经典算法 | 给定n个矩形,判断这些矩形是否在不重合的情况下组成一个大矩形的算法
2018-01-30 17:01
615 查看
GivenN axis-aligned rectangles where N > 0, determine if they all together forman exact cover of a rectangular region.
Eachrectangle is represented as a bottom-left point and a top-right point. Forexample, a unit square is represented as [1,1,2,2]. (coordinate of bottom-leftpoint is (1, 1) and top-right point is (2, 2)).
Example1:
rectangles = [
[1,1,3,3],
[3,1,4,2],
[3,2,4,4],
[1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,4]
]
Return true. All 5 rectangles together form an exact cover ofa rectangular region.
Example2:
rectangles = [
[1,1,2,3],
[1,3,2,4],
[3,1,4,2],
[3,2,4,4]
]
Return false. Because there is a gap between the tworectangular regions.
Example3:
rectangles = [
[1,1,3,3],
[3,1,4,2],
[1,3,2,4],
[3,2,4,4]
]
Return false. Because there is a gap in the top center.
Example4:
rectangles = [
[1,1,3,3],
[3,1,4,2],
[1,3,2,4],
[2,2,4,4]
]
Return false. Because two of the rectangles overlap with eachother.
这一题我也没想到会这么难,这一题要求你对于给定的所有矩形,判断其是否能在不相交的情况下组成一个大矩形。
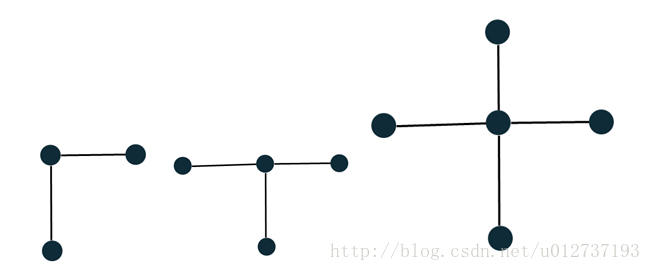
每个矩形的四个端点在大矩形中只有可能是以上三种情况的一种,
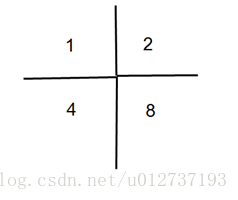
每个矩形有4个端点,并且每个端点在大矩形中有4个区域,当某个端点在这4个区域的某个区域覆盖了超过一个的时候,这个时候必有两个矩形重叠,
所有在大矩形四个端点的端点有且只有一个区域被覆盖,在大矩形四条边上的端点只能有两个区域被覆盖或者是无区域覆盖
在大矩形里面的端点只能有两个相邻区域覆盖或者是四个区域覆盖
对于输入的所有矩形,对其四个端点计算覆盖值,当所有矩形输入完毕之后,统计所有端点的覆盖值是否合法就能得到这种情况的合法性
这个技巧还能用来判断多个矩形组成的大矩形在小矩形两两覆盖合法的情况下是否有空腔的问题,但是不能用来判断多个矩形是否两两重叠
class Solution {
public:
bool setIn(int x, int y, int whatDrt, unordered_map<string, int> &mark)
{
unordered_map<string, int> ::iterator it;
string tmp;
if (x == 3 && y == 1)
int j_mark = 1;
tmp = to_string(x) + "," + to_string(y);
it = mark.find(tmp);
if (it == mark.end())
{
mark.insert(pair <string,int>(tmp, whatDrt));
}
else
{
int t = (*it).second;
if (((*it).second&whatDrt) != 0)
return false;
(*it).second ^= whatDrt;
}
return true;
}
bool putOn(unordered_map<string, int> &mark,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
{
if (!setIn(x1, y1, 2, mark)) return false;
if (!setIn(x1, y2, 8, mark)) return false;
if (!setIn(x2, y1, 1, mark)) return false;
if (!setIn(x2, y2, 4, mark)) return false;
return true;
}
bool isRectangleCover(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles) {
unordered_map <string, int> mark;
string tmp; int x1=INT_MAX, x2=0, y1= INT_MAX, y2=0,count=0;
for (int i = 0; i < rectangles.size(); i++)
{
x1 = min(x1, rectangles[i][0]);
y1 = min(y1, rectangles[i][1]);
