Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
2013-04-13 13:33
513 查看
本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13
原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7552455
更多请查看专栏,地址http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/linux-kernel-net.html
作者:闫明
注:标题中的”(上)“,”(下)“表示分析过程基于数据包的传递方向:”(上)“表示分析是从底层向上分析、”(下)“表示分析是从上向下分析。
上篇博文分析传输层最终会调用函数ip_queue_xmit()函数,将发送数据的任务交给网络层,下面就分析了下该函数:
该函数的主要函数调用关系图如下:
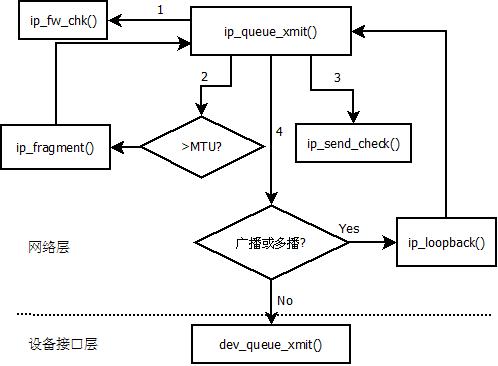
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/*
* Queues a packet to be sent, and starts the transmitter
* if necessary. if free = 1 then we free the block after
* transmit, otherwise we don't. If free==2 we not only
* free the block but also don't assign a new ip seq number.
* This routine also needs to put in the total length,
* and compute the checksum
*/
void ip_queue_xmit(struct sock *sk, //发送数据的队列所对应的sock结构
struct device *dev,//发送该数据包的网卡设备
struct sk_buff *skb,//封装好的sk_buff结构,要发送的数据在该结构中
int free)//主要配合TCP协议使用,用于数据包的重发,UDP等协议调用是free=1
{
struct iphdr *iph;//IP数据报首部指针
unsigned char *ptr;
/* Sanity check */
if (dev == NULL)
{
printk("IP: ip_queue_xmit dev = NULL\n");
return;
}
IS_SKB(skb);
/*
* Do some book-keeping in the packet for later
*/
skb->dev = dev;//进一步完整sk_buff的相应字段
skb->when = jiffies;//用于TCP协议的超时重传
/*
* Find the IP header and set the length. This is bad
* but once we get the skb data handling code in the
* hardware will push its header sensibly and we will
* set skb->ip_hdr to avoid this mess and the fixed
* header length problem
*/
ptr = skb->data;//指针指向sk_buff中的数据部分
ptr += dev->hard_header_len;//hard_header_len为硬件首部长度,在net_init.c的函数eth_setup()函数中设置的,dev->hard_header_len = ETH_HLEN; 以太网首部长度为14
iph = (struct iphdr *)ptr;//prt已经指向IP数据包的首部
skb->ip_hdr = iph;
iph->tot_len = ntohs(skb->len-dev->hard_header_len);//计算IP数据报的总长度
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_FIREWALL
if(ip_fw_chk(iph, dev, ip_fw_blk_chain, ip_fw_blk_policy, 0) != 1)
/* just don't send this packet */
return;
#endif
/*
* No reassigning numbers to fragments...
*/
if(free!=2)
iph->id = htons(ip_id_count++);
else
free=1;
/* All buffers without an owner socket get freed */
if (sk == NULL)
free = 1;
skb->free = free;//设置skb的free值,free=1,发送后立即释放;free=2,不但释放缓存,而且不分配新的序列号
/*
* Do we need to fragment. Again this is inefficient.
* We need to somehow lock the original buffer and use
* bits of it.
*/
//数据帧中的数据部分必须小于等于MTU
if(skb->len > dev->mtu + dev->hard_header_len)//发送的数据长度大于数据帧的数据部分和帧首部之和,则需要分片
{
ip_fragment(sk,skb,dev,0);//对数据报分片后继续调用ip _queue_xmit()函数发送数据
IS_SKB(skb);
kfree_skb(skb,FREE_WRITE);
return;
}
/*
* Add an IP checksum
*/
ip_send_check(iph);//IP数据报首部检查
/*
* Print the frame when debugging
*/
/*
* More debugging. You cannot queue a packet already on a list
* Spot this and moan loudly.
