【KDD 2019】Graph-based Semi-Supervised & Active Learning for Edge Flows
摘要
We present a graph-based semi-supervised learning (SSL) method for learning edge flows defined on a graph. Specifically, given flow measurements on a subset of edges, we want to predict the flows on the remaining edges. To this end, we develop a computational framework that imposes certain constraints on the overall flows,such as (approximate) flow conservation. These constraints render our approach different from classical graph-based SSL for vertex labels, which posits that tightly connected nodes share similar labels and leverages the graph structure accordingly to extrapolate from a few vertex labels to the unlabeled vertices.
提出了一种基于图的半监督学习(SSL)方法来学习定义在图上的边流。具体地说,给定一个边子集上的流量测量值,我们要预测其余边上的流。为此,我们开发了一个计算框架,该框架对整体流施加了某些约束,例如(近似)流守恒。这些约束使得我们的方法不同于经典的基于图的顶点标签SSL,后者假设紧密连接的节点共享相似的标签,并相应地利用图结构从几个顶点标签外推到未标记的顶点。
We derive bounds for our method’s reconstruction error and demonstrate its strong performance on synthetic and real-world flow networks from transportation, physical infrastructure, and the Web. Furthermore, we provide two active learning algorithms for selecting informative edges on which to measure flow, which has applications for optimal sensor deployment. The first strategy
selects edges to minimize the reconstruction error bound and works well on flows that are approximately divergence-free. The second approach clusters the graph and selects bottleneck edges that cross cluster-boundaries, which works well on flows with global trends.
我们推导了我们的方法重建误差的界,并证明了它在交通、物理基础设施和网络等综合和真实世界流量网络中的强大性能。此外,我们还提供了两种主动学习算法来选择用于测量流量的信息边缘,这对于传感器的优化配置具有一定的应用价值。第一种策略选择边缘以最小化重建误差边界,并且在近似无散度的流上工作良好。第二种方法对图进行聚类,并选择跨越聚类边界的瓶颈边缘,这对具有全局趋势的流很有效。
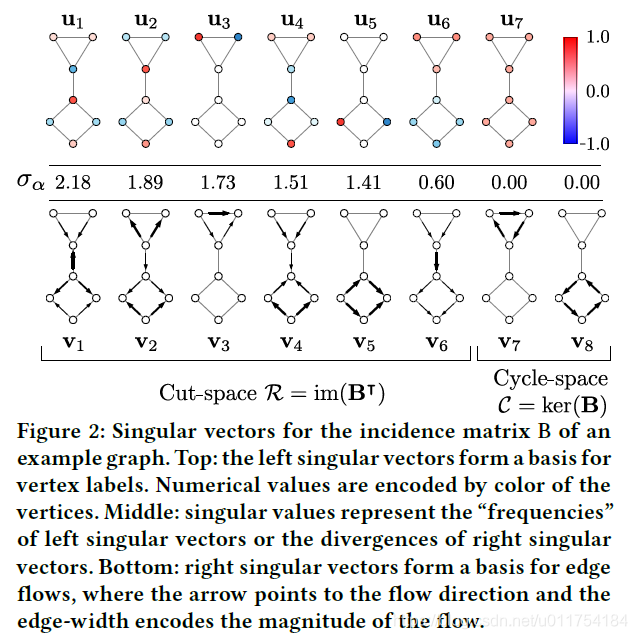
框架

- 【论文笔记01】Learning Loss for Active Learning, CVPR 2019
- 论文阅读《ActiveStereoNet:End-to-End Self-Supervised Learning for Active Stereo Systems》
- Two-Phase Learning for Weakly Supervised Object Localization
- Jointly Learning Explainable Rules for Recommendation with Knowledge Graph
- Learning Conditioned Graph Structures for Interpretable Visual Question Answering
- 深度对抗网络用于分割(语义分割)——Adversarial Learning for Semi-Supervised Semantic Segmentation
- Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Graphs 论文笔记
- Learning Entity and Relation Embeddings for Knowledge Graph Completion
- Reading Notes: Ranking Graph Embedding for Learning to Rerank
- 论文笔记-深度估计(4) Semi-Supervised Deep Learning for Monocular Depth Map Prediction
- 【KDD 2019】Heterogeneous Graph Neural Network
- Learning Informative Edge Maps for Indoor Scene Layout Prediction
- Dynamic Graph CNN for Learning on Point Clouds 解析
- 【软件分析与挖掘】A Comparative Study of Supervised Learning Algorithms for Re-opened Bug Prediction
- 自监督学习(十六)Transitive Invariance for Self-supervised Visual Representation Learning
- Weakly- and Semi-Supervised Learning of a Deep Convolutional Network for Semantic Image Segmentation
- 【2019 ITIP】Spatial-Temporal Attention-Aware Learning for Video-Based Person Re-Identification
- Suggestive Annotation: A Deep Active Learning Framework for Biomedical Image Segmentation
- 阅读论文:Suggestive Annotation: A Deep Active Learning Framework for Biomedical Image Segmentation
- Learning Disentangled Semantic Representation for Domain Adaptation-IJCAI-2019文章解读
