Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(三)--驱动程序层+链路层(上)
2013-04-13 13:23
429 查看
本文分析基于Linux Kernel 1.2.13
原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7497260
更多请看专栏,地址http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/linux-kernel-net.html
作者:闫明
注:标题中的”(上)“,”(下)“表示分析过程基于数据包的传递方向:”(上)“表示分析是从底层向上分析、”(下)“表示分析是从上向下分析。
经过前面两篇博文的分析,已经对Linux的内核网络栈的结构有了一个模糊的认识,这里我们开始从底层开始详细分析Linux内核网络栈的实现。由于这是早期版本,代码的层次隔离做的还不是很好,这里说是从底层分析,但是不免会牵扯上层或下层的函数,许多关键代码都在驱动的文件夹下。
我们首先有第一篇博文中知道在网络栈初始化的时候在net/socket.c中的函数sock_init()函数中当proto_init()完成后会执行dev_init()来进行网络设备模块的初始化。
首先说明一下,在drivers/net/space.c中定义了设备首节点地址dev_base,其实际上是回环设备的地址。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
struct device loopback_dev = {
"lo", /* Software Loopback interface */
0x0, /* recv memory end */
0x0, /* recv memory start */
0x0, /* memory end */
0x0, /* memory start */
0, /* base I/O address */
0, /* IRQ */
0, 0, 0, /* flags */
NEXT_DEV, /* next device */
loopback_init /* loopback_init should set up the rest */
};
struct device *dev_base = &loopback_dev;
而NEXT_DEV宏定义即定义了下一个网络设备的地址,这样可以把设备串成链。
附网络设备的定义(include/linux/netdevice.h)如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/*
* The DEVICE structure.
* Actually, this whole structure is a big mistake. It mixes I/O
* data with strictly "high-level" data, and it has to know about
* almost every data structure used in the INET module.
*/
struct device
{
/*
* This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure
* (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name
* the interface.
*/
char *name;
/* I/O specific fields - FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one */
unsigned long rmem_end; /* shmem "recv" end */
unsigned long rmem_start; /* shmem "recv" start */
unsigned long mem_end; /* sahared mem end */
unsigned long mem_start; /* shared mem start */
unsigned long base_addr; /* device I/O address */
unsigned char irq; /* device IRQ number */
/* Low-level status flags. */
volatile unsigned char start, /* start an operation */
tbusy, /* transmitter busy */
interrupt; /* interrupt arrived */
struct device *next;
/* The device initialization function. Called only once. */
int (*init)(struct device *dev);
/* Some hardware also needs these fields, but they are not part of the
usual set specified in Space.c. */
unsigned char if_port; /* Selectable AUI, TP,..*/
unsigned char dma; /* DMA channel */
struct enet_statistics* (*get_stats)(struct device *dev);
/*
* This marks the end of the "visible" part of the structure. All
* fields hereafter are internal to the system, and may change at
* will (read: may be cleaned up at will).
*/
/* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */
unsigned long trans_start; /* Time (in jiffies) of last Tx */
unsigned long last_rx; /* Time of last Rx */
unsigned short flags; /* interface flags (a la BSD) */
unsigned short family; /* address family ID (AF_INET) */
unsigned short metric; /* routing metric (not used) */
unsigned short mtu; /* interface MTU value */
unsigned short type; /* interface hardware type */
unsigned short hard_header_len; /* hardware hdr length */
void *priv; /* pointer to private data */
/* Interface address info. */
unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw bcast add */
unsigned char dev_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw address */
unsigned char addr_len; /* hardware address length */
unsigned long pa_addr; /* protocol address */
unsigned long pa_brdaddr; /* protocol broadcast addr */
unsigned long pa_dstaddr; /* protocol P-P other side addr */
unsigned long pa_mask; /* protocol netmask */
unsigned short pa_alen; /* protocol address length */
struct dev_mc_list *mc_list; /* Multicast mac addresses */
int mc_count; /* Number of installed mcasts */
struct ip_mc_list *ip_mc_list; /* IP multicast filter chain */
/* For load balancing driver pair support */
unsigned long pkt_queue; /* Packets queued */
struct device *slave; /* Slave device */
/* Pointer to the interface buffers. */
struct sk_buff_head buffs[DEV_NUMBUFFS];
/* Pointers to interface service routines. */
int (*open)(struct device *dev);
int (*stop)(struct device *dev);
int (*hard_start_xmit) (struct sk_buff *skb,
struct device *dev);
int (*hard_header) (unsigned char *buff,
struct device *dev,
unsigned short type,
void *daddr,
void *saddr,
unsigned len,
struct sk_buff *skb);
int (*rebuild_header)(void *eth, struct device *dev,
unsigned long raddr, struct sk_buff *skb);
unsigned short (*type_trans) (struct sk_buff *skb,
struct device *dev);
#define HAVE_MULTICAST
void (*set_multicast_list)(struct device *dev,
int num_addrs, void *addrs);
#define HAVE_SET_MAC_ADDR
int (*set_mac_address)(struct device *dev, void *addr);
#define HAVE_PRIVATE_IOCTL
int (*do_ioctl)(struct device *dev, struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd);
#define HAVE_SET_CONFIG
int (*set_config)(struct device *dev, struct ifmap *map);
};
dev_init()网络设备的初始化函数如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/*
* Initialize the DEV module. At boot time this walks the device list and
* unhooks any devices that fail to initialise (normally hardware not
* present) and leaves us with a valid list of present and active devices.
*
* The PCMCIA code may need to change this a little, and add a pair
* of register_inet_device() unregister_inet_device() calls. This will be
* needed for ethernet as modules support.
*/
void dev_init(void)
{
struct device *dev, *dev2;
/*
* Add the devices.
