Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)(A、B、C)
2018-02-03 11:26
645 查看
地址:点击打开链接
A. Water The Garden
It is winter now, and Max decided it's about time he watered the garden.
The garden can be represented as n consecutive garden beds, numbered from 1 to n. k beds
contain water taps (i-th tap is located in the bed xi),
which, if turned on, start delivering water to neighbouring beds. If the tap on the bed xi is
turned on, then after one second has passed, the bed xi will
be watered; after two seconds have passed, the beds from the segment [xi - 1, xi + 1] will
be watered (if they exist); after j seconds have passed (j is
an integer number), the beds from the segment [xi - (j - 1), xi + (j - 1)] will
be watered (if they exist). Nothing changes during the seconds, so, for example, we can't say that the segment [xi - 2.5, xi + 2.5] will
be watered after 2.5seconds have passed; only the segment [xi - 2, xi + 2] will
be watered at that moment.

The
garden from test 1. White colour denotes a garden bed without a tap, red colour — a garden bed with a tap.

The
garden from test 1 after 2 seconds
have passed after turning on the tap. White colour denotes an unwatered garden bed, blue colour — a watered bed.
Max wants to turn on all the water taps at the same moment, and now he wonders, what is the minimum number of seconds that have to pass after he turns on some taps until the whole garden is watered.
Help him to find the answer!
Input
The first line contains one integer t — the number of test cases to solve (1 ≤ t ≤ 200).
Then t test cases follow. The first line of each test case contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 200, 1 ≤ k ≤ n)
— the number of garden beds and water taps, respectively.
Next line contains k integers xi (1 ≤ xi ≤ n)
— the location of i-th water tap. It is guaranteed that for each
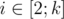
condition xi - 1 < xiholds.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases doesn't exceed 200.
Note that in hacks you have to set t = 1.
Output
For each test case print one integer — the minimum number of seconds that have to pass after Max turns on some of the water taps, until the whole garden is watered.
Example
input
output
Note
The first example consists of 3 tests:
There are 5 garden beds, and a water tap in the bed 3.
If we turn it on, then after 1 second passes, only bed 3 will
be watered; after 2seconds pass, beds [1, 3] will
be watered, and after 3 seconds pass, everything will be watered.
There are 3 garden beds, and there is a water tap in each one. If we turn all of them on, then everything will be watered after 1 second
passes.
There are 4 garden beds, and only one tap in the bed 1.
It will take 4 seconds to water, for example, bed 4.
题意:
有一排田地,有k个田地具有水管,且有水管的地的水向边两边进行蔓延,问最少多长时间能够浇完所有地?
思路:
模拟一遍,一遍一遍的从头开始走
代码:#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x7f7f7f7f
#define mod 1000000009
#define maxn 200 +100
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int b[maxn];//注意体会b
int l;
int main(){
int n,k;
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n>>k;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
cin>>l;
a[l]=1;
b[l]=1;
}
bool flag=false;
int ans=1;
while(true){
flag=false;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(b[i]==0) flag=true;
if(b[i]==1){
a[i-1]=1;
//b[i-1]=1;
a[i+1]=1;
//b[i+1]=1;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
b[i]=a[i];
}
if(!flag) break;
ans++;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}B.
Tea Queue
Recently n students from city S moved to city P to attend a programming camp.
They moved there by train. In the evening, all students in the train decided that they want to drink some tea. Of course, no two people can use the same teapot simultaneously, so the students had to form a queue to get their tea.
i-th student comes to the end of the queue at the beginning of li-th
second. If there are multiple students coming to the queue in the same moment, then the student with greater index comes after the student with lesser index. Students in the queue behave as follows: if there is nobody in the queue before the student, then
he uses the teapot for exactly one second and leaves the queue with his tea; otherwise the student waits for the people before him to get their tea. If at the beginning of ri-th
second student i still cannot get his tea (there is someone before him in the queue), then he leaves the queue without
getting any tea.
For each student determine the second he will use the teapot and get his tea (if he actually gets it).
Input
The first line contains one integer t — the number of test cases to solve (1 ≤ t ≤ 1000).
Then t test cases follow. The first line of each test case contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000)
— the number of students.
Then n lines follow. Each line contains two integer li, ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 5000)
— the second i-th student comes to the end of the queue, and the second he leaves the queue if he still cannot get his
tea.
