OpenCV —FileStorage类的数据读写操作与示例
2018-01-12 21:16
603 查看
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/iracer/article/details/51339377
OpenCV的许多应用都需要使用数据的存储于读取,例如经过3D校准后的相机,需要存储校准结果矩阵,以方便下次调用该数据;基于机器学习的应用,同样需要将学习得到的参数保存等。OpenCV通过XML/YAML格式实现数据持久化。本文简要梳理了使用FileStorage类进行基本数据持久化操作,给出了示例代码。
主要内容包括:
构造函数
operator <<
FileStorage::open
FileStorage::isOpened
FileStorage::release
FileStorage::getFirstTopLevelNode
FileStorage::root
FileStorage::operator[]
创建写入器、创建读取器
写入数值、写入矩阵、写入自定义数据结构、写入当前时间
读取数值、读取矩阵、读取自定义数据结构、读取当前时间
关闭写入器、关闭读取器
FileStorage类将各种OpenCV数据结构的数据存储为XML 或 YAML格式。同时,也可以将其他类型的数值数据存储为这两种格式。
FileStorage类的构造函数为:
[cpp] view
plain copy
cv::FileStorage(const string& source, int flags, const string& encoding=string());
参数:
source –存储或读取数据的文件名(字符串),其扩展名(.xml 或 .yml/.yaml)决定文件格式。
flags – 操作模式,包括:
FileStorage::READ 打开文件进行读操作
FileStorage::WRITE 打开文件进行写操作
FileStorage::APPEND打开文件进行附加操作
FileStorage::MEMORY 从source读数据,或向内部缓存写入数据(由FileStorage::release返回)
encoding – 文件编码方式。目前不支持UTF-16 XML 编码,应使用 8-bit 编码。
向filestorage中写入数据
[cpp] view
plain copy
template<typename_Tp> FileStorage& operator<<(FileStorage& fs, const _Tp& value)
template<typename_Tp> FileStorage& operator<<(FileStorage& fs, const vector<_Tp>& vec)
参数:
fs – 已经打开的用于写数据的file storage对象
value – 待写入fs 的数据.
vec – 待写入fs 的向量值
以下代码分别演示写入数值、矩阵、多个变量、当前时间和关闭文件:
[cpp] view
plain copy
// 1.create our writter
cv::FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
// 2.Save an int
int imageWidth= 5;
int imageHeight= 10;
fs << "imageWidth" << imageWidth;
fs << "imageHeight" << imageHeight;
// 3.Write a Mat
cv::Mat m1= Mat::eye(3,
1b024
3, CV_8U);
cv::Mat m2= Mat::ones(3,3, CV_8U);
cv::Mat resultMat= (m1+1).mul(m1+2);
fs << "resultMat" << resultMat;
// 4.Write multi-variables
cv::Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3,3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1);
cv::Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5,1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0);
fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs;
// 5.Save local time
time_t rawtime; time(&rawtime); //#include <time.h>
fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime));
// 6.close the file opened
fs.release();
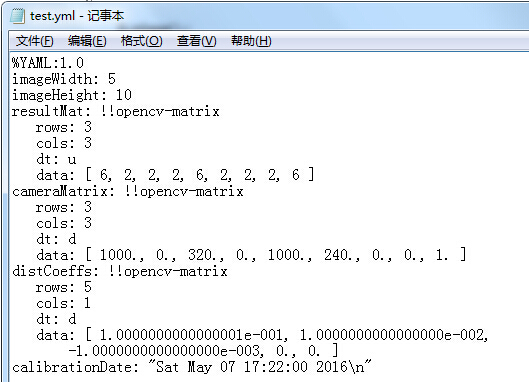
生成的文件test.yml
打开一个文件
[cpp] view
plain copy
boolFileStorage::open(const string& filename, int flags, const string&encoding=string())
参数:
filename – 待打开的文件名,其扩展名(.xml 或 .yml/.yaml) 决定文件格式(XML
或 YAML)
flags – 操作模式。见构造函数
encoding – 文件编码方式。
[cpp] view
plain copy
// open a file
cv::FileStorage fs;
fs.open("test.yml",FileStorage::WRITE);
// ... some process here
fs.release();
检查文件是否已经打开,调用:
[cpp] view
plain copy
boolFileStorage::isOpened()
返回:
ture – 如果对象关联了当前文件;
false – 其他情况。
尝试打开文件后调用此方法是个比较好的做法。
[cpp] view
plain copy
// Checks whether the file is opened
cv::FileStorage fs;
fs.open("test.yml",FileStorage::WRITE);
bool flag = fs.isOpened();
cout<<"flag = "<<flag<<endl<<endl;
// if failed to open a file
if(!fs.isOpened()){