* If the call to dev->init fails, the dev is removed
* from the chain disconnecting the device until the
* next reboot.
*/
dev2 = NULL;
for (dev = dev_base; dev != NULL; dev=dev->next) //循环移除设备由璞傅絛ev_base指向的网络设备链表
{
if (dev->init && dev->init(dev)) //如果设备有初始化函数并且初始化失败,则从链表摘除设备(init()函数成功返回0)
{
/*
* It failed to come up. Unhook it.这个函数还挺有技巧性的,从默认配置的设备中扫描不存在的设备,将其移除
*/
if (dev2 == NULL)
dev_base = dev->next;
else
dev2->next = dev->next;
}
else
{
dev2 = dev;
}
}
}
这里我们看一下dev_base这个队列是如何定义的,这里我们仅仅看eth网卡的定义方式即可
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/* "eth0" defaults to autoprobe (== 0), other use a base of 0xffe0 (== -0x20),
which means "don't probe". These entries exist to only to provide empty
slots which may be enabled at boot-time. */
static struct device eth3_dev = {
"eth3", 0,0,0,0,0xffe0 /* I/O base*/, 0,0,0,0, NEXT_DEV, ethif_probe };
static struct device eth2_dev = {
"eth2", 0,0,0,0,0xffe0 /* I/O base*/, 0,0,0,0, eth3_dev, ethif_probe };
static struct device eth1_dev = {
"eth1", 0,0,0,0,0xffe0 /* I/O base*/, 0,0,0,0, eth2_dev, ethif_probe };
static struct device eth0_dev = {
"eth0", 0, 0, 0, 0, ETH0_ADDR, ETH0_IRQ, 0, 0, 0, eth1_dev, ethif_probe };
# undef NEXT_DEV
# define NEXT_DEV (eth0_dev)
可以看出eth系列网卡设备的init函数定义为ethif_probe(),该函数会调用具体网卡的探测函数,我们还是以 NS8390 ethernet网卡为例来分析,该网卡的驱动实现文件为drivers/net/ne.c
ethif_probe()函数会调用函数ne_probe()探测函数,而该函数对设备地址进行检查后调用ne_probe1()函数,具体工作有ne_probe1()函数完成。
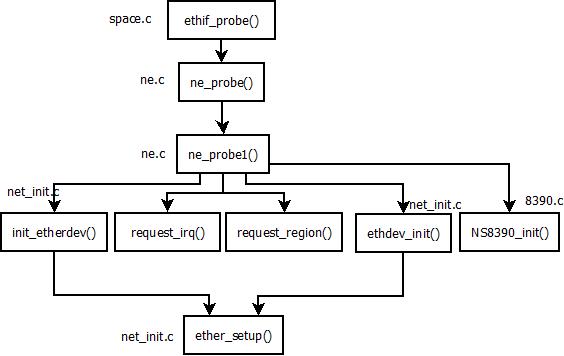
函数如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static int ne_probe1(struct device *dev, int ioaddr)
{
.....................//合法性检查
/* Fixup for users that don't know that IRQ 2 is really IRQ 9,
or don't know which one to set. */
dev->irq = 9;//设置中断类型号
/* Snarf the interrupt now. There's no point in waiting since we cannot
share and the board will usually be enabled. */
{
int irqval = request_irq (dev->irq, ei_interrupt, 0, wordlength==2 ? "ne2000":"ne1000");//注册申请中断,中断处理函数为ei_interrupt
if (irqval) {
printk (" unable to get IRQ %d (irqval=%d).\n", dev->irq, irqval);
return EAGAIN;
}
}
dev->base_addr = ioaddr;
request_region(ioaddr, NE_IO_EXTENT, wordlength==2 ? "ne2000":"ne1000");//申请内存空间
for(i = 0; i < ETHER_ADDR_LEN; i++)
dev->dev_addr[i] = SA_prom[i];
ethdev_init(dev);//调用函数对dev设备结构体进行初始化
printk("\n%s: %s found at %#x, using IRQ %d.\n",
dev->name, name, ioaddr, dev->irq);
if (ei_debug > 0)
printk(version);
ei_status.name = name;
ei_status.tx_start_page = start_page;
ei_status.stop_page = stop_page;
ei_status.word16 = (wordlength == 2);
ei_status.rx_start_page = start_page + TX_PAGES;
#ifdef PACKETBUF_MEMSIZE
/* Allow the packet buffer size to be overridden by know-it-alls. */
ei_status.stop_page = ei_status.tx_start_page + PACKETBUF_MEMSIZE;
#endif
ei_status.reset_8390 = &ne_reset_8390;
ei_status.block_input = &ne_block_input;
ei_status.block_output = &ne_block_output;
NS8390_init(dev, 0);//配置网卡中的寄存器等到默认状态
return 0;
}
初始化函数ethdev_init()在文件drivers/net/8390.c中。如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/* Initialize the rest of the 8390 device structure. */
int ethdev_init(struct device *dev)
{
if (ei_debug > 1)
printk(version);
if (dev->priv == NULL) {//申请私有空间存储具体网卡的结构体信息
struct ei_device *ei_local;//8390网卡设备的结构体
dev->priv = kmalloc(sizeof(struct ei_device), GFP_KERNEL);//申请内核内存空间
memset(dev->priv, 0, sizeof(struct ei_device));
ei_local = (struct ei_device *)dev->priv;
#ifndef NO_PINGPONG
ei_local->pingpong = 1;
#endif
}
/* The open call may be overridden by the card-specific code. */
if (dev->open == NULL)
dev->open = &ei_open;//设备的打开函数
/* We should have a dev->stop entry also. */
dev->hard_start_xmit = &ei_start_xmit;//设备的发送函数,定义在8390.c中
dev->get_stats = get_stats;
#ifdef HAVE_MULTICAST
dev->set_multicast_list = &set_multicast_list;
#endif
ether_setup(dev);//进一步调用函数设置dev设备结构体
return 0;
}
ether_setup()函数的实现如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
void ether_setup(struct device *dev)
{
int i;
/* Fill in the fields of the device structure with ethernet-generic values.