x2 = max(x2, rectangles[i][2]);
y2 = max(y2, rectangles[i][3]);
if (!putOn(mark, rectangles[i][0], rectangles[i][1], rectangles[i][2], rectangles[i][3])) return false;
}
string tmp1 = to_string(x1) + ',' + to_string(y1);
string tmp2 = to_string(x1) + ',' + to_string(y2);
string tmp3 = to_string(x2) + ',' + to_string(y1);
string tmp4 = to_string(x2) + ',' + to_string(y2);
unordered_map<string, int> ::iterator it;
for (it = mark.begin(); it != mark.end(); it++)
{
if ((*it).first == tmp1 || (*it).first == tmp2 || (*it).first == tmp3 || (*it).first == tmp4) { count++; continue; }
string x = (*it).first;
if ((*it).second == 14 || (*it).second == 13 || (*it).second == 11 || (*it).second == 7 || (*it).second == 9 || (*it).second == 6) return false;
if ((*it).second == 1 || (*it).second == 2 || (*it).second == 4 || (*it).second == 8) return false;
}
if (count != 4) return false;
return true;
}
};
Eachrectangle is represented as a bottom-left point and a top-right point. Forexample, a unit square is represented as [1,1,2,2]. (coordinate of bottom-leftpoint is (1, 1) and top-right point is (2, 2)).
Example1:
rectangles = [
[1,1,3,3],
[3,1,4,2],
[3,2,4,4],
[1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,4]
]
Return true. All 5 rectangles together form an exact cover ofa rectangular region.
Example2:
rectangles = [
[1,1,2,3],
[1,3,2,4],
[3,1,4,2],
[3,2,4,4]
]
Return false. Because there is a gap between the tworectangular regions.
Example3:
rectangles = [
[1,1,3,3],
[3,1,4,2],
[1,3,2,4],
[3,2,4,4]
]
Return false. Because there is a gap in the top center.
Example4:
rectangles = [
[1,1,3,3],
[3,1,4,2],
[1,3,2,4],
[2,2,4,4]
]
Return false. Because two of the rectangles overlap with eachother.
这一题我也没想到会这么难,这一题要求你对于给定的所有矩形,判断其是否能在不相交的情况下组成一个大矩形。

每个矩形的四个端点在大矩形中只有可能是以上三种情况的一种,

每个矩形有4个端点,并且每个端点在大矩形中有4个区域,当某个端点在这4个区域的某个区域覆盖了超过一个的时候,这个时候必有两个矩形重叠,
所有在大矩形四个端点的端点有且只有一个区域被覆盖,在大矩形四条边上的端点只能有两个区域被覆盖或者是无区域覆盖
在大矩形里面的端点只能有两个相邻区域覆盖或者是四个区域覆盖
对于输入的所有矩形,对其四个端点计算覆盖值,当所有矩形输入完毕之后,统计所有端点的覆盖值是否合法就能得到这种情况的合法性
这个技巧还能用来判断多个矩形组成的大矩形在小矩形两两覆盖合法的情况下是否有空腔的问题,但是不能用来判断多个矩形是否两两重叠
class Solution {
public:
bool setIn(int x, int y, int whatDrt, unordered_map<string, int> &mark)
{
unordered_map<string, int> ::iterator it;
string tmp;
if (x == 3 && y == 1)
int j_mark = 1;
tmp = to_string(x) + "," + to_string(y);
it = mark.find(tmp);
if (it == mark.end())
{
mark.insert(pair <string,int>(tmp, whatDrt));
}
else
{
int t = (*it).second;
if (((*it).second&whatDrt) != 0)
return false;