*/
if (skb->next != NULL)//说明该数据包仍然存在于某个缓存队列
{
printk("ip_queue_xmit: next != NULL\n");
skb_unlink(skb);//将其从缓存链表中删除,否则可能导致内核错误
}
/*
* If a sender wishes the packet to remain unfreed
* we add it to his send queue. This arguably belongs
* in the TCP level since nobody else uses it. BUT
* remember IPng might change all the rules.
*/
if (!free)//free=0
{
unsigned long flags;
/* The socket now has more outstanding blocks */
sk->packets_out++;
/* Protect the list for a moment */
save_flags(flags);
cli();
if (skb->link3 != NULL)//link3指向数据报道呃重发队列
{
printk("ip.c: link3 != NULL\n");
skb->link3 = NULL;
}
//sk中send_tail和send_head是用户缓存的单向链表表尾和表头
if (sk->send_head == NULL)
{
sk->send_tail = skb;
sk->send_head = skb;
}
else
{
sk->send_tail->link3 = skb;//link3指针用于数据包的连接
sk->send_tail = skb;
}
/* skb->link3 is NULL */
/* Interrupt restore */
restore_flags(flags);
}
else
/* Remember who owns the buffer */
skb->sk = sk;
/*
* If the indicated interface is up and running, send the packet.
*/
ip_statistics.IpOutRequests++;
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_ACCT
ip_acct_cnt(iph,dev, ip_acct_chain);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST //这部分是IP数据报的多播处理
/*
* Multicasts are looped back for other local users
*/
.......................................
#endif
if((dev->flags&IFF_BROADCAST) && iph->daddr==dev->pa_brdaddr && !(dev->flags&IFF_LOOPBACK))//广播数据包的处理
ip_loopback(dev,skb);
if (dev->flags & IFF_UP)//设备状态正常
{
/*
* If we have an owner use its priority setting,
* otherwise use NORMAL
*/
//调用设备接口层函数发送数据: dev_queue_xmit()函数
if (sk != NULL)
{
dev_queue_xmit(skb, dev, sk->priority);
}
else
{
dev_queue_xmit(skb, dev, SOPRI_NORMAL);
}
}
else//设备状态不正常
{
ip_statistics.IpOutDiscards++;
if (free)
kfree_skb(skb, FREE_WRITE);
}
}
这个函数中对长度过长的数据包进行了分片,ip_fragment()函数,该函数没有详细分析。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
void ip_fragment(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, struct device *dev, int is_frag)
{
struct iphdr *iph;
unsigned char *raw;
unsigned char *ptr;
struct sk_buff *skb2;
int left, mtu, hlen, len;
int offset;
unsigned long flags;
/*
* Point into the IP datagram header.
*/
raw = skb->data;
iph = (struct iphdr *) (raw + dev->hard_header_len);
skb->ip_hdr = iph;
/*
* Setup starting values.
*/
hlen = (iph->ihl * sizeof(unsigned long));
left = ntohs(iph->tot_len) - hlen; /* Space per frame */
hlen += dev->hard_header_len; /* Total header size */
mtu = (dev->mtu - hlen); /* Size of data space */
ptr = (raw + hlen); /* Where to start from */
/*
* Check for any "DF" flag. [DF means do not fragment]
*/
if (ntohs(iph->frag_off) & IP_DF)
{
/*
* Reply giving the MTU of the failed hop.