This should be in a common file instead of per-driver. */
for (i = 0; i < DEV_NUMBUFFS; i++)
skb_queue_head_init(&dev->buffs[i]);//缓冲队列初始化
/* register boot-defined "eth" devices */
if (dev->name && (strncmp(dev->name, "eth", 3) == 0)) {//定义eth网卡的名称
i = simple_strtoul(dev->name + 3, NULL, 0);
if (ethdev_index[i] == NULL) {
ethdev_index[i] = dev;
}
else if (dev != ethdev_index[i]) {
/* Really shouldn't happen! */
printk("ether_setup: Ouch! Someone else took %s\n",
dev->name);
}
}
dev->hard_header = eth_header;//该函数的作用是创建链路层首部,定义在eth.c中
dev->rebuild_header = eth_rebuild_header;//该函数的作用是重建链路层首部,用于ARP协议
dev->type_trans = eth_type_trans;
dev->type = ARPHRD_ETHER;
dev->hard_header_len = ETH_HLEN;
dev->mtu = 1500; /* eth_mtu */
dev->addr_len = ETH_ALEN;
for (i = 0; i < ETH_ALEN; i++) {
dev->broadcast[i]=0xff;
}
/* New-style flags. */
dev->flags = IFF_BROADCAST|IFF_MULTICAST;
dev->family = AF_INET;
dev->pa_addr = 0;
dev->pa_brdaddr = 0;
dev->pa_mask = 0;
dev->pa_alen = sizeof(unsigned long);
}
这样,网络设备的初始化工作就完成了。
在drivers/net/8390.c中实现了该网卡的设备的基本操作函数,
设备的打开函数ei_open()比较简单,下面列出该设备的发送和接收函数,在这里不做具体的分析,如果想更多了解请点击前面分析过的DM9000网卡驱动,下面给出链接:
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(一)
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(二)
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(三)
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(四)
其基本结构是一致的。
ei_start_xmit()
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static int ei_start_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb, struct device *dev)
{
int e8390_base = dev->base_addr;
struct ei_device *ei_local = (struct ei_device *) dev->priv;
int length, send_length;
unsigned long flags;
/*
* We normally shouldn't be called if dev->tbusy is set, but the
* existing code does anyway. If it has been too long since the
* last Tx, we assume the board has died and kick it.
*/
if (dev->tbusy) { /* Do timeouts, just like the 8003 driver. */
int txsr = inb(e8390_base+EN0_TSR), isr;
int tickssofar = jiffies - dev->trans_start;
if (tickssofar < TX_TIMEOUT || (tickssofar < (TX_TIMEOUT+5) && ! (txsr & ENTSR_PTX))) {
return 1;
}
isr = inb(e8390_base+EN0_ISR);
if (dev->start == 0) {
printk("%s: xmit on stopped card\n", dev->name);
return 1;
}
printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: transmit timed out, TX status %#2x, ISR %#2x.\n",
dev->name, txsr, isr);
/* Does the 8390 thinks it has posted an interrupt? */
if (isr)
printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: Possible IRQ conflict on IRQ%d?\n", dev->name, dev->irq);
else {
/* The 8390 probably hasn't gotten on the cable yet. */
printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: Possible network cable problem?\n", dev->name);
if(ei_local->stat.tx_packets==0)
ei_local->interface_num ^= 1; /* Try a different xcvr. */
}
/* Try to restart the card. Perhaps the user has fixed something. */
ei_reset_8390(dev);
NS8390_init(dev, 1);
dev->trans_start = jiffies;
}
/* Sending a NULL skb means some higher layer thinks we've missed an
tx-done interrupt. Caution: dev_tint() handles the cli()/sti()
itself. */
if (skb == NULL) {
dev_tint(dev);
return 0;
}
length = skb->len;
if (skb->len <= 0)
return 0;
save_flags(flags);
cli();
/* Block a timer-based transmit from overlapping. */
if ((set_bit(0, (void*)&dev->tbusy) != 0) || ei_local->irqlock) {
printk("%s: Tx access conflict. irq=%d lock=%d tx1=%d tx2=%d last=%d\n",
dev->name, dev->interrupt, ei_local->irqlock, ei_local->tx1,
ei_local->tx2, ei_local->lasttx);
restore_flags(flags);
return 1;
}
/* Mask interrupts from the ethercard. */
outb(0x00, e8390_base + EN0_IMR);
ei_local->irqlock = 1;
restore_flags(flags);
send_length = ETH_ZLEN < length ? length : ETH_ZLEN;
if (ei_local->pingpong) {
int output_page;
if (ei_local->tx1 == 0) {
output_page = ei_local->tx_start_page;
ei_local->tx1 = send_length;
if (ei_debug && ei_local->tx2 > 0)
printk("%s: idle transmitter tx2=%d, lasttx=%d, txing=%d.\n",
dev->name, ei_local->tx2, ei_local->lasttx,
ei_local->txing);
} else if (ei_local->tx2 == 0) {
output_page = ei_local->tx_start_page + 6;
ei_local->tx2 = send_length;
if (ei_debug && ei_local->tx1 > 0)
printk("%s: idle transmitter, tx1=%d, lasttx=%d, txing=%d.\n",
dev->name, ei_local->tx1, ei_local->lasttx,
ei_local->txing);
} else { /* We should never get here. */
if (ei_debug)
printk("%s: No Tx buffers free. irq=%d tx1=%d tx2=%d last=%d\n",
dev->name, dev->interrupt, ei_local->tx1,
ei_local->tx2, ei_local->lasttx);
ei_local->irqlock = 0;
dev->tbusy = 1;
outb_p(ENISR_ALL, e8390_base + EN0_IMR);
return 1;
}
ei_block_output(dev, length, skb->data, output_page);
if (! ei_local->txing) {
ei_local->txing = 1;
NS8390_trigger_send(dev, send_length, output_page);
dev->trans_start = jiffies;
if (output_page == ei_local->tx_start_page)
ei_local->tx1 = -1, ei_local->lasttx = -1;
else
ei_local->tx2 = -1, ei_local->lasttx = -2;
} else
ei_local->txqueue++;
