实现迷宫和表达式计算问题
2017-12-13 16:05
501 查看
1.实现迷宫的递归非递归。
1)迷宫的非递归算法
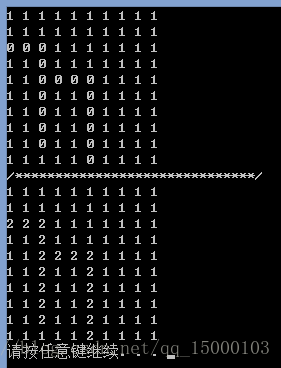
运行结果如下:
2)迷宫的递归算法

递归算法解决迷宫问题的解法图如下:
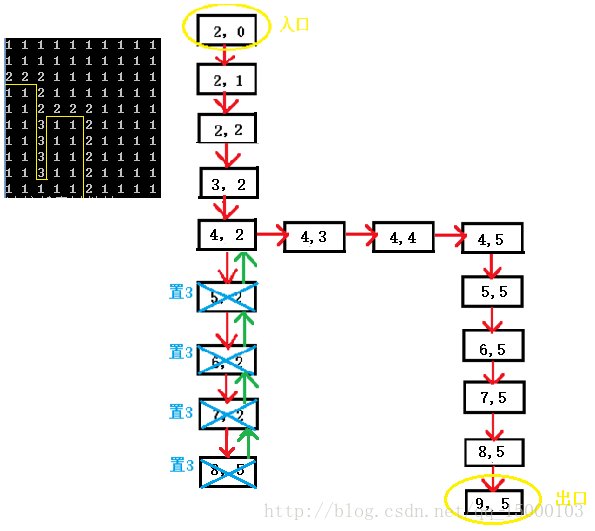
当递归调用到点(8,2)时,没有可通行的点,递归函数会推出当前栈帧,返回到上一层栈帧中,如果还没有可通行的继续返回,直到(4,2)时(4,3)可通行就继续调用函数直到找到出口。
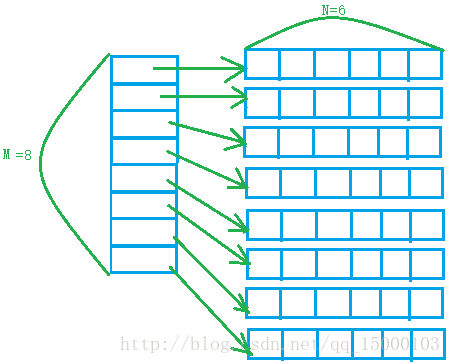
3)如何动态开辟二维数组
采用指针数组的方法,每个指针元素指向一块空间,如需要M*N大小的数组,可以先开长度为M大的指针数组,每个指针指向一个1 *N的一维数组。
2.实现迷宫的最优解问题。
上述解决迷宫方法存在的问题:
并不能遍历迷宫的所有通路,找到迷宫通路中最短的一条路径。并考虑如果迷宫中带有环路如何找到最短路径。
故而,提出解法如下:
代码如下:
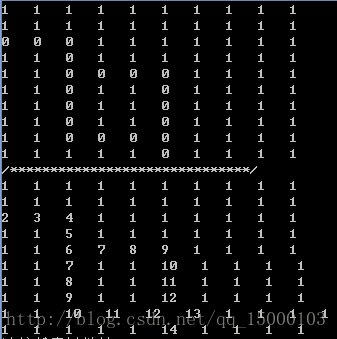
运行结果如下图所示:
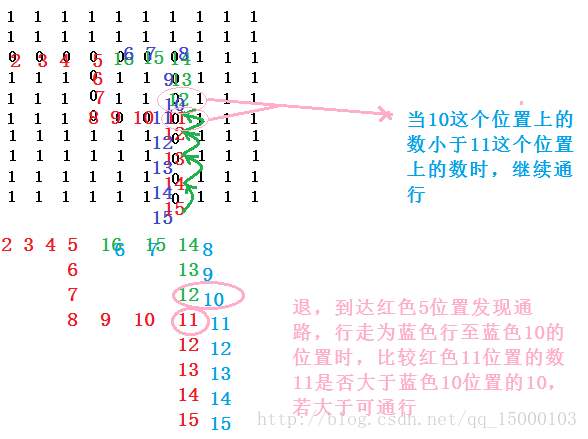
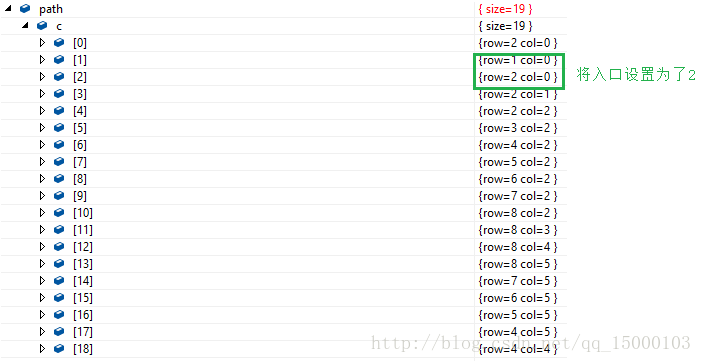
path栈内如下图,同时解释了入口处设为2的过程
若:
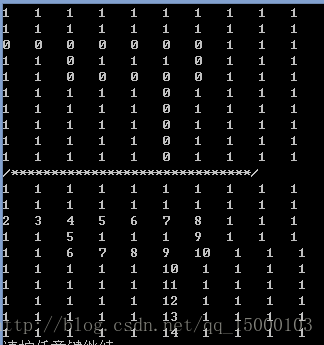
结果如下:
3.实现表达式计算问题。
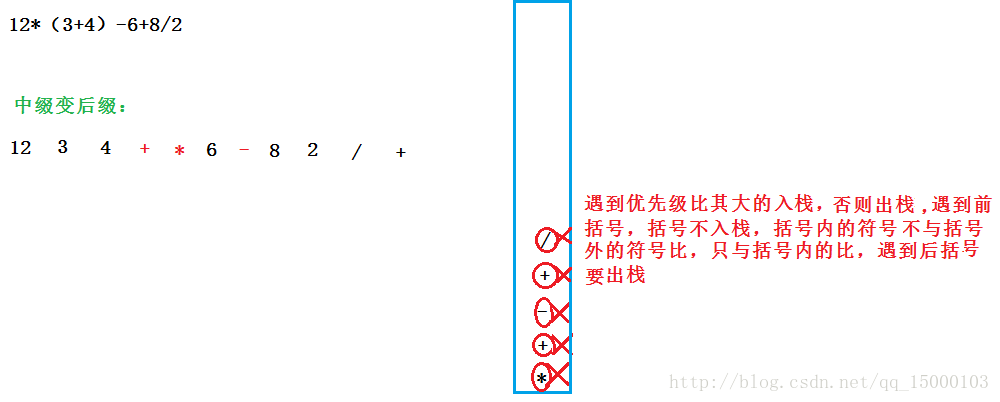
1)将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式
2)由后缀表达式计算值