*/
ip_statistics.IpFragFails++;
icmp_send(skb,ICMP_DEST_UNREACH, ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED, dev->mtu, dev);
return;
}
/*
* The protocol doesn't seem to say what to do in the case that the
* frame + options doesn't fit the mtu. As it used to fall down dead
* in this case we were fortunate it didn't happen
*/
if(mtu<8)
{
/* It's wrong but it's better than nothing */
icmp_send(skb,ICMP_DEST_UNREACH,ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED,dev->mtu, dev);
ip_statistics.IpFragFails++;
return;
}
/*
* Fragment the datagram.
*/
/*
* The initial offset is 0 for a complete frame. When
* fragmenting fragments it's wherever this one starts.
*/
if (is_frag & 2)
offset = (ntohs(iph->frag_off) & 0x1fff) << 3;
else
offset = 0;
/*
* Keep copying data until we run out.
*/
while(left > 0)
{
len = left;
/* IF: it doesn't fit, use 'mtu' - the data space left */
if (len > mtu)
len = mtu;
/* IF: we are not sending upto and including the packet end
then align the next start on an eight byte boundary */
if (len < left)
{
len/=8;
len*=8;
}
/*
* Allocate buffer.
*/
if ((skb2 = alloc_skb(len + hlen,GFP_ATOMIC)) == NULL)
{
printk("IP: frag: no memory for new fragment!\n");
ip_statistics.IpFragFails++;
return;
}
/*
* Set up data on packet
*/
skb2->arp = skb->arp;
if(skb->free==0)
printk("IP fragmenter: BUG free!=1 in fragmenter\n");
skb2->free = 1;
skb2->len = len + hlen;
skb2->h.raw=(char *) skb2->data;
/*
* Charge the memory for the fragment to any owner
* it might possess
*/
save_flags(flags);
if (sk)
{
cli();
sk->wmem_alloc += skb2->mem_len;
skb2->sk=sk;
}
restore_flags(flags);
skb2->raddr = skb->raddr; /* For rebuild_header - must be here */
/*
* Copy the packet header into the new buffer.
*/
memcpy(skb2->h.raw, raw, hlen);
/*
* Copy a block of the IP datagram.
*/
memcpy(skb2->h.raw + hlen, ptr, len);
left -= len;
skb2->h.raw+=dev->hard_header_len;
/*
* Fill in the new header fields.
*/
iph = (struct iphdr *)(skb2->h.raw/*+dev->hard_header_len*/);
iph->frag_off = htons((offset >> 3));
/*
* Added AC : If we are fragmenting a fragment thats not the
* last fragment then keep MF on each bit
*/
if (left > 0 || (is_frag & 1))
iph->frag_off |= htons(IP_MF);
ptr += len;
offset += len;
/*
* Put this fragment into the sending queue.
*/
ip_statistics.IpFragCreates++;
ip_queue_xmit(sk, dev, skb2, 2);//还是调用ip_queue_xmit()函数来发送分片后的数据
}
ip_statistics.IpFragOKs++;
}
网络层的发送函数调用了设备接口层,相当于网络模型的链路层的发送函数dev_queue_xmit()
该函数的调用关系如下:

[cpp] view
plaincopy
/*
* Send (or queue for sending) a packet.
*
* IMPORTANT: When this is called to resend frames. The caller MUST
* already have locked the sk_buff. Apart from that we do the
* rest of the magic.
*/
void dev_queue_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb, struct device *dev, int pri)
{
unsigned long flags;
int nitcount;
struct packet_type *ptype;
int where = 0; /* used to say if the packet should go */
/* at the front or the back of the */
/* queue - front is a retransmit try */
/* where=0 表示是刚从上层传递的新数据包;where=1 表示从硬件队列中取出的数据包*/
if (dev == NULL)
{
printk("dev.c: dev_queue_xmit: dev = NULL\n");
return;
}
if(pri>=0 && !skb_device_locked(skb))//锁定该skb再进行操作,避免造成内核的不一致情况
skb_device_lock(skb); /* Shove a lock on the frame */
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAVE_BALANCING
save_flags(flags);
cli();
if(dev->slave!=NULL && dev->slave->pkt_queue < dev->pkt_queue &&
(dev->slave->flags & IFF_UP))
dev=dev->slave;
restore_flags(flags);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SKB_CHECK
IS_SKB(skb);
#endif
skb->dev = dev;
/*
* This just eliminates some race conditions, but not all...
