** list) const;
// 返回mSensorList中第一个类型与type一致的sensor
Sensor const* getDefaultSensor(int type);
// 调用mSensorServer->createSensorEventConnection创建一个连接(ISensorEventConnection)
// 并用此连接做为参数创建一个SensorEventQueue对象并返回
sp<SensorEventQueue> createEventQueue();
private:
// DeathRecipient interface
void sensorManagerDied();
// 调用getService获取SensorService客户端并保存在mSensorServer中
// 调用mSensorServer->getSensorList获取sensor列表,并保存在mSensors和mSensorList中
status_t assertStateLocked() const;
private:
mutable Mutex mLock;
mutable sp<ISensorServer> mSensorServer; // SensorService客户端
mutable Sensor const** mSensorList; // sensor列表
mutable Vector<Sensor> mSensors; // sensor列表
mutable sp<IBinder::DeathRecipient> mDeathObserver;
}
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class ISensorEventConnection : public IInterface
{
public:
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(SensorEventConnection);
virtual sp<SensorChannel> getSensorChannel() const = 0;
virtual status_t enableDisable(int handle, bool enabled) = 0;
virtual status_t setEventRate(int handle, nsecs_t ns) = 0;
};
2.4 SensorService.cpp
SensorService作为一个轻量级的system service,它运行于SystemServer内,即在system_init<system_init.cpp>调用SensorService::instantiate();SensorService主要功能如下:
1) SensorService::instantiate创建实例对象,并增加到ServiceManager中,且创建并启动线程,并执行threadLoop
2) threadLoop从sensor驱动获取原始数据,然后通过SensorEventConnection把事件发送给客户端
3) BnSensorServer的成员函数负责让客户端获取sensor列表和创建SensorEventConnection
SensorService与客户端的接口定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class ISensorServer : public IInterface
{
public:
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(SensorServer);
virtual Vector<Sensor> getSensorList() = 0;
virtual sp<ISensorEventConnection> createSensorEventConnection() = 0;
};
SensorService定义如下:
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class SensorService :
public BinderService<SensorService>, //创建SensorService对象,并增加到ServiceManager中
public BnSensorServer, // 申明了SensorService与客户端(SensorManager)间的binder接口
protected Thread // 线程辅助类,调用run创建并启动线程,然后在线程主函数内回调threadLoop函数,
// 所以在使用它时,做一个派生,并根据需要重写threadLoop即可
{
friend class BinderService<SensorService>;
static const nsecs_t MINIMUM_EVENTS_PERIOD = 1000000; // 1000 Hz
SensorService();
virtual ~SensorService();
/*
在addService时,第一次构建sp强引用对象时,会调用onFirstRef函数
实现功能如下:
1) 获取SensorDevice实例
2) 调用SensorDevice.getSensorList获取sensor_t列表
3) 根据硬件sensor_t创建HardwareSensor,然后加入mSensorList(Sensor)
和mSensorMap(HardwareSensor)中
4) 根据硬件sensor_t创建对应的senosr(如GravitySensor),
然后加入mVirtualSensorList和mSensorList中
5) mUserSensorList = mSensorList;
6) run("SensorService", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);运行线程,并执行threadLoop
*/
virtual void onFirstRef();
// Thread interface
/*
1) 调用SensorDevice.poll获取sensors_event_t事件
2) 获取已经激活的sensor列表mActiveVirtualSensors
3) 对每一个事件,执行SensorFusion.process
4) 对每一个事件,执行HardwareSensor.process(事件无变化,直接copy)
5) 调用SensorService::SensorEventConnection::sendEvents,把事件发
送给所有的listener
*/
virtual bool threadLoop();
// ISensorServer interface
// 返回mUserSensorList
virtual Vector<Sensor> getSensorList();
// 实例化SensorEventConnection并返回
virtual sp<ISensorEventConnection> createSensorEventConnection();
virtual status_t dump(int fd, const Vector<String16>& args);
//====================================================================
//============== SensorEventConnection start ========================
class SensorEventConnection : public BnSensorEventConnection {
virtual ~SensorEventConnection();
virtual void onFirstRef();
// 返回mChannel
virtual sp<SensorChannel> getSensorChannel() const;
