Python3.5内置模块之shelve模块、xml模块、configparser模块、hashlib、hmac模块用法分析
本文实例讲述了Python3.5内置模块之shelve模块、xml模块、configparser模块、hashlib、hmac模块用法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
1、shelve模块
shelve类似于一个key-value数据库,可以很方便的用来保存Python的内存对象,其内部使用pickle来序列化数据,
简单来说,使用者可以将一个列表、字典、或者用户自定义的类实例保存到shelve中,下次需要用的时候直接取出来,
就是一个Python内存对象,不需要像传统数据库一样,先取出数据,然后用这些数据重新构造一遍所需要的对象。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:ZhengzhengLiu
import shelve
import datetime
d = shelve.open('shelve_test') # 打开一个文件
info = {
"age":23,
"job":"IT"
}
name = ["alex", "rain", "test"]
d["name"] = name # 持久化列表
d["info"] = info # 持久化字典
d["data"] = datetime.datetime.now()
d.close()
运行结果:产生3个文件

从shelve中数据读取:get方法
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:ZhengzhengLiu
import shelve
import datetime
d = shelve.open('shelve_test') # 打开一个文件
print(d.get("name"))
print(d.get("info"))
print(d.get("data"))
运行结果:
['alex', 'rain', 'test']
{'job': 'IT', 'age': 23}
2017-09-29 18:31:12.013709
2、xml模块
xml是实现不同语言或程序之间进行数据交换的协议,跟json差不多,但json使用起来更简单,在json还没诞生时,
大家只能选择用xml,至今很多传统公司如金融行业的很多系统的接口还主要是xml。xml的格式如下,就是通过<>节点来区别数据结构的。
(1)xml文件示例代码如下:文件名为:xml_test.xml
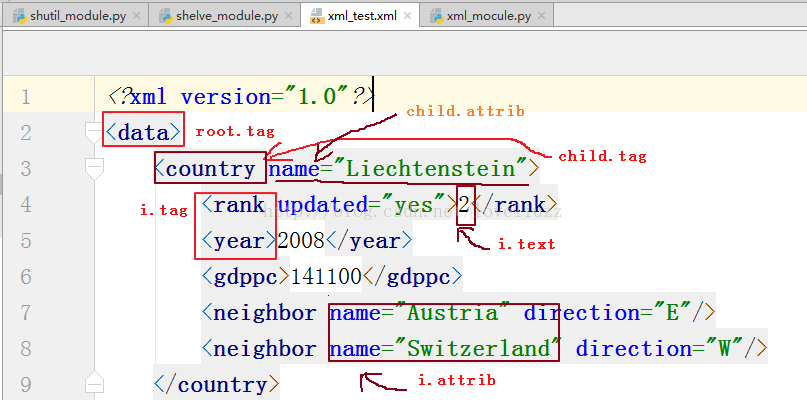
<?xml version="1.0"?> <data> <country name="Liechtenstein"> <rank updated="yes">2</rank> <year>2008</year> <gdppc>141100</gdppc> <neighbor name="Austria" direction="E"/> <neighbor name="Switzerland" direction="W"/> </country> <country name="Singapore"> <rank updated="yes">5</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>59900</gdppc> <neighbor name="Malaysia" direction="N"/> </country> <country name="Panama"> <rank updated="yes">69</rank> <year>2011</year> <gdppc>13600</gdppc> <neighbor name="Costa Rica" direction="W"/> <neighbor name="Colombia" direction="E"/> </country> </data>
(2)Python中操作xml模块
xml协议在各种语言里的都是支持的,在python中可以用以下模块操作xml 。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:ZhengzhengLiu
#python中操作xml模块
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse("xml_test.xml") #要处理的xml文件名
root = tree.getroot() #root是一个内存对象
print(root)
print(root.tag) #打印标签名
#print(ET.parse("xml_test.xml").getroot().tag)
# 遍历xml文档
for child in root:
print(child.tag, child.attrib) #打印下一级的标签名和属性
for i in child:
print(i.tag,i.attrib,i.text)
运行结果:
<Element 'data' at 0x0062E8A0>
data
country {'name': 'Liechtenstein'}
rank {'updated': 'yes'} 2
year {} 2008
gdppc {} 141100
neighbor {'direction': 'E', 'name': 'Austria'} None
neighbor {'direction': 'W', 'name': 'Switzerland'} None
country {'name': 'Singapore'}
rank {'updated': 'yes'} 5
year {} 2011
gdppc {} 59900
neighbor {'direction': 'N', 'name': 'Malaysia'} None
country {'name': 'Panama'}
rank {'updated': 'yes'} 69
year {} 2011
gdppc {} 13600
neighbor {'direction': 'W', 'name': 'Costa Rica'} None
neighbor {'direction': 'E', 'name': 'Colombia'} None
只遍历节点year,代码如下:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:ZhengzhengLiu
#python中操作xml模块
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
tree = ET.parse("xml_test.xml") #要处理的xml文件名
root = tree.getroot() #root是一个内存对象
print(root)
print(root.tag) #打印标签名
# 只遍历year 节点
for node in root.iter('year'):
print(node.tag, node.text)
运行结果:
<Element 'data' at 0x0050E8D0>
data
year 2008
year 2011
year 2011
3、configparser模块
用于生成和修改常见配置文档,常见文档格式如下:
[DEFAULT] ServerAliveInterval = 45 Compression = yes CompressionLevel = 9 ForwardX11 = yes [bitbucket.org] User = hg [topsecret.server.com] Port = 50022 ForwardX11 = no
Python生成配置文档:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:ZhengzhengLiu
#python生成配置文档
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config["DEFAULT"] = {'ServerAliveInterval': '45',
'Compression': 'yes',
'CompressionLevel': '9'}
config['bitbucket.org'] = {}
config['bitbucket.org']['User'] = 'hg'
config['topsecret.server.com'] = {}
topsecret = config['topsecret.server.com']
topsecret['Host Port'] = '50022' # mutates the parser
topsecret['ForwardX11'] = 'no' # same here
config['DEFAULT']['ForwardX11'] = 'yes'
with open('example.ini', 'w') as configfile:
config.write(configfile)
4、hashlib模块
做一个映射关系,将字符串转成数字,用于加密相关的操作。
3.x里主要提供 SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 ,MD5 算法。
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author:ZhengzhengLiu
import hashlib
m = hashlib.md5() #生成对象
m.update(b"Hello")
m.update(b"It's me")
print(m.digest())
m.update(b"It's been a long time since last time we ...")
