Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
2012-10-18 23:39
585 查看
在android中,Activity是四大组件中比较重要的一个(当然其他的也比较重要),那么android中是怎样管理这些activity的?应用的进程和主线程是怎么创建的,应用的消息循环又是在什么时候创建的?在这篇文章中将详细介绍:
先来看下涉及到的类,通过以下类图对整体先有个大概的印象:
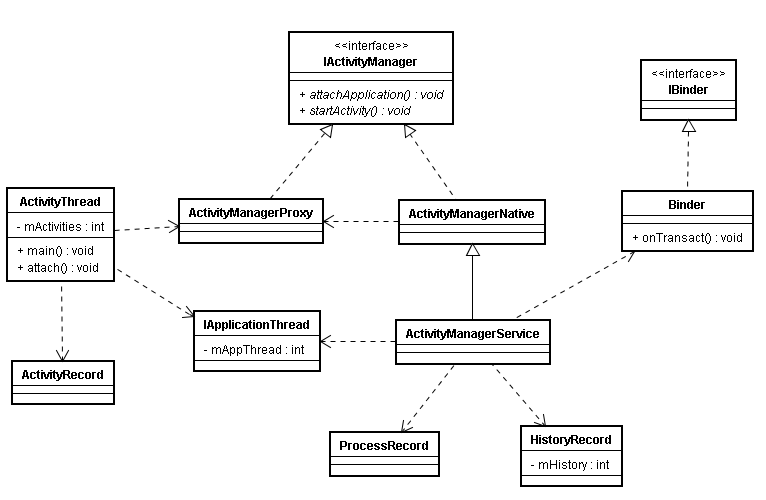
ActivityThread:
ActivityThread主要用来启动应用程序的主线程,并且管理在应用端跟用户打交道的activity。在应用端的activity信息全部被存储在ActivityThread的成员变量mActivities中。
[java]
view plaincopyprint?
final HashMap<IBinder, ActivityRecord> mActivities=
new HashMap<IBinder, ActivityRecord>();
在建立消息循环之前,会通过thread.attach(false)来初始化应用程序的运行环境,并建立activityThread和ActivityManagerService之间的桥mAppThread,
mAppThread是IApplicationThread的一个实例。
[java]
view plaincopyprint?
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("<pre-initialized>"); RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder()); IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try { mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread); }
catch (RemoteException ex) { }
把r加入到mHistory中。
[c-sharp]
view plaincopyprint?
mHistory.add(addPos, r);
涉及的主要类图:

再来看下ApplicationThread中的scheduleLaunchActivity方法:
[c-sharp]
view plaincopyprint?
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token,
int ident, ActivityInfo info, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward) { ActivityRecord r =
new ActivityRecord(); r.token = token; r.ident = ident; r.intent = intent; r.activityInfo = info; r.state = state; r.pendingResults = pendingResults; r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents; r.startsNotResumed = notResumed;
r.isForward = isForward; queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r); }
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident, ActivityInfo info, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward) { ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(); r.token = token; r.ident = ident; r.intent = intent; r.activityInfo = info; r.state = state; r.pendingResults = pendingResults; r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents; r.startsNotResumed = notResumed; r.isForward = isForward; queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r); }
在这个里面主要是根据服务端返回回来的信息创建客户端activity记录ActivityRecord.
并通过Handler发送消息到消息队列,进入消息循环。在ActivityThread.handleMessage()中处理消息。最终在handleLaunchActivity方法中把ActivityRecord记录加入到mActivities(mActivities.put(r.token,r))中,并启动activity(涉及到window、view、windowManager,详情请看handleResumeActivity()方法和上一篇关于window、WindowManager的介绍)
总结:
在客户端和服务端分别有一个管理activity的地方,服务端是在mHistory中,处于mHistory栈顶的就是当前处于running状态的activity,客户端是在mActivities中。
在startActivity时,首先会在ActivityManagerService中建立HistoryRecord,并加入到mHistory中,然后通过scheduleLaunchActivity在客户端创建ActivityRecord记录并加入到mActivities中。最终在ActivityThread发起请求,进入消息循环,完成activity的启动和窗口的管理等
先来看下涉及到的类,通过以下类图对整体先有个大概的印象:

ActivityThread:
ActivityThread主要用来启动应用程序的主线程,并且管理在应用端跟用户打交道的activity。在应用端的activity信息全部被存储在ActivityThread的成员变量mActivities中。
[java]
view plaincopyprint?
final HashMap<IBinder, ActivityRecord> mActivities=
new HashMap<IBinder, ActivityRecord>();
[java] view plaincopyprint? /*** 应用程序的启动入口 . ,主线程在启动的时候系统会自动建立消息循环机制。*/public static final void main(String[] args) { SamplingProfilerIntegration.start(); Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>"); Looper.prepareMainLooper(); ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); thread.attach(false); Looper.loop(); if (Process.supportsProcesses()) { throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited"); } thread.detach(); String name = (thread.mInitialApplication != null) ? thread.mInitialApplication.getPackageName() : "<unknown>";Slog.i(TAG, "Main thread of " + name + " is now exiting"); } /*** 应用程序的启动入口 . ,主线程在启动的时候系统会自动建立消息循环机制。*/public static final void main(String[] args) { SamplingProfilerIntegration.start(); Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>"); Looper.prepareMainLooper(); ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread(); thread.attach(false); Looper.loop(); if (Process.supportsProcesses()) { throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited"); } thread.detach(); String name = (thread.mInitialApplication != null) ? thread.mInitialApplication.getPackageName() : "<unknown>";Slog.i(TAG, "Main thread of " + name + " is now exiting"); }
在建立消息循环之前,会通过thread.attach(false)来初始化应用程序的运行环境,并建立activityThread和ActivityManagerService之间的桥mAppThread,
mAppThread是IApplicationThread的一个实例。
[java]
view plaincopyprint?
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("<pre-initialized>"); RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder()); IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try { mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread); }
catch (RemoteException ex) { }
[c-sharp] view plaincopyprint? HistoryRecord r = new HistoryRecord(this, callerApp, callingUid,intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mConfiguration,resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified); HistoryRecord r = new HistoryRecord(this, callerApp, callingUid,intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mConfiguration,resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified);
把r加入到mHistory中。
[c-sharp]
view plaincopyprint?
mHistory.add(addPos, r);
[c-sharp] view plaincopyprint? app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r,System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, r.icicle, results, newIntents, !andResume, isNextTransitionForward()); app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r,System.identityHashCode(r), r.info, r.icicle, results, newIntents, !andResume, isNextTransitionForward());
涉及的主要类图:

再来看下ApplicationThread中的scheduleLaunchActivity方法:
[c-sharp]
view plaincopyprint?
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token,
int ident, ActivityInfo info, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward) { ActivityRecord r =
new ActivityRecord(); r.token = token; r.ident = ident; r.intent = intent; r.activityInfo = info; r.state = state; r.pendingResults = pendingResults; r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents; r.startsNotResumed = notResumed;
r.isForward = isForward; queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r); }
public final void scheduleLaunchActivity(Intent intent, IBinder token, int ident, ActivityInfo info, Bundle state, List<ResultInfo> pendingResults, List<Intent> pendingNewIntents, boolean notResumed, boolean isForward) { ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(); r.token = token; r.ident = ident; r.intent = intent; r.activityInfo = info; r.state = state; r.pendingResults = pendingResults; r.pendingIntents = pendingNewIntents; r.startsNotResumed = notResumed; r.isForward = isForward; queueOrSendMessage(H.LAUNCH_ACTIVITY, r); }
在这个里面主要是根据服务端返回回来的信息创建客户端activity记录ActivityRecord.
并通过Handler发送消息到消息队列,进入消息循环。在ActivityThread.handleMessage()中处理消息。最终在handleLaunchActivity方法中把ActivityRecord记录加入到mActivities(mActivities.put(r.token,r))中,并启动activity(涉及到window、view、windowManager,详情请看handleResumeActivity()方法和上一篇关于window、WindowManager的介绍)
总结:
在客户端和服务端分别有一个管理activity的地方,服务端是在mHistory中,处于mHistory栈顶的就是当前处于running状态的activity,客户端是在mActivities中。
在startActivity时,首先会在ActivityManagerService中建立HistoryRecord,并加入到mHistory中,然后通过scheduleLaunchActivity在客户端创建ActivityRecord记录并加入到mActivities中。最终在ActivityThread发起请求,进入消息循环,完成activity的启动和窗口的管理等
相关文章推荐
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- 【转】Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android 之ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 与activity的管理和创建
- Android系统进程之Activity管理——ActivityManagerService(AMS)
- Android入门进阶教程(16)-ActivityThead、ActivityManagerService 详解
- Android 7.0 ActivityManagerService(8) 进程管理相关流程分析(2) updateOomAdjLocked
- Android 7.0 ActivityManagerService(7) 进程管理相关流程分析(1)
- Android 7.0 ActivityManagerService(9) 进程管理相关流程分析(3) computeOomAdjLocked