// 调用SensorService::enable或SensorService::disable
virtual status_t enableDisable(int handle, bool enabled);
// 调用SensorService::setEventRate
virtual status_t setEventRate(int handle, nsecs_t ns);
sp<SensorService> const mService; // 保存当前SensorService实例
sp<SensorChannel> const mChannel; // SensorChannel实例
mutable Mutex mConnectionLock;
// protected by SensorService::mLock
SortedVector<int> mSensorInfo;
public:
/*
1) 把当前service保存在mService中
2) 创建SensorChannel实例,并保存在mChannel中
(在SensorChannel::SensorChannel中创建pipe,并把收和发都设置非阻塞)
*/
SensorEventConnection(const sp<SensorService>& service);
// 调用连接中的mChannel->write (SensorChannel::write),把符合条件的事件写入pipe
status_t sendEvents(sensors_event_t const* buffer, size_t count,
sensors_event_t* scratch = NULL);
bool hasSensor(int32_t handle) const; //检查handle是否在mSensorInfo中
bool hasAnySensor() const; //检查mSensorInfo中是否有sensor
bool addSensor(int32_t handle); //把handle增加到mSensorInfo列表中
bool removeSensor(int32_t handle); //把handle从mSensorInfo中删除
};
//============== SensorEventConnection end ========================
//====================================================================
class SensorRecord {
SortedVector< wp<SensorEventConnection> > mConnections;
public:
SensorRecord(const sp<SensorEventConnection>& connection);
bool addConnection(const sp<SensorEventConnection>& connection);
bool removeConnection(const wp<SensorEventConnection>& connection);
size_t getNumConnections() const { return mConnections.size(); }
};
SortedVector< wp<SensorEventConnection> > getActiveConnections() const;
DefaultKeyedVector<int, SensorInterface*> getActiveVirtualSensors() const;
String8 getSensorName(int handle) const;
void recordLastValue(sensors_event_t const * buffer, size_t count);
static void sortEventBuffer(sensors_event_t* buffer, size_t count);
void registerSensor(SensorInterface* sensor);
void registerVirtualSensor(SensorInterface* sensor);
// constants
Vector<Sensor> mSensorList; // Sensor列表
Vector<Sensor> mUserSensorList; //与mSensorList一样
DefaultKeyedVector<int, SensorInterface*> mSensorMap; //其成员为HardwareSensor
Vector<SensorInterface *> mVirtualSensorList; //其成员为HardwareSensor
status_t mInitCheck;
// protected by mLock
mutable Mutex mLock;
DefaultKeyedVector<int, SensorRecord*> mActiveSensors; //成员为SensorRecord
DefaultKeyedVector<int, SensorInterface*> mActiveVirtualSensors; //成员为HardwareSensor
SortedVector< wp<SensorEventConnection> > mActiveConnections;
// The size of this vector is constant, only the items are mutable
KeyedVector<int32_t, sensors_event_t> mLastEventSeen;
public:
static char const* getServiceName() { return "sensorservice"; }
void cleanupConnection(SensorEventConnection* connection);
/*
1) 调用HardwareSensor::activate,即SensorDevice::activate
2) 然后创建SensorRecord并增加到列表mActiveSensors
3) 把此HardwareSensor增加到连接的mSensorInfo
4) 把此连接增加到mActiveConnections中
*/
status_t enable(const sp<SensorEventConnection>& connection, int handle);
/*
1) 把此sensor从连接的mSensorInfo中删除
2) 把此连接从mActiveConnections中删除
3) 调用HardwareSensor::activate,即SensorDevice::activate
*/
status_t disable(const sp<SensorEventConnection>& connection, int handle);
/*
1)调用HardwareSensor::setDelay,即SensorDevice::setDelay
*/
status_t setEventRate(const sp<SensorEventConnection>& connection, int handle, nsecs_t ns);
}
2.5 SensorDevice.cpp
SensorDevice封装了对SensorHAL层代码的调用,主要包含以下功能:1) 获取sensor列表(getSensorList)
2) 获取sensor事件(poll)
3) Enable或Disable sensor (activate)
4) 设置delay时间
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class SensorDevice : public Singleton<SensorDevice> {
friend class Singleton<SensorDevice>;
