Python爬虫之Requests库1
2018-04-02 00:35
309 查看
Requests库1:入门
Requests库1入门1Requests库的下载安装
2值得参考的Requests官方文档
3Requests安装小测
本系列是为了复习以前学过的Python爬虫的知识,并且打算更加深入爬虫领域。
参考资料:
以前学过的北京理工大学嵩天老师在中国大学MOOC开设的教程的《python网络爬虫与信息提取》;
由O’REILLY社区,Ryan Mitchell出版的《Python网络数据采集》,这也是一本好书。
1、Requests库的下载安装
Win平台在cmd命令台运行pip install requests即可。
2、值得参考的Requests官方文档
随着这些天来的学习,我越发觉得学习编程的过程中不时参考一下官方文档是十分重要的,它能让我们发现新函数、新命令,全面了解库的各种模块和类,知道库中模块的官方用法,而这些都是听别人讲课、看视频所不能达到的。前提是你的英语还可以,不用太好,关键是要有看英语的耐心。这里我不想批判中国几十年来最失败的集体教育实验——英语教育,但事实就是如此,我们往往很少和外国人直接交往,因而听说的需求较少,但是读英语书、看英文文档的需求很高,而且是刚需。十几年的英语教育既没有让人全面掌握英语,也没有满足我们的刚需,只引发了很多人对英语的厌烦。但是,这里最需要的就是耐心了。
好了,闲话少提,看一下文档中对Requests库的描述:
Requests is an elegant and simple HTTP library for Python, built for human beings. You are currently looking at the documentation of the development release.
是哒,Requests就是一个优雅而使用简洁的库,随着使用我们会了解到它的好用之处。
这里是它的英文文档,也有中文版文档。当然,我们可以先看中文的,知道意思后再看英文的,以了解一些专业词汇,积累一点基础。
或者,我们可以在cmd命令行中输入
pydoc requests或
python -m pydoc requests查看一下文档字符串。结果发现只有一点用法介绍,其它的大部分都是关于该库的信息:
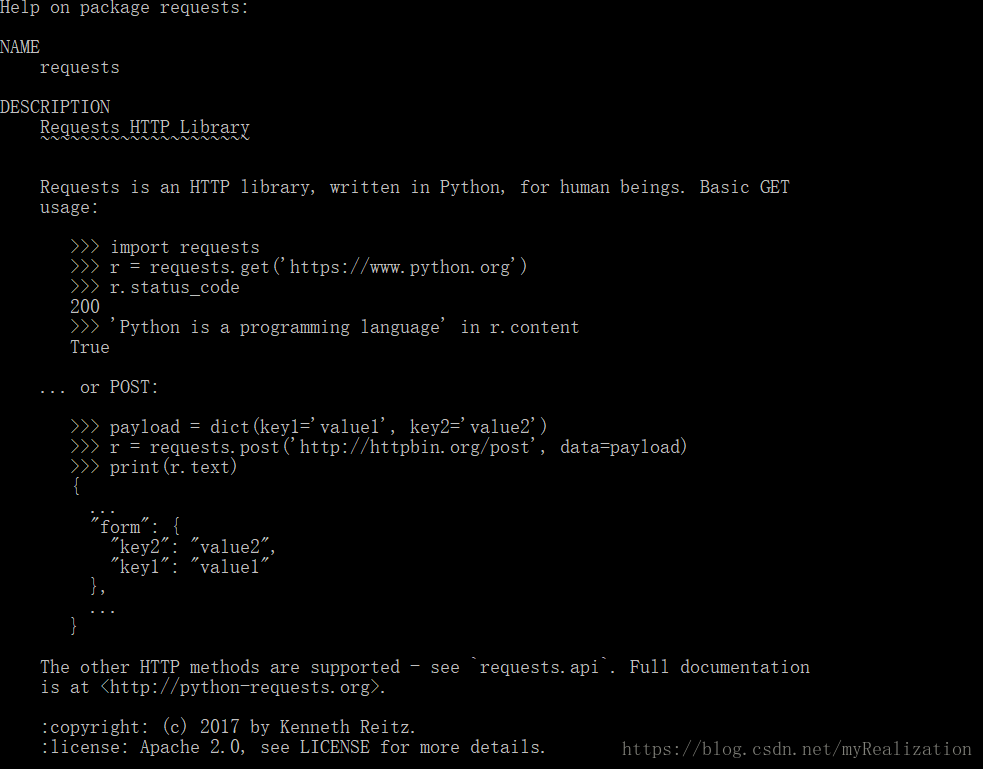
于是,我们还可以在Python交互式模式中用
dir(requests)来全面查看该库中的类、函数和变量,结果如下(我分成了几段):
['ConnectTimeout', 'ConnectionError', 'DependencyWarning', 'FileModeWarning', 'HTTPError', 'NullHandler', 'PreparedRequest', 'ReadTimeout', 'Request', 'RequestException', 'RequestsDependencyWarning', 'Response', 'Session', 'Timeout', 'TooManyRedirects', 'URLRequired', '__author__', '__author_email__', '__build__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__cake__', '__copyright__', '__description__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__license__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__path__', '__spec__', '__title__', '__url__', '__version__', '_internal_utils', 'adapters', 'api', 'auth', 'certs', 'chardet', 'check_compatibility', 'codes', 'compat', 'cookies', 'delete', 'exceptions', 'get', 'head', 'hooks', 'logging', 'models', 'options', 'packages', 'patch', 'post', 'put', 'pyopenssl', 'request', 'session', 'sessions', 'status_codes', 'structures', 'urllib3', 'utils', 'warnings']
这就是全部的Requests,接下来我们就可以用
help()查看想要详细了解的函数的参数和用法,如我输入了
help(requests.request),结果如下:
Help on function request in module requests.api:
request(method, url, **kwargs)
Constructs and sends a :class:`Request <Request>`.