*/
if (skb->next != NULL) //这种条件似乎永远不能成立,因为发送数据包前,数据包已经从缓存队列摘下
{//以防内核代码有BUG
/*
* Make sure we haven't missed an interrupt.
*/
printk("dev_queue_xmit: worked around a missed interrupt\n");
start_bh_atomic();
dev->hard_start_xmit(NULL, dev);
end_bh_atomic();
return;
}
/*
* Negative priority is used to flag a frame that is being pulled from the
* queue front as a retransmit attempt. It therefore goes back on the queue
* start on a failure.
*/
if (pri < 0) //优先级小于0表示是从硬件队列中取出的数据包
{
pri = -pri-1;
where = 1;
}
if (pri >= DEV_NUMBUFFS)
{
printk("bad priority in dev_queue_xmit.\n");
pri = 1;
}
/*
* If the address has not been resolved. Call the device header rebuilder.
* This can cover all protocols and technically not just ARP either.
*/
if (!skb->arp && dev->rebuild_header(skb->data, dev, skb->raddr, skb)) {//用于ARP协议,并重建MAC帧首部
return;
}
save_flags(flags);
cli();
if (!where) {//表示是新数据包,需要将其加入设备队列中
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAVE_BALANCING
skb->in_dev_queue=1;//该数据包在设备队列
#endif
skb_queue_tail(dev->buffs + pri,skb);//将发送数据包加入硬件队列
skb_device_unlock(skb); /* Buffer is on the device queue and can be freed safely */
skb = skb_dequeue(dev->buffs + pri);//从硬件队列中取出一个数据包
skb_device_lock(skb); /* New buffer needs locking down */
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAVE_BALANCING
skb->in_dev_queue=0;
#endif
}
restore_flags(flags);
/* copy outgoing packets to any sniffer packet handlers */
if(!where)//对于新的数据包,则遍历网络层协议队列,内核支持混杂模式
{
for (nitcount= dev_nit, ptype = ptype_base; nitcount > 0 && ptype != NULL; ptype = ptype->next)
{
/* Never send packets back to the socket
* they originated from - MvS (miquels@drinkel.ow.org)
*/
if (ptype->type == htons(ETH_P_ALL) &&
(ptype->dev == dev || !ptype->dev) &&
((struct sock *)ptype->data != skb->sk))
{
struct sk_buff *skb2;
if ((skb2 = skb_clone(skb, GFP_ATOMIC)) == NULL)
break;
/*
* The protocol knows this has (for other paths) been taken off
* and adds it back.
*/
skb2->len-=skb->dev->hard_header_len;
ptype->func(skb2, skb->dev, ptype);//IP层函数对应func为ip_rcv(),将发送的数据回送一份给对应的网络层协议
nitcount--;//用于及时退出循环
}
}
}
start_bh_atomic();//开始原子操作
if (dev->hard_start_xmit(skb, dev) == 0) {//调用硬件的发送函数发送数据
end_bh_atomic();//结束原子操作
/*
* Packet is now solely the responsibility of the driver
*/
return;//到这里说明数据包成功发送
}
//数据包没有成功发送,进行处理,将数据包从新加入硬件队列
end_bh_atomic();
/*
* Transmission failed, put skb back into a list. Once on the list it's safe and
* no longer device locked (it can be freed safely from the device queue)
*/
cli();
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAVE_BALANCING
skb->in_dev_queue=1;
dev->pkt_queue++;
#endif
skb_device_unlock(skb);//对SKB解锁
skb_queue_head(dev->buffs + pri,skb);//这次采用头插法插入硬件发送队列
restore_flags(flags);
}
具体的硬件发送函数dev->hard_start_xmit的实现将做下篇博文中分析。
原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7552455
更多请查看专栏,地址http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/linux-kernel-net.html
作者:闫明
注:标题中的”(上)“,”(下)“表示分析过程基于数据包的传递方向:”(上)“表示分析是从底层向上分析、”(下)“表示分析是从上向下分析。
上篇博文分析传输层最终会调用函数ip_queue_xmit()函数,将发送数据的任务交给网络层,下面就分析了下该函数:
该函数的主要函数调用关系图如下:

[cpp] view
plaincopy
/*
* Queues a packet to be sent, and starts the transmitter
* if necessary. if free = 1 then we free the block after
* transmit, otherwise we don't. If free==2 we not only
* free the block but also don't assign a new ip seq number.
