Java ArrayList源码分析
2018-01-14 12:14
375 查看
ArrayList概述
ArrayList是List接口最常用的实现类,底层由数组实现,可存入null值,每个ArrayList都有一个容量(capacity)属性,初始值是10,表示底层数组的存储空间,容器内当前元素个数大于数组存储容量时,ArrayList会自动完成容量扩增,因此我们在向ArrayList中添加元素时无需考虑容量,容器内部已经帮我们完成了容量扩容过程。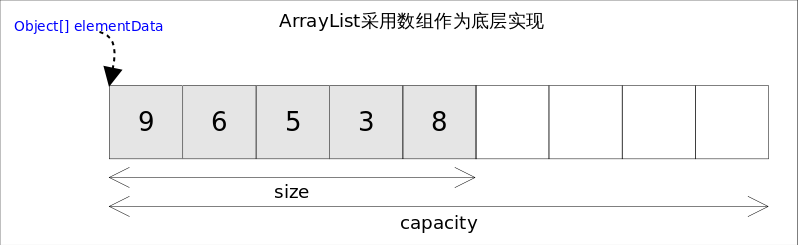
ArrayList具有public ArrayList() ;public ArrayList(int initialCapacity);public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)三个构造器,创建ArrayList时可以指定容量或选择用其他Collection为当前ArrayList赋值(底层采用数组复制的方式实现)或采用无参构造器创建默认容量的数组,size小于当前元素个数时,将自动完成容量扩充。
常用方法剖析
add方法//添加元素至数组尾部
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // 容量自增
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
//添加元素至制定位置(index)
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);//检查容量
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // 容量自增
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,size - index);//从index+1元素向后移动
elementData[index] = element;//为新添加元素赋值
size++;
}
//插入复杂度与位置与移动元素个数有关,此方法具有线性的时间复杂度addAll方法
//添加多个元素至数组尾部
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();//待添加集合转化为对象数组
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // 扩充容量
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, size, numNew);//数组复制
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
//从指定位置添加多个元素
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // 扩充容量
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,numMoved);//数组复制
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
//添加过程不光与元素个数有关与待添加位置也有关reomve方法
//从指定为主删除元素并返回待删除元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);//检查数组
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,numMoved);//数组向前移动
elementData[--size] = null; // 为GC方便回收,将末尾置为null
return oldValue;
}
//删除原数组中与目标对象相同的元素
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}set/get方法
//为指定位置元素赋值
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);//检查数组状态
E oldValue = elementData(index);//检查为否出现数组下标越界异常
elementData[index] = element;//用新值替换原元素值
return oldValue;//返回原元素值
}
//获取某一元素的值
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);//检查为否出现数组下标越界异常
return elementData(index);//返回索引位置的元素值
}grow方法(实现自动容量扩充)
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;//原容量
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);//扩充为原容量1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);//数组元素复制
}
相关文章推荐
- 分析Java中ArrayList与LinkedList列表结构的源码
- java 集合ArrayList及LinkList源码分析
- Java集合源码学习笔记(二)ArrayList分析
- Java ArrayList源码分析
- java ArrayList源码分析
- Java容器类源码-ArrayList的最全的源码分析
- java 集合ArrayList及LinkList源码分析
- java核心之集合框架——ArrayList源码分析
- Java-Collection源码分析(四)——ArrayList
- 【Java基础】Java学习之ArrayList源码常用方法分析
- 【转】java源码分析ArrayList
- Java ArrayList源码分析
- Java - ArrayList源码分析
- Java-ArrayList源码分析及示例
- JDK源码分析之java.util.ArrayList
- java集合03--ArrayList源码分析
- java非并发容器ArrayList 和 LinkedList 优缺点比较及其实现源码分析
- Java 集合框架03---ArrayList的源码分析
- Java集合源码分析(一)ArrayList
- Java ArrayList源码分析