dev->tbusy = (ei_local->tx1 && ei_local->tx2);
} else { /* No pingpong, just a single Tx buffer. */
ei_block_output(dev, length, skb->data, ei_local->tx_start_page);
ei_local->txing = 1;
NS8390_trigger_send(dev, send_length, ei_local->tx_start_page);
dev->trans_start = jiffies;
dev->tbusy = 1;
}
/* Turn 8390 interrupts back on. */
ei_local->irqlock = 0;
outb_p(ENISR_ALL, e8390_base + EN0_IMR);
dev_kfree_skb (skb, FREE_WRITE);
return 0;
}
ei_receive()函数
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static void ei_receive(struct device *dev)
{
int e8390_base = dev->base_addr;
struct ei_device *ei_local = (struct ei_device *) dev->priv;
int rxing_page, this_frame, next_frame, current_offset;
int rx_pkt_count = 0;
struct e8390_pkt_hdr rx_frame;
int num_rx_pages = ei_local->stop_page-ei_local->rx_start_page;
while (++rx_pkt_count < 10) {
int pkt_len;
/* Get the rx page (incoming packet pointer). */
outb_p(E8390_NODMA+E8390_PAGE1, e8390_base + E8390_CMD);
rxing_page = inb_p(e8390_base + EN1_CURPAG);
outb_p(E8390_NODMA+E8390_PAGE0, e8390_base + E8390_CMD);
/* Remove one frame from the ring. Boundary is always a page behind. */
this_frame = inb_p(e8390_base + EN0_BOUNDARY) + 1;
if (this_frame >= ei_local->stop_page)
this_frame = ei_local->rx_start_page;
/* Someday we'll omit the previous, iff we never get this message.
(There is at least one clone claimed to have a problem.) */
if (ei_debug > 0 && this_frame != ei_local->current_page)
printk("%s: mismatched read page pointers %2x vs %2x.\n",
dev->name, this_frame, ei_local->current_page);
if (this_frame == rxing_page) /* Read all the frames? */
break; /* Done for now */
current_offset = this_frame << 8;
ei_block_input(dev, sizeof(rx_frame), (char *)&rx_frame,
current_offset);
pkt_len = rx_frame.count - sizeof(rx_frame);
next_frame = this_frame + 1 + ((pkt_len+4)>>8);
/* Check for bogosity warned by 3c503 book: the status byte is never
written. This happened a lot during testing! This code should be
cleaned up someday. */
if (rx_frame.next != next_frame
&& rx_frame.next != next_frame + 1
&& rx_frame.next != next_frame - num_rx_pages
&& rx_frame.next != next_frame + 1 - num_rx_pages) {
ei_local->current_page = rxing_page;
outb(ei_local->current_page-1, e8390_base+EN0_BOUNDARY);
ei_local->stat.rx_errors++;
continue;
}
if (pkt_len < 60 || pkt_len > 1518) {
if (ei_debug)
printk("%s: bogus packet size: %d, status=%#2x nxpg=%#2x.\n",
dev->name, rx_frame.count, rx_frame.status,
rx_frame.next);
ei_local->stat.rx_errors++;
} else if ((rx_frame.status & 0x0F) == ENRSR_RXOK) {
struct sk_buff *skb;
skb = alloc_skb(pkt_len, GFP_ATOMIC);
if (skb == NULL) {
if (ei_debug > 1)
printk("%s: Couldn't allocate a sk_buff of size %d.\n",
dev->name, pkt_len);
ei_local->stat.rx_dropped++;
break;
} else {
skb->len = pkt_len;
skb->dev = dev;
ei_block_input(dev, pkt_len, (char *) skb->data,
current_offset + sizeof(rx_frame));
netif_rx(skb);
ei_local->stat.rx_packets++;
}
} else {
int errs = rx_frame.status;
if (ei_debug)
printk("%s: bogus packet: status=%#2x nxpg=%#2x size=%d\n",
dev->name, rx_frame.status, rx_frame.next,
rx_frame.count);
if (errs & ENRSR_FO)
ei_local->stat.rx_fifo_errors++;
}
next_frame = rx_frame.next;
/* This _should_ never happen: it's here for avoiding bad clones. */
if (next_frame >= ei_local->stop_page) {
printk("%s: next frame inconsistency, %#2x\n", dev->name,
next_frame);
next_frame = ei_local->rx_start_page;
}
ei_local->current_page = next_frame;
outb_p(next_frame-1, e8390_base+EN0_BOUNDARY);
}
/* If any worth-while packets have been received, dev_rint()
has done a mark_bh(NET_BH) for us and will work on them
when we get to the bottom-half routine. */
/* Record the maximum Rx packet queue. */
if (rx_pkt_count > high_water_mark)
high_water_mark = rx_pkt_count;
/* Bug alert! Reset ENISR_OVER to avoid spurious overruns! */
outb_p(ENISR_RX+ENISR_RX_ERR+ENISR_OVER, e8390_base+EN0_ISR);
return;
}
原创作品,转载请标明http://blog.csdn.net/yming0221/article/details/7497260
更多请看专栏,地址http://blog.csdn.net/column/details/linux-kernel-net.html
作者:闫明
注:标题中的”(上)“,”(下)“表示分析过程基于数据包的传递方向:”(上)“表示分析是从底层向上分析、”(下)“表示分析是从上向下分析。
经过前面两篇博文的分析,已经对Linux的内核网络栈的结构有了一个模糊的认识,这里我们开始从底层开始详细分析Linux内核网络栈的实现。由于这是早期版本,代码的层次隔离做的还不是很好,这里说是从底层分析,但是不免会牵扯上层或下层的函数,许多关键代码都在驱动的文件夹下。
我们首先有第一篇博文中知道在网络栈初始化的时候在net/socket.c中的函数sock_init()函数中当proto_init()完成后会执行dev_init()来进行网络设备模块的初始化。
首先说明一下,在drivers/net/space.c中定义了设备首节点地址dev_base,其实际上是回环设备的地址。
[cpp] view
plaincopy
struct device loopback_dev = {
"lo", /* Software Loopback interface */
0x0, /* recv memory end */
0x0, /* recv memory start */
0x0, /* memory end */
0x0, /* memory start */
0, /* base I/O address */
0, /* IRQ */
0, 0, 0, /* flags */
NEXT_DEV, /* next device */
loopback_init /* loopback_init should set up the rest */
};
struct device *dev_base = &loopback_dev;
而NEXT_DEV宏定义即定义了下一个网络设备的地址,这样可以把设备串成链。
附网络设备的定义(include/linux/netdevice.h)如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/*
* The DEVICE structure.