(*it).second ^= whatDrt;
}
return true;
}
bool putOn(unordered_map<string, int> &mark,int x1,int y1,int x2,int y2)
{
if (!setIn(x1, y1, 2, mark)) return false;
if (!setIn(x1, y2, 8, mark)) return false;
if (!setIn(x2, y1, 1, mark)) return false;
if (!setIn(x2, y2, 4, mark)) return false;
return true;
}
bool isRectangleCover(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles) {
unordered_map <string, int> mark;
string tmp; int x1=INT_MAX, x2=0, y1= INT_MAX, y2=0,count=0;
for (int i = 0; i < rectangles.size(); i++)
{
x1 = min(x1, rectangles[i][0]);
y1 = min(y1, rectangles[i][1]);
x2 = max(x2, rectangles[i][2]);
y2 = max(y2, rectangles[i][3]);
if (!putOn(mark, rectangles[i][0], rectangles[i][1], rectangles[i][2], rectangles[i][3])) return false;
}
string tmp1 = to_string(x1) + ',' + to_string(y1);
string tmp2 = to_string(x1) + ',' + to_string(y2);
string tmp3 = to_string(x2) + ',' + to_string(y1);
string tmp4 = to_string(x2) + ',' + to_string(y2);
unordered_map<string, int> ::iterator it;
for (it = mark.begin(); it != mark.end(); it++)
{
if ((*it).first == tmp1 || (*it).first == tmp2 || (*it).first == tmp3 || (*it).first == tmp4) { count++; continue; }
string x = (*it).first;
if ((*it).second == 14 || (*it).second == 13 || (*it).second == 11 || (*it).second == 7 || (*it).second == 9 || (*it).second == 6) return false;
if ((*it).second == 1 || (*it).second == 2 || (*it).second == 4 || (*it).second == 8) return false;
}
if (count != 4) return false;
return true;
}
};
相关文章推荐
- 动态规划-请编写一个高效算法,判断C串是否由A和B交错组成。
- 面试题精选(76):给定BST先序遍历序列,不构造BST的情况下判断BST是否每个node都只有一个child
- 给定n个数,每个都可以使用无数次,用这些数的和 是否可以组成一个给定的数字
- 【算法】计算机图形学的一些经典小题:判断点在多边形内,随机生成三角形内的点,判断两个矩形是否相交等
- 描述一个运行时间为O(nlgn)的算法,使之能在给定一个由n个整数构成的集合S和另一个整数 X 时,判断出S中是否存在有两个其和刚好等于 X 的元素。
- 题目:请给出一个运行时间为Θ(nlgn)的算法,使之能在给定一个由n个整数构成的集合S和另一个整数x时,判断出S中是否存在有两个其和等于x的元素。
- 程序员面试金典——解题总结: 9.18高难度题 18.13给定一份几百万个单词的清单,设计一个算法,创建由字母组成的最大矩形
- 经典算法面试题目-判断一个字符串中的字符是否唯一(1.1)
- 给定一个由非负整数和整数m组成的数组,可以将该数组分成m个非空的连续子数组。 写一个算法来最小化这些m个子阵列之间的最大和。
- 题目1.请给出一个运行时间为O(nlgn)的算法,使之能在给定一个由n个整数构成的集合S和另一个证书x时,判断出S中是否存在有两个其和等于x的元素。
- 给定BST先序遍历序列,不构造BST的情况下判断BST是否每个node都只有一个child
- 经典算法面试题目-判断一个字符串中的字符是否唯一(1.1)
- 已知一个矩阵 A(m*n) 的元素每行每列都按从小到大有序, 试设计一个算法判断任一给定值 k 是否在矩阵 A(m*n) 中
- 给定四条线段判断是否可以构成一个矩形
- 算法学习----给定入栈的顺序,判断另一个顺序是否为该入栈顺序的一个弹出顺序
- 判断一个点是否在矩形内PtInRegion-解决PtInRect不能正确判断不同形式TRent的情况
- 经典算法之判断一个整数是否为素数
- 设计一个算法,判断给定的一棵二叉树是否是二叉排序树(二叉树的所有关键字均为正整数)
- 算法:如何判断平面上的四个点是不是组成一个矩形
- 每天一道算法题(一):给定一个整数,判断这个数是否是回文
