多种方法求解八数码问题
2012-01-15 20:33
357 查看
AI的实验报告,改了改发上来。希望路过的大牛指教。很是纳闷我的ida*怎么还没有双搜快。还有发现基于不在位启发的A*和Ida*都挺慢。尤其是ida* 搜索31步的居然要十几秒。是我写的代码有问题吗?忘路过的大牛指导啊!!!!
另外声明一下,有些东西也是看网上各路牛人的blog学来的,由于比较杂,再次无法一一列出,总之再次感谢把自己的思考的结果放到网上与大家分享的大牛们。谢谢!
八数码问题
八数码问题也称为九宫问题。在3×3的棋盘,摆有八个棋子,每个棋子上标有1至8的某一数字,不同棋子上标的数字不相同。棋盘上还有一个空格,与空格相邻的棋子可以移到空格中。要求解决的问题是:给出一个初始状态和一个目标状态,找出一种从初始转变成目标状态的移动棋子步数最少的移动步骤。所谓问题的一个状态就是棋子在棋盘上的一种摆法。棋子移动后,状态就会发生改变。解八数码问题实际上就是找出从初始状态到达目标状态所经过的一系列中间过渡状态。
八数码问题一般使用搜索法来解。搜索法有广度优先搜索法、双向广度优先算法、深度优先搜索法、A*算法等。这里通过用不同方法解八数码问题来比较一下不同搜索法的效果。
一、BFS
由于状态最多只有9! =362880,最先想到的应该就是暴力搜索。在此对其进行一定的优化,首先将每个状态,利用状态压缩的思想装换成两个int型变量,然后对于close表里的所有状态则采取一次全部初始化,再利用状态的进行排序,排序完成后在之后的查询close表过程中就可以使用二分的思想,减少操作,每次查找所需要操作次数为logn<20次。Open表则用队列存储。
每一个节点的存储
struct state{
int sta,pos;
}
全排列表示其状态,然后将状态压缩在一个int上,由于每个数字只能用三位2进制表示,所以会出现重复,在这里,1~8用二进制0~7表示,空位9也用0表示,为区分这两个数,再使用一个int,表示空位所在的位置。例如下面这个状态:
Int sta =
Int pos = 8(从0开始)
之后判断两个状态是否相同,可以使用位运算快速进行。例如判断当前状态是否与目标态一致则为
if(!(a.sta^target.sta)&&a.pos ==target.pos)
{
printf("%d\n",depth);
return true;
}
如何判断是否有解:
利用奇偶性判断所给出的初始状态有无解.
判别方法是:
以数组为一维的举例子.
将八数码的一个结点表示成一个数组a[9],空格用0表示,设临时函数p(x)定义为:x数所在位置前面的数比x小的数的个数,
其中0空格不算在之内,那设目标状态为b[9],那r=sigma(p(x)) sigma()表示取所有的x:1-8并求和,
那对于初始状态a[9],t=sigma(p(x)),如果r和t同为奇数或者同为偶数,那么该状态有解,否则无解。
之后节点的存储与判断是否有解,基本相同,不再赘述。
代码:
二、BFS+hash
采用第一种方法需要花较多时间初始化,且查找close表较为耗时,可以采用hash函数来优化,在这里只使用一个简单的哈希函数,即模一个大质数。这样查找close表的时间减少,程序的效率得到了提升
代码:
三、双向广搜
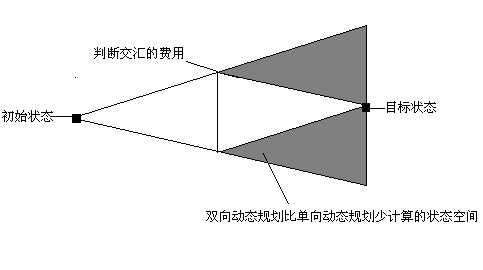
接下来采用一种更快速的方式。由于目标态和初始态都已知,可以采用从两态同时开始搜,当搜到同一个节点时,搜索结束,将两边的步数加起来输出。在这里我在每个节点里,用一个值标记,此节点是由哪个状态访问的,故只需用一个队列交替扩展。如图所示,双向广搜少扩展许多节点,时间效率得到大幅提升。
代码:
四、A*
主要有两种可行的启发函数 :出现在教科书上当典型的不在位数(difference) ,以及曼哈顿路径长(manhattan).