* This routine also needs to put in the total length,
* and compute the checksum
*/
void ip_queue_xmit(struct sock *sk, //发送数据的队列所对应的sock结构
struct device *dev,//发送该数据包的网卡设备
struct sk_buff *skb,//封装好的sk_buff结构,要发送的数据在该结构中
int free)//主要配合TCP协议使用,用于数据包的重发,UDP等协议调用是free=1
{
struct iphdr *iph;//IP数据报首部指针
unsigned char *ptr;
/* Sanity check */
if (dev == NULL)
{
printk("IP: ip_queue_xmit dev = NULL\n");
return;
}
IS_SKB(skb);
/*
* Do some book-keeping in the packet for later
*/
skb->dev = dev;//进一步完整sk_buff的相应字段
skb->when = jiffies;//用于TCP协议的超时重传
/*
* Find the IP header and set the length. This is bad
* but once we get the skb data handling code in the
* hardware will push its header sensibly and we will
* set skb->ip_hdr to avoid this mess and the fixed
* header length problem
*/
ptr = skb->data;//指针指向sk_buff中的数据部分
ptr += dev->hard_header_len;//hard_header_len为硬件首部长度,在net_init.c的函数eth_setup()函数中设置的,dev->hard_header_len = ETH_HLEN; 以太网首部长度为14
iph = (struct iphdr *)ptr;//prt已经指向IP数据包的首部
skb->ip_hdr = iph;
iph->tot_len = ntohs(skb->len-dev->hard_header_len);//计算IP数据报的总长度
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_FIREWALL
if(ip_fw_chk(iph, dev, ip_fw_blk_chain, ip_fw_blk_policy, 0) != 1)
/* just don't send this packet */
return;
#endif
/*
* No reassigning numbers to fragments...
*/
if(free!=2)
iph->id = htons(ip_id_count++);
else
free=1;
/* All buffers without an owner socket get freed */
if (sk == NULL)
free = 1;
skb->free = free;//设置skb的free值,free=1,发送后立即释放;free=2,不但释放缓存,而且不分配新的序列号
/*
* Do we need to fragment. Again this is inefficient.
* We need to somehow lock the original buffer and use
* bits of it.
*/
//数据帧中的数据部分必须小于等于MTU
if(skb->len > dev->mtu + dev->hard_header_len)//发送的数据长度大于数据帧的数据部分和帧首部之和,则需要分片
{
ip_fragment(sk,skb,dev,0);//对数据报分片后继续调用ip _queue_xmit()函数发送数据
IS_SKB(skb);
kfree_skb(skb,FREE_WRITE);
return;
}
/*
* Add an IP checksum
*/
ip_send_check(iph);//IP数据报首部检查
/*
* Print the frame when debugging
*/
/*
* More debugging. You cannot queue a packet already on a list
* Spot this and moan loudly.
*/
if (skb->next != NULL)//说明该数据包仍然存在于某个缓存队列
{
printk("ip_queue_xmit: next != NULL\n");
skb_unlink(skb);//将其从缓存链表中删除,否则可能导致内核错误
}
/*
* If a sender wishes the packet to remain unfreed
* we add it to his send queue. This arguably belongs
* in the TCP level since nobody else uses it. BUT
* remember IPng might change all the rules.