struct sensors_poll_device_t* mSensorDevice; // sensor设备
struct sensors_module_t* mSensorModule;
mutable Mutex mLock; // protect mActivationCount[].rates
// fixed-size array after construction
struct Info {
Info() : delay(0) { }
KeyedVector<void*, nsecs_t> rates;
nsecs_t delay;
status_t setDelayForIdent(void* ident, int64_t ns);
nsecs_t selectDelay();
};
DefaultKeyedVector<int, Info> mActivationCount;
/*
1) 调用hw_get_module(SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,..)获取sensors_module_t,
并保存在mSensorModule中
2) 调用mSensorModule->common->methods->open,以返回sensors_poll_device_t,
并保存在mSensorDevice中
3) 调用mSensorModule->get_sensors_list所有可访问的sensor_t
4) 调用mSensorDevice->activate激活所有的sensor
*/
SensorDevice();
public:
// 调用mSensorModule->get_sensors_list实现
ssize_t getSensorList(sensor_t const** list);
status_t initCheck() const;
// 调用mSensorDevice->poll实现
ssize_t poll(sensors_event_t* buffer, size_t count);
// 调用mSensorDevice->activate实现
status_t activate(void* ident, int handle, int enabled);
// 调用mSensorDevice->setDelay实现
status_t setDelay(void* ident, int handle, int64_t ns);
void dump(String8& result, char* buffer, size_t SIZE);
};
2.6 Sensor HAL
定义:/hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h实现:/hardware/mychip/sensor/st/sensors.c
2.6.1 struct sensors_poll_device_t 定义
[cpp]view plaincopy
struct sensors_poll_device_t {
struct hw_device_t common;
// Activate/deactivate one sensor.
int (*activate)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int enabled);
// Set the delay between sensor events in nanoseconds for a given sensor.
int (*setDelay)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int64_t ns);
// Returns an array of sensor data.
int (*poll)(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
sensors_event_t* data, int count);
};
2.6.2 struct sensors_module_t 定义
[cpp]view plaincopy
struct sensors_module_t {
struct hw_module_t common;
/**
* Enumerate all available sensors. The list is returned in "list".
* @return number of sensors in the list
*/
int (*get_sensors_list)(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list);
};
2.6.3 struct sensor_t 定义
[cpp]view plaincopy
struct sensor_t {
/* name of this sensors */
const char* name;
/* vendor of the hardware part */
const char* vendor;
/* version of the hardware part + driver. The value of this field
* must increase when the driver is updated in a way that changes the
* output of this sensor. This is important for fused sensors when the
* fusion algorithm is updated.
*/
int version;
/* handle that identifies this sensors. This handle is used to activate
* and deactivate this sensor. The value of the handle must be 8 bits
* in this version of the API.
*/
int handle;
/* this sensor's type. */
int type;
/* maximaum range of this sensor's value in SI units */
float maxRange;
/* smallest difference between two values reported by this sensor */
float resolution;
/* rough estimate of this sensor's power consumption in mA */
float power;
/* minimum delay allowed between events in microseconds. A value of zero
* means that this sensor doesn't report events at a constant rate, but
* rather only when a new data is available */
int32_t minDelay;
/* reserved fields, must be zero */
void* reserved[8];
};
2.6.4 struct sensors_event_t 定义
[cpp]view plaincopy
typedef struct {
union {
float v[3];
struct {
float x;
float y;
float z;
};
struct {
float azimuth;
float pitch;
float roll;
};
};
int8_t status;
uint8_t reserved[3];
} sensors_vec_t;
/**
* Union of the various types of sensor data
* that can be returned.
