Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十六)细谈Hibernate(七)Hibernate自身一对多和多对多关系映射
2012-05-26 11:04
639 查看
欢迎阅读本专题其他博客:
细谈Hibernate(十)hibernate查询排序和组件映射 细谈Hibernate(十一)hibernate复合主键映射
一对多关系映射大家都明白,关系双方都一个含有对方多个引用,但自身一对多很多同学都不明白什么意思,那么首先我就说明一下什么是自身一对多,其实也很好理解,自身一对多就是自身含有本身的多个引用,例如新闻类别,新闻包含体育新闻和政治新闻,体育新闻内有含有足球新闻和篮球新闻,其实他们都属于新闻,只是名字不同而已,下面我们就以新闻类别为例来具体说明一下:
首先我们来看一下新闻类别的类图:
类图:category
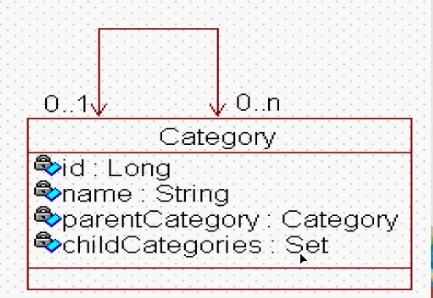
从上面的图我们可以看出:每一个新闻类别都有一个父类别和一个孩子类别的set集合,这个父类别和孩子类别里面都是自身的引用,这样就行了自身一对多的对象关系
下面看一下具体的新闻实体类:Category.java
看完具体的实体类之后我们下面看一下其具体的配置,其实他的配置中没什么特别的地方,仅仅只是他的配置中包含了一对多和多对一的共同标签存在而已:他即含有多的一方的<set>标签。也含有一的一方的<many-to-one>标签:
Category.hbm.xml配置文件
下面我们来看一下在自身一对多的关系下进行增删改查的示例:
在很多实际开发过程中,多对多的映射关系也是比较常见的,最为明显的例子就是我们常用的学生选课示例,一个学生可以选多门课,一门课也可以由多个学生去选,这样就形成了多对多的映射关系,现在我们就以学生选课的实例来看一看多对多关系映射。由于在多对多映射中,双向多对多用的的比较多,并且单向多对多也比较简单,所以我们就以双向多对多进行讲解
我们先把必要的实体类和实体映射文件写好:
先简单看一下实体类:
student.java
Course.java
下一步编写实体映射文件:
Student.hbm.xml
下面具体看一下增删改查的具体测试的关键代码:
增加数据测试:
测试结论:如果想保存数据成功,不管是主控方还是被控方,如果想通过一次保存即可把双方数据保存,需要把实体配置中的cascade属性设置为all或者save-update,由于设置为all包含delete,在删除数据中,删除一条信息会导致相对应表的多条或者全部信息被删掉,所以一般配置save-update。
本文出自 “曹胜欢” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://javacsh.blog.51cto.com/3545281/1129078
细谈Hibernate(十)hibernate查询排序和组件映射 细谈Hibernate(十一)hibernate复合主键映射
细谈Hibernate(十二)hibernate查询排序组件映射
细谈Hibernate(十三)session缓存机制和三种对象状态一对多关系映射大家都明白,关系双方都一个含有对方多个引用,但自身一对多很多同学都不明白什么意思,那么首先我就说明一下什么是自身一对多,其实也很好理解,自身一对多就是自身含有本身的多个引用,例如新闻类别,新闻包含体育新闻和政治新闻,体育新闻内有含有足球新闻和篮球新闻,其实他们都属于新闻,只是名字不同而已,下面我们就以新闻类别为例来具体说明一下:
首先我们来看一下新闻类别的类图:
类图:category

从上面的图我们可以看出:每一个新闻类别都有一个父类别和一个孩子类别的set集合,这个父类别和孩子类别里面都是自身的引用,这样就行了自身一对多的对象关系
下面看一下具体的新闻实体类:Category.java
public class Category { private Long id; private String name; private Category parentCategory; private Set<Category> childCategories; public Category(String name, Category parentCategory, Set<Category> childCategories) { this.name = name; this.parentCategory = parentCategory; this.childCategories = childCategories; } public Category() { } *******set、get方法省略 }看完具体的实体类之后我们下面看一下其具体的配置,其实他的配置中没什么特别的地方,仅仅只是他的配置中包含了一对多和多对一的共同标签存在而已:他即含有多的一方的<set>标签。也含有一的一方的<many-to-one>标签:
Category.hbm.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <class name="com.shengsiyuan.hibernate.Category" table="categories"> <id name="id" column="id" type="long"> <generator class="increment"></generator> </id> <property name="name" type="string" > <column name="name" length="50" ></column> </property> <set name="childCategories" cascade="all" inverse="true"> <key column="category_id"></key> <one-to-many class="com.shengsiyuan.hibernate.Category"/> </set> <many-to-one name="parentCategory" column="category_id" class="com.shengsiyuan.hibernate.Category"> </many-to-one> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
下面我们来看一下在自身一对多的关系下进行增删改查的示例:
import java.util.HashSet; import org.hibernate.Session; import org.hibernate.SessionFactory; import org.hibernate.Transaction; import org.hibernate.cfg.Configuration; public class HibernateTest2 { private static SessionFactory sessionFactory; static { try { sessionFactory = new Configuration().configure() .buildSessionFactory(); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Session session = sessionFactory.openSession(); Transaction tx = null; try { tx = session.beginTransaction(); Category category1 = new Category("level1", null, new HashSet<Category>()); Category category2 = new Category("level2", null, new HashSet<Category>()); Category category3 = new Category("level2", null, new HashSet<Category>()); Category category4 = new Category("level3", null, new HashSet<Category>()); Category category5 = new Category("level3", null, new HashSet<Category>()); Category category6 = new Category("level3", null, new HashSet<Category>()); Category category7 = new Category("level3", null, new HashSet<Category>()); category2.setParentCategory(category1); category3.setParentCategory(category1); category1.getChildCategories().add(category2); category1.getChildCategories().add(category3); category4.setParentCategory(category2); category5.setParentCategory(category2); category2.getChildCategories().add(category4); category2.getChildCategories().add(category5); category6.setParentCategory(category3); category7.setParentCategory(category3); category3.getChildCategories().add(category6); category3.getChildCategories().add(category7); Category category = (Category)session.get(Category.class, new Long(1)); System.out.println(category.getChildCategories().iterator().next().getName()); session.delete(category); tx.commit(); } catch(Exception ex) { if(null != tx) { tx.rollback(); } } finally { session.close(); } } }在很多实际开发过程中,多对多的映射关系也是比较常见的,最为明显的例子就是我们常用的学生选课示例,一个学生可以选多门课,一门课也可以由多个学生去选,这样就形成了多对多的映射关系,现在我们就以学生选课的实例来看一看多对多关系映射。由于在多对多映射中,双向多对多用的的比较多,并且单向多对多也比较简单,所以我们就以双向多对多进行讲解