在节点中,加一个int型变量存储此节点的估价。此时的open表次用优先级队列存储,其实质上是一个小顶堆,这样每一次调整的复杂度将为logn,能更快的得到离目标态最近的节点进行扩展。由于每次扩展的都是离目标最近的节点,所以时间效率有所提高,但是若启发函数效率不高,减少的扩展节点的时间可能还不足以抵过小顶堆调整的时间,结果就是时间效率可能比普通的bfs还差。
代码:
基于不在位的启发方式:
五、IDA*
由于普通的深搜在此问题上,要么搜索到错误的结果,要么需要搜索所有的状态,才能确定是否是最优,故在这里使用IDA*。IDA*是一种迭代加深的深度搜索,若在此深度下没有搜到目标点,则将深度加一重新搜索。无须状态判重,无需估价排序,用不到哈希表,堆上也不必应用,空间需求变的超级少,实现也最简单。在深搜过程中,根据启发函数做剪枝,可以使效率达到很高。另外在求路径的时候,IDA*也是最方便的。
基于不在位启发:
基于manhattan距离启发:
六、其他优化
状态还可以压缩到一个int上,完全采用位运算来完成。
前面的hash函数还可以继续优化,对于全排列有一种非常好的hash哈希函数叫康托展开。
首先看几个康托展开的实例(9的全排列):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9——展开为 0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 8——展开为 1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 8 7 9——展开为 2。
由这些最开始的方法我们可以发现一个规律:从第一个数开始,依次判断判断这些数是当前没有出现过的数的第几个(由0开始),记为a1, a2, ... ,a(n - 1)。不难发现如1 2 3 4 5 6 8 7 9,由1至6都是当前没有出现过的第0个数,而8是7,8,9中的第1个(由0开始),9是7,9中的第1个,7是第0个。故a1 = a2 = ... = a6 = 0,a7 = 1,a8 = 1,a9 =0。
之后排列数(康托展开的值)等于
a1 * (n - 1)! + a2 * (n - 2)! + ... + ak *(n - k)! + ... + an * 0!
再举几个例子:
3 5 7 4 1 2 9 6 8——展开为 98884。
5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 9——展开为 184800。
往回转换也很简单,分步取模就可以了,在此就不赘述了。
七、总结
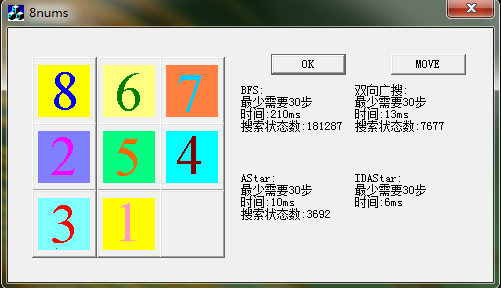
为了更直观的对比结果,做一个简单MFC程序来显示结果。上面是搜索时间,下面是搜索的状态数。
另外声明一下,有些东西也是看网上各路牛人的blog学来的,由于比较杂,再次无法一一列出,总之再次感谢把自己的思考的结果放到网上与大家分享的大牛们。谢谢!
八数码问题
八数码问题也称为九宫问题。在3×3的棋盘,摆有八个棋子,每个棋子上标有1至8的某一数字,不同棋子上标的数字不相同。棋盘上还有一个空格,与空格相邻的棋子可以移到空格中。要求解决的问题是:给出一个初始状态和一个目标状态,找出一种从初始转变成目标状态的移动棋子步数最少的移动步骤。所谓问题的一个状态就是棋子在棋盘上的一种摆法。棋子移动后,状态就会发生改变。解八数码问题实际上就是找出从初始状态到达目标状态所经过的一系列中间过渡状态。
八数码问题一般使用搜索法来解。搜索法有广度优先搜索法、双向广度优先算法、深度优先搜索法、A*算法等。这里通过用不同方法解八数码问题来比较一下不同搜索法的效果。
一、BFS
由于状态最多只有9! =362880,最先想到的应该就是暴力搜索。在此对其进行一定的优化,首先将每个状态,利用状态压缩的思想装换成两个int型变量,然后对于close表里的所有状态则采取一次全部初始化,再利用状态的进行排序,排序完成后在之后的查询close表过程中就可以使用二分的思想,减少操作,每次查找所需要操作次数为logn<20次。Open表则用队列存储。
每一个节点的存储
struct state{
int sta,pos;
}
全排列表示其状态,然后将状态压缩在一个int上,由于每个数字只能用三位2进制表示,所以会出现重复,在这里,1~8用二进制0~7表示,空位9也用0表示,为区分这两个数,再使用一个int,表示空位所在的位置。例如下面这个状态:
Int sta =
Int pos = 8(从0开始)
之后判断两个状态是否相同,可以使用位运算快速进行。例如判断当前状态是否与目标态一致则为
if(!(a.sta^target.sta)&&a.pos ==target.pos)
{
printf("%d\n",depth);
return true;
}
如何判断是否有解:
利用奇偶性判断所给出的初始状态有无解.
