Boost学习-学习笔记-windows开发环境搭建
一、获取boost库,由于有些时候下的比较慢,当然获取最新版本的话可以去官网(进官网: http://www.boost.org),我采用的boost库版本号为1.69,提供百度云下载链接:
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/11DKaT8BjqNN-kqAVqzLRYw
提取码:1ny2
复制这段内容后打开百度网盘手机App,操作更方便哦
二、转载
因为boost都是使用模板的技术,所以所有代码都是写在一个.hpp头文件中。这样boost中的大部分内容是不需要编译生成相应的链接库,只需要设置下面的包含目录(或者设置一下环境变量),在源文件中包含相应的头文件就可以使用了。少部分库需要生成链接库来使用。
下面介绍完整安装boost库的方法:
1、首先到boost官网去下载最新的版本的boost库:
2、解压文件,在命令提示符中打开到boost库的根目录下:
双击bootstrap.bat文件,生成bjam.exe,执行以下命令:
bjam --toolset=msvc --build-type=complete stage
或者直接双击bjam.exe.
等待程序编译完成,大约要两个小时左右,会在boost根目录下生成bin.v2和stage两个文件夹,其中bin.v2下是生成的中间文件,大小在2.7G左右,可以直接删除。stage下才是生成的dll和lib文件。
bjam说明
boost自带一套编译工具bjam,bjam本身是跨平台的,并且也要自行编译出来。在boost目录下有bootstrap.sh和bootstrap.bat两个脚本分别用来编译*nix和windows下的bjam。bootstrap脚本可以传入参数,以在编译bjam过程中生成特定的编译boost的配置。这些配置保存在新生成的project-config.jam里,但还可以在运行bjam的时候再传入参数来覆盖。同时生成的b2是bjam的代理,运行哪个的效果都差不多。
在终端下运行
bjam --show-libraries
会列出所有要编译的库。
真正编译时,可以传入–with-xxx来选择编译哪些库,或者传入–without-xxx来选择不编译哪些库。如果不传则会读取project-config.jam的设置,如果也没有则是编译全部的库。
更多的参数可以用
bjam --help
来查看。例如编译成静态库还是动态库,运行时库是静态的还是动态的,编译完后要不要安装等。
注意:
旧版本的boost可能会存在编译问题,尽量用新的就好。bjam在*nix和windows支持的参数有不同。
3、打开vs:
视图->属性管理器->当前项目->Debug|Win32->Microsoft.Cpp.Win32.user双击
在弹出的属性对话框中:
通用属性->VC++目录:"包含目录": boost的根目录,例: D:\Visual Stdio 2013\lipeng\boost\boost_1_58_0
"库目录": stage下的链接库目录,例:D:\Visual Stdio 2013\lipeng\boost\boost_1_58_0\stage\lib
通用属性->链接器->常规:"附加库目录":同上面的"库目录",例:D:\Visual Stdio 2013\lipeng\boost\boost_1_58_0\stage\lib
至此环境就配置好了,下面测试一下:
[code]#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <algorithm>
#include <boost/timer.hpp>
#include <boost/progress.hpp>
#include <libs/date_time/src/gregorian/greg_names.hpp>
#include <libs/date_time/src/gregorian/date_generators.cpp>
#include <libs/date_time/src/gregorian/greg_month.cpp>
#include <libs/date_time/src/gregorian/gregorian_types.cpp>
#include <boost/date_time/posix_time/posix_time.hpp>
using namespace boost;
int main()
{
boost::timer t;