*/
if (!free)//free=0
{
unsigned long flags;
/* The socket now has more outstanding blocks */
sk->packets_out++;
/* Protect the list for a moment */
save_flags(flags);
cli();
if (skb->link3 != NULL)//link3指向数据报道呃重发队列
{
printk("ip.c: link3 != NULL\n");
skb->link3 = NULL;
}
//sk中send_tail和send_head是用户缓存的单向链表表尾和表头
if (sk->send_head == NULL)
{
sk->send_tail = skb;
sk->send_head = skb;
}
else
{
sk->send_tail->link3 = skb;//link3指针用于数据包的连接
sk->send_tail = skb;
}
/* skb->link3 is NULL */
/* Interrupt restore */
restore_flags(flags);
}
else
/* Remember who owns the buffer */
skb->sk = sk;
/*
* If the indicated interface is up and running, send the packet.
*/
ip_statistics.IpOutRequests++;
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_ACCT
ip_acct_cnt(iph,dev, ip_acct_chain);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_IP_MULTICAST //这部分是IP数据报的多播处理
/*
* Multicasts are looped back for other local users
*/
.......................................
#endif
if((dev->flags&IFF_BROADCAST) && iph->daddr==dev->pa_brdaddr && !(dev->flags&IFF_LOOPBACK))//广播数据包的处理
ip_loopback(dev,skb);
if (dev->flags & IFF_UP)//设备状态正常
{
/*
* If we have an owner use its priority setting,
* otherwise use NORMAL
*/
//调用设备接口层函数发送数据: dev_queue_xmit()函数
if (sk != NULL)
{
dev_queue_xmit(skb, dev, sk->priority);
}
else
{
dev_queue_xmit(skb, dev, SOPRI_NORMAL);
}
}
else//设备状态不正常
{
ip_statistics.IpOutDiscards++;
if (free)
kfree_skb(skb, FREE_WRITE);
}
}
这个函数中对长度过长的数据包进行了分片,ip_fragment()函数,该函数没有详细分析。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
void ip_fragment(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, struct device *dev, int is_frag)
{
struct iphdr *iph;
unsigned char *raw;
unsigned char *ptr;
struct sk_buff *skb2;
int left, mtu, hlen, len;
int offset;
unsigned long flags;
/*
* Point into the IP datagram header.
*/
raw = skb->data;
iph = (struct iphdr *) (raw + dev->hard_header_len);
skb->ip_hdr = iph;
/*
* Setup starting values.
*/
hlen = (iph->ihl * sizeof(unsigned long));
left = ntohs(iph->tot_len) - hlen; /* Space per frame */
hlen += dev->hard_header_len; /* Total header size */
mtu = (dev->mtu - hlen); /* Size of data space */
ptr = (raw + hlen); /* Where to start from */
/*
* Check for any "DF" flag. [DF means do not fragment]
*/
if (ntohs(iph->frag_off) & IP_DF)
{
/*
* Reply giving the MTU of the failed hop.
*/
ip_statistics.IpFragFails++;
icmp_send(skb,ICMP_DEST_UNREACH, ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED, dev->mtu, dev);
return;
}
/*
* The protocol doesn't seem to say what to do in the case that the
* frame + options doesn't fit the mtu. As it used to fall down dead
* in this case we were fortunate it didn't happen
*/
if(mtu<8)
{
/* It's wrong but it's better than nothing */
icmp_send(skb,ICMP_DEST_UNREACH,ICMP_FRAG_NEEDED,dev->mtu, dev);
ip_statistics.IpFragFails++;
return;
}
/*
* Fragment the datagram.
*/
/*
* The initial offset is 0 for a complete frame. When
* fragmenting fragments it's wherever this one starts.
*/
if (is_frag & 2)
offset = (ntohs(iph->frag_off) & 0x1fff) << 3;
else
offset = 0;
/*
* Keep copying data until we run out.