cout<<"failed to open file test.yml "<<endl<<endl;
return 1;
}
运行结果:
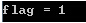
存储或读取操作完成后,需要关闭文件并释放缓存,调用
[cpp] view
plain copy
void FileStorage::release()
[cpp] view
plain copy
cv::FileStorage fs("test.yml", fs::WRITE);
//... some processing here
fs.release();
返回映射(mapping)顶层的第一个元素:
[cpp] view
plain copy
FileStorage::getFirstTopLevelNode()
[cpp] view
plain copy
// open a file for reading
fs.open("test.yml", FileStorage::READ);
// get the first top level node
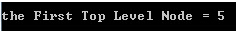
int firstNode = fs.getFirstTopLevelNode();
cout<<"the First Top Level Node = "<<firstNode<<endl<<endl;
运行结果
返回顶层映射(mapping)
[cpp] view
plain copy
FileNode FileStorage::root(int streamidx=0)
参数:
streamidx – 从0开始的字符串索引。大部分情况文件中只有一个串,但YAML支持多个串,因此可以有多个。
Returns: 顶层映射
返回指定的顶层映射元素
[cpp] view
plain copy
FileNode FileStorage::operator[](const string& nodename) const
FileNode FileStorage::operator[](const char* nodename) const
参数:
nodename – 文件节点名(见下文FileNode类)
返回:名称为nodename的节点数据
[cpp] view
plain copy
// read data using operator []
cv::FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::READ);
int width;
int height;
fs["imageWidth"]>>width;
fs["imageHeight"]>>height;
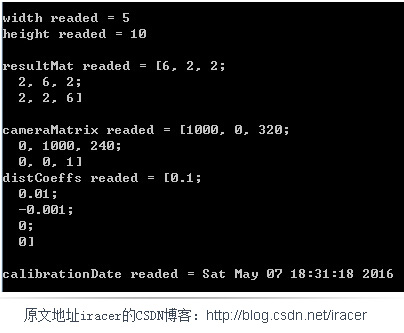
cout<<"width readed = "<<width<<endl;
cout<<"height readed = "<<height<<endl<<endl;
// read Mat
cv::Mat resultMatRead;
fs["resultMat"]>>resultMatRead;
cout<<"resultMat readed = "<<resultMatRead<<endl<<endl;
cv::Mat cameraMatrixRead,distCoeffsRead;
fs["cameraMatrix"]>>cameraMatrixRead;
fs["distCoeffs"]>>distCoeffsRead;
cout<<"cameraMatrix readed = "<<cameraMatrixRead<<endl;
cout<<"distCoeffs readed = "<<distCoeffsRead<<endl<<endl;
// read string
string timeRead;
fs["calibrationDate"]>>timeRead;
cout<<"calibrationDate readed = "<<timeRead<<endl<<endl;
fs.release();
运行结果
OpenCV的许多应用都需要使用数据的存储于读取,例如经过3D校准后的相机,需要存储校准结果矩阵,以方便下次调用该数据;基于机器学习的应用,同样需要将学习得到的参数保存等。OpenCV通过XML/YAML格式实现数据持久化。本文简要梳理了使用FileStorage类进行基本数据持久化操作,给出了示例代码。
主要内容包括:
FileStorage类
构造函数operator <<
FileStorage::open
FileStorage::isOpened
FileStorage::release
FileStorage::getFirstTopLevelNode
FileStorage::root
FileStorage::operator[]
示例代码
创建写入器、创建读取器写入数值、写入矩阵、写入自定义数据结构、写入当前时间
读取数值、读取矩阵、读取自定义数据结构、读取当前时间
关闭写入器、关闭读取器
FileStorage类
FileStorage类将各种OpenCV数据结构的数据存储为XML 或 YAML格式。同时,也可以将其他类型的数值数据存储为这两种格式。
构造函数
FileStorage类的构造函数为:[cpp] view
plain copy
cv::FileStorage(const string& source, int flags, const string& encoding=string());
参数:
source –存储或读取数据的文件名(字符串),其扩展名(.xml 或 .yml/.yaml)决定文件格式。
flags – 操作模式,包括:
FileStorage::READ 打开文件进行读操作
FileStorage::WRITE 打开文件进行写操作
FileStorage::APPEND打开文件进行附加操作
FileStorage::MEMORY 从source读数据,或向内部缓存写入数据(由FileStorage::release返回)
encoding – 文件编码方式。目前不支持UTF-16 XML 编码,应使用 8-bit 编码。
写数据operator
<<
向filestorage中写入数据[cpp] view
plain copy
template<typename_Tp> FileStorage& operator<<(FileStorage& fs, const _Tp& value)
template<typename_Tp> FileStorage& operator<<(FileStorage& fs, const vector<_Tp>& vec)
参数:
fs – 已经打开的用于写数据的file storage对象
value – 待写入fs 的数据.
