IntelliJ IDEA下自动生成Hibernate映射文件以及实体类
2019-04-16 17:31
316 查看
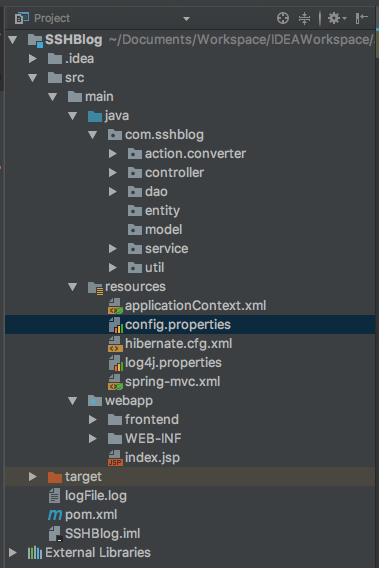
1、构建项目并添加项目结构配置以及配置初始参数
1.1、如图将基本的架子搭建好
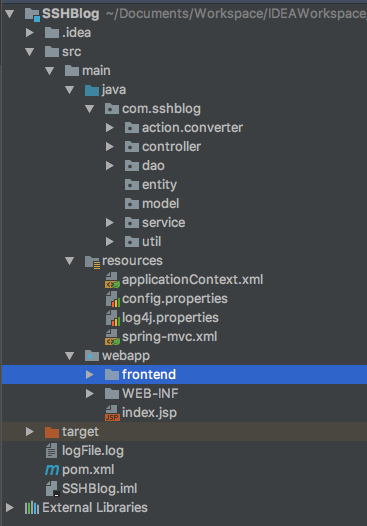
1.2、点击File,弹出的菜单中点击Project Structure;
1.3、点击左侧的Modules,再点击“+”号,再在弹出的菜单中选择Hibernate;
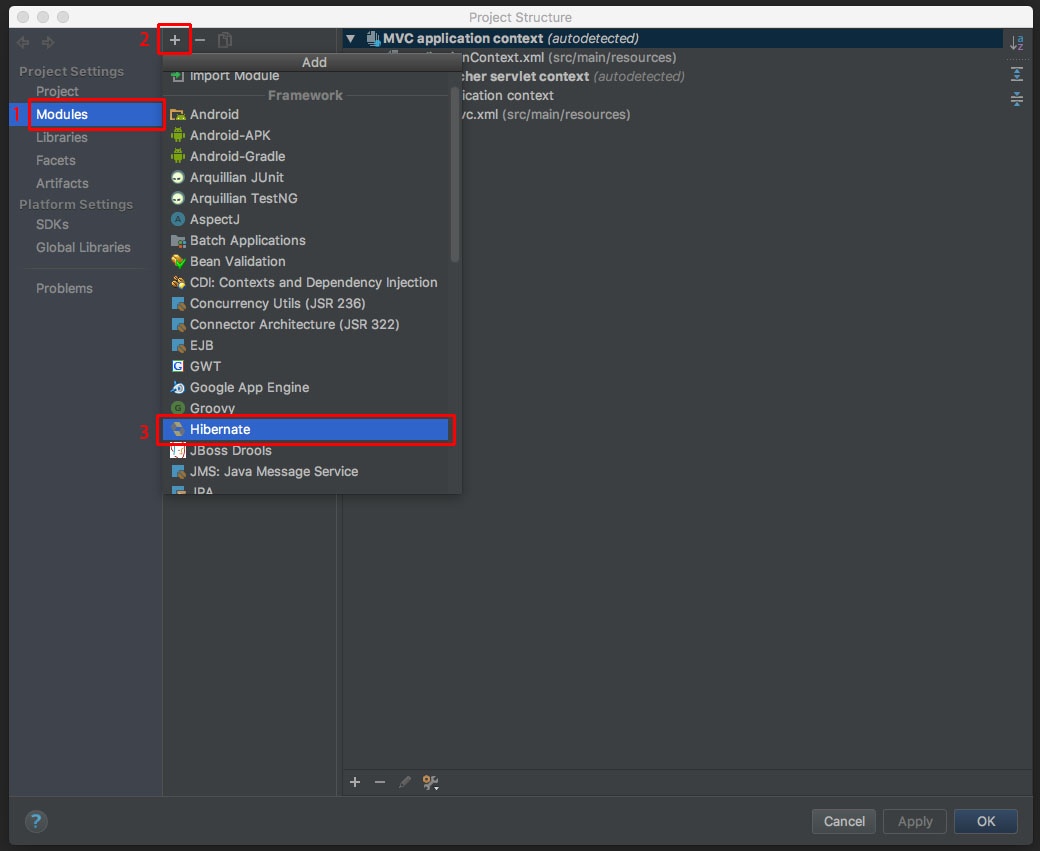
1.4、在这时,项目中多出了一个Hibernate,点击Hibernate,再点击“+”号,选择hibernate.hbm.xml;
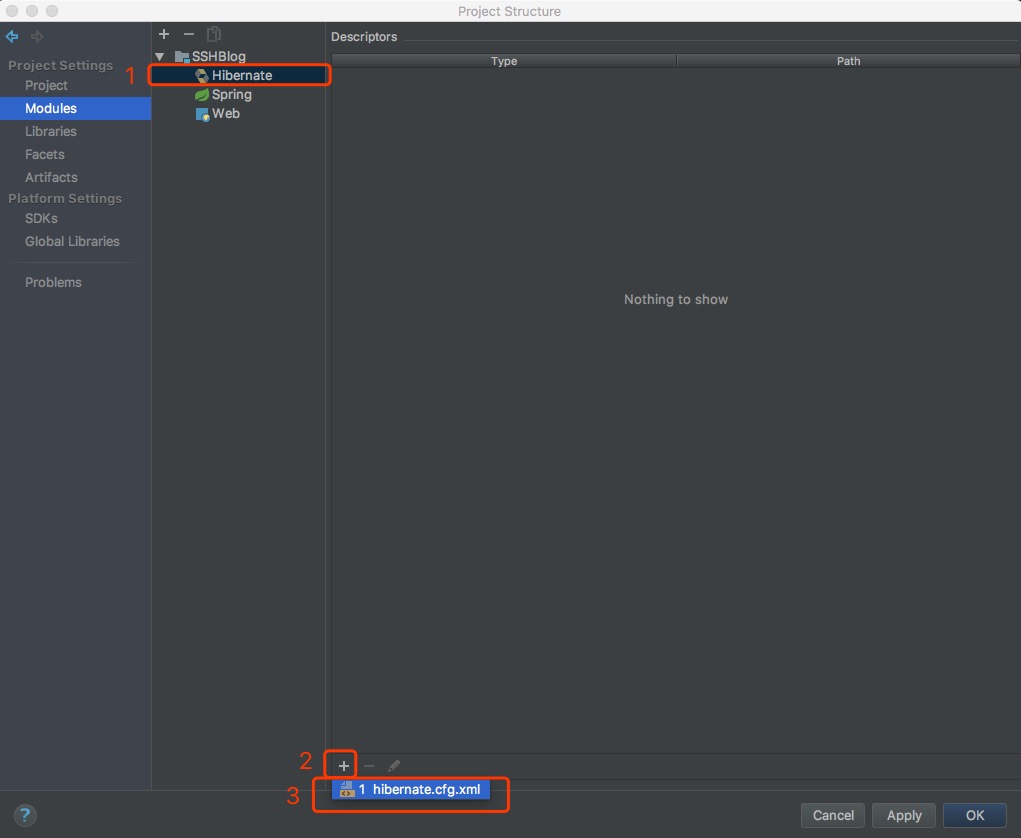
1.5、弹出的窗口中选择Hibernate的版本,然后点击OK;
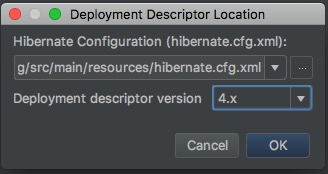
1.6、点击OK后在原来1.4步骤的窗口中的Apply按妞应用到项目;
1.7、这时项目架子中多出了一个名为hibernate.hbm.xml的配置文件;
1.8、在hibernate.hbm.xml中配置如下配置;
- <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
- <!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
- "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD//EN"
- "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd">