It is guaranteed that for every
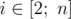
condition li - 1 ≤ li holds.
The sum of n over all test cases doesn't exceed 1000.
Note that in hacks you have to set t = 1.
Output
For each test case print n integers. i-th
of them must be equal to the second when i-th student gets his tea, or 0 if
he leaves without tea.
Example
input
output
Note
The example contains 2 tests:
During 1-st second, students 1 and 2 come
to the queue, and student 1 gets his tea. Student 2 gets
his tea during 2-nd second.
During 1-st second, students 1 and 2 come
to the queue, student 1 gets his tea, and student 2 leaves
without tea. During 2-nd second, student 3 comes
and gets his tea.
题意:有n个人想要喝茶,每个人都有离开的时间和到达的时间,要求输出每个人喝到茶的时间,若没有喝茶,则输出0。
思路:注意记录一下上一个人喝茶的时间,然后再和上一个人的时间进行比较即可,大致分为三种情况,详见代码:#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x7f7f7f7f
#define mod 1000000009
#define maxn 2000+100
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int l[maxn],r[maxn];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
scanf("%d",&n);
int cur=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&l[i],&r[i]);}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(l[i]>=cur){
a[i]=l[i];
cur=l[i]+1;
}
else if(r[i]<cur){
a[i]=0;
continue;
}
else {
a[i]=cur;
cur+=1;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(i==1) printf("%d",a[i]);
else printf(" %d",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}C.
Swap Adjacent Elements
You have an array a consisting of n integers.
Each integer from 1 to n appears
exactly once in this array.
For some indices i (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1)
it is possible to swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th,
for other indices it is not possible. You may perform any number of swapping operations any order. There is no limit on the number of times you swap i-th
element with (i + 1)-th (if the position is not forbidden).
Can you make this array sorted in ascending order performing some sequence of swapping operations?
Input
The first line contains one integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 200000)
— the number of elements in the array.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2,
..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 200000)
— the elements of the array. Each integer from 1 to n appears
exactly once.
The third line contains a string of n - 1 characters, each character is either 0 or 1.
If i-th character is 1,
then you can swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th
any number of times, otherwise it is forbidden to swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th.
Output
If it is possible to sort the array in ascending order using any sequence of swaps you are allowed to make, print YES. Otherwise, print NO.
Examples
input
output
input
output
Note
In the first example you may swap a3 and a4,
and then swap a4 and a5.
题意:
有n个数1-n,前n-1个数被0或则1标记,若为1那么可以与前1个数字进行交换,问能否序列上升?
思路:
只有当某个数到他的位置之间数全部为1才可以,否则就会中断
代码:#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x7f7f7f7f
#define mod 1000000009
#define maxn 200000+100
using namespace std;
int n,m,tt,b[200005],vis[200005],x,y,sum[200005];
struct Node
{
int x,id;
}a[200005];
bool cmp(Node a,Node b)
{
return a.x<b.x;
}
bool cmp2(Node a,Node b)
{
return a.id<b.id;
}
string s;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i].x);
a[i].id=i;
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
a[i].x=i;
vis[i]=a[i].id;
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp2);
cin>>s;
sum[0]=s[0]-'0';
for(int i=1;i<s.size();i++){
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+s[i]-'0';
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(a[i].x!=i) {
if(sum[vis[i]-2]-sum[i-2]<vis[i]-i){ //-1是因为从0开始,再减1是因为判断其前一个,而不是判断当前位置
printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
printf("YES\n");
return 0;
}
A. Water The Garden
It is winter now, and Max decided it's about time he watered the garden.
The garden can be represented as n consecutive garden beds, numbered from 1 to n. k beds
contain water taps (i-th tap is located in the bed xi),
which, if turned on, start delivering water to neighbouring beds. If the tap on the bed xi is
turned on, then after one second has passed, the bed xi will
be watered; after two seconds have passed, the beds from the segment [xi - 1, xi + 1] will
be watered (if they exist); after j seconds have passed (j is
an integer number), the beds from the segment [xi - (j - 1), xi + (j - 1)] will
be watered (if they exist). Nothing changes during the seconds, so, for example, we can't say that the segment [xi - 2.5, xi + 2.5] will
be watered after 2.5seconds have passed; only the segment [xi - 2, xi + 2] will
be watered at that moment.