*/
typedef struct sensors_event_t {
/* must be sizeof(struct sensors_event_t) */
int32_t version;
/* sensor identifier */
int32_t sensor;
/* sensor type */
int32_t type;
/* reserved */
int32_t reserved0;
/* time is in nanosecond */
int64_t timestamp;
union {
float data[16];
/* acceleration values are in meter per second per second (m/s^2) */
sensors_vec_t acceleration;
/* magnetic vector values are in micro-Tesla (uT) */
sensors_vec_t magnetic;
/* orientation values are in degrees */
sensors_vec_t orientation;
/* gyroscope values are in rad/s */
sensors_vec_t gyro;
/* temperature is in degrees centigrade (Celsius) */
float temperature;
/* distance in centimeters */
float distance;
/* light in SI lux units */
float light;
/* pressure in hectopascal (hPa) */
float pressure;
/* relative humidity in percent */
float relative_humidity;
};
uint32_t reserved1[4];
} sensors_event_t;
2.6.5 struct sensors_module_t 实现
[cpp]view plaincopy
#include <hardware/sensors.h>
#include "nusensors.h"
/*
* the AK8973 has a 8-bit ADC but the firmware seems to average 16 samples,
* or at least makes its calibration on 12-bits values. This increases the
* resolution by 4 bits.
*/
static const struct sensor_t sSensorList[] = {
{ "MMA8452Q 3-axis Accelerometer",
"Freescale Semiconductor",
1, SENSORS_HANDLE_BASE+ID_A,
SENSOR_TYPE_ACCELEROMETER, 4.0f*9.81f, (4.0f*9.81f)/256.0f, 0.2f, 0, { } },
{ "AK8975 3-axis Magnetic field sensor",
"Asahi Kasei",
1, SENSORS_HANDLE_BASE+ID_M,
SENSOR_TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD, 2000.0f, 1.0f/16.0f, 6.8f, 0, { } },
{ "AK8975 Orientation sensor",
"Asahi Kasei",
1, SENSORS_HANDLE_BASE+ID_O,
SENSOR_TYPE_ORIENTATION, 360.0f, 1.0f, 7.0f, 0, { } },
{ "ST 3-axis Gyroscope sensor",
"STMicroelectronics",
1, SENSORS_HANDLE_BASE+ID_GY,
SENSOR_TYPE_GYROSCOPE, RANGE_GYRO, CONVERT_GYRO, 6.1f, 1190, { } },
{ "AL3006Proximity sensor",
"Dyna Image Corporation",
1, SENSORS_HANDLE_BASE+ID_P,
SENSOR_TYPE_PROXIMITY,
PROXIMITY_THRESHOLD_CM, PROXIMITY_THRESHOLD_CM,
0.5f, 0, { } },
{ "AL3006 light sensor",
"Dyna Image Corporation",
1, SENSORS_HANDLE_BASE+ID_L,
SENSOR_TYPE_LIGHT, 10240.0f, 1.0f, 0.5f, 0, { } },
};
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device);
static int sensors__get_sensors_list(struct sensors_module_t* module,
struct sensor_t const** list)
{
*list = sSensorList;
return ARRAY_SIZE(sSensorList);
}
static struct hw_module_methods_t sensors_module_methods = {
.open = open_sensors
};
const struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "MMA8451Q & AK8973A & gyro Sensors Module",
.author = "The Android Project",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
},
.get_sensors_list = sensors__get_sensors_list
};
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device)
{
return init_nusensors(module, device); //待后面讲解
}
2.6.6 struct sensors_poll_device_t 实现
实现代码位于:/hardware/mychip/sensor/st/nusensors.cpp从上面的代码中可以看出,当调用init_nusensors时,它将返回sensors_poll_device_t,然后就可以调用sensors_poll_device_t 的以下方法进行相关操作:
1) activate
2) setDelay
3) poll
6.1) struct sensors_poll_context_t 定义
[cpp]
view plaincopy
struct sensors_poll_context_t {
struct sensors_poll_device_t device; // must be first
sensors_poll_context_t();
~sensors_poll_context_t();
int activate(int handle, int enabled);
int setDelay(int handle, int64_t ns);
int pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count);
private:
enum {
light = 0,
proximity = 1,
mma = 2,
akm = 3,
gyro = 4,
numSensorDrivers,
numFds,
};
static const size_t wake = numFds - 1;
static const char WAKE_MESSAGE = 'W';