*/
while(left > 0)
{
len = left;
/* IF: it doesn't fit, use 'mtu' - the data space left */
if (len > mtu)
len = mtu;
/* IF: we are not sending upto and including the packet end
then align the next start on an eight byte boundary */
if (len < left)
{
len/=8;
len*=8;
}
/*
* Allocate buffer.
*/
if ((skb2 = alloc_skb(len + hlen,GFP_ATOMIC)) == NULL)
{
printk("IP: frag: no memory for new fragment!\n");
ip_statistics.IpFragFails++;
return;
}
/*
* Set up data on packet
*/
skb2->arp = skb->arp;
if(skb->free==0)
printk("IP fragmenter: BUG free!=1 in fragmenter\n");
skb2->free = 1;
skb2->len = len + hlen;
skb2->h.raw=(char *) skb2->data;
/*
* Charge the memory for the fragment to any owner
* it might possess
*/
save_flags(flags);
if (sk)
{
cli();
sk->wmem_alloc += skb2->mem_len;
skb2->sk=sk;
}
restore_flags(flags);
skb2->raddr = skb->raddr; /* For rebuild_header - must be here */
/*
* Copy the packet header into the new buffer.
*/
memcpy(skb2->h.raw, raw, hlen);
/*
* Copy a block of the IP datagram.
*/
memcpy(skb2->h.raw + hlen, ptr, len);
left -= len;
skb2->h.raw+=dev->hard_header_len;
/*
* Fill in the new header fields.
*/
iph = (struct iphdr *)(skb2->h.raw/*+dev->hard_header_len*/);
iph->frag_off = htons((offset >> 3));
/*
* Added AC : If we are fragmenting a fragment thats not the
* last fragment then keep MF on each bit
*/
if (left > 0 || (is_frag & 1))
iph->frag_off |= htons(IP_MF);
ptr += len;
offset += len;
/*
* Put this fragment into the sending queue.
*/
ip_statistics.IpFragCreates++;
ip_queue_xmit(sk, dev, skb2, 2);//还是调用ip_queue_xmit()函数来发送分片后的数据
}
ip_statistics.IpFragOKs++;
}
网络层的发送函数调用了设备接口层,相当于网络模型的链路层的发送函数dev_queue_xmit()
该函数的调用关系如下:

[cpp] view
plaincopy
/*
* Send (or queue for sending) a packet.
*
* IMPORTANT: When this is called to resend frames. The caller MUST
* already have locked the sk_buff. Apart from that we do the
* rest of the magic.
*/
void dev_queue_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb, struct device *dev, int pri)
{
unsigned long flags;
int nitcount;
struct packet_type *ptype;
int where = 0; /* used to say if the packet should go */
/* at the front or the back of the */
/* queue - front is a retransmit try */
/* where=0 表示是刚从上层传递的新数据包;where=1 表示从硬件队列中取出的数据包*/
if (dev == NULL)
{
printk("dev.c: dev_queue_xmit: dev = NULL\n");
return;
}
if(pri>=0 && !skb_device_locked(skb))//锁定该skb再进行操作,避免造成内核的不一致情况
skb_device_lock(skb); /* Shove a lock on the frame */
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAVE_BALANCING
save_flags(flags);
cli();
if(dev->slave!=NULL && dev->slave->pkt_queue < dev->pkt_queue &&
(dev->slave->flags & IFF_UP))
dev=dev->slave;
restore_flags(flags);
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_SKB_CHECK
IS_SKB(skb);
#endif
skb->dev = dev;
/*
* This just eliminates some race conditions, but not all...
*/
if (skb->next != NULL) //这种条件似乎永远不能成立,因为发送数据包前,数据包已经从缓存队列摘下
{//以防内核代码有BUG
/*
* Make sure we haven't missed an interrupt.
