TensorFlow(2) 非线性回归(一个隐藏层)
2018-04-24 14:57
85 查看
非线性回归
#使用numpy生成200个随机点
#np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,200)#表示在-0.5到0.5之间生成200个随机点,均匀分布
#np.newaxis:将原本[0,1,2,3]排列的矩阵转置为
[1,
2,
3]这样的排列
x_data=np.linspace(-0.5,0.5,200)[:,np.newaxis] #表示生成200行一列的数据
#生成一些干扰项,和x_data形状一致
noise=np.random.normal(0,0.02,x_data.shape)
y_data=np.square(x_data)+noise
#定义两个占位符placeholder
x=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])#[None,1]表示形状,随机行,1列
y=tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,1])
#定义神经网络的中间层
Weights_L1=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([1,10]))#连接输入层和中间层的神经元。输入层是一个神经元,中间层有10个神经元
biaes_L1=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,10]))#偏执值全部初始化为0 ,也是1个输入神经元和10个中间神经元
Wx_plus_b_L1=tf.matmul(x,Weights_L1)+biaes_L1#tf.matmul(x,Weights_L1)表示一个矩阵的乘法
L1=tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L1)#中间层输出,双曲正切函数作为激活函数
#定义神经网络输出层
Weights_L2=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([10,1]))
biaes_L2=tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1,1]))#表示只有一个输出层
Wx_plus_b_L2=tf.matmul(L1,Weights_L2)+biaes_L2
prediction=tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L2)
#二次代价函数
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-prediction))
#使用梯度下降法训练
train_step=tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
with tf.Session() as sess:
#变量的初始化
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
#训练
for _ in range(2000):
#训练通过feed_dict()传值
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={x:x_data,y:y_data})
#获得预测值
prediction_value=sess.run(prediction,feed_dict={x:x_data})
#画图
plt.figure()
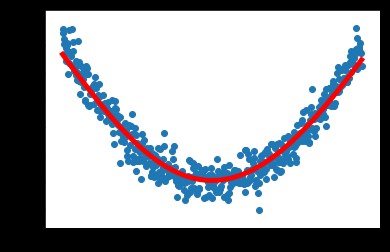
plt.scatter(x_data,y_data) #x_data,y_data的散点图
plt.plot(x_data,prediction_value,'r-',lw=5)#红色实线
plt.show()结果图:
阅读更多
相关文章推荐
- Tensorflow 入门学习3 Hello TensorFlow 建立一个隐藏层的神经网络实现回归分析
- 使用TensorFlow定义拥有一个隐藏层的神经网络
- 使用TensorFlow定义拥有一个隐藏层的神经网络
- 一个很好玩的jquery例子:小方块先逐渐显示,后向右滑动,再向左滑回,最后向上隐藏
- 一个较优雅的GridView隐藏列取值解决方案 (转)
- PHP开发小技巧①⑧—将一个字符串部分字符用*替代隐藏
- 判断一个窗口是显示还是隐藏
- 多卡服务器下隐藏部分 GPU 和 TensorFlow 的显存使用设置
- Tensorflow的一个简单实例,线性回归
- Flex如何真正隐藏一个组件
- Lua5.1.1的一个隐藏BUG
- 如何把.rar文件隐藏在一个图片内
- Tensorflow实现一个简单的二分类问题
- 如何在内核层隐藏一个文件
- React Native:自定义一个导航栏,改变状态栏背景,隐藏状态栏
- 一个综合运用各种组件的tensorflow程序
- Replica Set配置一个隐藏的副本集成员
- Replica Set配置一个隐藏的副本集成员
- 利用tensorflow 一步一步实现一个简单神经网络,线性回归
- 任何一台装XP的电脑都隐藏着一个巨大的秘密,你绝对不知道