struct pollfd mPollFds[numFds];
int mWritePipeFd;
SensorBase* mSensors[numSensorDrivers];
int handleToDriver(int handle) const {
switch (handle) {
case ID_A:
return mma;
case ID_M:
case ID_O:
return akm;
case ID_P:
return proximity;
case ID_L:
return light;
case ID_GY:
return gyro;
}
return -EINVAL;
}
}
6.2) init_nusensors 实现
[cpp]
view plaincopy
int init_nusensors(hw_module_t const* module, hw_device_t** device)
{
int status = -EINVAL;
sensors_poll_context_t *dev = new sensors_poll_context_t();
memset(&dev->device, 0, sizeof(sensors_poll_device_t));
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = 0;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast<hw_module_t*>(module);
dev->device.common.close = poll__close;
dev->device.activate = poll__activate;
dev->device.setDelay = poll__setDelay;
dev->device.poll = poll__poll;
*device = &dev->device.common;
status = 0;
return status;
}
由以上代码可见,sensors_poll_device_t的activate、setDelay和poll的实现函数分别为:
(1) poll__activate
(2) poll__setDelay
(3) poll__poll
下面讲解以上三个关键函数的实现
6.3) struct sensors_poll_context_t 的实现
[cpp]
view plaincopy
sensors_poll_context_t::sensors_poll_context_t()
{
mSensors[light] = new LightSensor();
mPollFds[light].fd = mSensors[light]->getFd();
mPollFds[light].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[light].revents = 0;
mSensors[proximity] = new ProximitySensor();
mPollFds[proximity].fd = mSensors[proximity]->getFd();
mPollFds[proximity].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[proximity].revents = 0;
mSensors[mma] = new MmaSensor(); //下面MmmaSensor为例进行分析
mPollFds[mma].fd = mSensors[mma]->getFd();
mPollFds[mma].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[mma].revents = 0;
mSensors[akm] = new AkmSensor();
mPollFds[akm].fd = mSensors[akm]->getFd();
mPollFds[akm].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[akm].revents = 0;
mSensors[gyro] = new GyroSensor();
mPollFds[gyro].fd = mSensors[gyro]->getFd();
mPollFds[gyro].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[gyro].revents = 0;
int wakeFds[2];
int result = pipe(wakeFds);
LOGE_IF(result<0, "error creating wake pipe (%s)", strerror(errno));
fcntl(wakeFds[0], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
fcntl(wakeFds[1], F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
mWritePipeFd = wakeFds[1];
mPollFds[wake].fd = wakeFds[0];
mPollFds[wake].events = POLLIN;
mPollFds[wake].revents = 0;
}
sensors_poll_context_t::~sensors_poll_context_t() {
for (int i=0 ; i<numSensorDrivers ; i++) {
delete mSensors[i];
}
close(mPollFds[wake].fd);
close(mWritePipeFd);
}
int sensors_poll_context_t::activate(int handle, int enabled) {
int index = handleToDriver(handle);
if (index < 0) return index;
int err = mSensors[index]->enable(handle, enabled);
if (enabled && !err) {
const char wakeMessage(WAKE_MESSAGE);
int result = write(mWritePipeFd, &wakeMessage, 1);
LOGE_IF(result<0, "error sending wake message (%s)", strerror(errno));
}
return err;
}
int sensors_poll_context_t::setDelay(int handle, int64_t ns) {
int index = handleToDriver(handle);
if (index < 0) return index;
return mSensors[index]->setDelay(handle, ns);
}
int sensors_poll_context_t::pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count)
{
int nbEvents = 0;
int n = 0;
do {
// see if we have some leftover from the last poll()
for (int i=0 ; count && i<numSensorDrivers ; i++) {
SensorBase* const sensor(mSensors[i]);
if ((mPollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) || (sensor->hasPendingEvents())) {
int nb = sensor->readEvents(data, count); // num of evens received.