代码如下:
测试代码如下:
运行结果如下:
1)迷宫的非递归算法
//Maze.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include"windows.h"
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
struct Pos
{
int row;
int col;
};
template<size_t N>
class Maze
{
public:
/*Maze(int maze[]
)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
_maze[i][j] = maze[i][j];
}
}
}*/
Maze(int* maze)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
_maze[i][j] = maze[i*N + j];
}
}
}
void Print()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
cout << _maze[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
bool CheckIsAccess(Pos pos)
{
//边界、是否为通路
if ((pos.row < N&&pos.row >= 0 && pos.col < N&&pos.col >= 0) && (_maze[pos.row][pos.col] == 0))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool GetPath(Pos entry, stack<Pos>& path)
{
path.push(entry);
while (!path.empty())
{
//探测
Pos cur = path.top();
_maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 2;//走过的路标记为2
//判断是否到出口
if (cur.row == N - 1)
{
return true;
}
//上
Pos next = cur;
next.row = next.row + 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(next))
{
path.push(next);
continue;
}
//下
next = cur;
next.row = next.row - 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(next))
{
path.push(next);
continue;
}
//左
next = cur;
next.col = next.col - 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(next))
{
path.push(next);
continue;
}
//右
next = cur;
next.col = next.col + 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(next))
{
path.push(next);
continue;
}
//此路不通,回溯
path.pop();
}
return false;
}
protected:
int _maze
;
};//Test.cpp
#include "Maze.h"
void TestMaze()
{
const size_t N = 10;
int maze
=
{
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }
};
Maze<10> mz((int*)maze);
//Maze<10> mz(maze);
mz.Print();
cout << "/******************************/" << endl;
Pos entry;
stack<Pos> path;
entry.row = 2;
entry.col = 0;
mz.GetPath(entry, path);
mz.Print();
}
int main()
{
TestMaze();
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果如下:

2)迷宫的递归算法
bool GetPath_R(Pos cur, stack<Pos>& path)
{
path.push(cur);
//探测
_maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 2;//走过的路标记为2
//判断是否到出口
if (cur.row == N - 1)
{
return true;
}
//上
Pos next = cur;
next.row = next.row + 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(next))
{
if (GetPath_R(next, path))
{
return true;
}
}
//下
next = cur;
next.row = next.row - 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(next))
{
if (GetPath_R(next, path))
{
return true;
}
}
//左
next = cur;
next.col = next.col - 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(next))
{
if (GetPath_R(next, path))
{
return true;
}
}
//右
next = cur;
next.col = next.col + 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(next))
{
if (GetPath_R(next, path))
{
return true;
}
}
//此路不通
_maze[cur.row][cur.col] = 3;//返回的路程标记为3
return false;
}
递归算法解决迷宫问题的解法图如下:

当递归调用到点(8,2)时,没有可通行的点,递归函数会推出当前栈帧,返回到上一层栈帧中,如果还没有可通行的继续返回,直到(4,2)时(4,3)可通行就继续调用函数直到找到出口。
3)如何动态开辟二维数组
采用指针数组的方法,每个指针元素指向一块空间,如需要M*N大小的数组,可以先开长度为M大的指针数组,每个指针指向一个1 *N的一维数组。

int** _maze=new int*[M];
for(size_t i=0;i<M;i++)
{
_maze[i]=new int
;
}2.实现迷宫的最优解问题。
上述解决迷宫方法存在的问题:
并不能遍历迷宫的所有通路,找到迷宫通路中最短的一条路径。并考虑如果迷宫中带有环路如何找到最短路径。
故而,提出解法如下:

代码如下:
bool CheckIsAccess(Pos cur, Pos next)
{
//1考虑边界;2是否为通路;3是否别人走过,自己没走过
if (next.row < N && next.row >= 0 && next.col < N && next.col >= 0 && (_maze[next.row][next.col] == 0 || _maze[cur.row][cur.col] < _maze[next.row][next.col]))
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
void GetShortPath(Pos cur, stack<Pos>& path, stack<Pos>& shortpath)
{
if (!path.empty())
{
Pos prev = path.top();
_maze[cur.row][cur.col] = _maze[prev.row][prev.col] + 1;//每走一步比前一个标记多1
}
path.push(cur);
//判断是否到出口
if (cur.row == N - 1)
{
if (shortpath.empty() || path.size() < shortpath.size())
{
shortpath = path;
}
}
//上
Pos next = cur;
next.row = next.row - 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(cur, next))
{
GetShortPath(next, path, shortpath);
}
//下
next = cur;
next.row = next.row + 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(cur, next))
{
GetShortPath(next, path, shortpath);
}
//左
next = cur;
next.col = next.col - 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(cur, next))
{
GetShortPath(next, path, shortpath);
}
//右
next = cur;
next.col = next.col + 1;
if (CheckIsAccess(cur, next))
{
GetShortPath(next, path, shortpath);
}
//此路不通
path.pop();
}void TestMaze2()
{
const size_t N = 10;
int maze
=
{
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }
};
Maze<10> mz((int*)maze);
//Maze<10> mz(maze);
mz.Print();
cout << "/******************************/" << endl;
Pos entry;
stack<Pos> path;
stack<Pos> shortpath;
entry.row = 2;
entry.col = 0;
mz.GetShortPath(entry, path, shortpath);
mz.Print();
}运行结果如下图所示:

path栈内如下图,同时解释了入口处设为2的过程

若:
int maze[10][10] =
{
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 },
{ 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1 }
};结果如下:

3.实现表达式计算问题。
1)将中缀表达式转换为后缀表达式

2)由后缀表达式计算值

代码如下:
//RPN.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include"assert.h"
using namespace std;
enum Cal_Type
{
OP_NUM,
OP_ADD,
OP_SUB,
OP_MUL,
OP_DIV,
};
struct Cell
{
Cal_Type _type; // 类型
int _value; // 值
};
class Calculator
{
public:
Calculator(Cell* exp, size_t n)
{
_rpn.resize(n);//改变容量,并初始化
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_rpn[i] = exp[i];//若_rpn未初始化,[]会出错
}
}
int Count()
{
stack<int> s;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _rpn.size();++i)
{
if(_rpn[i]._type == OP_NUM)//是数值则入栈
{
s.push(_rpn[i]._value);
}
else if (_rpn[i]._type != OP_NUM)
{
int right = s.top();
s.pop();
int left = s.top();
s.pop();
switch (_rpn[i]._type)
{
case OP_ADD:
s.push(left + right);
break;
case OP_SUB:
s.push(left - right);
break;
case OP_MUL:
s.push(left * right);
break;
case OP_DIV:
s.push(left / right);
break;
default:
assert(false);
}
}
else
{
assert(false);
}
}
return s.top();
}
protected:
vector<Cell> _rpn; // 表达式
};测试代码如下:
#include"RPN.h"
int main()
{
Cell exp[] =
{
{OP_NUM, 2},
{OP_NUM, 3},
{OP_NUM, 4},
{OP_MUL, 0},
{OP_SUB, 0},
{OP_NUM, 5},
{OP_ADD, 0},
};
Calculator cal(exp, sizeof(exp)/sizeof(Cell));
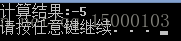
cout << "计算结果:" << cal.Count() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}运行结果如下:

相关文章推荐
- C++实现 逆波兰表达式计算问题
- 完全利用栈实现表达式的计算问题
- 用C++程序实现复杂表达式的计算问题
- C++实现 逆波兰表达式计算问题
- 由SAT问题展开说(2)[演化计算c#实现下]
- CodeDom计算器——动态计算数学表达式的实现
- 应用stack 计算表达式(中缀表达式,+ - × / ^)及计算器的实现
- 数据结构中用C#实现“表达式计算”
- 堆栈的应用(2) 中缀算术表达式到后缀(逆波兰记法reverse polish notation)的转换及其计算 C++实现
- 数据结构之应用"栈(Stack)"实现: 解析算术表达式及计算
- C语言算法实现迷宫问题2
- 表达式计算java实现
- 算数表达式的计算——Expression 类与stack混合的实现
- 调用编译器接口ICodeCompiler实现数学表达式计算
- 数据结构习作之应用 "栈(Stack)" 实现: 解析算术表达式及计算求值 (C#/Java) (技术含量少许)
- [转载]数据结构中用C#实现"表达式计算"
- 数据结构之应用"栈(Stack)"实现: 解析算术表达式及计算
- 一个表达式计算案例的设计和实现
- 表达式的计算问题
- 数据结构之应用 "栈(Stack)" 实现: 解析算术表达式及计算求值 (C#/Java) (转载)
