hdu2845 Beans
2012-05-07 21:08
190 查看
Problem Description
Bean-eating is an interesting game, everyone owns an M*N matrix, which is filled with different qualities beans. Meantime, there is only one bean in any 1*1 grid. Now you want to eat the beans and collect the qualities, but everyone
must obey by the following rules: if you eat the bean at the coordinate(x, y), you can’t eat the beans anyway at the coordinates listed (if exiting): (x, y-1), (x, y+1), and the both rows whose abscissas are x-1 and x+1.
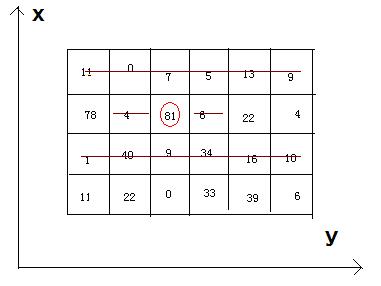
Now, how much qualities can you eat and then get ?
Input
There are a few cases. In each case, there are two integer M (row number) and N (column number). The next M lines each contain N integers, representing the qualities of the beans. We can make sure that the quality of bean isn't beyond
1000, and 1<=M*N<=200000.
Output
For each case, you just output the MAX qualities you can eat and then get.
Sample Input
Sample Output
Source
2009 Multi-University Training Contest 4 - Host by HDU
Recommend
gaojie
简单的dp,对每行找一遍不连续取的最大值,之后对这些最大值再找一遍不连续的最大值即可。
笔误,WA一次。
Bean-eating is an interesting game, everyone owns an M*N matrix, which is filled with different qualities beans. Meantime, there is only one bean in any 1*1 grid. Now you want to eat the beans and collect the qualities, but everyone
must obey by the following rules: if you eat the bean at the coordinate(x, y), you can’t eat the beans anyway at the coordinates listed (if exiting): (x, y-1), (x, y+1), and the both rows whose abscissas are x-1 and x+1.

Now, how much qualities can you eat and then get ?
Input
There are a few cases. In each case, there are two integer M (row number) and N (column number). The next M lines each contain N integers, representing the qualities of the beans. We can make sure that the quality of bean isn't beyond
1000, and 1<=M*N<=200000.
Output
For each case, you just output the MAX qualities you can eat and then get.
Sample Input
4 6 11 0 7 5 13 9 78 4 81 6 22 4 1 40 9 34 16 10 11 22 0 33 39 6
Sample Output
242
Source
2009 Multi-University Training Contest 4 - Host by HDU
Recommend
gaojie
简单的dp,对每行找一遍不连续取的最大值,之后对这些最大值再找一遍不连续的最大值即可。
笔误,WA一次。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef struct
{
int choose;
int notch;
}DP;
vector <int> a[200005];
DP dp[200005];
int sum[200005];
int main()
{
int i,j,n,m,x,T;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
a[i].clear();
for (j=0;j<m;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
a[i].push_back(x);
}
}
memset(sum,0,sizeof(sum));
for (i=0;i<n;i++)
{
dp[0].choose=a[i][0];
dp[0].notch=0;
for (j=1;j<m;j++)
{
if (j==1) dp[j].choose=a[i][1];
else dp[j].choose=max(dp[j-2].choose,dp[j-2].notch)+a[i][j];
dp[j].notch=max(dp[j-1].choose,dp[j-1].notch);
}
sum[i]=max(dp[m-1].choose,dp[m-1].notch);
}
dp[0].choose=sum[0];
dp[0].notch=0;
for (i=1;i<n;i++)
{
if (i==1) dp[i].choose=sum[i];
else dp[i].choose=max(dp[i-2].choose,dp[i-2].notch)+sum[i];
dp[i].notch=max(dp[i-1].choose,dp[i-1].notch);
}
printf("%d\n",max(dp[n-1].choose,dp[n-1].notch));
}
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- hdu2845 Beans--DP
- HDU2845-Beans
- hdu2845 Beans (最大不连续子序列和)
- HDU2845--Beans
- HDU2845_Beans【不连续的最大子段和】【元素压缩】
- hdu2845之Beans,DP
- hdu2845_Beans
- hdu2845 Beans (%)
- hdu2845: Beans
- hdu2845 Beans(DP)
- HDU2845 Beans(DP)
- Beans Development Kit (BDK)分析(三)
- 使用消息驱动Beans
- Spilling the Spanish Beans
- 解决 java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: org /apache/xmlbeans/XmlException
- when to use Java Beans
- 在桌面应用程序中实现 Beans 和数据绑定
- nested exception is org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name '(inner bean)#1': Can
- Enterprise JavaBeans, Fourth Edition [ILLUSTRATED]
- HDU 2845 Beans
