基于python的BP神经网络及异或实现过程解析
2019-12-08 07:09
796 查看
BP神经网络是最简单的神经网络模型了,三层能够模拟非线性函数效果。

难点:
- 如何确定初始化参数?
- 如何确定隐含层节点数量?
- 迭代多少次?如何更快收敛?
- 如何获得全局最优解?
'''
neural networks
created on 2019.9.24
author: vince
'''
import math
import logging
import numpy
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
'''
neural network
'''
class NeuralNetwork:
def __init__(self, layer_nums, iter_num = 10000, batch_size = 1):
self.__ILI = 0;
self.__HLI = 1;
self.__OLI = 2;
self.__TLN = 3;
if len(layer_nums) != self.__TLN:
raise Exception("layer_nums length must be 3");
self.__layer_nums = layer_nums; #array [layer0_num, layer1_num ...layerN_num]
self.__iter_num = iter_num;
self.__batch_size = batch_size;
def train(self, X, Y):
X = numpy.array(X);
Y = numpy.array(Y);
self.L = [];
#initialize parameters
self.__weight = [];
self.__bias = [];
self.__step_len = [];
for layer_index in range(1, self.__TLN):
self.__weight.append(numpy.random.rand(self.__layer_nums[layer_index - 1], self.__layer_nums[layer_index]) * 2 - 1.0);
self.__bias.append(numpy.random.rand(self.__layer_nums[layer_index]) * 2 - 1.0);
self.__step_len.append(0.3);
logging.info("bias:%s" % (self.__bias));
logging.info("weight:%s" % (self.__weight));
for iter_index in range(self.__iter_num):
sample_index = random.randint(0, len(X) - 1);
logging.debug("-----round:%s, select sample %s-----" % (iter_index, sample_index));
output = self.forward_pass(X[sample_index]);
g = (-output[2] + Y[sample_index]) * self.activation_drive(output[2]);
logging.debug("g:%s" % (g));
for j in range(len(output[1])):
self.__weight[1][j] += self.__step_len[1] * g * output[1][j];
self.__bias[1] -= self.__step_len[1] * g;
e = [];
for i in range(self.__layer_nums[self.__HLI]):
e.append(numpy.dot(g, self.__weight[1][i]) * self.activation_drive(output[1][i]));
e = numpy.array(e);
logging.debug("e:%s" % (e));
for j in range(len(output[0])):
self.__weight[0][j] += self.__step_len[0] * e * output[0][j];
self.__bias[0] -= self.__step_len[0] * e;
l = 0;
for i in range(len(X)):