- <hibernate-configuration>
- <session-factory>
- <!--数据库连接url配置-->
- <property name="connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/SSHBlog?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull</property>
- <!--数据库驱动配置-->
- <property name="connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
- <!--数据库用户名配置-->
- <property name="connection.username">root</property>
- <!--数据库密码配置-->
- <property name="connection.password"></property>
- <!-- DB schema will be updated if needed -->
- <!-- <property name="hbm2ddl.auto">update</property> -->
- </session-factory>
- </hibernate-configuration>
1.9、第一步配置完毕。
2、配置数据库
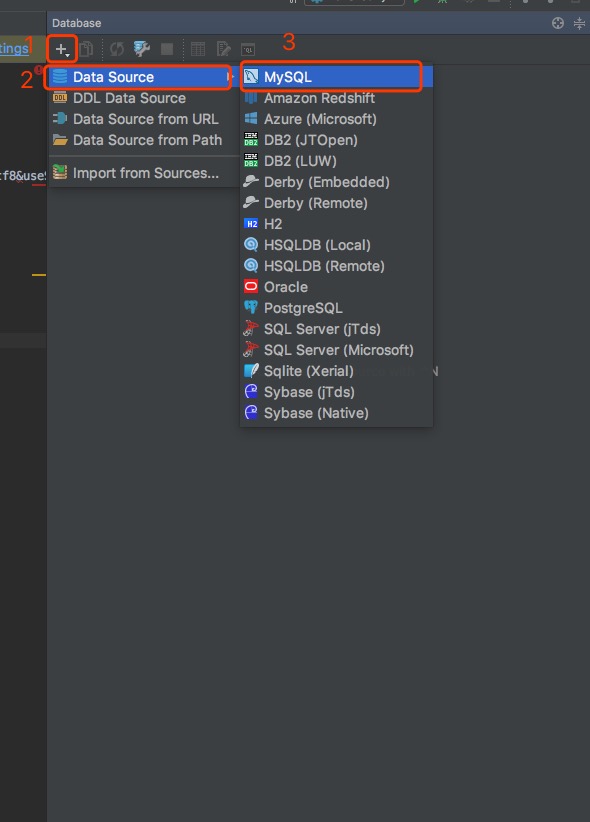
2.1、点击左下角按钮,使窗口样式如图所示;
2.2、选择数据库;
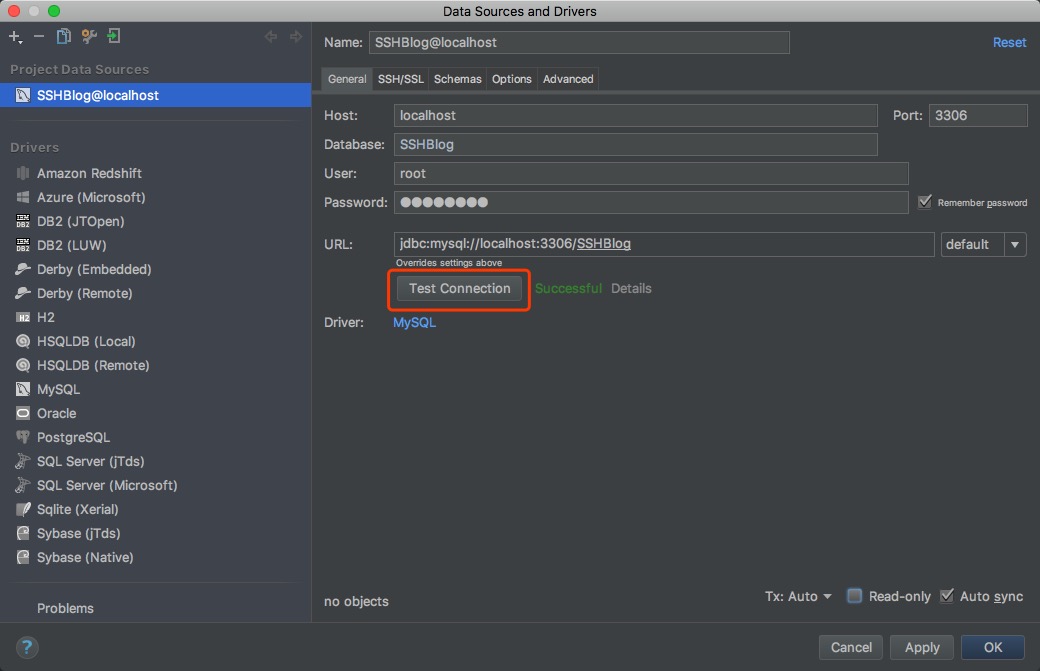
2.4、配置数据库后测试连接是否成功,若成功后点击确定;
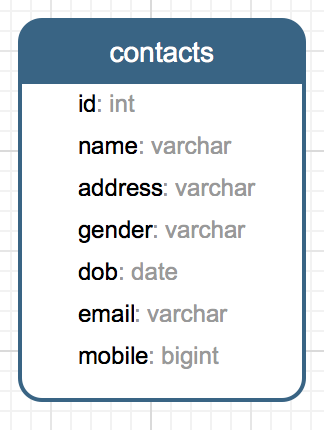