* Actually, this whole structure is a big mistake. It mixes I/O
* data with strictly "high-level" data, and it has to know about
* almost every data structure used in the INET module.
*/
struct device
{
/*
* This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure
* (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name
* the interface.
*/
char *name;
/* I/O specific fields - FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one */
unsigned long rmem_end; /* shmem "recv" end */
unsigned long rmem_start; /* shmem "recv" start */
unsigned long mem_end; /* sahared mem end */
unsigned long mem_start; /* shared mem start */
unsigned long base_addr; /* device I/O address */
unsigned char irq; /* device IRQ number */
/* Low-level status flags. */
volatile unsigned char start, /* start an operation */
tbusy, /* transmitter busy */
interrupt; /* interrupt arrived */
struct device *next;
/* The device initialization function. Called only once. */
int (*init)(struct device *dev);
/* Some hardware also needs these fields, but they are not part of the
usual set specified in Space.c. */
unsigned char if_port; /* Selectable AUI, TP,..*/
unsigned char dma; /* DMA channel */
struct enet_statistics* (*get_stats)(struct device *dev);
/*
* This marks the end of the "visible" part of the structure. All
* fields hereafter are internal to the system, and may change at
* will (read: may be cleaned up at will).
*/
/* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */
unsigned long trans_start; /* Time (in jiffies) of last Tx */
unsigned long last_rx; /* Time of last Rx */
unsigned short flags; /* interface flags (a la BSD) */
unsigned short family; /* address family ID (AF_INET) */
unsigned short metric; /* routing metric (not used) */
unsigned short mtu; /* interface MTU value */
unsigned short type; /* interface hardware type */
unsigned short hard_header_len; /* hardware hdr length */
void *priv; /* pointer to private data */
/* Interface address info. */
unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw bcast add */
unsigned char dev_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw address */
unsigned char addr_len; /* hardware address length */
unsigned long pa_addr; /* protocol address */
unsigned long pa_brdaddr; /* protocol broadcast addr */
unsigned long pa_dstaddr; /* protocol P-P other side addr */
unsigned long pa_mask; /* protocol netmask */
unsigned short pa_alen; /* protocol address length */
struct dev_mc_list *mc_list; /* Multicast mac addresses */
int mc_count; /* Number of installed mcasts */
struct ip_mc_list *ip_mc_list; /* IP multicast filter chain */
/* For load balancing driver pair support */
unsigned long pkt_queue; /* Packets queued */
struct device *slave; /* Slave device */
/* Pointer to the interface buffers. */
struct sk_buff_head buffs[DEV_NUMBUFFS];
/* Pointers to interface service routines. */
int (*open)(struct device *dev);
int (*stop)(struct device *dev);
int (*hard_start_xmit) (struct sk_buff *skb,
struct device *dev);
int (*hard_header) (unsigned char *buff,
struct device *dev,
unsigned short type,
void *daddr,
void *saddr,
unsigned len,
struct sk_buff *skb);
int (*rebuild_header)(void *eth, struct device *dev,
unsigned long raddr, struct sk_buff *skb);
unsigned short (*type_trans) (struct sk_buff *skb,
struct device *dev);
#define HAVE_MULTICAST
void (*set_multicast_list)(struct device *dev,
int num_addrs, void *addrs);
#define HAVE_SET_MAC_ADDR
int (*set_mac_address)(struct device *dev, void *addr);
#define HAVE_PRIVATE_IOCTL
int (*do_ioctl)(struct device *dev, struct ifreq *ifr, int cmd);
#define HAVE_SET_CONFIG
int (*set_config)(struct device *dev, struct ifmap *map);
};
dev_init()网络设备的初始化函数如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/*
* Initialize the DEV module. At boot time this walks the device list and
* unhooks any devices that fail to initialise (normally hardware not
* present) and leaves us with a valid list of present and active devices.
*
* The PCMCIA code may need to change this a little, and add a pair
* of register_inet_device() unregister_inet_device() calls. This will be
* needed for ethernet as modules support.
*/
void dev_init(void)
{
struct device *dev, *dev2;
/*
* Add the devices.
* If the call to dev->init fails, the dev is removed
* from the chain disconnecting the device until the
* next reboot.