predictions = self.forward_pass(X[i])[2];
l += 0.5 * numpy.sum((predictions - Y[i]) ** 2);
l /= len(X);
self.L.append(l);
logging.debug("bias:%s" % (self.__bias));
logging.debug("weight:%s" % (self.__weight));
logging.debug("loss:%s" % (l));
logging.info("bias:%s" % (self.__bias));
logging.info("weight:%s" % (self.__weight));
logging.info("L:%s" % (self.L));
def activation(self, z):
return (1.0 / (1.0 + numpy.exp(-z)));
def activation_drive(self, y):
return y * (1.0 - y);
def forward_pass(self, x):
data = numpy.copy(x);
result = [];
result.append(data);
for layer_index in range(self.__TLN - 1):
data = self.activation(numpy.dot(data, self.__weight[layer_index]) - self.__bias[layer_index]);
result.append(data);
return numpy.array(result);
def predict(self, x):
return self.forward_pass(x)[self.__OLI];
def main():
logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO,
format = '%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s',
datefmt = '%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S');
logging.info("trainning begin.");
nn = NeuralNetwork([2, 2, 1]);
X = numpy.array([[0, 0], [1, 0], [1, 1], [0, 1]]);
Y = numpy.array([0, 1, 0, 1]);
nn.train(X, Y);
logging.info("trainning end. predict begin.");
for x in X:
print(x, nn.predict(x));
plt.plot(nn.L)
plt.show();
if __name__ == "__main__":
main();
具体收敛效果
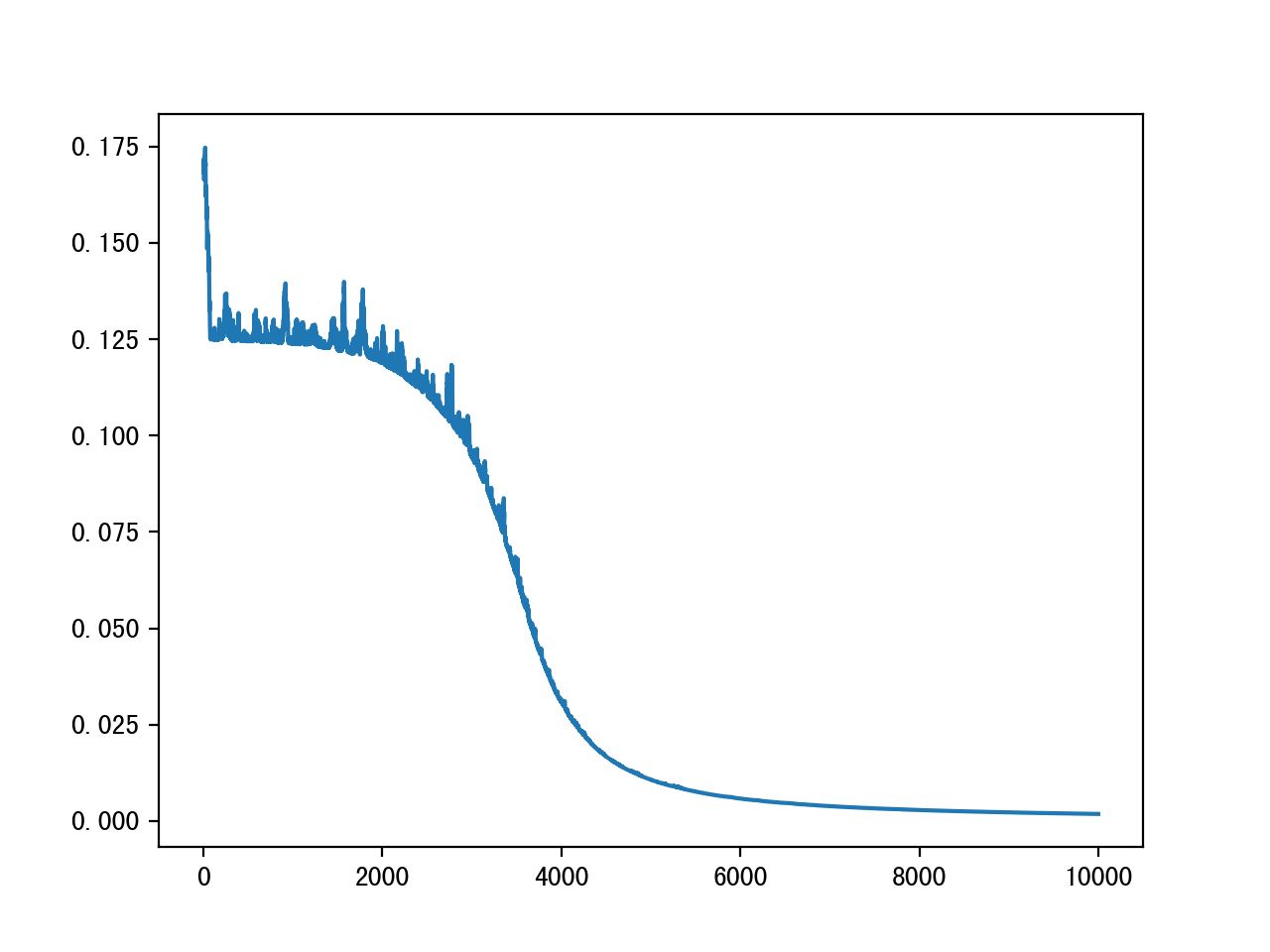
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助
您可能感兴趣的文章:
相关文章推荐
- 基于Python实现大文件分割和命名脚本过程解析
- 基于Python实现签到脚本过程解析
- 训练三层BP神经网络实现异或运算 Python 代码实现
- python腾讯语音合成实现过程解析
- 深度学习入门基于python的理论与实现 4章gradient_simplenet.py 完全解析
- 基于纯JS实现多张图片的懒加载Lazy过程解析
- Python实现网页截图(PyQT5)过程解析
- Python实现串口通信(pyserial)过程解析
- 基于Python实现剪切板实时监控方法解析
- BP神经网络求解异或问题(Python实现)
- python基于xml parse实现解析cdatasection数据
- Python实现朴素贝叶斯的学习与分类过程解析
- 基于python全局设置id 自动化测试元素定位过程解析
- python实现广度优先搜索过程解析
- python实现一个函数版的名片管理系统过程解析
- python实现WebSocket服务端过程解析
- python分布式编程实现过程解析
- BP神经网络Python实现异或问题
- Python基于Opencv来快速实现人脸识别过程详解(完整版)
- python爬虫 基于requests模块发起ajax的get请求实现解析