The
garden from test 1. White colour denotes a garden bed without a tap, red colour — a garden bed with a tap.

The
garden from test 1 after 2 seconds
have passed after turning on the tap. White colour denotes an unwatered garden bed, blue colour — a watered bed.
Max wants to turn on all the water taps at the same moment, and now he wonders, what is the minimum number of seconds that have to pass after he turns on some taps until the whole garden is watered.
Help him to find the answer!
Input
The first line contains one integer t — the number of test cases to solve (1 ≤ t ≤ 200).
Then t test cases follow. The first line of each test case contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n ≤ 200, 1 ≤ k ≤ n)
— the number of garden beds and water taps, respectively.
Next line contains k integers xi (1 ≤ xi ≤ n)
— the location of i-th water tap. It is guaranteed that for each
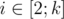
condition xi - 1 < xiholds.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n over all test cases doesn't exceed 200.
Note that in hacks you have to set t = 1.
Output
For each test case print one integer — the minimum number of seconds that have to pass after Max turns on some of the water taps, until the whole garden is watered.
Example
input
3 5 1 3 3 3 1 2 3 4 1 1
output
3 1 4
Note
The first example consists of 3 tests:
There are 5 garden beds, and a water tap in the bed 3.
If we turn it on, then after 1 second passes, only bed 3 will
be watered; after 2seconds pass, beds [1, 3] will
be watered, and after 3 seconds pass, everything will be watered.
There are 3 garden beds, and there is a water tap in each one. If we turn all of them on, then everything will be watered after 1 second
passes.
There are 4 garden beds, and only one tap in the bed 1.
It will take 4 seconds to water, for example, bed 4.
题意:
有一排田地,有k个田地具有水管,且有水管的地的水向边两边进行蔓延,问最少多长时间能够浇完所有地?
思路:
模拟一遍,一遍一遍的从头开始走
代码:#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x7f7f7f7f
#define mod 1000000009
#define maxn 200 +100
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int b[maxn];//注意体会b
int l;
int main(){
int n,k;
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
cin>>n>>k;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
cin>>l;
a[l]=1;
b[l]=1;
}
bool flag=false;
int ans=1;
while(true){
flag=false;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(b[i]==0) flag=true;
if(b[i]==1){
a[i-1]=1;
//b[i-1]=1;
a[i+1]=1;
//b[i+1]=1;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
b[i]=a[i];
}
if(!flag) break;
ans++;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}B.
Tea Queue
Recently n students from city S moved to city P to attend a programming camp.
They moved there by train. In the evening, all students in the train decided that they want to drink some tea. Of course, no two people can use the same teapot simultaneously, so the students had to form a queue to get their tea.
i-th student comes to the end of the queue at the beginning of li-th
second. If there are multiple students coming to the queue in the same moment, then the student with greater index comes after the student with lesser index. Students in the queue behave as follows: if there is nobody in the queue before the student, then
he uses the teapot for exactly one second and leaves the queue with his tea; otherwise the student waits for the people before him to get their tea. If at the beginning of ri-th
second student i still cannot get his tea (there is someone before him in the queue), then he leaves the queue without
getting any tea.
For each student determine the second he will use the teapot and get his tea (if he actually gets it).
Input
The first line contains one integer t — the number of test cases to solve (1 ≤ t ≤ 1000).
Then t test cases follow. The first line of each test case contains one integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000)
— the number of students.
Then n lines follow. Each line contains two integer li, ri (1 ≤ li ≤ ri ≤ 5000)
— the second i-th student comes to the end of the queue, and the second he leaves the queue if he still cannot get his
tea.
It is guaranteed that for every
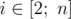
condition li - 1 ≤ li holds.
The sum of n over all test cases doesn't exceed 1000.
Note that in hacks you have to set t = 1.
Output
For each test case print n integers. i-th
of them must be equal to the second when i-th student gets his tea, or 0 if
he leaves without tea.
Example
input
2 2 1 3 1 4 3 1 5 1 1 2 3
output
1 2 1 0 2
Note
The example contains 2 tests:
During 1-st second, students 1 and 2 come
to the queue, and student 1 gets his tea. Student 2 gets
his tea during 2-nd second.