判别方法是:
以数组为一维的举例子.
将八数码的一个结点表示成一个数组a[9],空格用0表示,设临时函数p(x)定义为:x数所在位置前面的数比x小的数的个数,
其中0空格不算在之内,那设目标状态为b[9],那r=sigma(p(x)) sigma()表示取所有的x:1-8并求和,
那对于初始状态a[9],t=sigma(p(x)),如果r和t同为奇数或者同为偶数,那么该状态有解,否则无解。
之后节点的存储与判断是否有解,基本相同,不再赘述。
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <time.h>
#define FUCK puts("fuck!")
#define STOP system("pause")
using namespace std;
struct state{
int sta,pos,step;
}st[400000],source,target;
int temp[10],tar[10],sou[10];
int d[9][4]={{0,4,0,2},{0,5,1,3},{0,6,2,0},{1,7,0,5},{2,8,4,6},{3,9,5,0},{4,0,0,8},{5,0,7,9},{6,0,8,0}};
int num;
int convert(int a[],state &b)
{
b.sta=0;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a[i]!=0)
b.sta |=((a[i]-1)<<(24-i*3));
else
{
b.pos = i;
b.sta |=(a[i]<<(24-i*3));
}
}
return 1;
}
state exchange(state a,int pos)
{
int temp = 7<<((9-pos)*3);
state s;
s.sta = a.sta;
temp = temp & a.sta;
temp = ((temp>>((9-pos)*3))<<((9-a.pos-1)*3));
s.sta |= temp;
s.sta &= ~(7<<((9-pos)*3));
s.pos = pos-1;
return s;
}
int search(state a)
{
int l,r,mid;
l = 0;
r = num-1;
while(l<r)
{
mid = (l+r)>>1;
if(a.sta<st[mid].sta)
r = mid;
else if(a.sta>st[mid].sta)
l = mid;
else
{
mid = mid - 2;
while((a.sta^st[mid].sta)||(a.pos^st[mid].pos))
mid++;
l = r;
}
}
return mid;
}
bool cmp(state a,state b)
{
if(a.sta!=b.sta)
return a.sta<b.sta;
else
return a.pos<b.pos;
}
int main()
{
num = 0;
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
clock_t start,end;
start = clock();
memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
for(int j=0;j<9;j++)temp[j] = j;
do{
convert(temp,st[num++]);
}while(next_permutation(temp,temp+9));
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)temp[j] = j+1;
temp[8]=0;
convert(temp,target);
sort(st,st+num,cmp);
end = clock();
printf("%dms\n",end-start);
while(1)
{
int i = 0;
for(int j=0;j<num;j++)st[j].step=0;
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')
sou[i++] = ch - '0';
else if(ch=='x')
sou[i++] =0;
}
convert(sou,source);
start = clock();
i = search(source);
queue<int>q;
q.push(i);
int index;
int count = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
count ++;
index = q.front();
if(!(st[index].sta^target.sta)&&st[index].pos == target.pos)
{
printf("%d\n",st[index].step);
break;
}
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j ++)
{
if(d[st[index].pos][j])
{
int flag = search(exchange(st[index],d[st[index].pos][j]));
if(!st[flag].step)
{
st[flag].step = st[index].step + 1;
q.push(flag);
}
}
}
q.pop();
}
while(!q.empty())q.pop();
end = clock();
printf("Time:%dms\nstate number:%d\n",end-start,count);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}二、BFS+hash
采用第一种方法需要花较多时间初始化,且查找close表较为耗时,可以采用hash函数来优化,在这里只使用一个简单的哈希函数,即模一个大质数。这样查找close表的时间减少,程序的效率得到了提升
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queu
4000
e>
#define FUCK puts("fuck!")