2.5、数据库如下;
3、生成Hibernate的实体类以及配置文件
3.1、点击窗口中的Persistence;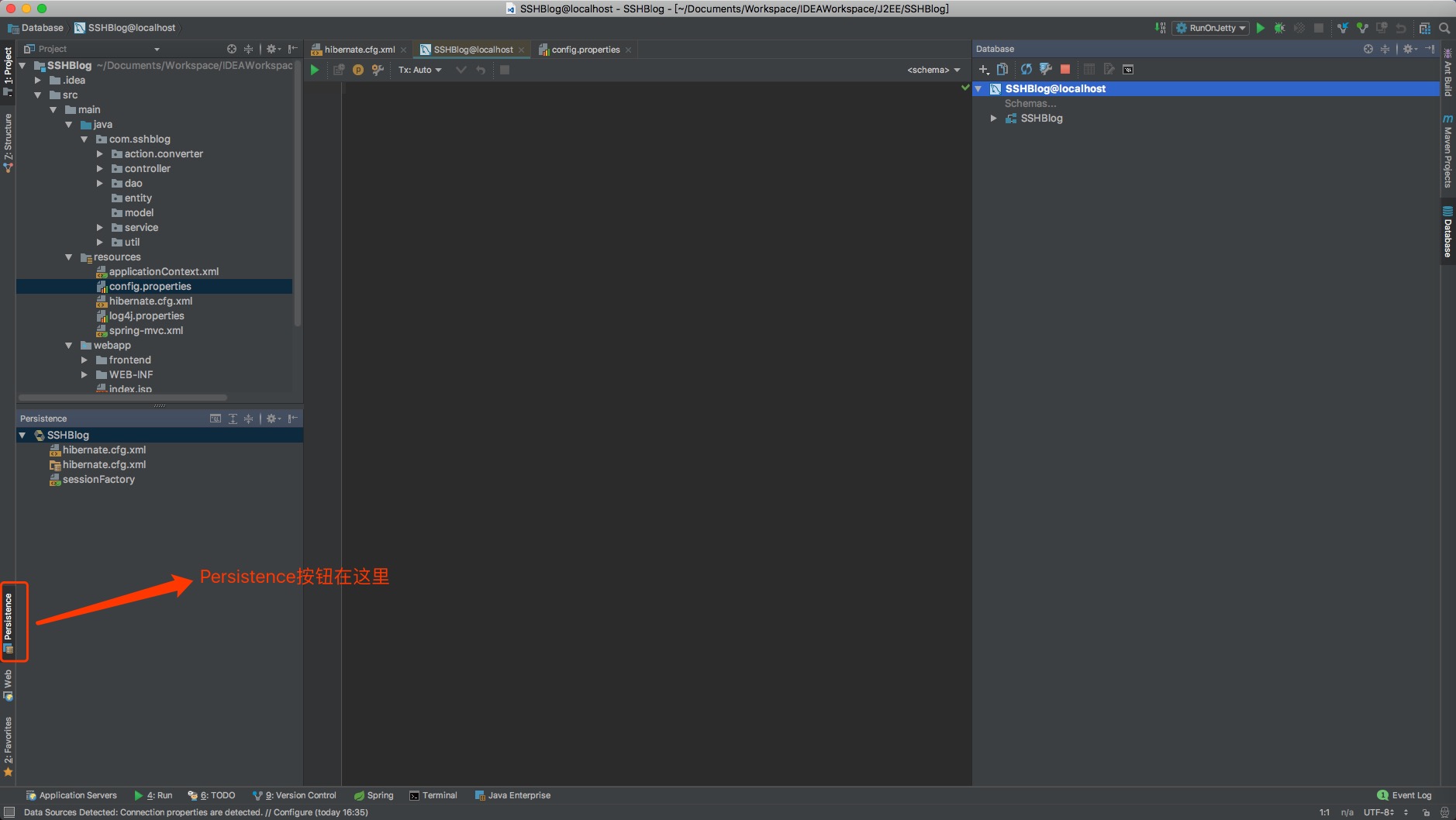
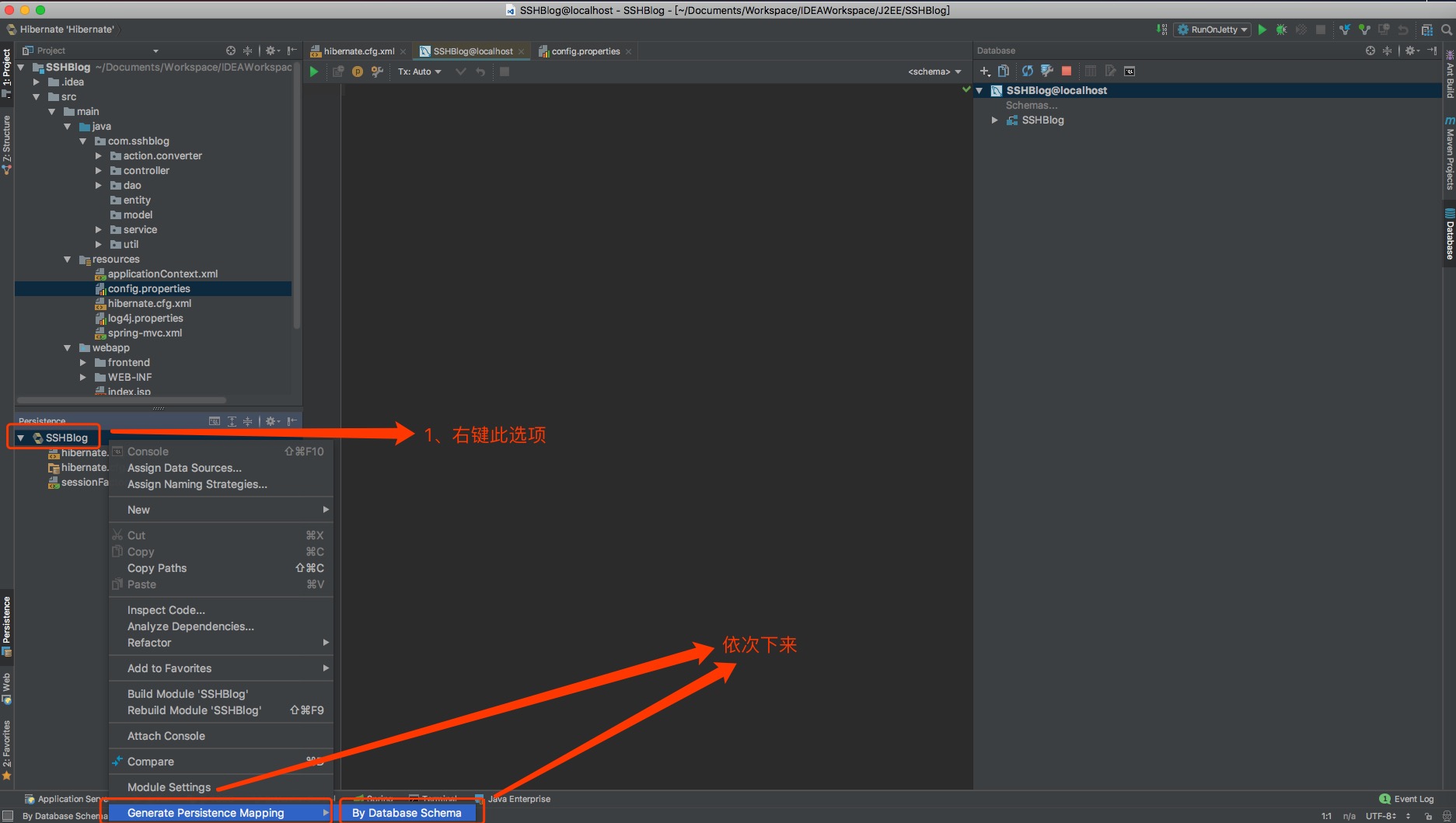
3.2、在Persistence中右键项目,然后点击Generate Persistence Mapping,选择By Database Schema;
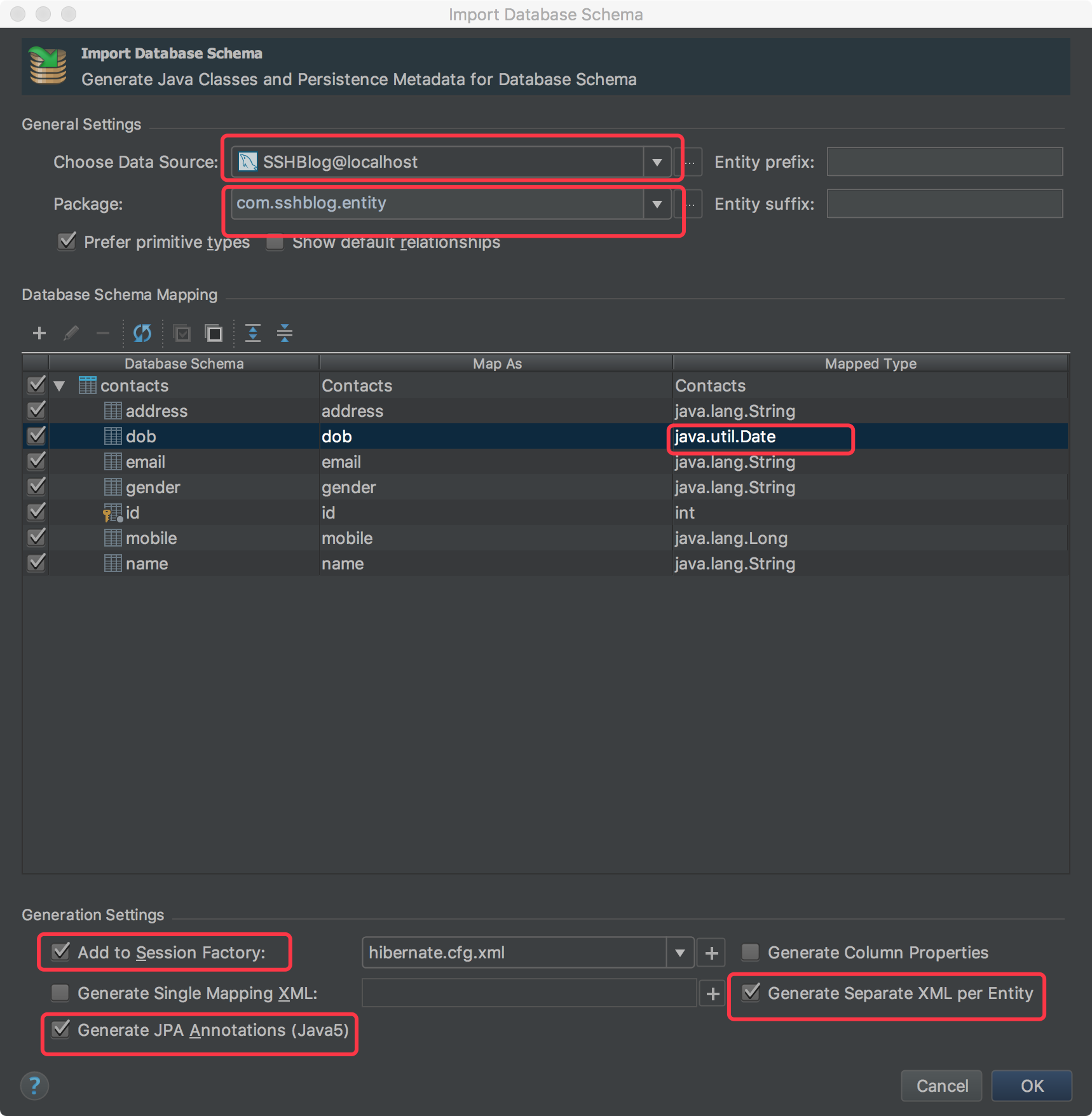
3.3、选择数据源,配置实体类包,选择要生成的实体类(其中日期类型的只能手动修改为java.util.Date),然后点击OK;
3.4、等待一段时间之后,发现项目中的实体类以及配置文件已经自动生成。
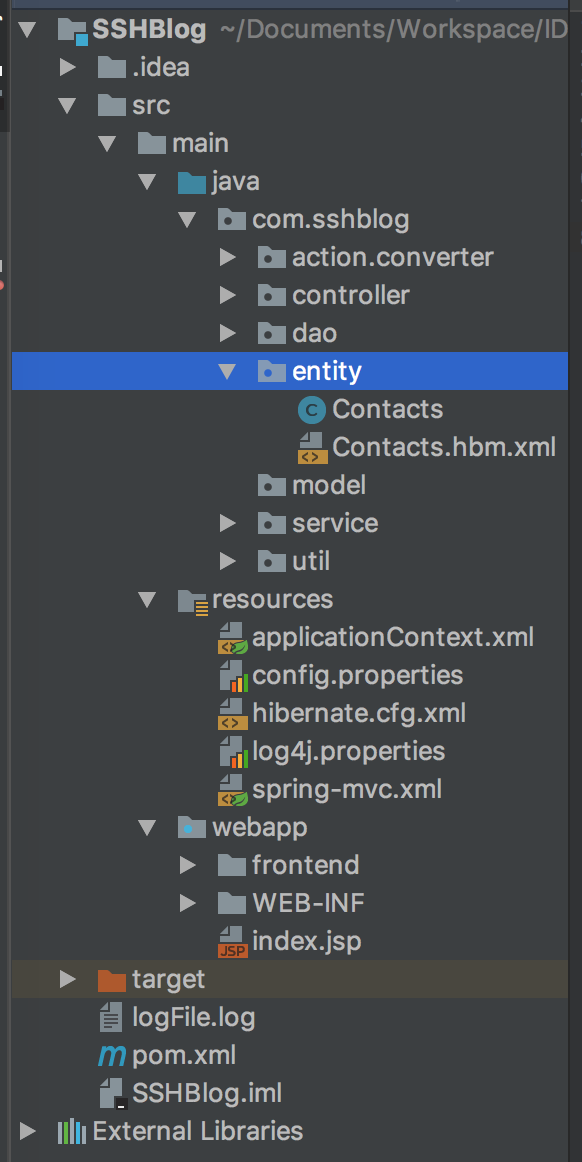
3.5、生成的实体类以及配置文件如下所示; 实体类:Contacts.java
- package com.sshblog.entity;
- import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
- import javax.persistence.*;
- import java.util.Date;
- @Entity
- @Table(name = "contacts")
- @JsonIgnoreProperties(value = {"hibernateLazyInitializer","handler","operations","roles","menus"})
- public class Contacts {
- private int id;
- private String name;
- private String address;