*/
printk("dev_queue_xmit: worked around a missed interrupt\n");
start_bh_atomic();
dev->hard_start_xmit(NULL, dev);
end_bh_atomic();
return;
}
/*
* Negative priority is used to flag a frame that is being pulled from the
* queue front as a retransmit attempt. It therefore goes back on the queue
* start on a failure.
*/
if (pri < 0) //优先级小于0表示是从硬件队列中取出的数据包
{
pri = -pri-1;
where = 1;
}
if (pri >= DEV_NUMBUFFS)
{
printk("bad priority in dev_queue_xmit.\n");
pri = 1;
}
/*
* If the address has not been resolved. Call the device header rebuilder.
* This can cover all protocols and technically not just ARP either.
*/
if (!skb->arp && dev->rebuild_header(skb->data, dev, skb->raddr, skb)) {//用于ARP协议,并重建MAC帧首部
return;
}
save_flags(flags);
cli();
if (!where) {//表示是新数据包,需要将其加入设备队列中
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAVE_BALANCING
skb->in_dev_queue=1;//该数据包在设备队列
#endif
skb_queue_tail(dev->buffs + pri,skb);//将发送数据包加入硬件队列
skb_device_unlock(skb); /* Buffer is on the device queue and can be freed safely */
skb = skb_dequeue(dev->buffs + pri);//从硬件队列中取出一个数据包
skb_device_lock(skb); /* New buffer needs locking down */
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAVE_BALANCING
skb->in_dev_queue=0;
#endif
}
restore_flags(flags);
/* copy outgoing packets to any sniffer packet handlers */
if(!where)//对于新的数据包,则遍历网络层协议队列,内核支持混杂模式
{
for (nitcount= dev_nit, ptype = ptype_base; nitcount > 0 && ptype != NULL; ptype = ptype->next)
{
/* Never send packets back to the socket
* they originated from - MvS (miquels@drinkel.ow.org)
*/
if (ptype->type == htons(ETH_P_ALL) &&
(ptype->dev == dev || !ptype->dev) &&
((struct sock *)ptype->data != skb->sk))
{
struct sk_buff *skb2;
if ((skb2 = skb_clone(skb, GFP_ATOMIC)) == NULL)
break;
/*
* The protocol knows this has (for other paths) been taken off
* and adds it back.
*/
skb2->len-=skb->dev->hard_header_len;
ptype->func(skb2, skb->dev, ptype);//IP层函数对应func为ip_rcv(),将发送的数据回送一份给对应的网络层协议
nitcount--;//用于及时退出循环
}
}
}
start_bh_atomic();//开始原子操作
if (dev->hard_start_xmit(skb, dev) == 0) {//调用硬件的发送函数发送数据
end_bh_atomic();//结束原子操作
/*
* Packet is now solely the responsibility of the driver
*/
return;//到这里说明数据包成功发送
}
//数据包没有成功发送,进行处理,将数据包从新加入硬件队列
end_bh_atomic();
/*
* Transmission failed, put skb back into a list. Once on the list it's safe and
* no longer device locked (it can be freed safely from the device queue)
*/
cli();
#ifdef CONFIG_SLAVE_BALANCING
skb->in_dev_queue=1;
dev->pkt_queue++;
#endif
skb_device_unlock(skb);//对SKB解锁
skb_queue_head(dev->buffs + pri,skb);//这次采用头插法插入硬件发送队列
restore_flags(flags);
}
具体的硬件发送函数dev->hard_start_xmit的实现将做下篇博文中分析。
相关文章推荐
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(四)--网络层之IP协议(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(四)--网络层之IP协议(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(四)--网络层之IP协议(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(一)--网络栈初始化
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(六)--应用层获取数据包(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(四)--网络层之IP协议(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(六)--应用层获取数据包(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十一)--驱动程序层(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(六)--应用层获取数据包(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(七)--数据包的传递过程(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(七)--数据包的传递过程(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(四)--网络层之IP协议(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(三)--驱动程序层+链路层(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(七)--数据包的传递过程(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(三)--驱动程序层+链路层(上)