#define STOP system("pause")
#define MAXN 388211
using namespace std;
struct state{
int sta,pos,step;
}st[MAXN],source,target;
int temp[10],tar[10],sou[10];
int d[9][4]={{0,4,0,2},{0,5,1,3},{0,6,2,0},{1,7,0,5},{2,8,4,6},{3,9,5,0},{4,0,0,8},{5,0,7,9},{6,0,8,0}};
int num;
int convert(int a[],state &b)
{
b.sta=0;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a[i]!=0)
b.sta |=((a[i]-1)<<(24-i*3));
else
{
b.pos = i;
b.sta |=(a[i]<<(24-i*3));
}
}
return 1;
}
state exchange(state a,int pos)
{
int temp = 7<<((9-pos)*3);
state s;
s.sta = a.sta;
temp = temp & a.sta;
temp = ((temp>>((9-pos)*3))<<((9-a.pos-1)*3));
s.sta |= temp;
s.sta &= ~(7<<((9-pos)*3));
s.pos = pos-1;
return s;
}
int search(state a)
{
int index = a.sta%MAXN;
bool flag = true;
while(flag)
{
if(!st[index].sta)
{
st[index].sta = a.sta;
st[index].pos = a.pos;
flag = false;
}
else if(!(st[index].sta^a.sta)&&!(st[index].pos^a.pos))
flag = false;
else
index = (index+1)%MAXN;
}
return index;
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
clock_t start,end;
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)temp[j] = j+1;
temp[8]=0;
convert(temp,target);
while(1)
{
int i = 0;
memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')
sou[i++] = ch - '0';
else if(ch=='x')
sou[i++] =0;
}
convert(sou,source);
start = clock();
i = search(source);
queue<int>q;
q.push(i);
int index;
int count = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
count ++;
index = q.front();
if(!(st[index].sta^target.sta)&&st[index].pos == target.pos)
{
printf("%d\n",st[index].step);
break;
}
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j ++)
{
if(d[st[index].pos][j])
{
int flag = search(exchange(st[index],d[st[index].pos][j]));
if(!st[flag].step)
{
st[flag].step = st[index].step + 1;
q.push(flag);
}
}
}
q.pop();
}
while(!q.empty())q.pop();
end = clock();
printf("Time:%dms\nstate number:%d\n",end-start,count);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}三、双向广搜
接下来采用一种更快速的方式。由于目标态和初始态都已知,可以采用从两态同时开始搜,当搜到同一个节点时,搜索结束,将两边的步数加起来输出。在这里我在每个节点里,用一个值标记,此节点是由哪个状态访问的,故只需用一个队列交替扩展。如图所示,双向广搜少扩展许多节点,时间效率得到大幅提升。

代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define FUCK puts("fuck!")
#define STOP system("pause")
#define MAXN 388211
using namespace std;
struct state{
int sta,pos,step;
int visit;
}st[MAXN],source,target;
int temp[10],tar[10],sou[10];
int d[9][4]={{0,4,0,2},{0,5,1,3},{0,6,2,0},{1,7,0,5},{2,8,4,6},{3,9,5,0},{4,0,0,8},{5,0,7,9},{6,0,8,0}};
int num;
int convert(int a[],state &b)
{
b.sta=0;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a[i]!=0)
b.sta |=((a[i]-1)<<(24-i*3));
else
{
b.pos = i;
b.sta |=(a[i]<<(24-i*3));
}
}
return 1;
}
state exchange(state a,int pos)
{
int temp = 7<<((9-pos)*3);
state s;
s.sta = a.sta;
temp = temp & a.sta;
temp = ((temp>>((9-pos)*3))<<((9-a.pos-1)*3));
s.sta |= temp;
s.sta &= ~(7<<((9-pos)*3));
s.pos = pos-1;
return s;
}
int search(state a)
{
int index = a.sta%MAXN;
bool flag = true;
while(flag)
{
if(!st[index].sta)
{
st[index].sta = a.sta;
st[index].pos = a.pos;
flag = false;
}
else if(!(st[index].sta^a.sta)&&!(st[index].pos^a.pos))
flag = false;
else
index = (index+1)%MAXN;
}
return index;
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
clock_t start,end;
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)temp[j] = j+1;
temp[8]=0;