*/
dev2 = NULL;
for (dev = dev_base; dev != NULL; dev=dev->next) //循环移除设备由璞傅絛ev_base指向的网络设备链表
{
if (dev->init && dev->init(dev)) //如果设备有初始化函数并且初始化失败,则从链表摘除设备(init()函数成功返回0)
{
/*
* It failed to come up. Unhook it.这个函数还挺有技巧性的,从默认配置的设备中扫描不存在的设备,将其移除
*/
if (dev2 == NULL)
dev_base = dev->next;
else
dev2->next = dev->next;
}
else
{
dev2 = dev;
}
}
}
这里我们看一下dev_base这个队列是如何定义的,这里我们仅仅看eth网卡的定义方式即可
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/* "eth0" defaults to autoprobe (== 0), other use a base of 0xffe0 (== -0x20),
which means "don't probe". These entries exist to only to provide empty
slots which may be enabled at boot-time. */
static struct device eth3_dev = {
"eth3", 0,0,0,0,0xffe0 /* I/O base*/, 0,0,0,0, NEXT_DEV, ethif_probe };
static struct device eth2_dev = {
"eth2", 0,0,0,0,0xffe0 /* I/O base*/, 0,0,0,0, eth3_dev, ethif_probe };
static struct device eth1_dev = {
"eth1", 0,0,0,0,0xffe0 /* I/O base*/, 0,0,0,0, eth2_dev, ethif_probe };
static struct device eth0_dev = {
"eth0", 0, 0, 0, 0, ETH0_ADDR, ETH0_IRQ, 0, 0, 0, eth1_dev, ethif_probe };
# undef NEXT_DEV
# define NEXT_DEV (eth0_dev)
可以看出eth系列网卡设备的init函数定义为ethif_probe(),该函数会调用具体网卡的探测函数,我们还是以 NS8390 ethernet网卡为例来分析,该网卡的驱动实现文件为drivers/net/ne.c
ethif_probe()函数会调用函数ne_probe()探测函数,而该函数对设备地址进行检查后调用ne_probe1()函数,具体工作有ne_probe1()函数完成。

函数如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static int ne_probe1(struct device *dev, int ioaddr)
{
.....................//合法性检查
/* Fixup for users that don't know that IRQ 2 is really IRQ 9,
or don't know which one to set. */
dev->irq = 9;//设置中断类型号
/* Snarf the interrupt now. There's no point in waiting since we cannot
share and the board will usually be enabled. */
{
int irqval = request_irq (dev->irq, ei_interrupt, 0, wordlength==2 ? "ne2000":"ne1000");//注册申请中断,中断处理函数为ei_interrupt
if (irqval) {
printk (" unable to get IRQ %d (irqval=%d).\n", dev->irq, irqval);
return EAGAIN;
}
}
dev->base_addr = ioaddr;
request_region(ioaddr, NE_IO_EXTENT, wordlength==2 ? "ne2000":"ne1000");//申请内存空间
for(i = 0; i < ETHER_ADDR_LEN; i++)
dev->dev_addr[i] = SA_prom[i];
ethdev_init(dev);//调用函数对dev设备结构体进行初始化
printk("\n%s: %s found at %#x, using IRQ %d.\n",
dev->name, name, ioaddr, dev->irq);
if (ei_debug > 0)
printk(version);
ei_status.name = name;
ei_status.tx_start_page = start_page;
ei_status.stop_page = stop_page;
ei_status.word16 = (wordlength == 2);
ei_status.rx_start_page = start_page + TX_PAGES;
#ifdef PACKETBUF_MEMSIZE
/* Allow the packet buffer size to be overridden by know-it-alls. */
ei_status.stop_page = ei_status.tx_start_page + PACKETBUF_MEMSIZE;
#endif
ei_status.reset_8390 = &ne_reset_8390;
ei_status.block_input = &ne_block_input;
ei_status.block_output = &ne_block_output;
NS8390_init(dev, 0);//配置网卡中的寄存器等到默认状态
return 0;
}
初始化函数ethdev_init()在文件drivers/net/8390.c中。如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
/* Initialize the rest of the 8390 device structure. */
int ethdev_init(struct device *dev)
{
if (ei_debug > 1)
printk(version);
if (dev->priv == NULL) {//申请私有空间存储具体网卡的结构体信息
struct ei_device *ei_local;//8390网卡设备的结构体
dev->priv = kmalloc(sizeof(struct ei_device), GFP_KERNEL);//申请内核内存空间
memset(dev->priv, 0, sizeof(struct ei_device));
ei_local = (struct ei_device *)dev->priv;
#ifndef NO_PINGPONG
ei_local->pingpong = 1;
#endif
}
/* The open call may be overridden by the card-specific code. */
if (dev->open == NULL)
dev->open = &ei_open;//设备的打开函数
/* We should have a dev->stop entry also. */
dev->hard_start_xmit = &ei_start_xmit;//设备的发送函数,定义在8390.c中
dev->get_stats = get_stats;
#ifdef HAVE_MULTICAST
dev->set_multicast_list = &set_multicast_list;
#endif
ether_setup(dev);//进一步调用函数设置dev设备结构体
return 0;
}
ether_setup()函数的实现如下:
[cpp] view
plaincopy
void ether_setup(struct device *dev)
{
int i;
/* Fill in the fields of the device structure with ethernet-generic values.