我们先把必要的实体类和实体映射文件写好:
先简单看一下实体类:
student.java
/** 学生实体类 */ public class Student { private Long id; //对象标识符(OID) private String name; //姓名 private String grade; //所在班级 private Set<Course> courses; //所有所选课程的集合 public Student(){} //无参数的构造方法 ******set、get方法省略 }Course.java
/** 课程实体类 */ public class Course { private Long id; //对象标识符(OID) private String name; //课程名 private Double creditHours; //课时数 private Set<Student> students; //选择了这门课程的学生的集合 public Course(){} //无参数的构造方法 ******set、get方法省略 }下一步编写实体映射文件:
Student.hbm.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <!-- 映射持久化类 --> <class name="com.zxf.domain.Student" table="student"> <!-- 映射对象标识符 --> <id name="id" column="id" type="long"> <generator class="native" /> </id> <!-- 映射普通属性 --> <property name="name" /> <property name="grade" /> <!-- 映射集合属性,指定连接表 --> <set name="courses" table="student_course"> <!-- 用key元素指定本持久类在连接表中的外键字段名 --> <key column="student_id" /> <!-- 映射多对多关联类 --> <many-to-many column="course_id" class="com.zxf.domain.Course" /> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping> Course.hbm.xml: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-mapping> <!-- 映射持久化类 --> <class name="com.zxf.domain.Course" table="course"> <!-- 映射对象标识符 --> <id name="id" column="id" type="long"> <generator class="native" /> </id> <!-- 映射普通属性 --> <property name="name" /> <property name="creditHours" column="credit_hours" /> <!-- 映射集合属性,指定连接表 --> <set name="students" table="student_course" inverse="true"> <!-- 用key元素指定本持久类在连接表中的外键字段名 --> <key column="course_id" /> <!-- 映射多对多关联类 --> <many-to-many column="student_id" class="com.zxf.domain.Student" /> </set> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
下面具体看一下增删改查的具体测试的关键代码:
增加数据测试:
tran = session.beginTransaction(); Student stu1 = new Student("xiaoli", "two"); Student stu2 = new Student("xiaoming", "two"); Student stu3 = new Student("xiaoqiang", "two"); Course course1 = new Course("java", 3.0); Course course2 = new Course("c#", 5.0); //stuset.add(stu1); //stuset.add(stu2); //course1.setStudents(stuset); //session.save(course1); couset.add(course1); couset.add(course2); stu1.setCourses(couset); session.save(stu1); tran.commit();测试结论:如果想保存数据成功,不管是主控方还是被控方,如果想通过一次保存即可把双方数据保存,需要把实体配置中的cascade属性设置为all或者save-update,由于设置为all包含delete,在删除数据中,删除一条信息会导致相对应表的多条或者全部信息被删掉,所以一般配置save-update。
本文出自 “曹胜欢” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://javacsh.blog.51cto.com/3545281/1129078
相关文章推荐
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十六)细谈Hibernate(七)Hibernate自身一对多和多对多关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十六)细谈Hibernate(七)Hibernate自身一对多和多对多关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十八)细谈Hibernate(九)hibernate一对一关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(六十一)细谈Hibernate(十二)hibernate查询排序组件映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十五)细谈Hibernate(六)Hibernate继承关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十七)细谈Hibernate(八)Hibernate集合Map关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(六十一)细谈Hibernate(十二)hibernate查询排序组件映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十四)细谈Hibernate(五)Hibernate一对多关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十五)细谈Hibernate(六)Hibernate继承关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(六十)细谈Hibernate(十一)hibernate复合主键映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十八)细谈Hibernate(九)hibernate一对一关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(六十)细谈Hibernate(十一)hibernate复合主键映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十七)细谈Hibernate(八)Hibernate集合Map关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十八)细谈Hibernate(九)hibernate一对一关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十七)细谈Hibernate(八)Hibernate集合Map关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十五)细谈Hibernate(六)Hibernate继承关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十五)细谈Hibernate(六)Hibernate继承关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十九)细谈Hibernate(十)hibernate查询排序和组件映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十四)细谈Hibernate(五)Hibernate一对多关系映射
- Java程序员从笨鸟到菜鸟之(五十九)细谈Hibernate(十)hibernate查询排序和组件映射