During 1-st second, students 1 and 2 come
to the queue, student 1 gets his tea, and student 2 leaves
without tea. During 2-nd second, student 3 comes
and gets his tea.
题意:有n个人想要喝茶,每个人都有离开的时间和到达的时间,要求输出每个人喝到茶的时间,若没有喝茶,则输出0。
思路:注意记录一下上一个人喝茶的时间,然后再和上一个人的时间进行比较即可,大致分为三种情况,详见代码:#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x7f7f7f7f
#define mod 1000000009
#define maxn 2000+100
using namespace std;
int a[maxn];
int l[maxn],r[maxn];
int main(){
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--){
int n;
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
scanf("%d",&n);
int cur=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&l[i],&r[i]);}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(l[i]>=cur){
a[i]=l[i];
cur=l[i]+1;
}
else if(r[i]<cur){
a[i]=0;
continue;
}
else {
a[i]=cur;
cur+=1;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(i==1) printf("%d",a[i]);
else printf(" %d",a[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}C.
Swap Adjacent Elements
You have an array a consisting of n integers.
Each integer from 1 to n appears
exactly once in this array.
For some indices i (1 ≤ i ≤ n - 1)
it is possible to swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th,
for other indices it is not possible. You may perform any number of swapping operations any order. There is no limit on the number of times you swap i-th
element with (i + 1)-th (if the position is not forbidden).
Can you make this array sorted in ascending order performing some sequence of swapping operations?
Input
The first line contains one integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 200000)
— the number of elements in the array.
The second line contains n integers a1, a2,
..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 200000)
— the elements of the array. Each integer from 1 to n appears
exactly once.
The third line contains a string of n - 1 characters, each character is either 0 or 1.
If i-th character is 1,
then you can swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th
any number of times, otherwise it is forbidden to swap i-th element with (i + 1)-th.
Output
If it is possible to sort the array in ascending order using any sequence of swaps you are allowed to make, print YES. Otherwise, print NO.
Examples
input
6 1 2 5 3 4 6 01110
output
YES
input
6 1 2 5 3 4 6 01010
output
NO
Note
In the first example you may swap a3 and a4,
and then swap a4 and a5.
题意:
有n个数1-n,前n-1个数被0或则1标记,若为1那么可以与前1个数字进行交换,问能否序列上升?
思路:
只有当某个数到他的位置之间数全部为1才可以,否则就会中断
代码:#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#define ll long long
#define inf 0x7f7f7f7f
#define mod 1000000009
#define maxn 200000+100
using namespace std;
int n,m,tt,b[200005],vis[200005],x,y,sum[200005];
struct Node
{
int x,id;
}a[200005];
bool cmp(Node a,Node b)
{
return a.x<b.x;
}
bool cmp2(Node a,Node b)
{
return a.id<b.id;
}
string s;
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i].x);
a[i].id=i;
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
a[i].x=i;
vis[i]=a[i].id;
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1,cmp2);
cin>>s;
sum[0]=s[0]-'0';
for(int i=1;i<s.size();i++){
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+s[i]-'0';
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(a[i].x!=i) {
if(sum[vis[i]-2]-sum[i-2]<vis[i]-i){ //-1是因为从0开始,再减1是因为判断其前一个,而不是判断当前位置
printf("NO\n");
return 0;
}
}
}
printf("YES\n");
return 0;
}
相关文章推荐
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Connected Components?(连通分量的个数,STL)
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) 【F】【线段树】
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)【A B C】【水】【模拟】
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) F. SUM and REPLACE(线段树,区间更新)
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)-F-SUM and REPLACE(线段树)
- [Codeforces]Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)
- Wannafly挑战赛9+Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) 920E E. Connected Components?
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) C. Swap Adjacent Elements
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) E. Congruence Equation
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)F. SUM and REPLACE
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2) F. SUM and REPLACE(线段树)
- Educational Codeforces Round 37 (Rated for Div. 2)-E-Connected Components?(模拟/暴力)
- Educational Codeforces Round 39 (Rated for Div. 2) codeforces946 A.Partition B.Weird Subtraction Process C.String Transformation
- Educational Codeforces Round 40 (Rated for Div. 2)
- Educational Codeforces Round 41 (Rated for Div. 2)
- Educational Codeforces Round 42 (Rated for Div. 2) D - Merge Equals