This should be in a common file instead of per-driver. */
for (i = 0; i < DEV_NUMBUFFS; i++)
skb_queue_head_init(&dev->buffs[i]);//缓冲队列初始化
/* register boot-defined "eth" devices */
if (dev->name && (strncmp(dev->name, "eth", 3) == 0)) {//定义eth网卡的名称
i = simple_strtoul(dev->name + 3, NULL, 0);
if (ethdev_index[i] == NULL) {
ethdev_index[i] = dev;
}
else if (dev != ethdev_index[i]) {
/* Really shouldn't happen! */
printk("ether_setup: Ouch! Someone else took %s\n",
dev->name);
}
}
dev->hard_header = eth_header;//该函数的作用是创建链路层首部,定义在eth.c中
dev->rebuild_header = eth_rebuild_header;//该函数的作用是重建链路层首部,用于ARP协议
dev->type_trans = eth_type_trans;
dev->type = ARPHRD_ETHER;
dev->hard_header_len = ETH_HLEN;
dev->mtu = 1500; /* eth_mtu */
dev->addr_len = ETH_ALEN;
for (i = 0; i < ETH_ALEN; i++) {
dev->broadcast[i]=0xff;
}
/* New-style flags. */
dev->flags = IFF_BROADCAST|IFF_MULTICAST;
dev->family = AF_INET;
dev->pa_addr = 0;
dev->pa_brdaddr = 0;
dev->pa_mask = 0;
dev->pa_alen = sizeof(unsigned long);
}
这样,网络设备的初始化工作就完成了。
在drivers/net/8390.c中实现了该网卡的设备的基本操作函数,

设备的打开函数ei_open()比较简单,下面列出该设备的发送和接收函数,在这里不做具体的分析,如果想更多了解请点击前面分析过的DM9000网卡驱动,下面给出链接:
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(一)
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(二)
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(三)
ARM-Linux驱动--DM9000网卡驱动分析(四)
其基本结构是一致的。
ei_start_xmit()
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static int ei_start_xmit(struct sk_buff *skb, struct device *dev)
{
int e8390_base = dev->base_addr;
struct ei_device *ei_local = (struct ei_device *) dev->priv;
int length, send_length;
unsigned long flags;
/*
* We normally shouldn't be called if dev->tbusy is set, but the
* existing code does anyway. If it has been too long since the
* last Tx, we assume the board has died and kick it.
*/
if (dev->tbusy) { /* Do timeouts, just like the 8003 driver. */
int txsr = inb(e8390_base+EN0_TSR), isr;
int tickssofar = jiffies - dev->trans_start;
if (tickssofar < TX_TIMEOUT || (tickssofar < (TX_TIMEOUT+5) && ! (txsr & ENTSR_PTX))) {
return 1;
}
isr = inb(e8390_base+EN0_ISR);
if (dev->start == 0) {
printk("%s: xmit on stopped card\n", dev->name);
return 1;
}
printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: transmit timed out, TX status %#2x, ISR %#2x.\n",
dev->name, txsr, isr);
/* Does the 8390 thinks it has posted an interrupt? */
if (isr)
printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: Possible IRQ conflict on IRQ%d?\n", dev->name, dev->irq);
else {
/* The 8390 probably hasn't gotten on the cable yet. */
printk(KERN_DEBUG "%s: Possible network cable problem?\n", dev->name);
if(ei_local->stat.tx_packets==0)
ei_local->interface_num ^= 1; /* Try a different xcvr. */
}
/* Try to restart the card. Perhaps the user has fixed something. */
ei_reset_8390(dev);
NS8390_init(dev, 1);
dev->trans_start = jiffies;
}
/* Sending a NULL skb means some higher layer thinks we've missed an
tx-done interrupt. Caution: dev_tint() handles the cli()/sti()
itself. */
if (skb == NULL) {
dev_tint(dev);
return 0;
}
length = skb->len;
if (skb->len <= 0)
return 0;
save_flags(flags);
cli();
/* Block a timer-based transmit from overlapping. */
if ((set_bit(0, (void*)&dev->tbusy) != 0) || ei_local->irqlock) {
printk("%s: Tx access conflict. irq=%d lock=%d tx1=%d tx2=%d last=%d\n",
dev->name, dev->interrupt, ei_local->irqlock, ei_local->tx1,
ei_local->tx2, ei_local->lasttx);
restore_flags(flags);
return 1;
}
/* Mask interrupts from the ethercard. */
outb(0x00, e8390_base + EN0_IMR);
ei_local->irqlock = 1;
restore_flags(flags);
send_length = ETH_ZLEN < length ? length : ETH_ZLEN;
if (ei_local->pingpong) {
int output_page;
if (ei_local->tx1 == 0) {
output_page = ei_local->tx_start_page;
ei_local->tx1 = send_length;
if (ei_debug && ei_local->tx2 > 0)
printk("%s: idle transmitter tx2=%d, lasttx=%d, txing=%d.\n",
dev->name, ei_local->tx2, ei_local->lasttx,
ei_local->txing);
} else if (ei_local->tx2 == 0) {
output_page = ei_local->tx_start_page + 6;
ei_local->tx2 = send_length;
if (ei_debug && ei_local->tx1 > 0)
printk("%s: idle transmitter, tx1=%d, lasttx=%d, txing=%d.\n",
dev->name, ei_local->tx1, ei_local->lasttx,
ei_local->txing);
} else { /* We should never get here. */
if (ei_debug)
printk("%s: No Tx buffers free. irq=%d tx1=%d tx2=%d last=%d\n",
dev->name, dev->interrupt, ei_local->tx1,
ei_local->tx2, ei_local->lasttx);
ei_local->irqlock = 0;
dev->tbusy = 1;
outb_p(ENISR_ALL, e8390_base + EN0_IMR);
return 1;
}
ei_block_output(dev, length, skb->data, output_page);
if (! ei_local->txing) {
ei_local->txing = 1;
NS8390_trigger_send(dev, send_length, output_page);
dev->trans_start = jiffies;
if (output_page == ei_local->tx_start_page)
ei_local->tx1 = -1, ei_local->lasttx = -1;
else
ei_local->tx2 = -1, ei_local->lasttx = -2;
} else
ei_local->txqueue++;
dev->tbusy = (ei_local->tx1 && ei_local->tx2);
} else { /* No pingpong, just a single Tx buffer. */