convert(temp,target);
while(1)
{
int i = 0;
memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')
sou[i++] = ch - '0';
else if(ch=='x')
sou[i++] =0;
}
convert(sou,source);
start = clock();
i = search(source);
queue<int>q;
q.push(i);
i = search(target);
st[i].visit = 1;
st[i].step = 1;
q.push(i);
if(!(source.sta^target.sta)&&!(source.pos^target.pos))
{
printf("0\n");
while(!q.empty())q.pop();
continue;
}
int index;
int count = 0;
bool isSolve = false;
while(!q.empty()&&!isSolve)
{
count ++;
index = q.front();
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j ++)
{
if(d[st[index].pos][j])
{
int flag = search(exchange(st[index],d[st[index].pos][j]));
if(!st[flag].step)
{
st[flag].step = st[index].step + 1;
st[flag].visit = st[index].visit;
q.push(flag);
}
else
{
if(st[flag].visit^st[index].visit)
{
isSolve = true;
printf("%d\n",st[index].step+st[flag].step);
}
}
}
}
q.pop();
}
while(!q.empty())q.pop();
end = clock();
printf("Time:%dms\nstate number:%d\n",end-start,count);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}四、A*
主要有两种可行的启发函数 :出现在教科书上当典型的不在位数(difference) ,以及曼哈顿路径长(manhattan).
在节点中,加一个int型变量存储此节点的估价。此时的open表次用优先级队列存储,其实质上是一个小顶堆,这样每一次调整的复杂度将为logn,能更快的得到离目标态最近的节点进行扩展。由于每次扩展的都是离目标最近的节点,所以时间效率有所提高,但是若启发函数效率不高,减少的扩展节点的时间可能还不足以抵过小顶堆调整的时间,结果就是时间效率可能比普通的bfs还差。
代码:
基于不在位的启发方式:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define FUCK puts("fuck!")
#define STOP system("pause")
#define MAXN 388211
using namespace std;
struct state{
int sta,pos,step;
int f;
}st[MAXN],source,target;
int temp[10],tar[10],sou[10];
int d[9][4]={{0,4,0,2},{0,5,1,3},{0,6,2,0},{1,7,0,5},{2,8,4,6},{3,9,5,0},{4,0,0,8},{5,0,7,9},{6,0,8,0}};
int num;
int h(state a)
{
int temp = target.sta;
int cnt=0;
for(int i = 0;i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a.pos==target.pos)
{
if(!(((temp>>(3*i))&7)^((a.sta>>(3*i))&7)))
cnt++;
}
else
{
if((!(((temp>>(3*i))&7)^((a.sta>>(3*i))&7)))&&((a.sta>>(3*i))&7))
cnt++;
}
}
return 9-cnt;
}
struct cmp
{
bool operator () (int u, int v)
{
return st[u].f > st[v].f;
}
};
int convert(int a[],state &b)
{
b.sta=0;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a[i]!=0)
b.sta |=((a[i]-1)<<(24-i*3));
else
{
b.pos = i;
b.sta |=(a[i]<<(24-i*3));
}
}
return 1;
}
state exchange(state a,int pos)
{
int temp = 7<<((9-pos)*3);
state s;
s.sta = a.sta;
temp = temp & a.sta;
temp = ((temp>>((9-pos)*3))<<((9-a.pos-1)*3));
s.sta |= temp;
s.sta &= ~(7<<((9-pos)*3));
s.pos = pos-1;
return s;
}
int search(state a)
{
int index = a.sta%MAXN;
bool flag = true;
while(flag)
{
if(!st[index].sta)
{
st[index].sta = a.sta;
st[index].pos = a.pos;
flag = false;
}
else if(!(st[index].sta^a.sta)&&!(st[index].pos^a.pos))
flag = false;
else
index = (index+1)%MAXN;
}
return index;
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
clock_t start,end;
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)temp[j] = j+1;
temp[8]=0;
convert(temp,target);
while(1)
{
int i = 0;
memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')
sou[i++] = ch - '0';
else if(ch=='x')
sou[i++] =0;
}
convert(sou,source);
start = clock();
i = search(source);
st[i].f = h(st[i]);
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,cmp>q;
q.push(i);
int index;
int count = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
count++;
index = q.top();
q.pop(); //!!!!