boost::progress_display pd(100);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) //进度条
{
++pd;
}
boost::gregorian::date dt(2009, 12, 8); //date_time 库
assert(dt.year() == 2009);
assert(dt.day() == 8);
boost::gregorian::date::ymd_type ymd = dt.year_month_day();
std::cout<<"\n"<<ymd.year<<"/"<<ymd.month<<"/"<<ymd.day<<" the day is "
<<dt.day_of_year() <<" days of this year"<< std::endl;
std::cout << boost::gregorian::to_iso_extended_string(dt) << std::endl; //转换为其他格式
std::cout << boost::gregorian::to_iso_string(dt) << std::endl;
std::cout << boost::gregorian::to_simple_string(dt) << std::endl<<std::endl;
//对数组排序操作
std::vector<int> test_vc(100);
std::vector<int>::iterator beg_it = test_vc.begin();
std::vector<int>::iterator end_it = test_vc.end();
std::srand(std::time(NULL));
std::for_each(beg_it, end_it, [](int& n){n = rand(); });
std::copy(beg_it, end_it, std::ostream_iterator<int>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl;
std::sort(beg_it, end_it, std::greater<int>());
std::copy(beg_it, end_it, std::ostream_iterator<int>(std::cout, " "));
std::cout << std::endl<<std::endl;
boost::posix_time::ptime pt(boost::gregorian::date(2005, 2, 6));
std::cout << t.elapsed() << "s" << std::endl; //程序运行时间
system("pause");
return 0;
}
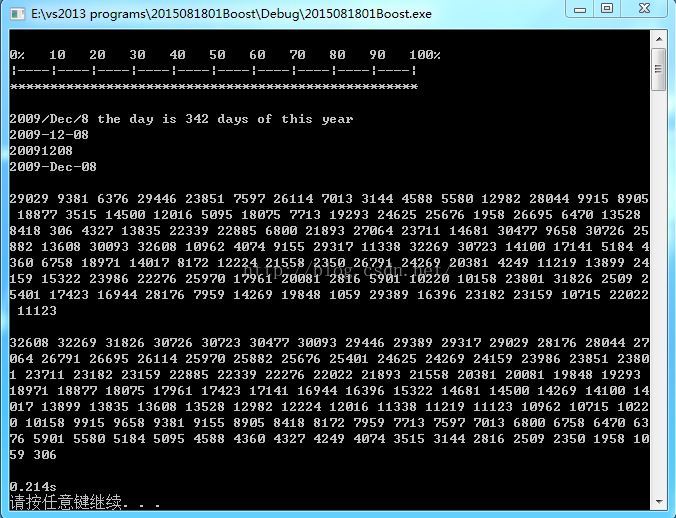
程序正确运行:
- Object C学习笔记6-如何在Windows环境搭建Object C开发环境
- Cocos2d-x学习笔记(一)——Windows开发环境和Android交叉编译环境搭建
- Protocol Buffers学习笔记 - Windows上搭建开发环境,开发Java序列化应用
- cocos2d-x学习笔记01:VS开发环境windows平台搭建
- Lua学习笔记1:开发环境搭建(windows和linux)
- Object C学习笔记6-如何在Windows环境搭建Object C开发环境
- Go语言学习笔记(一) : 搭建Windows下的Go开发环境
- 【Cocos2D-X 学习笔记】windows如何搭建Cocos2D-x开发环境
- Spark2.x学习笔记:6、在Windows平台下搭建Spark开发环境(Intellij IDEA)
- cocos2d-x 2.1.4学习笔记01:windows平台搭建cocos2d-x开发环境
- 我的嵌入式学习笔记(1)-- 搭建开发环境
- GTK+学习:概述 、搭建环境(Windows,Linux)、开发
- Cocos2d-x引擎学习笔记之(一)Win32下开发环境的搭建
- GTK+学习:概述 、搭建环境(Windows,Linux)、开发 收藏
- cocos2d-x学习笔记01:VS开发环境搭建
- 【Cocos2d-X开发学习笔记】第01期:PC开发环境的详细搭建
- Drools学习笔记3-开发环境搭建
- nao机器人学习笔记6:深层开发的环境搭建
- OK6410 Linux开发环境搭建--编译以及ubuntu的使用方法学习笔记
- Struts2学习笔记2-搭建开发环境3步走