vec – 待写入fs 的向量值
以下代码分别演示写入数值、矩阵、多个变量、当前时间和关闭文件:
[cpp] view
plain copy
// 1.create our writter
cv::FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
// 2.Save an int
int imageWidth= 5;
int imageHeight= 10;
fs << "imageWidth" << imageWidth;
fs << "imageHeight" << imageHeight;
// 3.Write a Mat
cv::Mat m1= Mat::eye(3,
1b024
3, CV_8U);
cv::Mat m2= Mat::ones(3,3, CV_8U);
cv::Mat resultMat= (m1+1).mul(m1+2);
fs << "resultMat" << resultMat;
// 4.Write multi-variables
cv::Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3,3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1);
cv::Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5,1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0);
fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs;
// 5.Save local time
time_t rawtime; time(&rawtime); //#include <time.h>
fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime));
// 6.close the file opened
fs.release();
生成的文件test.yml

FileStorage::open
打开一个文件[cpp] view
plain copy
boolFileStorage::open(const string& filename, int flags, const string&encoding=string())
参数:
filename – 待打开的文件名,其扩展名(.xml 或 .yml/.yaml) 决定文件格式(XML
或 YAML)
flags – 操作模式。见构造函数
encoding – 文件编码方式。
[cpp] view
plain copy
// open a file
cv::FileStorage fs;
fs.open("test.yml",FileStorage::WRITE);
// ... some process here
fs.release();
FileStorage::isOpened
检查文件是否已经打开,调用:[cpp] view
plain copy
boolFileStorage::isOpened()
返回:
ture – 如果对象关联了当前文件;
false – 其他情况。
尝试打开文件后调用此方法是个比较好的做法。
[cpp] view
plain copy
// Checks whether the file is opened
cv::FileStorage fs;
fs.open("test.yml",FileStorage::WRITE);
bool flag = fs.isOpened();
cout<<"flag = "<<flag<<endl<<endl;
// if failed to open a file
if(!fs.isOpened()){
cout<<"failed to open file test.yml "<<endl<<endl;
return 1;
}
运行结果:
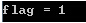
FileStorage::release
存储或读取操作完成后,需要关闭文件并释放缓存,调用[cpp] view
plain copy
void FileStorage::release()
[cpp] view
plain copy
cv::FileStorage fs("test.yml", fs::WRITE);
//... some processing here
fs.release();
FileStorage::getFirstTopLevelNode
返回映射(mapping)顶层的第一个元素:[cpp] view
plain copy
FileStorage::getFirstTopLevelNode()
[cpp] view
plain copy
// open a file for reading
fs.open("test.yml", FileStorage::READ);
// get the first top level node
int firstNode = fs.getFirstTopLevelNode();
cout<<"the First Top Level Node = "<<firstNode<<endl<<endl;
运行结果

FileStorage::root
返回顶层映射(mapping)[cpp] view
plain copy
FileNode FileStorage::root(int streamidx=0)
参数:
streamidx – 从0开始的字符串索引。大部分情况文件中只有一个串,但YAML支持多个串,因此可以有多个。
Returns: 顶层映射
读数据:FileStorage::operator[]
返回指定的顶层映射元素[cpp] view
plain copy
FileNode FileStorage::operator[](const string& nodename) const
FileNode FileStorage::operator[](const char* nodename) const
参数:
nodename – 文件节点名(见下文FileNode类)
返回:名称为nodename的节点数据
[cpp] view
plain copy
// read data using operator []
cv::FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::READ);
int width;
int height;
fs["imageWidth"]>>width;
fs["imageHeight"]>>height;
cout<<"width readed = "<<width<<endl;
cout<<"height readed = "<<height<<endl<<endl;
// read Mat
cv::Mat resultMatRead;
fs["resultMat"]>>resultMatRead;
cout<<"resultMat readed = "<<resultMatRead<<endl<<endl;
cv::Mat cameraMatrixRead,distCoeffsRead;
fs["cameraMatrix"]>>cameraMatrixRead;
fs["distCoeffs"]>>distCoeffsRead;
cout<<"cameraMatrix readed = "<<cameraMatrixRead<<endl;
cout<<"distCoeffs readed = "<<distCoeffsRead<<endl<<endl;
// read string
string timeRead;
fs["calibrationDate"]>>timeRead;
cout<<"calibrationDate readed = "<<timeRead<<endl<<endl;
fs.release();
运行结果

相关文章推荐
- OpenCV —数据持久化: FileStorage类的数据存取操作与示例
- OpenCV —数据持久化: FileStorage类的数据存取操作与示例
- OpenCV FileStorage类的数据读写操作
- opencv数据读写操作
- OpenCV学习笔记 cv.Mat 与 .txt 文件数据的读写操作
- android读写sd卡操作写入数据读取数据示例
- OpenCV数据读写操作
- OpenCV学习笔记 cv.Mat 与 .txt 文件数据的读写操作
- OpenCV数据读写操作
- OpenCV cv.Mat与.txt文件数据的读写操作
- OpenCv中FileStorage类读写XML文件的示例Demo
- OpenCV数据读写操作
- OpenCV数据读写操作 .
- OpenCV学习笔记 cv.Mat 与 .txt 文件数据的读写操作
- OpenCV学习笔记 cv.Mat 与 .txt 文件数据的读写操作
- OpenCV学习笔记 cv.Mat 与 .txt 文件数据的读写操作
- OpenCV数据读写操作
- MapReduce从HBase读写数据简单示例
- 文件基本操作示例-文件读写
- 【opencv】Mat 数据操作