- private String gender;
- private Date dob;
- private String email;
- private Long mobile;
- @Id
- @Column(name = "id")
- public int getId() {
- return id;
- }
- public void setId(int id)< 20000 /span> {
- this.id = id;
- }
- @Basic
- @Column(name = "name")
- public String getName() {
- return name;
- }
- public void setName(String name) {
- this.name = name;
- }
- @Basic
- @Column(name = "address")
- public String getAddress() {
- return address;
- }
- public void setAddress(String address) {
- this.address = address;
- }
- @Basic
- @Column(name = "gender")
- public String getGender() {
- return gender;
- }
- public void setGender(String gender) {
- this.gender = gender;
- }
- @Basic
- @Column(name = "dob")
- public Date getDob() {
- return dob;
- }
- public void setDob(Date dob) {
- this.dob = dob;
- }
- @Basic
- @Column(name = "email")
- public String getEmail() {
- return email;
- }
- public void setEmail(String email) {
- this.email = email;
- }
- @Basic
- @Column(name = "mobile")
- public Long getMobile() {
- return mobile;
- }
- public void setMobile(Long mobile) {
- this.mobile = mobile;
- }
- @Override
- public boolean equals(Object o) {
- if (this == o) return true;
- if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
- Contacts contacts = (Contacts) o;
- if (id != contacts.id) return false;
- if (name != null ? !name.equals(contacts.name) : contacts.name != null) return false;
- if (address != null ? !address.equals(contacts.address) : contacts.address != null) return false;
- if (gender != null ? !gender.equals(contacts.gender) : contacts.gender != null) return false;