if(!(st[index].sta^target.sta)&&st[index].pos == target.pos)
{
printf("%d\n",st[index].step);
break;
}
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j ++)
{
if(d[st[index].pos][j])
{
int flag = search(exchange(st[index],d[st[index].pos][j]));
if(!st[flag].step||st[flag].step > st[index].step + 1)
{
st[flag].step = st[index].step + 1;
st[flag].f = st[flag].step + h(st[flag]);
q.push(flag);
}
}
}
}
while(!q.empty())q.pop();
end = clock();
printf("Time:%dms\nstate number:%d\n",end-start,count);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}基于manhattan距离启发:#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define FUCK puts("fuck!")
#define STOP system("pause")
#define MAXN 388211
using namespace std;
struct state{
int sta,pos,step;
int f;
}st[MAXN],source,target;
int temp[10],tar[10],sou[10];
int d[9][4]={{0,4,0,2},{0,5,1,3},{0,6,2,0},{1,7,0,5},{2,8,4,6},{3,9,5,0},{4,0,0,8},{5,0,7,9},{6,0,8,0}};
int num;
int manhattan[10][10] = //第i个数及其所处不同位置的Manhattan路径长度
{
{-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1},
{-1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4},
{-1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3},
{-1, 2, 1, 0, 3, 2, 1, 4, 3, 2},
{-1, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3},
{-1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2},
{-1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 3, 2, 1},
{-1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2},
{-1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 1},
{-1, 4, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0}
};
int h(state a)
{
int cnt=0;
for(int i = 0;i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a.pos != i)
cnt += manhattan[((a.sta>>(3*(8-i)))&7)+1][i+1];
}
return cnt;
}
class cmp
{
public:
bool operator () (int u, int v)
{
return st[u].f > st[v].f;
}
};
int convert(int a[],state &b)
{
b.sta=0;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a[i]!=0)
b.sta |=((a[i]-1)<<(24-i*3));
else
{
b.pos = i;
b.sta |=(a[i]<<(24-i*3));
}
}
return 1;
}
state exchange(state a,int pos)
{
int temp = 7<<((9-pos)*3);
state s;
s.sta = a.sta;
temp = temp & a.sta;
temp = ((temp>>((9-pos)*3))<<((9-a.pos-1)*3));
s.sta |= temp;
s.sta &= ~(7<<((9-pos)*3));
s.pos = pos-1;
return s;
}
int search(state a)
{
int index = a.sta%MAXN;
bool flag = true;
while(flag)
{
if(!st[index].sta)
{
st[index].sta = a.sta;
st[index].pos = a.pos;
flag = false;
}
else if(!(st[index].sta^a.sta)&&!(st[index].pos^a.pos))
flag = false;
else
index = (index+1)%MAXN;
}
return index;
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
clock_t start,end;
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)temp[j] = j+1;
temp[8]=0;
convert(temp,target);
while(1)
{
int i = 0;
memset(st,0,sizeof(st));
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')
sou[i++] = ch - '0';
else if(ch=='x')
sou[i++] =0;
}
convert(sou,source);
start = clock();
i = search(source);
st[i].f = h(st[i]);
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,cmp>q;
q.push(i);
int index;
int count = 0;
while(!q.empty())
{
count++;
index = q.top();
q.pop(); //!!!!
if(!(st[index].sta^target.sta)&&st[index].pos == target.pos)
{
printf("%d\n",st[index].step);
break;
}
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j ++)
{
if(d[st[index].pos][j])
{
int flag = search(exchange(st[index],d[st[index].pos][j]));
if(!st[flag].step||st[flag].step > st[index].step + 1)
{
st[flag].step = st[index].step + 1;
st[flag].f = st[flag].step + h(st[flag]);
q.push(flag);
}
}
}
}
while(!q.empty())q.pop();
end = clock();
printf("Time:%dms\nstate number:%d\n",end-start,count);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}五、IDA*
由于普通的深搜在此问题上,要么搜索到错误的结果,要么需要搜索所有的状态,才能确定是否是最优,故在这里使用IDA*。IDA*是一种迭代加深的深度搜索,若在此深度下没有搜到目标点,则将深度加一重新搜索。无须状态判重,无需估价排序,用不到哈希表,堆上也不必应用,空间需求变的超级少,实现也最简单。在深搜过程中,根据启发函数做剪枝,可以使效率达到很高。另外在求路径的时候,IDA*也是最方便的。
基于不在位启发:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define FUCK puts("fuck!")
