MySQL子查询(嵌套查询)
一个查询语句嵌套在另一个查询语句内部的查询
常用操作符:ANY(SOME), ALL, IN, EXISTS
比较运算符:>, >=, <, <=, != 等
创建两个表,表明分别是tb1,tb2,并向其各插入了数据。
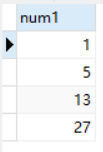

1.带ANY(SOME)关键字的子查询
这里any和some是同义词,都是表示满足任一条件。
例:查询tb1中的所有数据,只要大于tb2表中数据的任意值,既符合查询条件。
select num1 from tb1 where num1>ANY(select num2 from tb2);

2.带ALL关键字的子查询
例:查询tb1中的所有数据,返回其中比tb2表中任何值都大的数据。
select num1 from tb1 where num1>ALL(select num2 from tb2);

3.带EXISTS关键字的子查询

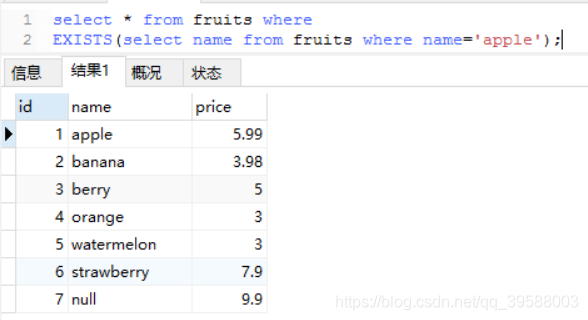
例1:查询fruits表中name字段下是否有apple,若有则查询fruits表中的记录,否则不查询。
select * from fruits where EXISTS(select name from fruits where name='apple');
例2:查询tb1表中是否存在num1=13的记录,若存在,则查询fruits表中price大于6.00的记录。
select * from fruits where price>6.00 and EXISTS (select num1 from tb1 where num1=13);

相反,可以使用 not exists 查询不存在的,用法相同。
4.带IN关键字的子查询
内层查询语句返回一个数据列,该数据列将提供给外层查询语句进行比较操作。
例如:查询tb1表中的num1字段下的数据作为数据列,fruits表中id字段下的数据与其进行比较,返回符合条件的记录。
select * from fruits where id IN (select num1 from tb1);

5.带比较运算符的子查询
select * from 表名 where 字段名 > (select ······);
- MYSQL子查询和嵌套查询优化实例解析
- 网站开发日记(14)-MYSQL子查询和嵌套查询优化
- Mysql子查询-select语句嵌套-检索多个表
- MySQL子查询优化实例
- sql子查询和嵌套查询
- Mysql子查询、UNION操作
- MySQL子查询优化---目标列中的子查询执行情况分析-02
- Mysql子查询IN中使用LIMIT应用示例
- [慢查优化]慎用MySQL子查询,尤其是看到DEPENDENT SUBQUERY标记时
- mysql子查询中的陷阱
- SQL Server学习笔记(一)【认识SQL Server查询及分组嵌套查询】
- 你必须掌握的一些常见的SQL语句,包含单表查询、高级查询(连接查询、复合条件查询、嵌套查询)
- Sql或者hql 查询时 需要多条件时可以使用嵌套查询
- 数据库-子查询《mysql子查询的弱点》
- 单表多条件查询,匿名类型,匿名对象,嵌套查询,Linq序列转换后调用外部方法
- mysql子查询 -exists,not exists
- [慢查优化]慎用MySQL子查询,尤其是看到DEPENDENT SUBQUERY标记时
- 高级子查询(嵌套查询)和(相关子查询)
- 如何能让mysql子查询中支持limit
- mysql子查询优化
