图像处理之颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient)
2011-11-27 08:20
323 查看
有过UI设计经验的一定对2D图形渲染中的Color Gradient 或多或少有些接触,很多编程
语言也提供了Gradient的接口,但是想知道它是怎么实现的嘛?
本文介绍三种简单的颜色梯度变化算法,就可以很容易实现常见的梯度变化算法
三种都要求提供两个参数即起始颜色RGB值, 最终颜色RGB的值。
垂直梯度颜色变化,效果如下:
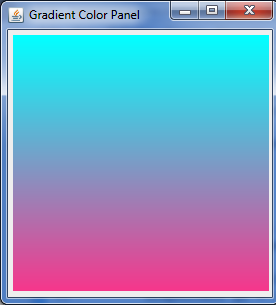
水平梯度颜色变化,效果如下:
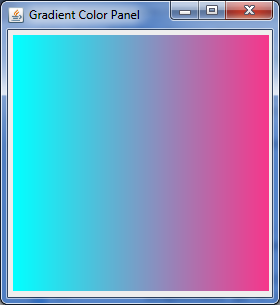
水平与垂直两个方向叠加梯度变化效果如下:
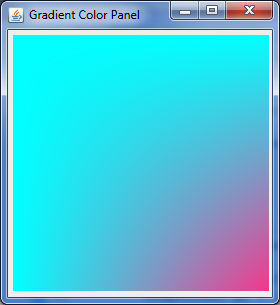
算法代码及其解释
计算起始颜色和终点颜色RGB之间差值代码如下:
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0]; float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1]; float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2]; 实现垂直梯度变化的代码如下: r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f); 实现水平梯度变化代码如下: // set gradient color valuefor each pixel r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)col/255.0f) +0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)col/255.0f) +0.5f); 实现水平和垂直两个方向上Gradient叠加代码如下: r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f); 程序对上面三种Gradient方法分别放在三个不同的方法中,根据参数调用。 程序的完全Java源代码如下:
本文出自 “流浪的鱼” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://gloomyfish.blog.51cto.com/8837804/1400412
语言也提供了Gradient的接口,但是想知道它是怎么实现的嘛?
本文介绍三种简单的颜色梯度变化算法,就可以很容易实现常见的梯度变化算法
三种都要求提供两个参数即起始颜色RGB值, 最终颜色RGB的值。
垂直梯度颜色变化,效果如下:

水平梯度颜色变化,效果如下:

水平与垂直两个方向叠加梯度变化效果如下:

算法代码及其解释
计算起始颜色和终点颜色RGB之间差值代码如下:
float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0]; float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1]; float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2]; 实现垂直梯度变化的代码如下: r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)row/255.0f) +0.5f); 实现水平梯度变化代码如下: // set gradient color valuefor each pixel r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)col/255.0f) +0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)col/255.0f) +0.5f); 实现水平和垂直两个方向上Gradient叠加代码如下: r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) +0.5f); 程序对上面三种Gradient方法分别放在三个不同的方法中,根据参数调用。 程序的完全Java源代码如下:
import java.awt.BorderLayout; import java.awt.Dimension; import java.awt.Graphics; import java.awt.Graphics2D; import java.awt.RenderingHints; import java.awt.image.BufferedImage; import javax.swing.JComponent; import javax.swing.JFrame; public class ColorGradientDemo extends JComponent { /** * */ private static final long serialVersionUID = -4134440495899912869L; private BufferedImage image = null; protected void paintComponent(Graphics g) { Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D)g; g2.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON); g2.drawImage(getImage(4), 5, 5, image.getWidth(), image.getHeight(), null); } public BufferedImage getImage(int type) { if(image == null) { image = new BufferedImage(256, 256, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB); int[] rgbData = new int[256*256]; if(type == 1) { generateVGradientImage(rgbData); } else if(type == 2) { generateHGradientImage(rgbData); } else { generateHVGradientImage(rgbData); } setRGB(image, 0, 0, 256, 256, rgbData); } return image; } private void generateVGradientImage(int[] rgbData) { int[] startColor = getStartColor(); int[] endColor = getEndColor(); float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0]; float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1]; float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2]; int a=255; int r=0, g=0, b=0; int index = 0; for(int row=0; row<256; row++) { for(int col=0; col<256; col++) { // set random color value for each pixel // set gradient color value for each pixel r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)row/255.0f) + 0.5f); rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) | ((r & 0xff) << 16) | ((g & 0xff) << 8) | ((b & 0xff)); index++; } } } private void generateHGradientImage(int[] rgbData) { int[] startColor = getStartColor(); int[] endColor = getEndColor(); float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0]; float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1]; float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2]; int a=255; int r=0, g=0, b=0; int index = 0; for(int row=0; row<256; row++) { for(int col=0; col<256; col++) { // set gradient color value for each pixel r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * ((float)col/255.0f) + 0.5f); rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) | ((r & 0xff) << 16) | ((g & 0xff) << 8) | ((b & 0xff)); index++; } } } private void generateHVGradientImage(int[] rgbData) { int[] startColor = getStartColor(); int[] endColor = getEndColor(); float rr = startColor[0] - endColor[0]; float gg = startColor[1] - endColor[1]; float bb = startColor[2] - endColor[2]; int a=255; int r=0, g=0, b=0; int index = 0; float size = (float)Math.pow(255.0d, 2.0); for(int row=0; row<256; row++) { for(int col=0; col<256; col++) { // set random color value for each pixel r = endColor[0] + (int)(rr * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f); g = endColor[1] + (int)(gg * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f); b = endColor[2] + (int)(bb * (((float)col * (float)row)/size) + 0.5f); rgbData[index] = ((a & 0xff) << 24) | ((r & 0xff) << 16) | ((g & 0xff) << 8) | ((b & 0xff)); index++; } } } public int[] getStartColor() { return new int[]{246,53,138}; } public int[] getEndColor() { return new int[]{0,255,255}; } public void setRGB( BufferedImage image, int x, int y, int width, int height, int[] pixels ) { int type = image.getType(); if ( type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB || type == BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB ) image.getRaster().setDataElements( x, y, width, height, pixels ); else image.setRGB( x, y, width, height, pixels, 0, width ); } public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame frame = new JFrame("Gradient Color Panel"); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); frame.getContentPane().setLayout(new BorderLayout()); // Display the window. frame.getContentPane().add(new ColorGradientDemo(), BorderLayout.CENTER); frame.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(280,305)); frame.pack(); frame.setVisible(true); } }本文出自 “流浪的鱼” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://gloomyfish.blog.51cto.com/8837804/1400412
相关文章推荐
- 图像处理之颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient)
- 图像处理------颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient)
- 图像处理之颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient)
- 图像处理------颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient) 分类: 视频图像处理 2015-07-24 09:23 27人阅读 评论(0) 收藏
- 图像处理------颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient)
- 图像处理------颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient)
- 图像处理------颜色梯度变化 (Color Gradient)
- 【OpenCV3图像处理】颜色空间转换(二)转换函数 cvtColor()
- java 图像处理之颜色矩阵(ColorMatrix)内附大量特效
- CCLayer(集中了触摸键盘重力消息的委托处理 子类:CCLayerRGBA、Color、Gradient-渐变颜色层 CCLayerMultiplex-内部有一个层数组可以方便的切换显示层)
- MATLAB图像处理_LAB与RGB颜色空间互转
- iOS图像处理(4)坐标变化
- 图像处理中的卷积---3.高斯卷积计算梯度
- 图像处理之常用颜色RGB、灰度值
- PHP 分配、取消图像颜色 imagecolorallocate 与 imagecolordeallocate 函数
- 处理多维度变化——桥接模式(三):跨平台图像浏览系统解决方案
- C语言处理图像之改变背景前景颜色
- Opencv 颜色空间处理(Color space processing)
- 数字图像的梯度概念(the gradient of the image)
- OpenCV - 图形图像处理 - 形态学处理 1931 1 Opencv图像识别从零到精通(17)----开运算、闭运算、顶帽、黑帽、形态学梯度、形态学角点、细化、填充 作者:qq_208236