D("nb = %d.", nb);
if (nb < count) {
// no more data for this sensor
mPollFds[i].revents = 0;
}
count -= nb;
nbEvents += nb;
data += nb;
}
}
if (count) {
// we still have some room, so try to see if we can get
// some events immediately or just wait if we don't have
// anything to return
n = poll(mPollFds, numFds, nbEvents ? 0 : -1);
if (n<0) {
LOGE("poll() failed (%s)", strerror(errno));
return -errno;
}
if (mPollFds[wake].revents & POLLIN) {
char msg;
int result = read(mPollFds[wake].fd, &msg, 1);
LOGE_IF(result<0, "error reading from wake pipe (%s)", strerror(errno));
LOGE_IF(msg != WAKE_MESSAGE, "unknown message on wake queue (0x%02x)", int(msg));
mPollFds[wake].revents = 0;
}
}
// if we have events and space, go read them
} while (n && count);
return nbEvents;
}
/*****************************************************************************/
static int poll__close(struct hw_device_t *dev)
{
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
if (ctx) {
delete ctx;
}
return 0;
}
static int poll__activate(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int enabled) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->activate(handle, enabled);
}
static int poll__setDelay(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
int handle, int64_t ns) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->setDelay(handle, ns);
}
static int poll__poll(struct sensors_poll_device_t *dev,
sensors_event_t* data, int count) {
sensors_poll_context_t *ctx = (sensors_poll_context_t *)dev;
return ctx->pollEvents(data, count);
}
下面MmaSensor为例进行分析。
2.7 MmaSensor.cpp
1) SensorBase的实现(SensorBase.cpp)[cpp]
view plaincopy
class SensorBase {
protected:
const char* dev_name; // "/dev/mma8452_daemon"
const char* data_name; // "gsensor"
int dev_fd; // 打开设备"/dev/mma8452_daemon"的fd
// 打开事件"/dev/input/eventx"的fd,其驱动的名字为"gsensor"
int data_fd;
// 打开与"gsensor"对应的事件"/dev/input/eventx"
static int openInput(const char* inputName);
//通过clock_gettime获取当前时间
static int64_t getTimestamp();
static int64_t timevalToNano(timeval const& t) {
return t.tv_sec*1000000000LL + t.tv_usec*1000;
}
int open_device(); //打开设备"dev/mma8452_daemon"
int close_device(); //关闭设备"dev/mma8452_daemon"
public:
// 调用openInput
SensorBase(
const char* dev_name,
const char* data_name);
virtual ~SensorBase();
virtual int readEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count) = 0;
virtual bool hasPendingEvents() const;
virtual int getFd() const; //返回data_fd
virtual int setDelay(int32_t handle, int64_t ns);
virtual int enable(int32_t handle, int enabled) = 0;
};
2) MmaSensor的实现
[cpp]
view plaincopy
class MmaSensor : public SensorBase {
public:
/*
1) 设置dev_name为 "/dev/mma8452_daemon"
2) 设置data_name为 "gsensor"
3) open设备 "/dev/mma8452_daemon"
*/
MmaSensor();
virtual ~MmaSensor();
enum {
Accelerometer = 0,
numSensors
};
// 调用ioctl(MMA_IOCTL_APP_SET_RATE)
virtual int setDelay(int32_t handle, int64_t ns);
/*
1) Activate: ioctl(MMA_IOCTL_START)
2) Deactivate: ioctl(MMA_IOCTL_CLOSE)
*/
virtual int enable(int32_t handle, int enabled);
/*
1) 从data_fd read input_event
2) 调用processEvent对事件进行处理
3) 把事件通过data返回
*/
virtual int readEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count);
void processEvent(int code, int value);
private:
int update_delay();
uint32_t mEnabled;
uint32_t mPendingMask;
InputEventCircularReader mInputReader;
sensors_event_t mPendingEvents[numSensors];
uint64_t mDelays[numSensors];
};
3. 加载HAL
HAL 为一个.so库,其加载过程相关代码如下:[cpp]
view plaincopy
#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1 "/system/lib/hw"
#define HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2 "/vendor/lib/hw"
#define SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID "sensors"
SensorDevice::SensorDevice()
: mSensorDevice(0),
mSensorModule(0)
{
status_t err = hw_get_module(SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(hw_module_t const**)&mSensorModule);