print(m.digest()) #2进制格式hash
print(len(m.hexdigest())) #16进制格式hash
print(m.hexdigest())
# ######## md5 ########
hash = hashlib.md5()
hash.update(b'admin')
print("md5:",hash.hexdigest())
# ######## sha1 ########
hash = hashlib.sha1()
hash.update(b'admin')
print("sha1:",hash.hexdigest())
# ######## sha256 ########
hash = hashlib.sha256()
hash.update(b'admin')
print("sha256:",hash.hexdigest())
运行结果:
b']\xde\xb4{/\x92Z\xd0\xbf$\x9cR\xe3Br\x8a'
b'\xa0\xe9\x89E\x03\xcb\x9f\x1a\x14\xaa\x07?<\xae\xfa\xa5'
32
a0e9894503cb9f1a14aa073f3caefaa5
md5: 21232f297a57a5a743894a0e4a801fc3
sha1: d033e22ae348aeb5660fc2140aec35850c4da997
sha256: 8c6976e5b5410415bde908bd4dee15dfb167a9c873fc4bb8a81f6f2ab448a918
5、hmac 模块
它内部对我们创建 key 和 内容 再进行处理然后再加密。
散列消息鉴别码,简称HMAC,是一种基于消息鉴别码MAC(Message Authentication Code)的鉴别机制。
使用HMAC时,消息通讯的双方,通过验证消息中加入的鉴别密钥K来鉴别消息的真伪;一般用于网络通信中消息加密。
前提是双方先要约定好key,就像接头暗号一样,然后消息发送把用key把消息加密,接收方用key + 消息明文再加密,
拿加密后的值 跟 发送者的相对比是否相等,这样就能验证消息的真实性,及发送者的合法性了。
import hmac h = hmac.new(b'zxc', 'cvb你好'.encode(encoding="utf-8")) print(h.digest()) print(h.hexdigest()) #运行结果: #b'\xc1\x89\t#VQ\xa4\x00\xbf\xed\xb2_\xc1s\xfa\xd2' #c18909235651a400bfedb25fc173fad2
更多关于Python相关内容感兴趣的读者可查看本站专题:《Python操作xml数据技巧总结》、《Python数据结构与算法教程》、《Python Socket编程技巧总结》、《Python函数使用技巧总结》、《Python字符串操作技巧汇总》、《Python入门与进阶经典教程》及《Python文件与目录操作技巧汇总》
希望本文所述对大家Python程序设计有所帮助。
您可能感兴趣的文章:
- Python3.5——内置模块详解之shelve模块、xml模块、configparser模块、hashlib、hmac模块
- Python3.5内置模块之time与datetime模块用法实例分析
- Python3.5内置模块之os模块、sys模块、shutil模块用法实例分析
- Python3.5内置模块之random模块用法实例分析
- Python time、datetime、os、random、sys、hashlib、json、shutil、logging、paramiko、subprocess、ConfigParser、xml、shelve模块的使用
- python-常用模块xml、shelve、configparser、hashlib
- Python3.5 Pandas模块之Series用法实例分析
- Python内置模块logging用法实例分析
- Python3.5 Pandas模块之DataFrame用法实例分析
- Python 第五篇(下):系统标准模块(shutil、logging、shelve、configparser、subprocess、xml、yaml、自定义模块)
- Python常用模块用法分析
- Python数据持久化shelve模块用法分析
- Python中random模块用法实例分析
- python 内置模块之hashlib、hmac、uuid
- Python常用模块用法分析
- python pickle 和 shelve模块的用法
- Python unittest模块用法实例分析
- python模块基础之json,requeste,xml,configparser,logging,subprocess,shutil。
- Python基础-configparser和hashlib模块
- python:xml模块用法-xml处理、修改、删除