#define STOP system("pause")
#define MAXN 388211
using namespace std;
struct state{
int sta,pos;
}source,target;
int temp[10],tar[10],sou[10];
int pathLimit;
int cnt;
int d[9][4]={{0,4,0,2},{0,5,1,3},{0,6,2,0},{1,7,0,5},{2,8,4,6},{3,9,5,0},{4,0,0,8},{5,0,7,9},{6,0,8,0}};
int h(state a)
{
int temp = target.sta;
int cnt=0;
for(int i = 0;i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a.pos==target.pos)
{
if(!(((temp>>(3*i))&7)^((a.sta>>(3*i))&7)))
cnt++;
}
else
{
if(!(((temp>>(3*i))&7)^((a.sta>>(3*i))&7))&&((a.sta>>(3*i))&7))
cnt++;
}
}
return 9-cnt;
}
int convert(int a[],state &b)
{
b.sta=0;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a[i]!=0)
b.sta |=((a[i]-1)<<(24-i*3));
else
{
b.pos = i;
b.sta |=(a[i]<<(24-i*3));
}
}
return 1;
}
state exchange(state a,int pos)
{
int temp = 7<<((9-pos)*3);
state s;
s.sta = a.sta;
temp = temp & a.sta;
temp = ((temp>>((9-pos)*3))<<((9-a.pos-1)*3));
s.sta |= temp;
s.sta &= ~(7<<((9-pos)*3));
s.pos = pos-1;
return s;
}
bool IDAStar(state &a,int depth,int diff,int prepos)
{
cnt++;
if(!(a.sta^target.sta)&&a.pos == target.pos)
{
printf("%d\n",depth);
return true;
}
if(depth >= pathLimit) return false;
if( depth + diff > pathLimit ) return false;
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j ++)
{
if(d[a.pos][j] == prepos+1) continue;
if(d[a.pos][j])
{
state next = exchange(a,d[a.pos][j]);
if(IDAStar(next,depth+1, h(next),a.pos))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
clock_t start,end;
int diff = 0;
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)temp[j] = j+1;
temp[8]=0;
convert(temp,target);
while(1)
{
int i = 0;
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')
sou[i++] = ch - '0';
else if(ch=='x')
sou[i++] =0;
}
start = clock();
cnt = 0;
convert(sou,source);
pathLimit = h(source);
diff = pathLimit;
while(!IDAStar(source,0,diff,-1))pathLimit++;
end = clock();
printf("Time:%dms\nstate number:%d\n",end-start,cnt);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}基于manhattan距离启发:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#define FUCK puts("fuck!")
#define STOP system("pause")
#define MAXN 388211
using namespace std;
struct state{
int sta,pos;
}source,target;
int temp[10],tar[10],sou[10];
int pathLimit;
int d[9][4]={{0,4,0,2},{0,5,1,3},{0,6,2,0},{1,7,0,5},{2,8,4,6},{3,9,5,0},{4,0,0,8},{5,0,7,9},{6,0,8,0}};
int manhattan[10][10] = //第i个数及其所处不同位置的Manhattan路径长度
{
{-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1},
{-1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4},
{-1, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3},
{-1, 2, 1, 0, 3, 2, 1, 4, 3, 2},
{-1, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2, 3},
{-1, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 1, 2, 1, 2},
{-1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 3, 2, 1},
{-1, 2, 3, 4, 1, 2, 3, 0, 1, 2},
{-1, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0, 1},
{-1, 4, 3, 2, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 0}