:param method: method for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param url: URL for the new :class:`Request` object.
:param params: (optional) Dictionary or bytes to be sent in the query string for the :class:`Request`.
:param data: (optional) Dictionary or list of tuples ``[(key, value)]`` (will be form-encoded), bytes, or file-like object to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param json: (optional) json data to send in the body of the :class:`Request`.
:param headers: (optional) Dictionary of HTTP Headers to send with the :class:`Request`.
:param cookies: (optional) Dict or CookieJar object to send with the :class:`Request`.
:param files: (optional) Dictionary of ``'name': file-like-objects`` (o
c406
r ``{'name': file-tuple}``) for multipart encoding upload.
``file-tuple`` can be a 2-tuple ``('filename', fileobj)``, 3-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type')``
or a 4-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type', custom_headers)``, where ``'content-type'`` is a string
defining the content type of the given file and ``custom_headers`` a dict-like object containing additional headers
to add for the file.
:param auth: (optional) Auth tuple to enable Basic/Digest/Custom HTTP Auth.
:param timeout: (optional) How many seconds to wait for the server to send data
before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout, read
timeout) <timeouts>` tuple.
:type timeout: float or tuple
:param allow_redirects: (optional) Boolean. Enable/disable GET/OPTIONS/POST/PUT/PATCH/DELETE/HEAD redirection. Defaults to ``True``.
:type allow_redirects: bool
:param proxies: (optional) Dictionary mapping protocol to the URL of the proxy.
:param verify: (optional) Either a boolean, in which case it controls whether we verify
the server's TLS certificate, or a string, in which case it must be a path
to a CA bundle to use. Defaults to ``True``.
:param stream: (optional) if ``False``, the response content will be immediately downloaded.
:param cert: (optional) if String, path to ssl client cert file (.pem). If Tuple, ('cert', 'key') pair.
:return: :class:`Response <Response>` object
:rtype: requests.Response
Usage::
>>> import requests
>>> req = requests.request('GET', 'http://httpbin.org/get')
<Response [200]>看吧,多全面。函数调用方法、具体参数详解、实例示范、返回类型……这不就是绝佳的老师吗?
接下来,我们还将继续用这种方法探索Requests库的全貌。
而上面的这个函数,也会是我们学习Requests的重重之重。
3、Requests安装小测
让我们测试一下,看看装好了没有,也看看它的功能如何。>>> import requests # 引入
>>> r = requests.get("http://www.baidu.com") # 爬取百度首页HTML文档
>>> r.status_code # 返回状态码,200表示正常
200
>>> r.encoding
'ISO-8859-1'
>>> r.headers
{'Server': 'bfe/1.0.8.18', 'Date': 'Wed, 14 Feb 2018 02:57:26 GMT', 'Content-Type': 'text/html', 'Last-Modified': 'Mon, 23 Jan 2017 13:27:56 GMT', 'Transfer-Encoding': 'chunked', 'Connection': 'Keep-Alive', 'Cache-Control': 'private, no-cache, no-store, proxy-revalidate, no-transform', 'Pragma': 'no-cache', 'Set-Cookie': 'BDORZ=27315; max-age=86400; domain=.baidu.com; path=/', 'Content-Encoding': 'gzip'}其他的暂时不用管,看到200就知道成了。
另外的就是接下来的事了。
相关文章推荐
- python3 [爬虫实战] selenium + requests 爬取安居客
- Python爬虫(2):Requests的基本用法
- 【极客学院】-python学习笔记-3-单线程爬虫 (request安装遇到问题及解决,应用requests提取信息)
- Python Requests爬虫——获取一个收藏夹下所有答案的图片
- Python爬虫工具之Requests
- Python爬虫—3第三方库_1_requests_进阶
- Python爬虫之使用Fiddler+Postman+Python的requests模块爬取各国国旗
- Python爬虫(3):Requests的高级用法
- python学习(6):python爬虫之requests和BeautifulSoup的使用
- Python - 通过requests实现腾讯新闻抓取爬虫
- Python爬虫(使用requests)
- python爬虫系列(2)—— requests和BeautifulSoup库的基本用法
- python 爬虫 之如何入门 Requests 提供了很好的指南【三】
- Python爬虫——4.4爬虫案例——requests和xpath爬取招聘网站信息
- Python爬虫大杀器之Requests快速入门
- python3爬虫初探(二)之requests
- python爬虫入门之requests
- python爬虫︱百度百科的requests请求、百度URL格式、网页保存、爬虫模块
- Python爬虫学习纪要(十):Requests 库学习笔记5
- Python爬虫(入门+进阶)学习笔记 1-3 使用Requests爬取豆瓣短评