- if (dob != null ? !dob.equals(contacts.dob) : contacts.dob != null) return false;
- if (email != null ? !email.equals(contacts.email) : contacts.email != null) return false;
- if (mobile != null ? !mobile.equals(contacts.mobile) : contacts.mobile != null) return false;
- return true;
- }
- @Override
- public int hashCode() {
- int result = id;
- result = 31 * result + (name != null ? name.hashCode() : 0);
- result = 31 * result + (address != null ? address.hashCode() : 0);
- result = 31 * result + (gender != null ? gender.hashCode() : 0);
- result = 31 * result + (dob != null ? dob.hashCode() : 0);
- result = 31 * result + (email != null ? email.hashCode() : 0);
- result = 31 * result + (mobile != null ? mobile.hashCode() : 0);
- return result;
- }
- }
- <?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
- <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC
- "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN"
- "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
- <hibernate-mapping>
- <class name="com.sshblog.entity.Contacts" table="contacts" schema="SSHBlog">
- <id name="id" column="id"/>
- <property name="name" column="name"/>
- <property name="address" column="address"/>
- <property name="gender" column="gender"/>
- <property name="dob" column="dob"/>
- <property name="email" column="email"/>
- <property name="mobile" column="mobile"/>
- </class>
- </hibernate-mapping>
4、使用IntelliJ IDEA生成实体类的好处
使用IntelliJ IDEA的Hibernate生成实体类的好处是方便编码,提升编码效率; 相比较Eclipse而言,IntelliJ IDEA自带Hibernate生成的机制,而Eclipse则需要下载插件。相关文章推荐
- IntelliJ IDEA下自动生成Hibernate映射文件以及实体类
- Mybatis自动生成实体类,映射文件,以及dao层接口。
- 用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- 神奇的Hibernate,表没有 主键,对应的映射文件就自动给我生成多了个实体类
- mybatis如何自动生成实体类,映射文件以及对应的dao层
- 使用Mybatis生成工具自动生成实体类和对应的mapper映射文件以及接口文件
- Myeclipse自动生成Hibernate配置文件及实体类映射ORM
- hibernate自动生成实体类和映射文件
- JPA项目使用myeclipse创建带注解的model实体类&web工程使用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- 用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- 用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- 用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- hibernate自动生成映射文件和java实体类出现的问题
- 用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- 用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- 用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- mybatis逆向工程自动生成实体类、接口以及映射Mapper.xml配置文件
- 用MyEclipse自动生成hibernate映射文件和实体类
- 关于MyEclipse中Hibernate实现数据库和到工程文件实体类的映射,自动生成POJO
- Hibernate单独使用 (二)表操作深入、主键、自动生成映射文件