b30a
};
int h(state a)
{
int cnt=0;
for(int i = 0;i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a.pos != i)
cnt += manhattan[((a.sta>>(3*(8-i)))&7)+1][i+1];
}
return cnt;
}
int convert(int a[],state &b)
{
b.sta=0;
for(int i = 0; i < 9; i ++)
{
if(a[i]!=0)
b.sta |=((a[i]-1)<<(24-i*3));
else
{
b.pos = i;
b.sta |=(a[i]<<(24-i*3));
}
}
return 1;
}
state exchange(state a,int pos)
{
int temp = 7<<((9-pos)*3);
state s;
s.sta = a.sta;
temp = temp & a.sta;
temp = ((temp>>((9-pos)*3))<<((9-a.pos-1)*3));
s.sta |= temp;
s.sta &= ~(7<<((9-pos)*3));
s.pos = pos-1;
return s;
}
bool IDAStar(state &a,int depth,int diff,int prepos)
{
if(!(a.sta^target.sta)&&a.pos == target.pos)
{
printf("%d\n",depth);
return true;
}
if(depth > pathLimit) return false;
if( depth + diff > pathLimit ) return false;
for(int j = 0; j < 4; j ++)
{
if(d[a.pos][j] == prepos+1) continue;
if(d[a.pos][j])
{
state next = exchange(a,d[a.pos][j]);
if(IDAStar(next,depth+1, h(next),a.pos))
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
clock_t start,end;
int diff = 0;
for(int j=0;j<8;j++)temp[j] = j+1;
temp[8]=0;
convert(temp,target);
while(1)
{
int i = 0;
char ch;
while((ch=getchar())!='\n')
{
if(ch<='9'&&ch>='0')
sou[i++] = ch - '0';
else if(ch=='x')
sou[i++] =0;
}
start = clock();
convert(sou,source);
pathLimit = h(source);
diff = pathLimit;
while(!IDAStar(source,0,diff,-1))pathLimit++;
end = clock();
printf("Time:%dms\ndepthlimit:%d\n",end-start,pathLimit);
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}六、其他优化
状态还可以压缩到一个int上,完全采用位运算来完成。
前面的hash函数还可以继续优化,对于全排列有一种非常好的hash哈希函数叫康托展开。
首先看几个康托展开的实例(9的全排列):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9——展开为 0。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 9 8——展开为 1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 8 7 9——展开为 2。
由这些最开始的方法我们可以发现一个规律:从第一个数开始,依次判断判断这些数是当前没有出现过的数的第几个(由0开始),记为a1, a2, ... ,a(n - 1)。不难发现如1 2 3 4 5 6 8 7 9,由1至6都是当前没有出现过的第0个数,而8是7,8,9中的第1个(由0开始),9是7,9中的第1个,7是第0个。故a1 = a2 = ... = a6 = 0,a7 = 1,a8 = 1,a9 =0。
之后排列数(康托展开的值)等于
a1 * (n - 1)! + a2 * (n - 2)! + ... + ak *(n - k)! + ... + an * 0!
再举几个例子:
3 5 7 4 1 2 9 6 8——展开为 98884。
5 6 7 8 1 2 3 4 9——展开为 184800。
往回转换也很简单,分步取模就可以了,在此就不赘述了。
七、总结
| BFS | BFS+HASH | DBFS | A*(diff) | A*(man) | IDA*(diff) | IDA*(man) | |
| 8672543x1(31) | 210ms | 102ms | 6ms | 322ms | 31ms | 1152ms | 7ms |
| 181440 | 181440 | 10034 | 147574 | 12290 | |||
| 64785x321(31) | 216ms | 104ms | 7ms | 330ms | 20ms | 1248ms | 8ms |
| 181441 | 181441 | 10321 | 143918 | 7567 | |||
| 8461375x2(27) | 204ms | 95ms | 2ms | 169ms | 13ms | 156ms | 5ms |
| 174213 | 174213 | 4115 | 68678 | 5595 |

相关文章推荐
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 多种方法求解八数码问题
- 实践多种搜索算法求解八数码问题python实现
- 实践多种搜索算法求解八数码问题python实现
- 在用SPCE3200做数码相册时遇到的几个问题及解决方法
- 求解约瑟夫问题两种方法
- HDU 1043 八数码问题的多种解法
- 人工智能一种现代的方法 --第3章 通过搜索进行问题求解
- PHP实现求解最长公共子串问题的方法
- 深度优先—递归方法 求解n皇后问题
- Rational Krylov Method(克雷洛夫法)求解特征值问题matlab代码示例(和Arnoldi方法比较)
- 解决ajax跨域问题的多种方法
- 凸包问题及其求解方法