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't load %s module (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorModule) {
err = sensors_open(&mSensorModule->common, &mSensorDevice);
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't open device for module %s (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorDevice) {
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = mSensorModule->get_sensors_list(mSensorModule, &list);
mActivationCount.setCapacity(count);
Info model;
for (size_t i=0 ; i<size_t(count) ; i++) {
mActivationCount.add(list[i].handle, model);
mSensorDevice->activate(mSensorDevice, list[i].handle, 0);
}
}
}
}
int hw_get_module(const char *id, const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
return hw_get_module_by_class(id, NULL, module);
}
int hw_get_module_by_class(const char *class_id, const char *inst,
const struct hw_module_t **module)
{
int status;
int i;
const struct hw_module_t *hmi = NULL;
char prop[PATH_MAX];
char path[PATH_MAX];
char name[PATH_MAX];
if (inst)
snprintf(name, PATH_MAX, "%s.%s", class_id, inst);
else
strlcpy(name, class_id, PATH_MAX);
/*
* Here we rely on the fact that calling dlopen multiple times on
* the same .so will simply increment a refcount (and not load
* a new copy of the library).
* We also assume that dlopen() is thread-safe.
*/
/* Loop through the configuration variants looking for a module */
for (i=0 ; i<HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT+1 ; i++) {
if (i < HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT) {
if (property_get(variant_keys[i], prop, NULL) == 0) {
continue;
}
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.%s.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH2, name, prop);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) break;
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.%s.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name, prop);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) break;
} else {
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "%s/%s.default.so",
HAL_LIBRARY_PATH1, name);
if (access(path, R_OK) == 0) break;
}
}
status = -ENOENT;
if (i < HAL_VARIANT_KEYS_COUNT+1) {
/* load the module, if this fails, we're doomed, and we should not try
* to load a different variant. */
status = load(class_id, path, module);
}
return status;
}
4. 启动SensorService
SensorService在SystemServer中启动(system_init.cpp),其相关代码如下:[cpp]
view plaincopy
extern "C" status_t system_init()
{
....
property_get("system_init.startsensorservice", propBuf, "1");
if (strcmp(propBuf, "1") == 0) {
// Start the sensor service
SensorService::instantiate();
}
...
return NO_ERROR;
}
5. SensorManager注册Listener过程
[cpp]view plaincopy
private SensorManager mSensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
registerListener(SensorManager.java)->
registerListenerImpl (SystemSensorManager.java)->
enableSensorLocked(SystemSensorManager.java)->
sensors_enable_sensor(android_hardware_SensorManager.cpp)->
SensorEventQueue::enableSensor(SensorEventQueue.cpp)->
1>SensorService::SensorEventConnection::enableDisable(handle, true) (SensorService.cpp)->
SensorService::enable(SensorService.cpp)->
HardwareSensor::activate(SensorInterface.cpp)->
SensorDevice::activate(SensorDevice.cpp)->
sensors_poll_device_t::activate(HAL)
2>SensorService::SensorEventConnection::setEventRate(SensorService.cpp)->
相关文章推荐
- Android4.2 G-Sensor工作流程
- Android4.2 G-Sensor工作流程
- Android 浅谈Sensor工作流程(一)
- <4>Android4.2 G-Sensor工作流程
- Android 浅谈Sensor工作流程(二)
- android中Sensor 工作流程
- Android传感器Sensor工作流程
- Android4.2 G-Sensor工作流程
- G-Sensor工作流程
- android中Sensor 工作流程
- Android4.0 G-Sensor工作流程
- Android4.2 G-Sensor工作流程
- sensor工作流程
- android中Sensor 工作流程
- Android4.0 G-Sensor工作流程
- Android Sensor工作流程(一)
- Android4.0 G-Sensor工作流程
- Android4.2 G-Sensor工作流程
- android中Sensor 工作流程
- android中Sensor 工作流程