ei_block_output(dev, length, skb->data, ei_local->tx_start_page);
ei_local->txing = 1;
NS8390_trigger_send(dev, send_length, ei_local->tx_start_page);
dev->trans_start = jiffies;
dev->tbusy = 1;
}
/* Turn 8390 interrupts back on. */
ei_local->irqlock = 0;
outb_p(ENISR_ALL, e8390_base + EN0_IMR);
dev_kfree_skb (skb, FREE_WRITE);
return 0;
}
ei_receive()函数
[cpp] view
plaincopy
static void ei_receive(struct device *dev)
{
int e8390_base = dev->base_addr;
struct ei_device *ei_local = (struct ei_device *) dev->priv;
int rxing_page, this_frame, next_frame, current_offset;
int rx_pkt_count = 0;
struct e8390_pkt_hdr rx_frame;
int num_rx_pages = ei_local->stop_page-ei_local->rx_start_page;
while (++rx_pkt_count < 10) {
int pkt_len;
/* Get the rx page (incoming packet pointer). */
outb_p(E8390_NODMA+E8390_PAGE1, e8390_base + E8390_CMD);
rxing_page = inb_p(e8390_base + EN1_CURPAG);
outb_p(E8390_NODMA+E8390_PAGE0, e8390_base + E8390_CMD);
/* Remove one frame from the ring. Boundary is always a page behind. */
this_frame = inb_p(e8390_base + EN0_BOUNDARY) + 1;
if (this_frame >= ei_local->stop_page)
this_frame = ei_local->rx_start_page;
/* Someday we'll omit the previous, iff we never get this message.
(There is at least one clone claimed to have a problem.) */
if (ei_debug > 0 && this_frame != ei_local->current_page)
printk("%s: mismatched read page pointers %2x vs %2x.\n",
dev->name, this_frame, ei_local->current_page);
if (this_frame == rxing_page) /* Read all the frames? */
break; /* Done for now */
current_offset = this_frame << 8;
ei_block_input(dev, sizeof(rx_frame), (char *)&rx_frame,
current_offset);
pkt_len = rx_frame.count - sizeof(rx_frame);
next_frame = this_frame + 1 + ((pkt_len+4)>>8);
/* Check for bogosity warned by 3c503 book: the status byte is never
written. This happened a lot during testing! This code should be
cleaned up someday. */
if (rx_frame.next != next_frame
&& rx_frame.next != next_frame + 1
&& rx_frame.next != next_frame - num_rx_pages
&& rx_frame.next != next_frame + 1 - num_rx_pages) {
ei_local->current_page = rxing_page;
outb(ei_local->current_page-1, e8390_base+EN0_BOUNDARY);
ei_local->stat.rx_errors++;
continue;
}
if (pkt_len < 60 || pkt_len > 1518) {
if (ei_debug)
printk("%s: bogus packet size: %d, status=%#2x nxpg=%#2x.\n",
dev->name, rx_frame.count, rx_frame.status,
rx_frame.next);
ei_local->stat.rx_errors++;
} else if ((rx_frame.status & 0x0F) == ENRSR_RXOK) {
struct sk_buff *skb;
skb = alloc_skb(pkt_len, GFP_ATOMIC);
if (skb == NULL) {
if (ei_debug > 1)
printk("%s: Couldn't allocate a sk_buff of size %d.\n",
dev->name, pkt_len);
ei_local->stat.rx_dropped++;
break;
} else {
skb->len = pkt_len;
skb->dev = dev;
ei_block_input(dev, pkt_len, (char *) skb->data,
current_offset + sizeof(rx_frame));
netif_rx(skb);
ei_local->stat.rx_packets++;
}
} else {
int errs = rx_frame.status;
if (ei_debug)
printk("%s: bogus packet: status=%#2x nxpg=%#2x size=%d\n",
dev->name, rx_frame.status, rx_frame.next,
rx_frame.count);
if (errs & ENRSR_FO)
ei_local->stat.rx_fifo_errors++;
}
next_frame = rx_frame.next;
/* This _should_ never happen: it's here for avoiding bad clones. */
if (next_frame >= ei_local->stop_page) {
printk("%s: next frame inconsistency, %#2x\n", dev->name,
next_frame);
next_frame = ei_local->rx_start_page;
}
ei_local->current_page = next_frame;
outb_p(next_frame-1, e8390_base+EN0_BOUNDARY);
}
/* If any worth-while packets have been received, dev_rint()
has done a mark_bh(NET_BH) for us and will work on them
when we get to the bottom-half routine. */
/* Record the maximum Rx packet queue. */
if (rx_pkt_count > high_water_mark)
high_water_mark = rx_pkt_count;
/* Bug alert! Reset ENISR_OVER to avoid spurious overruns! */
outb_p(ENISR_RX+ENISR_RX_ERR+ENISR_OVER, e8390_base+EN0_ISR);
return;
}
相关文章推荐
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(三)--驱动程序层+链路层(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(三)--驱动程序层+链路层(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(七)--数据包的传递过程(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(五)--传输层之UDP协议(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(九)--传输层之UDP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(五)--传输层之UDP协议(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(五)--传输层之UDP协议(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十一)--驱动程序层(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(六)--应用层获取数据包(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十一)--驱动程序层(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(一)--网络栈初始化
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(六)--应用层获取数据包(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十)--网络层之IP协议(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(六)--应用层获取数据包(上)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(十一)--驱动程序层(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(七)--数据包的传递过程(下)
- Linux内核--网络栈实现分析(七)--数据包的传递过程(下)
